What causes Edwards syndrome?
There is no effective long-term treatment for babies with Edwards syndrome. Parents in this situation face a very hard choice. They can choose to try to keep their babies alive in the neonatal intensive care unit.
What are the symptoms of Edward syndrome?
Edwards Syndrome Risk Factors. Babies born with the Edwards syndrome often have petite heads, clinched fists and curved feet, and may have kidney, heart and skeletal issues. A lot of babies with Edwards syndrome die before birth, and of those born alive have 90% chances of death within the very first year.
What are symptoms of Edwards syndrome?
Jan 10, 2022 · There is no definitive treatment for Edwards syndrome. Health care providers and parents often have difficulty in making treatment decisions. Parents of the child with Edward syndrome often have to decide between palliative care (or comfort care) and prolonging life with intensive treatment or surgery.
How rare is Edwards syndrome?
Dec 03, 2021 · The treatment of Edwards syndrome is not definitive. It is often difficult for health care providers and parents to make treatment decisions for their children. The decision to provide palliative care (or comfort care) to prolong a child’s life with intensive treatment or surgery is often difficult for parents of Edward syndrome children.
See more
There is no specific treatment to clinically address Edwards syndrome or to substantially improve your life expectancy, beyond managing certain complications. Physical and psychological therapies (especially for the family and through support groups) seek to facilitate, as far as possible, the arrival of the inevitable outcome.

What are the treatments options for Edwards syndrome?
There is no definitive treatment for Edwards syndrome. Health care providers and parents often have difficulty in making treatment decisions. Parents of the child with Edward syndrome often have to decide between palliative care (or comfort care) and prolonging life with intensive treatment or surgery.Jan 10, 2022
How long is the average lifespan of a person with Edward syndrome?
The full form of Edwards' syndrome is considered to be a life-limiting condition which means it affects how long the baby can live. Around 5 in 10 (52.5%) may live longer than 1 week and around 1 in 10 (12.3%) may live longer than 5 years.Jun 14, 2021
Why is Edwards syndrome not curable?
An unusually small placenta might be noted during the birth of the child. Medical science has not found a cure for Edward's syndrome at this time. Babies with the syndrome commonly present with major physical abnormalities and doctors face hard choices in regards to their treatment.Feb 14, 2010
Are there any treatments or cures for trisomy 18?
There are no treatments or cures for the extra chromosome that causes trisomy 18. Treatment for babies and children with trisomy 18 is focused on the symptoms they have.
What are the specific symptoms of Edwards syndrome?
Edwards Syndrome SymptomsMicrocephaly (small and abnormally shaped head)Micrognathia (abnormally small jaw and mouth)Long, overlapping fingers and underdeveloped fingernails.Scrunched fists.Low-set ears.Arched spine and abnormally shaped chest.Crossed legs.Umbilical hernia.More items...
What is the main cause of Edwards syndrome?
Edwards syndrome is a genetic condition in babies that causes severe disability. It is caused by an extra copy of chromosome 18 and babies born with the condition usually do not survive for much longer than a week.
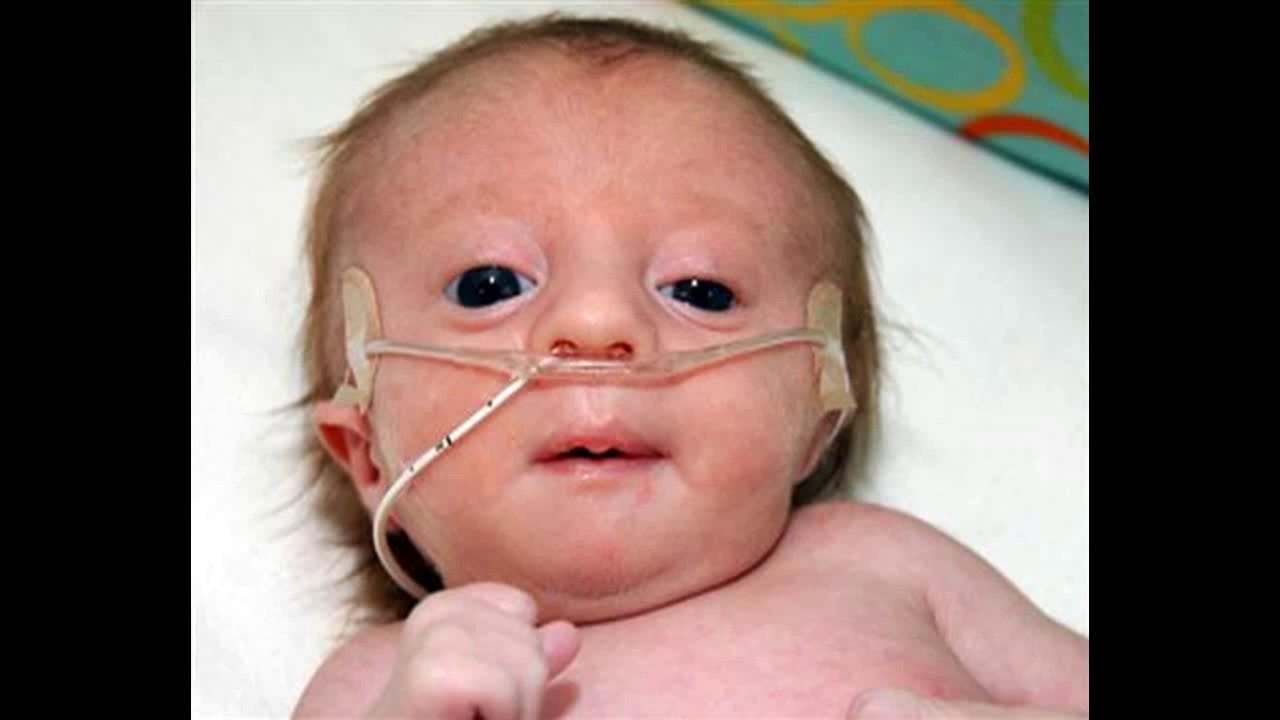
What does Edwards syndrome look like?
