
Full Answer
What is a Hummer H1?
However, we did up your distance to find you some cars. You’ll want to modify your search if they’re too far away!
Why is H1 the same as H2?
H2 tag SEO is slightly different from H1 tags because you can obviously have more of them. The H2 heading tags are the most important subheadings you can use. They break your piece into sections, similar to chapters in a book, and highlight the main points of your content—not just for readers but for search engines as well.
How to choose an antihistamine?
- Research health conditions
- Check your symptoms
- Prepare for a doctor's visit or test
- Find the best treatments and procedures for you
- Explore options for better nutrition and exercise
What are some examples of antihistamine?
Prescription antihistamines include:
- Azelastine eyedrops ( Optivar)
- Azelastine nasal sprays ( Astelin, Astepro)
- Carbinoxamine ( Palgic)
- Cyproheptadine
- Desloratadine ( Clarinex)
- Emedastine eyedrops ( Emadine)
- Hydroxyzine ( Atarax, Vistaril)
- Levocabastine eyedrops ( Livostin)
- Levocetirizine oral ( Xyzal)
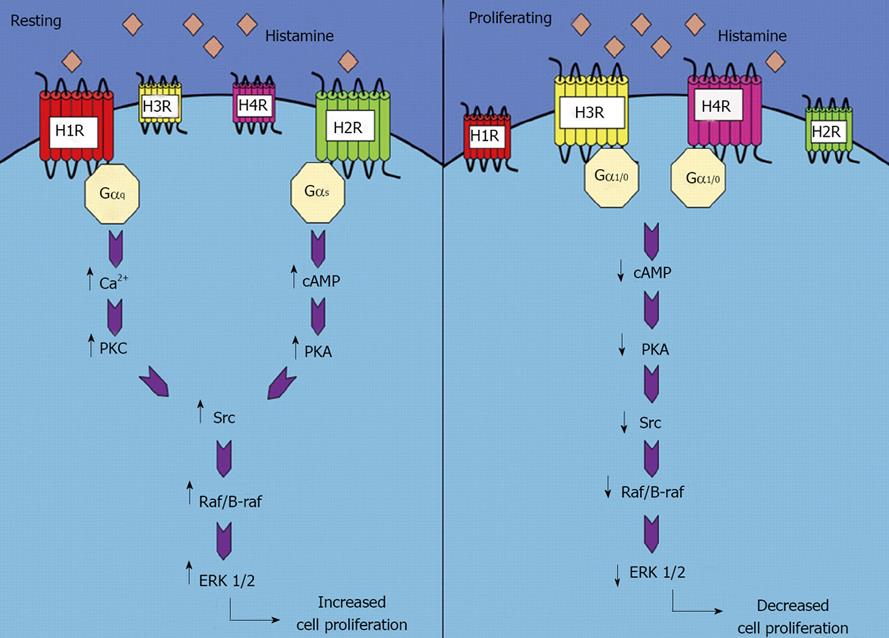
Which drug is an H1 histamine blocker?
Commonly used H1 antagonists currently available in the United States are cetirizine, levocetirizine, desloratadine, loratadine, and fexofenadine.
What are H1-antihistamines used for?
H1-antihistamines are inverse agonists that combine with and stabilize inactive conformation of H1-receptors. Thus they interfere with actions of histamine at H1-receptors. They are widely used for treatment of allergic rhinitis, allergic conjunctivitis, urticaria, coughs, colds and insomnia.
What is the best H1 blocker?
The most used topical H1-antihistamines are azelastine (ocular and nasal) and ketotifen (ocular) [12]. Second generation H1-antihistamines are favoured compared to those of the first generation, both in the light of their anti-allergic-anti-inflammatory activity and of their good safety profile [13].
Is Benadryl an H1 or h2 blocker?
Diphenhydramine (Benadryl, Benylin, Diphen) Diphenhydramine is a sedating peripheral H1 receptor antagonist. It is used for symptomatic relief of allergic symptoms caused by histamine released in response to allergens.
What are the main side effects of H1 receptor antihistamine?
