Explore
Treatment options in heparin-induced thrombocytopenia First-line therapies for HIT are argatroban or lepirudin. Patient-specific factors determine which drug should be used, and taking advantage of their differences allows effective anticoagulation with minimal risk of bleeding.
Why is heparin usually administered before dialysis treatment?
Oct 16, 2021 · The first step in the treatment is the discontinuation of all forms of heparin, including heparin flushes, heparin-coated catheters, and heparin in the dialysate. Next, an alternative anticoagulant must be initiated to prevent or treat any HIT-induced thrombosis.
What medication is used to treat thrombocytopenia?
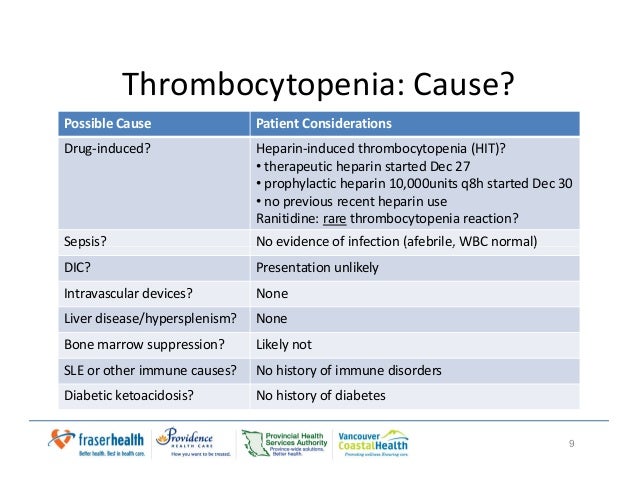
Heparin-induced thrombocytopenia (HIT) is a prothrombotic disorder caused by antibodies that recognize complexes of platelet factor 4 (PF4) and heparin. HIT is frequently considered in the differential diagnosis of thrombocytopenia occurring in patients on heparin therapy. HIT is a challenging diagnosis because of routine heparin use in hospitalized patients, the common …
Can Lovenox be administered with heparin?
Mar 08, 2012 · PRT-060318, a novel syk inhibitor, prevents heparin-induced thrombocytopenia and thrombosis in a transgenic mouse model. The Syk-kinase inhibitor R406 impairs platelet activation and monocyte tissue factor expression triggered …
How is heparin used to treat deep vein thrombosis (DVT)?
Sep 10, 2021 · If heparin-induced thrombocytopenia (HIT) is suspected, the first step is to discontinue all heparin products immediately and avoid any further exposure. An order to simply "discontinue heparin"...
What is heparin induced thrombocytopenia and how is it treated?
Patients with HIT are at high risk for thrombotic events and should be treated with alternative anticoagulants, typically a direct thrombin inhibitor (DTI). The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved the DTI argatroban (Acova) for prophylaxis and treatment of thrombosis in patients with HIT.Sep 10, 2021
What happens heparin induced thrombocytopenia?
Heparin molecules bind with a protein to form something called heparin-PF4. When you have heparin-induced thrombocytopenia, your immune system sees heparin-PF4 as an intruder and attacks it, setting off a chain reaction that leads to blood clots.Apr 14, 2021
Can you recover from heparin induced thrombocytopenia?
After the cessation of heparin, platelet counts typically recover in 4-14 days, although some patients have a more prolonged recovery period and rare patients recover from (unrecognized) HIT and normalize their platelet counts despite ongoing heparin therapy.
How is drug induced thrombocytopenia treated?
Treatment of DITP involves discontinuation of the offending drug. The platelet count usually starts to recover after 4 or 5 half-lives of the responsible drug or drug metabolite. High doses of intravenous immunoglobulin can be given to patients with severe thrombocytopenia and bleeding.Nov 30, 2018
How is HIT treated?
Treatment of HIT entails immediate withdrawal of all heparin, including heparin-containing flushes and catheters. Heparin cessation alone, however, is often insufficient to prevent thrombosis.
How long does it take to recover from heparin-induced thrombocytopenia?
All patients who develop HIT antibodies will subsequently develop clinical syndrome of HIT. HIT antibodies begin to disappear in 4–10 days after cessation of heparin treatment.
What is the antidote for heparin?
Expert opinion: Despite of the low therapeutic index, protamine is the only registered antidote of heparins. The toxicology of protamine depends on a complex interaction of the high molecular weight, a cationic peptide with the surfaces of the vasculature and blood cells.
When should I worry about heparin-induced thrombocytopenia?
HIT should be suspected when patients present with new thrombocytopenia or thrombosis in the context of confirmed or suspected use of heparin (unfractionated heparin, low molecular weight heparin, or, rarely, fondaparinux) within the past 100 days, particularly in the context of recent cardiac or orthopaedic surgery.Jan 8, 2015
How do you reverse thrombocytopenia?
TreatmentBlood or platelet transfusions. If your platelet level becomes too low, your doctor can replace lost blood with transfusions of packed red blood cells or platelets.Medications. ... Surgery. ... Plasma exchange.Apr 8, 2020
What medications should be avoided with thrombocytopenia?
