Explore
• The symptoms of EPI can be a lot like other medical conditions that affect the stomach and bowels.1-4,7-11This can sometimes make EPI hard to diagnose. That’s why it’s important to be open and honest with your doctor about all of your stomach and bowel problems • Tell your doctor about:
Why is epi hard to diagnose?
WHAT ARE THE SYMPTOMS OF EPI?
- Diarrhea. A symptom of fat malabsorption, diarrhea is commonly experienced by people with EPI.
- Gas and bloating. ...
- Stomach pain. ...
- Unexplained weight loss. ...
- Foul-smelling, oily stools (steatorrhea) Steatorrhea is a type of bowel movement that is oily, floats, smells really bad, and is difficult to flush.
What to eat with EPI?
- Take digestive enzymes at the beginning of your meal or snack, and the right amount of them. “Work with your oncologist and/or dietitian .” Marie Durbin
- Eat small, frequent meals. ...
- Find what foods work for you. ...
- Eat your food with minimal fluids. ...
- Exercise. ...
- Know where the nearest bathrooms are. ...
- Get resources. ...
- Build a support system. ...
How to treat epi naturally?
Your doctor will likely first recommend dietary and lifestyle changes to alleviate your symptoms, regardless of the underlying cause of your EPI. If you have severe EPI or have had digestive tract surgery, your doctor will prescribe enzymes to replace the ones your pancreas normally releases.
Is epi curable?
Can exocrine pancreatic insufficiency be reversed?
You can't cure EPI, but pancreatic enzyme replacement therapy can greatly reduce uncomfortable digestive symptoms. Follow your healthcare provider's recommendations for taking PERT, and be sure to take it with every meal or snack. A dietitian can help you get the fats, nutrients and vitamins you need for good health.
How can I treat my EPI at home?
Dietary and lifestyle changes can improve the symptoms of EPI....Keys to a Pancreatic Insufficiency DietGet plenty of fluids. It's important to stay hydrated throughout the day, Dr. ... Eat small, healthy meals more often. ... Use dietary supplements. ... Avoid a high-fiber diet. ... Stop drinking alcohol (and quit smoking, too).
How is PEI treated?
The most effective treatment for PEI is pancreatic enzyme replacement therapy (PERT), which involves taking a medication called pancrelipase (Cotazym®, Creon®, Pancrease® MT) to provide the body with enzymes that break down fats and proteins.
What happens if EPI goes untreated?
If left untreated, exocrine pancreatic insufficiency can lead to feeling malnourished, fatigued and weak. This is due to the poor absorption of vitamins and nutrients. Eventually, it can lead to thinning bones (osteoporosis) or anemia (a deficiency of red blood cells).
What foods to avoid if you have EPI?
Off the EPI Menu: Foods to Avoid In general, try to limit the amount of fat you eat — especially the saturated fats in animal-based foods, such as butter, cream, fatty cuts of red meat, organ meat, and poultry skin.
What vitamin is good for pancreas?
"Vitamins C and E and selenium are good for your general health. And it may be that they help to prevent against pancreatic cancer as well....Vitamin E can be found in food such as:vegetable oils.nuts.seeds.egg yolk.
Does EPI show up on CT scan?
An X-ray or computed tomography (CT) scan may help, and a fecal fat test can be effective, although it requires large stool samples. These tests are commonly used to help diagnose EPI: A fecal fat test involves looking at a stool sample under a microscope. The most common test, according to Dr.
Can you live a normal life with pancreatic insufficiency?
If your condition is well managed, it's possible to live a healthy life — even into your advanced years — when you have EPI.
What food should I eat with pancreatic enzyme insufficiency?
Go for lean proteins, like chicken or turkey breasts, egg whites, or tuna packed in water. This will provide your body with the fuel it needs while keeping your meals low in fat. Avoid too much fiber. Though it's usually part of a healthy diet, fiber can keep your pancreatic enzymes from digesting fat as well.
What does EPI poop look like?
People with EPI are not able to absorb all the fat that they eat, so undigested fat is excreted, resulting in stools that look oily or greasy. Not all people experience this symptom.
