Medication
Calcifediol and calcitriol are still under investigation as possible treatments in early AKI [138,139,140]. Alkaline phosphatase is an enzyme expressed along the proximal tubule and has the ability to reduce renal inflammation.
Procedures
If you have AKI that requires dialysis, also referred to as AKI-D, you may be treated in the hospital—since many people with AKI are in the hospital already for an injury, illness, or other condition—or at a dialysis center, under the care of a nephrologist (kidney doctor).
Therapy
Prerenal acute kidney injury (AKI), (which used to be called acute renal failure), occurs when a sudden reduction in blood flow to the kidney (renal hypoperfusion) causes a loss of kidney function. In prerenal acute kidney injury, there is nothing wrong with the kidney itself.
Nutrition
The main goal of your healthcare provider is to treat what is causing your acute kidney injury. Your healthcare provider will work to treat all of your symptoms and complications until your kidneys recover.
Which medications are used in the treatment of acute kidney injury (AKI)?
How is Aki treated in the hospital?
What is prerenal acute kidney injury AKI?
How will my healthcare provider treat my acute kidney injury?

What causes Prerenal AKI?
Notable causes of prerenal AKI include low blood volume (e.g., dehydration), low blood pressure, heart failure (leading to cardiorenal syndrome), hepatorenal syndrome in the context of liver cirrhosis, and local changes to the blood vessels supplying the kidney.
What is the best treatment for AKI?
Some people need to be treated in a hospital and stay until their kidneys heal. Possible treatments include: Medicines to control your blood pressure and adjust the electrolytes in your blood. Treatments to keep the right amount of fluid in your body (e.g. diuretics to make you pee out extra fluid)
Does AKI require immediate treatment?
Acute kidney injury means your kidneys stop working suddenly. AKI requires immediate treatment and may be reversible if diagnosed and treated quickly—unlike chronic kidney disease (CKD), which is kidney damage that typically progresses slowly over a period of time and is not reversible.
How do you manage post renal AKI?
Postrenal acute kidney injury requires immediate treatment. When detected early, it usually can be reversed by removing or bypassing the obstruction in the urinary tract, before any permanent damage to the kidneys occurs. If the blockage is a kidney stone, your doctor can remove or destroy the stone.
What drugs should be stopped in AKI?
Clinicians managing patients with AKI therefore frequently stop drugs that lower blood pressure (particularly ACEI and ARBs, which selectively reduce glomerular pressure) and diuretics. ACEIs, ARBs and potassium-sparing diuretics may also be stopped because of hyperkalaemia.
How long does it take for AKI to resolve?
In some cases AKI may resolve in a couple of days with fluid and antibiotics. In other cases the illness affecting the kidneys and the rest of the body may be so severe that recovery takes two or three weeks or even longer.
Is AKI Stage 1 Serious?
The severity of AKI is described by categorising into three stages, with stage 1 being the least severe and stage 3 being the most severe (see Box 1).
Is AKI curable?
Most people with AKI make a full recovery, but some people go on to develop chronic kidney disease or long-term kidney failure as a result. In severe cases, dialysis, where a machine filters the blood to rid the body of harmful waste, extra salt and water, may be needed.
What is the most common cause of AKI?
Low blood pressure (called “hypotension”) or shock. Blood or fluid loss (such as bleeding, severe diarrhea) Heart attack, heart failure, and other conditions leading to decreased heart function.
How can you tell the difference between renal Aki and Prerenal?
Response to fluid repletion is still regarded as the gold standard in the differentiation between prerenal and intrinsic AKI. Return of renal function to baseline within 24 to 72 hours is considered to indicate prerenal AKI, whereas persistent renal failure indicates intrinsic disease.
What are the stages of AKI?
AKI has four phases.Onset phase: Kidney injury occurs.Oliguric (anuric) phase: Urine output decreases from renal tubule damage.Diuretic phase: The kidneys try to heal and urine output increases, but tubule scarring and damage occur.Recovery phase: Tubular edema resolves and renal function improves.
Can Lasix be given in AKI?
The severity of acute kidney injury has a significant effect on the diuretic response to furosemide; a good 'urinary response' may be considered as a 'proxy' for having some residual renal function. The current evidence does not suggest that furosemide can reduce mortality in patients with acute kidney injury.
What Is Acute Kidney Injury (AKI)?
Acute kidney injury (AKI) is a sudden episode of kidney failure or kidney damage that happens within a few hours or a few days. AKI causes a build-...