If you have ITP, you should avoid medicines that increase risks for bleeding. Some of these include warfarin, aspirin, or ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin). You should also limit alcohol. It can decrease the ability of your blood to clot.Jun 17, 2020
What are 3 causes of thrombocytopenia?
What causes thrombocytopenia?Alcohol use disorder and alcoholism.Autoimmune disease which causes ITP. ... Bone marrow diseases, including aplastic anemia, leukemia, certain lymphomas and myelodysplastic syndromes.Cancer treatments like chemotherapy and radiation therapy.More items...•Nov 23, 2020
Can you give heparin with low platelets?
Low-molecular weight heparin (LMWH) is recommended for patients with cancer-associated thrombosis19 and the dose can be adjusted for severe thrombocytopenia.Apr 24, 2018
What is heparin induced thrombocytopenia?
Heparin‐induced thro mbocytopenia (HIT) is a potentially devastating immune mediated adverse drug reaction caused by the emergence of antibodies that activate platelets in the presence of heparin. Despite thrombocytopenia, bleeding is rare; rather, HIT is strongly associated with thromboembolic complications involving both ...
Is heparin induced thrombocytopenia a thromboembolic event?
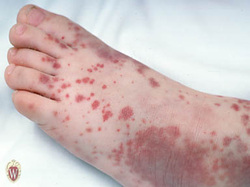
Heparin induced thrombocytopenia (HIT) is an immune ‐mediated event that can have severe life‐ and limb‐threatening complications. Despite thrombocytopenia, bleeding is rare; rather, HIT is strongly associated with thromboembolic complications.
Can danaparoid be reversed?
Excessive anticoagulation associated with danaparoid can completely be reversed with protamine sulfate. In patients with a history of HIT, heparin can safely be used intraoperatively during cardiac surgery. Prostacyclin analogues are safe anticoagulants for haemodialysis in patients with HIT. Abbreviations.
What is heparin induced thrombocytopenia?
Heparin-induced thrombocytopenia (HIT), formerly HIT type II, is a prothrombotic and potentially lethal disorder caused by platelet, endothelial, and monocyte-activating antibodies that target multimolecular complexes of platelet factor 4 (PF4) and heparin. 1 Although HIT was first described more than 50 years ago, 2 not until the 1990s was the target antigen identified, the now widely used anti-PF4/heparin ELISA developed, 1 and the first effective therapies approved. Since that time, a major emphasis of training and contemporary literature has been early disease recognition and prompt initiation of therapy. 3, 4
How long does it take for a platelet count to drop after heparin?
In heparin-naive patients, HIT classically presents with a platelet count fall beginning 5 to 14 days after initial exposure while drug is still present. 23 Rapid-onset HIT, in which the platelet count drops within hours of heparin administration, may occur in patients with preexisting anti-PF4/heparin antibodies.
What are the drawbacks of parenteral anticoagulants?
First, management is complex, cumbersome, and prone to error. Approved agents require continuous intravenous infusion, serial monitoring, and frequent dose adjustments. Indeed, these drugs are sufficiently complex that many institutions have reassigned primary responsibility for their management to dedicated pharmacist-directed anticoagulation services. 89 Desirudin and fondaparinux offer hope of reducing therapeutic complexity. Neither appears to require routine laboratory monitoring or dose adjustment. Both are administered subcutaneously and have negligible effect on the International Normalized Ratio (INR), thereby facilitating transition to outpatient therapy. In theory, new oral inhibitors of thrombin and FXa constitute rational therapies for HIT and also offer the promise of simplifying management. Dabigatran, apixaban, and rivaroxaban do not induce platelet aggregation or PF4 release in the presence of HIT-positive sera in vitro 90 and warrant further investigation, although no published clinical data are available to support their use.
What percentage of platelets fall after heparin?
Percentage fall is measured from peak platelet count after heparin exposure to its nadir. A 50% or greater reduction occurs in the large majority of patients, although approximately 10% evince a more modest decline of 30% to 50%. 26
What are the risk factors for heparin?
Heparin-related risk factors include type of heparin and duration of exposure. Low molecular weight heparin (LMWH) is associated with a 5- to 10-fold lower risk of HIT than unfractionated heparin (UFH) 7, 8 but accounts for a growing proportion of cases because of its increasing use.
What causes thrombocytopenia in hospital?
Common causes of hospital-acquired thrombocytopenia include infection, medications other than heparin, DIC, hemodilution, and intravascular devices, such as balloon pumps, ventricular assist devices, and extracorporeal circuits.
What are the two types of tests that are used to determine if a patient has heparin-dependent
Because of the challenges of clinical diagnosis, physicians rely heavily on laboratory testing. Standard tests fall into 2 categories: functional assays , which detect patient antibodies that induce heparin-dependent platelet activation; and immunologic assays , which identify circulating anti-PF4/heparin antibodies, irrespective of their capacity to activate platelets ( Table 3 ).