How serious is pancreatic insufficiency?
Damage to the cells producing pancreatic enzymes leads to exocrine pancreatic insufficiency, which is a serious problem leading to malnutrition, complications, and poor quality of life.
How do you know if you have exocrine pancreatic insufficiency?
You may not have any symptoms at first. But once your pancreas gets so damaged that it starts to hurt your ability to absorb fat, you may get some symptoms, such as: Pain or tenderness in your belly. Bad-smelling bowel movements.
How to treat exocrine pancreatic insufficiency?
If your pancreas doesn’t function properly, you may need to do the digestive work for it. A healthy diet, the right supplements, and enzyme replacement therapy can all help you treat EPI. By Beth W. Orenstein Medically Reviewed by Robert Jasmer, MD. Last Updated: January 2, 2020.
What diseases affect the pancreas?
These include tumors, pancreatic surgery, chronic pancreatitis (inflammation of the pancreas), cystic fibrosis, and celiac disease, according to a review of EPI diagnosis and treatment concepts published in November 2013 in the World Journal of Gastroenterology.
What is it called when your pancreas doesn't produce enzymes?
If your pancreas doesn’t produce the enzymes needed for proper digestion, you have what’s called exocrine pancreatic insufficiency ( EPI ). It’s a treatable condition, and to best understand your options, it helps to first have a working knowledge of the condition itself. “EPI is malnutrition specifically linked to the failure ...
What is the treatment for EPI?
If it’s not possible to resolve the underlying condition or the treatment doesn’t relieve your symptoms, such as with poorly responsive celiac (i.e., symptoms persist even though the person with celiac is on a gluten-free diet ), EPI needs to be treated with diet modifications, vitamin and mineral supplements, and pancreatic enzyme replacement therapy (PERT), according to Dr. Gardner. “The goal of EPI treatment is to replace the digestive function of the pancreas,” Gardner says. Here’s how the three elements of EPI treatment can help do this.
Why do I need a low fat diet?
Depending on what’s causing your symptoms, your doctor may recommend you stick to a low-fat diet, in part because EPI leads to difficulty absorbing nutrients from food, according to Gardner. A low-fat diet can help minimize the pain, bloating, gas , and stomach discomfort that can occur with fat maldigestion.
What to eat for children with CF?
People with EPI are advised to eat plenty of fruits and vegetables, which are good sources of vitamins and minerals, Gardner says.
What to eat when you have EPI?
People with EPI are advised to eat plenty of fruits and vegetables, which are good sources of vitamins and minerals, Gardner says. Eating smaller meals, more frequently, may help reduce stomach pain, he adds.
What is the definition of pancreatic exocrine insufficiency?
Pancreatic exocrine insufficiency (PEI) can be defined as a reduction in pancreatic enzyme activity in the intestinal lumen to a level that is below the threshold required to maintain normal digestion. This concept is crucial for the understanding of PEI and has several important consequences for the diagnosis and treatment of this condition. First, pancreatic exocrine secretion can be significantly reduced without PEI being present. In a landmark paper four decades ago, DiMagno et al[1] demonstrated that steatorrhea does not occur until pancreatic lipase output is reduced to 5%-10% of normal output. Hence, the demonstration of moderately reduced bicarbonate or enzyme output in sensitive tests of pancreatic secretion, such as the secretin/cholecystokinin-stimulation test, is a reliable indicator of chronic pancreatitis (CP) but does not necessarily indicate PEI. Second, any pathology, including extrapancreatic conditions, that interrupt the chain of events required for the normal digestion of ingested food by pancreatic digestive enzymes may cause PEI. Thus, “pancreatic exocrine insufficiency” is a denomination that, from a semantic point of view, is too narrow for this condition; “pancreatic maldigestion” could be an alternative and probably more correct term. Diseases of the pancreatic parenchyma, such as CP, cystic fibrosis and status post necrotizing acute pancreatitis, are the most common causes of PEI. However, PEI may also be caused by obstruction of the pancreatic duct system due to a tumor or a stricture, by reduced stimulatory capacity in the intestine secondary to untreated celiac disease[2] or Crohn’s disease, by increased intraluminal inactivation of pancreatic enzymes in Zollinger-Ellison syndrome[3] or by impaired mixing of ingested food and the pancreatic juice after upper gastrointestinal surgery[4] (Figure (Figure11).