What Are The Signs and Symptoms of Acute Kidney Injury?
Signs and symptoms of acute kidney injury differ depending on the cause and may include: 1. Too little urine leaving the body 2. Swelling in legs,...
What Causes Acute Kidney Injury?
Acute kidney injury can have many different causes. AKI can be caused by the following:Decreased blood flowSome diseases and conditions can slow bl...
How long does it take for a prerenal acute kidney injury to heal?
Depending on the cause, the condition often reverses itself within a couple of days after normal blood flow to the kidneys has been restored.
What causes acute kidney injury?
Causes of prerenal acute kidney injury include: 1 Severe blood loss and low blood pressure related to major cardiac or abdominal surgery, severe infection ( sepsis ), or injury. 2 Medicines that interfere with the blood supply to the kidneys. Medicines such as ACE inhibitors and common pain medicines ( NSAIDs ) commonly cause prerenal acute kidney injury in people who already have an increased risk for kidney problems. 3 Severe dehydration caused by excessive fluid loss. 4 Severe burns. 5 Pancreatitis and liver diseases, such as cirrhosis , that create fluid shifts in the abdomen.
What causes a decrease in blood pressure in the kidneys?
It can be a complication of almost any disease, condition, or medicine that causes a decrease in the normal amount of blood and fluid in the body. Causes of prerenal acute kidney injury include: Severe blood loss and low blood pressure related to major cardiac or abdominal surgery, severe infection ( sepsis ), or injury. ...
Can NSAIDs cause kidney problems?
Medicines such as ACE inhibitors and common pain medicines ( NSAIDs ) commonly cause prerenal acute kidney injury in people who already have an increased risk for kidney problems.
Can acute kidney injury cause tissue death?
But if it is not reversed or treated successfully and quickly, prerenal acute kidney injury can cause tissue death in the kidneys and lead to intrinsic (intrarenal) acute kidney injury. This information does not replace the advice of a doctor.
What is AKI in medical terms?
Treatment for acute kidney injury (AKI) can vary by person and depends on the cause. After an AKI diagnosis, the primary goal of your care team is to treat whatever is causing your acute kidney injury, so your kidneys can regain function. Acute kidney injury is also sometimes called acute renal failure (ARF) or acute kidney failure (AKF).
What happens if AKI is not reversed?
If AKI is not reversed, it may lead to permanent kidney failure and require further treatment, including ongoing dialysis or a transplant. Your care team will help you manage your treatment plan for kidney failure.
What does it mean when your kidneys stop working?
Acute kidney injury means your kidneys stop working suddenly. AKI requires immediate treatment and may be reversible if diagnosed and treated quickly—unlike chronic kidney disease (CKD), which is kidney damage that typically progresses slowly over a period of time and is not reversible. Some people diagnosed with AKI will need dialysis ...
What medications can cause kidney damage?
Do not stop taking any medication without first talking to your doctor. Common medications with possible risks for people with AKI include: NSAIDs —nonsteroidal anti -inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are common pain relievers that can be harmful to damaged kidneys. NSAIDs include: ibuprofen and naproxen, among others.
How does dialysis work?
Dialysis works by filtering toxins, waste, and fluid from your blood through a dialyzer inside a dialysis machine. Your blood is accessed through your catheter site and circulated through the machine and cleaned before being returned to your body.
What to do if your kidneys are hurt?
Talk to your doctor about your current medications. Talk to your doctor immediately about any medications, vitamins, or supplements you’re taking. When your kidneys are injured, many medications require close adjustment because they’re cleared through your kidneys and could cause additional harm.
What antibiotics should I avoid with AKI?
Antibiotics to avoid with AKI include: Bactrim, aminoglycosides (given intravenously), such as gentamicin and tobramycin. Diabetes medications —many diabetes medications may need to be avoided or adjusted if you have AKI. Check with your doctor about any diabetes medications you are prescribed.
What is AKI in kidneys?
AKI is defined as an abrupt (within hours) decrease in kidney function, which encompasses both injury (structural damage) and impairment (loss of function). It is a syndrome that rarely has a sole and distinct pathophysiology.
What is AKI in nephrology?
AKI from glomerular damage occurs in severe cases of acute glomerulonephritis ( GN). AKI from vascular damage occurs because injury to intra-renal vessels decreases renal perfusion and diminishes GFR and finally acute interstitial nep hritis occurs due to an allergic reaction to a variety medications or an infection.
Why is AKI important?