Some of the common side effects of first-generation antihistamines include:Drowsiness.Dry mouth, dry eyes.Blurred or double vision.Dizziness and headache.Low blood pressure.Mucous thickening in the airways.Rapid heart rate.Difficulty urinating and constipation.
Do H1-antihistamines reduce stomach acid?
Therefore, these antihistamines will reduce the amount of gastric acid being secreted in the stomach. Uses: The H1-antihistamines are used to treat allergic symptoms such as hives, itchy skin, itchy eyes, runny nose, and sneezing....Edit This Favorite.Edit This FavoriteCategory:Share:Yes No, Keep Private2 more rows
Can I take antihistamine if I have Covid?
You may take an expectorant/cough suppressant combination as needed for cough and congestion. Take an antihistamine/decongestant combination for your allergy symptoms and congestion. If you have uncontrolled blood pressure, then you should avoid the decongestant component.
Are antihistamines good for Covid?
And, while people can agree that this is a thing, a proper treatment for the condition has been tough to come by. Now, a new case report has suggested that there may be an easily accessible solution for some symptoms caused by long COVID: antihistamines.
How do you remove histamine from your body?
Antihistamines block histamine activity, seeking to stop the allergic reaction. Many allergy medications on the shelves of your local drugstore work as antihistamines. But there are also certain foods and plant extracts that may similarly block the effects of histamine.
What's the difference between H1 and H2 antihistamines?
H1 receptor antagonists are typically utilized to suppress the body's histamine-mediated effects in anaphylactoid or anaphylactic reactions. H2 antagonists are competitive antagonists at the parietal cell H2 receptor and are typically used to suppress gastric acid secretion.
What is the most powerful antihistamine?
Cetirizine is the most potent antihistamine available and has been subjected to more clinical study than any other.
What is the difference between an antihistamine and a histamine blocker?
Abstract. Background: Histamine is responsible for the wheal and flare reaction in various allergic conditions. Classical antihistamines are the drugs which block the H 1 receptors and are widely used in various allergic conditions, whereas H 2 blockers are mainly used for acid peptic disease.
Abstract
Anaphylaxis is an acute systemic allergic reaction, which can be life‐threatening. H1‐antihistamines are commonly used as an adjuvant therapy in the treatment of anaphylaxis.
Plain language summary
Anaphylaxis is a rare, but potentially life‐threatening emergency. Evidence from the United Kingdom suggests that incidence may be increasing rapidly. Common triggers of anaphylaxis include a variety of foods, drugs and insect venoms.
Background
Anaphylaxis is described as a potentially life‐threatening, acute systemic allergic reaction with many possible trigger factors, including foods, insect venoms, medications, anaesthetics, latex rubber and exercise ( Brown 2001; Brown 2004a; Kemp 2002; Lieberman 2003; Sampson 2005; Simons 2002 ).
Objectives
To assess the benefits and harm of H1‐antihistamines in the treatment of anaphylaxis.
Results
In the previous version we searched the Searching the four databases until June 2006 and this yielded 2070 citations.
Discussion
We have found no high quality evidence either for or against the use of H1‐antihistamines in anaphylaxis.
Authors' conclusions
We found no relevant evidence. We are therefore unable to make recommendations about H1‐antihistamine use in the treatment of anaphylaxis. Guidelines on the management of anaphylaxis need to be much more explicit about the basis of their recommendations regarding the use of H1‐antihistamines.
What is H1 and H2?
H1 and H2 Histamine Blockers (Antihistamines) Pharmacy and Therapeutics. “There are two known histamine receptors, designated H1 and H2. H1 receptor antagonists are typically utilized to suppress the body’s histamine-mediated effects in anaphylactoid or anaphylactic reactions.
How long does it take for H2 antagonists to work?
The onset of action is within 30 minutes if given IV, and within 1 hour if given PO. By either route, the duration of action is 10-12 hours. H2 Blockers do not alter the pH of gastric ...
How long does H2 blocker work?
H2 blockers begin working within an hour and last for up to 12 hours.
Do H2 blockers alter gastric fluid?
H2 Blockers do not alter the pH of gastric fluid already present within the stomach at the time of their administration.”. ** H1 histamine blockers are divided into 1st generation and 2nd generation H1 blockers. Source: https://www.openanesthesia.org/h2-blockers_onset_time/. print.