How to measure exocrine pancreatic function?
Exocrine pancreatic function can be measured by so-called direct pancreatic function tests. In these tests, pancreatic secretion is stimulated by secretin and/or cerulein[45] or by the ingestion of a standard test meal[46]. After stimulation, samples of the pancreatic juice are aspirated from a tube that has been placed in the duodenum, and the concentrations of pancreatic digestive enzymes and bicarbonate are measured. A peak bicarbonate concentration in pancreatic secretion significantly below normal values (a cut-off value of 80 mEq has been advocated by most authorities) in the secretin test has long been considered as the most sensitive test for early CP. A drawback of the direct function tests is that they require the placement of a large-bore tube in the duodenum during the complete duration of the test, which is poorly tolerated by patients. It is also important to keep in mind that a mild reduction in pancreatic exocrine function, occasionally called “exocrine pancreatic dysfunction” or “mild pancreatic exocrine insufficiency”, is not equivalent to clinically significant PEI. PEI, based on its definition, is a reduction in exocrine pancreatic function to a level that results in maldigestion. Since the introduction of highly sensitive pancreatic imaging methods, such as MRI, modern CT and endoscopic ultrasound, the need to rely on pancreatic function testing for the diagnosis of CP has diminished, and most centers have abandoned the classic secretin test.
What is the role of pancreatic juice in digestion?
The pancreatic juice plays a pivotal role in the digestion and absorption of nutrients [5]. Pancreatic enzyme secretion is stimulated during the cephalic[6] and gastric[7] phases to a certain degree, but the most important stimulation occurs during the intestinal phase, when chyme enters the duodenum. The presence of fatty acids, amino acids and gastric acid in the duodenum is the most potent stimulator of exocrine pancreatic secretion[8]. Vagal and neural reflexes stimulate pancreatic secretion during the cephalic and gastric phases[6,7]. During the intestinal phase, cells in the duodenal mucosa release CCK, which stimulates the secretion of pancreatic enzymes from acinar cells[9], and secretin, which elicits water and bicarbonate secretion from ductal cells[10,11].