It is obvious that all clinical phenotypes of AKI cannot fit into a single pathophysiologic pathway. AKI facilitates organ cross-talk and distant organ injury. These innovations will aid in the design of epidemiologic studies and randomised trials of preventive and therapeutic interventions.
What is CI-AKI?
Contrast induced AKI (CI-AKI) previously known as contrast induced nephropathy (CIN) is a syndrome in which acute renal dysfunction is diagnosed following intravascular administration of contrast agents. Contrast agents are used widely for diagnostic and therapeutic purposes. Their nephrotoxic potential was first suggested at least 50 years ago and today are considered one of the most common causes of AKI among hospitalised patients. 86, 87 The risk of CIN has long been assumed to be proportional to the degree of preexisting renal dysfunction and it is associated with extended length of hospital stay, accelerated onset of end stage renal disease, need for dialysis, increased mortality and increased costs. 86, 88 – 90 Although in the past many different definitions were used to define CI-AKI, the new KDIGO definition of AKI applies to CI-AKI and will help us to use a common language in research and in clinical diagnosis of this syndrome. The pathophysiology of CI-AKI is not very well defined. Animal models of CI-AKI suggest several potential mechanisms of nephrotoxicity, including renal ischaemia, vasoconstriction, formation of reactive oxygen species and direct tubular toxicity, which lead to decreased renal perfusion. 91 – 94 However, the physiologic relevance of these models may be limited since multiple renal insults are required to express the desired phenotype and such injury is not typically seen in human patients. The causal association between contrast media and nephrotoxicity has been established from several studies. However the non-existence of a uniform definition and poorly designed studies may have led to overestimation of the frequency and severity of CI-AKI. 95 – 98
What is the clinical phenotype of AKI?
Essentially AKI is a term used to describe the clinical syndrome that occurs when renal function is acutely decreased to a point that the body accumulates waste products and becomes unable to maintain electrolyte, acid-base and water balance. 58.
What causes AKI in the nephron?
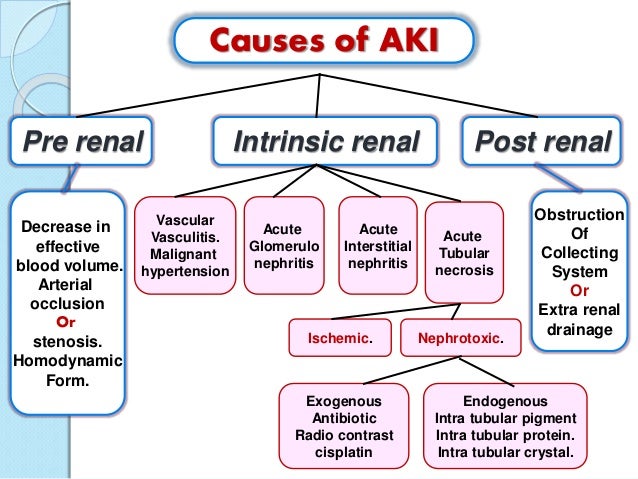
There are numerous potential causes of AKI, mainly related to a focal mismatch between oxygen and nutrient delivery (because of impaired microcirculation) to the nephrons and increased energy demands (due to cellular stress). 58 For many years the diagnosis and management of AKI was based on the concept of classification to three main categories: pre-renal, intrinsic and post-renal ( Figure 1 ). 59 – 61
What are the four structures of the kidney?
Generally, four structures of the kidney are involved including tubules, glomeruli, the interstitium, and intra-renal blood vessels . ( Figure 1 and Table 3) Acute tubular necrosis (ATN) is the term used to designate AKI resulting from damage to the tubules. It is the most common type of intrinsic kidney injury.
What Are The Three Types Of Aki
There are many causes of AKI, including infections, heart disease, liver disease, autoimmune diseases, cancer, hypertension, and traumatisms. In short, causes are uncountable.
How Do You Detox Your Kidneys
In the last few decades, kidney detoxing and kidney cleansing programs have gained a lot of popularity. However, so far, there isnt any convincing scientific evidence that cleansing programs do anything.
Original Articlemild Elevation Of Urinary Biomarkers In Prerenal Acute Kidney Injury
Prerenal acute kidney injury is thought to be a reversible loss of renal function without structural damage. Although prerenal and intrinsic AKI frequently coexist in clinical situations, serum creatinine and urine output provide no information to support their differentiation.