What is antihistamine? What are its functions?
While the term antihistamine can broadly include any agent that blocks any histamine receptor, in practice it is usually used to denote those blocking the H 1 type of receptors ( H 1 receptor antagonists ), those involved in allergic reactions. Agents blocking the H 2 type of receptors are usually called histamine H 2 receptor antagonists, and include the agents used to inhibit gastric secretion in peptic ulcer.
What is the H1 receptor?
Any substance that reduces the effect of histamine or blocks histamine receptors, usually the histamine 1 (H1) receptor. It is used in the treatment of allergic conjunctivitis and also in the temporary relief of minor allergic symptoms of the eye. Common agents include antazoline sulfate, azelastine hydrochloride, cetirizine, chlorphenamine, emedastine, epinastine hydrochloride, ketotifen, levocabastine, loratadine and olopatadine. See hypersensitivity; mast cell stabilizers.
What are the two groups of drugs that block H1 receptors?
One of a group of drugs which act against histamine-a powerful and highly irritant agent released in the body by MAST CELLS, after contact with certain ALLERGENS. Antihistamine drugs fall into two groups-those that block H 1 receptors and act mainly on blood vessels, and those that block H 2 receptors and act mainly on the secretion of acid in the stomach. H 1 receptor blockers include diphenhydramine, chlorpheniramine (chlorphenamine) (Piriton), terfenadine (Triludan), promethazine (Phenergan), cyproheptadine (Periactin), mequitazine (Primalan) and phenindamine (Thephorin). H 2 receptor blockers are not usually referred to as antihistamines, although this is what they are. They include CIMETIDINE (Tagamet), and RANITIDINE (Zantac).
What is H1 antihistamine?
In the elderly, H1-antihistamine therapy is commonly prescribed for treatment of rhinitis, conjunctivitis, pruritus, eczema, urticaria, and for prophylaxis of anaphylactoid reactions.
Is H1 receptor antagonist safe?
Second-generation H1-receptor antagonists provide excellent, safe, and effective alternatives to first-generation antihistamines in this population, as in younger patients. As with all medications, the choice of which agent to use must be tailored to the needs of the individual.
Can antihistamines be used for urticaria?
First-generation antihistamines should not be used for treatment of allergic rhinitis or urticaria in the elderly. Age-related physiological changes can enhance or complicate the actions of H1-receptor antagonists, especially when these drugs are taken concurrently with other medications and/or in the presence of comorbid disease.
What is an antihistamine?
An antihistamine is a prescription or over-the-counter medication that blocks some of what histamine does. “Anti” means against, so antihistamines are medicines that work against or block histamine. Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission.
Why do people take antihistamines?
Antihistamines are most commonly used by people who have allergic reactions to pollen and other allergens. They are also used to treat a variety of other conditions such as stomach problems, colds, anxiety and more.
What is the chemical that causes coughing and sneezing?
Antihistamines. When histamine, a chemical created by your immune system, overreacts to an allergen such as pollen and pet dander, it can cause symptoms such as coughing, sneezing and watery eyes. Antihistamines are medications that help with allergies, and also with stomach problems, cold, anxiety and more. Antihistamines are a class of drugs ...
When were antihistamines first approved?
They began to be approved in the United States in the 1930s and are still prescribed today. They work on histamine receptor in the brain and spinal cord along with other types of receptors. Most notable about this generation of antihistamines is that they cross the blood-brain barrier, which results in drowsiness.
What happens when you have an allergy to something that is harmless?
In the case of an allergy, substances that are usually harmless and don’t bother some people, such as dust or animal dander, do bother you! Your body views these substances as “foreign,” which then triggers an overreaction by your body’s defense system that includes the release of histamine.
Can you take more than one antihistamine at a time?
They are highly schooled in the actions and effects and side effects of drugs. You may need to try different antihistamines (but no more than one at a time unless directed by your physician) to find the best medication to manage your symptoms.
Can you combine antihistamines?
Antihistamines should not be combined unless directed to do so by your healthcare provider under their guidance and supervision. Antihistamines should be used only as directed or you could experience serious side effects. Read labels very carefully.