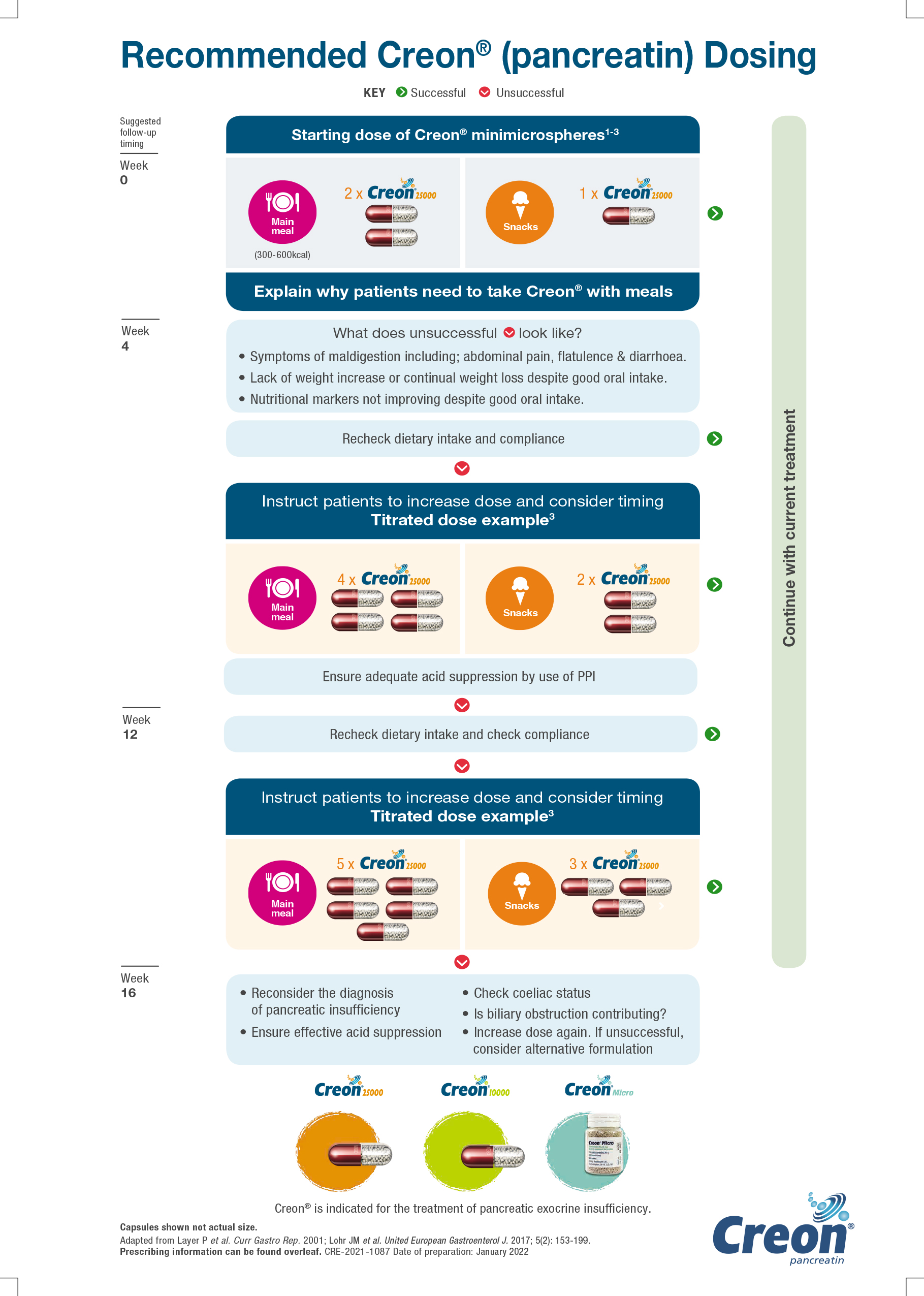
How many lipase units are needed for pancreatic enzyme replacement?
The dose should be in proportion to the fat content of the meal, usually 40-50000 lipase units per main meal, and half the dose is required for a snack.
Does smoking cause pancreatitis?
Smoking is a risk factor for pancreatic cancer, acute pancreatitis and CP[53], and is also associated with an increased probability of reduced pancreatic exocrine function based on the endoscopic pancreatic function test in cases with CP[54].
Is a low fat diet safe for steatorrhea?
Historically, a low-fat diet has been recommended in PEI to reduce steatorrhea. This recommendation has been abandoned in modern dietary counseling in PEI due to the risk of aggravating PEI-related weight loss and deficiencies of lipid-soluble vitamins[18,51]. By optimization of the PERT dose and supportive treatment with PPI, most PEI patients will tolerate a normal-fat diet. Dietary consultation should include advice for sufficient caloric intake and normal fat content. Small, frequent meals are usually better tolerated than large, high-caloric meals. Deficiencies of fat-soluble vitamins are very common in PEI patients, and vitamin supplementation therapy should be given if necessary[15]. Support for alcohol abstinence should be offered to all patients with alcohol-related CP. In addition to the general health benefits of alcohol withdrawal, this withdrawal has also been demonstrated to slow the further deterioration of pancreatic exocrine function[52]. Smoking is a risk factor for pancreatic cancer, acute pancreatitis and CP[53], and is also associated with an increased probability of reduced pancreatic exocrine function based on the endoscopic pancreatic function test in cases with CP[54]. Continued smoking has been associated with earlier development of calcifications in patients with CP[55]. Smoking cessation should be encouraged in all patients with CP with or without PEI.
Is PEI a malnutrition?
These deficiencies in turn place patients at risk of malnutrition-related complications, such as osteoporosis[15,16]. Hence, an early and accurate diagnosis of PEI is of high clinical importance.