Acute Kidney Failure Prerenal Causes
Prerenal failure is the most common type of acute renal failure . The kidneys do not receive enough blood to filter. Prerenal failure can be caused by the following conditions:
Acute Kidney Injury And Extra
Recent evidence in both basic science and clinical research are beginning to change our view for AKI from a single organ failure syndrome, to a syndrome where the kidney plays an active role in the evolution of multi-organ dysfunction.
How Can I Prevent Acute Kidney Injury
Because AKI happens suddenly, it can be hard to predict or prevent it. But taking good care of your kidneys can help prevent AKI, chronic kidney disease and kidney failure/ESRD. Follow these general rules to keep your kidneys as healthy as possible:
What Is The Treatment For Acute Kidney Injury
The treatment for AKI depends on what caused it to happen. Most people need to stay in the hospital during treatment and until their kidneys recover. While you are being treated for the problem that caused your AKI, you may also have treatments to prevent problems that can make it harder for your kidneys to heal. Some possible treatments include:
How to differentiate AKI from CKD?
The best way to differentiate between AKI and CKD is to look at the baseline SCr or GFR. AKI refers to an abrupt increase in SCr or drop in GFR from baseline. It is possible to have AKI on CKD. If previous laboratory values are not available history, physical examination and clinical investigations may be helpful.
What causes AKI?
Prerenal AKI is probable the most common type and is caused by hemodynamic changes resulting in reduced perfusion of kidneys.
How severe is AKI?
How severe is this patient's AKI? 1 AKIN Stage I: increase in SCr >0.3 (26 μmol/L) OR >50% – 100% from baseline, urine putput <0.5 mL/kg/hr for >6 hours 2 AKIN Stage II: Increase in SCr >100% – 200% from baseline, urine output <0.5 mL/kg/hr for >12 hours 3 AKIN Stage III: Increase in SCr >200 from baseline OR SCr >4 after a rise of at least 0.5 mg/dL OR on renal replacement therapy, urine putput <0.3 mL/kg/hr for >24 hours or anuric >12 hours
What is globular AKI?
Glomerular AKI is usually associated with proteinuria and dysmorphic red blood cells and RBC casts in the urine.
Is AKI worse than AKI?
AKI is an independent risk factor for mortality. Survival of patients with AKI is significantly worse than those without AKI even after adjustments for other risk factors.
Does creatinine increase with AKI?
There is no consensus on the magnitude of rise of serum creatinine to indicate AKI. Many studies refer to a rise in creatinine of 0.5 mg/dl but there is evidence that even a smaller rise in SCr may be significant. SCr does not reflect GFR.
Which biomarker is more sensitive to kidney injury?
More recently urinary and serum biomarkers such as neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL), interleukin 18 (IL-18) and kidney injury molecule 1 (KIM-1), Liver fatty acid binding protein (LFABP) and others have been shown to be more sensitive than SCr in detecting early kidney injury.
What is the goal of prerenal azotemia treatment?
The goal of treatment for prerenal azotemia is to restore normal blood flow to the kidneys. Time is of the essence in this treatment, as permanent kidney damage could result from the loss of blood if it continues for too long. The exact treatment will depend on what caused the interruption of blood flow.
What is the difference between primary and post renal azotemia?
Primary renal azotemia arises as a result of damage to the kidneys themselves or problems occurring inside the organs. Postrenal azotemia is a consequence of blockage of the urinary tract downstream from the kidneys.
What is prerenal azotemia?
Prerenal azotemia refers to the condition when it arises from factors leading into but not inside the kidneys, usually involving blood flow to the kidneys. Although the symptoms are similar, the treatment options for the three different. types of disorder are different. #1.
What is the test for azotemia?
When azotemia is diagnosed, one test that works well to pinpoint whether the cause is prerenal, renal, or post-renal is to test for blood levels of serum urea nitrogen, or blood urea nitrogen (BUN) compared to creatinine. BUN is a waste product generated by liver function.
What is the best treatment for dehydration?
This can also involve dietary. measures or sometimes medications, although the obvious treatment – – drinking plenty of water – – is usually the appropriate one.
Can prerenal azotemia cause kidney damage?
Causes. There is usually no kidney disease properly so called associated with prerenal azotemia. However, kidney damage can result from obstructed blood flow, so it can be an accompanying syndrome along with azotemia even though it is not the proximate cause.
Can kidney failure be irreversible?
Otherwise, irreversible kidney damage could result. With severe kidney failure, the only workable therapies are renal replacement therapies, including dialysis or even a kidney transplant. Successful intervention to identify and treat the cause of prerenal azotemia can prevent this necessity from arising.