Lifestyle and Home Remedies
To improve your symptoms of EPI, talk to your doctor about potential lifestyle changes and accommodations that you can implement. The following are some steps you can take to improve your quality of life with EPI: 2
Prescriptions
If your doctor suspects that you have EPI, they may prescribe prescription medications to manage symptoms, including pancreatic enzyme replacement therapy (PERT).
Summary
If you are diagnosed with EPI, your doctor may recommend prescription medications and dietary and lifestyle modifications, such as cutting back or quitting smoking or drinking alcohol, as these lifestyle choices can promote inflammation.
A Word From Verywell
EPI can be greatly improved with PERT prescriptions. Pancreatic functioning can be improved when drinking and smoking are avoided or eliminated completely. That said, consult with your gastroenterologist about supplementing your low-fat meals with fat-soluble vitamins (A, D, E, K), as many people with EPI are low in these vitamins.
What vitamins do you need to eat if you have pancreatic insufficiency?
Your doctor may prescribe vitamin and mineral supplements to help you maintain proper levels of the fat-soluble vitamins A, D, E, and K . Eating healthy with EPI and cystic fibrosis (CF)
What is the condition of the pancreas that causes inability to digest food?
Exocrine pancreatic insufficiency (EPI) is a condition characterized by deficiency of the exocrine pancreatic enzymes, resulting in the inability to digest food properly, or maldigestion.
What is the best treatment for EPI?
Pancreatic enzyme replacement therapies. Your doctor may start you on a prescription treatment called pancreatic enzyme replacement therapy, or PERT. PERTs are the main treatment for EPI—they replace the digestive enzymes that your pancreas isn’t producing anymore.
What happens if you have EPI?
CARBOHYDRATES can be found in bread and pasta. Carbohydrates are broken down into sugars. If you have EPI, your pancreas cannot properly break down foods, resulting in poor digestion of nutrients—especially fats. Eating healthy is important for all of us.
What is the treatment for exocrine pancreatic insufficiency?
The main treatment for exocrine pancreatic insufficiency, or EPI, is pancreatic enzyme replacement therapy.
What supplements are prescribed for the pancreas?
Your doctor may also prescribe vitamin and mineral supplements. According to the National Pancreas Foundation, these can include vitamins A , D , E, and K.
What is the treatment for EPI?
The main treatment for EPI, according to the AGA, is pancreatic enzyme replacement therapy (PERT).
Does PERT help with pancreatitis?
Research has consistently shown the benefits of PERT medications. A analysis of 17 studies, published in 2017 in the BMJ journal Gut, found that PERT improved fat absorption, decreased abdominal pain and other gastrointestinal symptoms, and improved quality of life without any adverse effects in patients with EPI from chronic pancreatitis.
What causes exocrine pancreatic insufficiency?
Pancreatitis, cystic fibrosis and other conditions that affect the pancreas cause exocrine pancreatic insufficiency (EPI). People with EPI don’t have enough pancreatic (digestive) enzymes to break down foods and absorb nutrients. It can lead to malnutrition. Pancreatic enzyme replacement therapy (PERT) can help.
What causes inflammation in the pancreas?
As many as 8 in 10 adults with this disorder develop EPI. Pancreatitis causes inflammation and swelling of the pancreas. Over time, chronic inflammation can damage the pancreatic cells that make digestive enzymes. Other causes of EPI in adults include:
What test is used to determine if you have an EPI?
You may get one or more of these pancreas function tests: Fecal elastase test ( FE-1) to check stool for the presence of the elastase enzyme that helps digest proteins. Little (or no) elastase can indicate EPI.
What enzymes are needed to break down fat?
The different types of pancreatic enzymes include: Amylase, which breaks down carbohydrates. Lipase, which breaks down fats. Protease and elastase, which break down proteins.
Why do I have EPI?
It makes enzymes that aid digestion and help your body absorb nutrients. When you have EPI, you don’t have enough digestive enzymes. Foods pass through your intestines in a more complete (undigested) state. As a result, your body doesn’t get the nutrients it needs from foods.
Can alcohol cause pancreatitis?
It’s helpful to avoid smoking and alcohol use. These substances make your pancreas work harder and can contribute to pancreatitis, which can lead to EPI. Your healthcare provider can offer support to stop using these substances.
Can cystic fibrosis cause EPI?
Because cystic fibrosis and SDS are inherited, you can’t prevent them or lower the risk of EPI with the conditions.
What is the term for a deficiency of exocrine pancreatic enzymes?
Exocrine pancreatic insufficiency (EPI) is defined by a deficiency of exocrine pancreatic enzymes resulting in an inability to maintain normal digestion. This inadequate digestion with nutrient and, especially, fat malabsorption occurs when intraduodenal levels of lipase fall below 5–10% of normal enzyme output [1], leading to pancreatic steatorrhea, weight loss, and a potential decrease in quality of life [2–5]. Furthermore, in EPI, due to cystic fibrosis (CF) or chronic pancreatitis, there is decreased bicarbonate output causing a lower intestinal pH, which precipitates bile salt acids and impairs micelle formation of fats [6, 7]. Fat maldigestion is compounded by decreased pancreatic secretion of lipase and colipase, further dampening hydrolysis of intraluminal fat.
What causes EPI after pancreatic surgery?
Factors that contribute to EPI following pancreatic surgery are a decrease in pancreatic tissue volume, extensive denervation following lymph node dissection , and surgically altered anatomy [6]. Conditions such as pancreatic cancer, intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms, premalignant mucinous cystic lesions, and benign tumors of the pancreas may all lead to EPI via obstruction of the pancreatic duct. The degree of EPI following pancreatic surgery is dependent on the extent of pancreatic resection combined with the degree of residual pancreatic parenchymal function with full manifestation of EPI seen following a total pancreatectomy [20, 21]. The mechanism of EPI in patients undergoing a Whipple procedure may be related to a mistiming of secreted endogenous pancreatic enzymes mixing with chyme.
How common is EPI after a pancreatectomy?
Large systematic reviews report a 19–80% incidence of EPI following a distal pancreatectomy [22–25]; however, this wide variation may be in part a result of the different diagnostic methods employed [22, 26]. Post-operative incidence of EPI after Whipple surgery is 56–98% [23, 24, 27–29]. In addition, Halloran et al. [28] analyzed 40 patients following resection for pancreatic malignancy and found that EPI was common and sustained after surgery, but was not associated with significant symptoms. These patients with newly developed EPI, however, did have a tendency towards poorer quality of life.
How much lipase is needed for EPI?
The existing studies vary on recommendations for dosing of exogenous pancreatic enzymes ranging from 25,000 to 80,000 lipase units per main meal , and there is uncertainty about administration of PERT before, during, or after the meal. In addition, the treatment goals differ from reducing pancreatic steatorrhea and elimination of maldigestion and malabsorption, to the prevention of malnutrition-related morbidity and mortality. This is all complicated by the myriad of pancreatic enzyme formulations at a wide array of dosing strengths. Thus, it is not surprising that confusion amongst physicians exists over the optimal dosage, administration schedule, and what to aim for in PERT.
What is the term for a process that causes irreversible changes in the pancreas?
Chronic pancreatitis. Chronic pancreatitis is an ongoing inflammatory process with irreversible morphological changes to the pancreas and a gradual loss in pancreatic parenchyma. There are three major groups of mutations that account for chronic pancreatitis (PRSS1, SPINK1, and CFTR).
Can EPI be diagnosed with pancreatic enzymes?
Many diagnostic tests are available to diagnose EPI, however, the criteria of choice remain unclear and the causes for a false-positive test are not yet understood. Despite multiple studies on the treatment of EPI using exogenous pancreatic enzymes, there remains confusion amongst medical practitioners with regard to the best approach to diagnose EPI, as well as dosing and administration of pancreatic enzymes.
Is pancreatic enzymes used in EPI?
Appropriate use of diagnostics and treatment approaches using pancreatic enzymes in EPI is essential for patients. This opinion piece aims to address the existing myths, remove the current confusion, and function as a practical guide to the diagnosis and treatment of EPI.
An Overview of Frequent Symptoms and Potential Complications
Verywell Health articles are reviewed by board-certified physicians and healthcare professionals. Medical Reviewers confirm the content is thorough and accurate, reflecting the latest evidence-based research. Content is reviewed before publication and upon substantial updates. Learn more.
Frequent Symptoms
In EPI, undigested and unabsorbed food in the digestive tract can lead to frequent gastrointestinal symptoms. These symptoms can range from mild to severe. Symptoms of EPI typically become more severe when 90% of your pancreas’s normal enzyme production is gone. 4 At this point, you’re more likely to have symptoms clearly associated with EPI.
Complications
If EPI is left untreated and becomes more severe, several complications can arise. Because complications are typically long term, they can have a significant effect on your quality of life. EPI complications may lead to skeletal, renal (kidney-related), and cardiovascular issues. 6 These include:
Summary
EPI is a rare malabsorptive condition in which the pancreas doesn't produce digestive enzymes. It is mostly seen in people with conditions affecting the pancreas, such as pancreatitis and cystic fibrosis.
A Word From Verywell
EPI can cause pain and discomfort, which can have a serious effect on your quality of life. Since EPI can share symptoms with many other gastrointestinal issues, work with your healthcare provider to make sure you have a correct diagnosis and your pain is being managed.
What is the function of the pancreas?
One of the main functions of the pancreas is to produce and release a number of enzymes that help the body break down food and absorb nutrients. But pancreatic cancer and its treatments can cause the pancreas to make fewer of these essential enzymes — a condition known as exocrine pancreatic insufficiency (EPI).
Can pancreatic enzymes be taken?
Studies show that pancreatic enzyme supplements, when taken properly, can be especially helpful.
Can EPI cause diarrhea?
Patients with EPI may experience a malabsorption of nutrients from foods, which can cause ongoing digestive issues like stomach pain, weight loss, gas, changes in stools, and diarrhea. EPI is common among pancreatic cancer patients, but there are many resources to help you manage it.

Adverse effects
Causes
Treatment
Diet
Interactions
Definition
- EPI is malnutrition specifically linked to the failure of the pancreas, says David C. Whitcomb, MD, PhD, chief of the division of gastroenterology, hepatology, and nutrition, and medical director of the Comprehensive Pancreas Program in the Liver-Pancreas Institute at the University of Pittsburgh and University of Pittsburgh Medical Center. EPI can also cause gastric discomfort, w…
Risks
- Your pancreas is made up of two small glands deep in your belly. One of its functions (the exocrine function) is to release enzymes that help break down the food you eat so your body can absorb its nutrients. Some people have diseases or conditions that affect the ability of their pancreas to release these enzymes. These include a tumor, pancreatic surgery, chronic pancreat…
Prevention
- Doctors can sometimes treat EPI at its root cause, like with celiac disease, for example, says Timothy B. Gardner, MD, an associate professor of medicine at the Geisel School of Medicine at Dartmouth in Lebanon, New Hampshire. Otherwise, EPI symptoms need to be treated with diet, vitamin and mineral supplements, and pancreatic enzyme replacement th...
Lifestyle and Home Remedies
- Today, people with EPI are advised to eat plenty of fruits and vegetables, which are good sources of vitamins and minerals, Gardner says. Also, eating smaller meals more frequently may help reduce stomach pain.
Prescriptions
- Its important that you take the enzymes just before and during meals or snacks, not after you eat, PCA notes. And take your medication with cold not hot drinks because heat can damage the enzymes.
Summary
- Pancreatic enzyme supplements are capsules that contain a mixture of digestive enzymes. They include lipase to break down fat, protease to assist with digestion of protein, and amylase for carbohydrates. The more fat in your meal, the higher dose of enzymes youre likely to need, Whitcomb says.
A Word from Verywell
- PERT can cause diarrhea or constipation, nausea, and gastric upset, according to PCA. You may need to experiment and find a brand you can best tolerate because different manufacturers use different coatings. If you take the enzymes with antacids, they may not be as effective, according to the Pancreatic Cancer Network.