Affected individuals may have heart defects and abnormalities of other organs that develop before birth. Other features of trisomy 18 include a small, abnormally shaped head; a small jaw and mouth; and clenched fists with overlapping fingers .Feb 16, 2021
Can you see Edwards syndrome on ultrasound?
Your healthcare provider will look for signs of Edwards syndrome (trisomy 18) during a prenatal ultrasound, including: Very little fetal activity.Dec 13, 2021
Can Edwards syndrome be prevented?
Most cases of Edwards' syndrome are not hereditary and cannot be prevented. However, parents who have had a child with Edwards' syndrome are at increased risk of having another child with the syndrome.
Can a baby with trisomy 18 survive?
Fifty per cent of babies born with trisomy 18 survive beyond their first six to nine days. About 12% of babies born with trisomy 18 survive the first year of life. It is difficult to predict the life expectancy of a baby with trisomy 18 if the baby does not have any immediate life-threatening problems.Jul 19, 2016
Does trisomy 18 show on ultrasound?
Trisomy 18, also known as Edwards' syndrome, is a genetic disorder that affects babies and can often be diagnosed before birth. A fetal ultrasound during pregnancy can show features that are suggestive of trisomy 18, and the detection rate is about 90% during pregnancy weeks 14-21.May 19, 2021
Are there prenatal tests for trisomy 18?
Nuchal translucency measurement First trimester screening is a prenatal test that offers early information about a baby's risk of certain chromosomal conditions, specifically, Down syndrome (trisomy 21) and extra sequences of chromosome 18 (trisomy 18).Nov 17, 2020
What is Edwards syndrome?
Edwards syndrome is a genetic condition in babies that causes severe disability. It is caused by an extra copy of chromosome 18 and babies born wit...
How does Edwards syndrome happen?
Children with Edwards syndrome have 3 copies of part or all of chromosome 18, instead of the usual 2 copies. It is also called Trisomy 18. This can...
What are the symptoms of Edwards syndrome?
Babies with Edwards syndrome may have: low birth weight small head and jaw an unusual-looking face and head unusual hands and feet with overlapping...
How is Edwards syndrome diagnosed?
Edwards syndrome can be suspected or even diagnosed during pregnancy. Sometimes the possibility of Edwards syndrome is raised after the 11 to 13-we...
How is Edwards syndrome treated?
There is no effective long-term treatment for babies with Edwards syndrome. Parents in this situation face a very hard choice. They can choose to t...
What is Edwards syndrome?
Edwards Syndrome depicts a group of birth defects due to the presence of added genetic material from chromosome 18. It is also known as Trisomy 18, because in majority of the cases there are three copies of chromosome 18 in the place of the usual two.
When is Edwards syndrome diagnosed?
Edwards Syndrome Diagnosis. Routine prenatal screening during 18th- 20th week of pregnancy can discover signs of the syndrome, and genetic testing can authenticate the existence of the aberrant genetic material. Babies who are born with the syndrome will require medical attention from a wide variety of specialists.
What tests are used to test for genetic defects?
Advanced Parental Testing: Based on early screening and ultrasounds, if a high risk of genetic abnormalities is identified, the pregnant woman may choose to have more advanced tests to check for any anomaly. Amniocentesis and Chorionic Villus Sampling (CVS) are the two procedures used to test for genetic defects.
Can a baby live on to adulthood?
Babies with lesser forms of deficiency may live on to see adulthood but will have extreme mental and physical handicaps. Tests such as Amniocentesis and Chorionic villus sampling (CVS) tests can help in prenatal diagnosis and are generally considered safe; though there is a small risk of miscarriage.
What is Edward syndrome?
Introduction. Edward syndrome, also called trisomy 18 syndrome, is an autosomal chromosomal disorder due to an extra copy of chromosome 18. Edward syndrome is one of the autosomal trisomy syndrome, second in frequency only to trisomy 21.
How prevalent is Edward syndrome?
In the last two decades, the prevalence of trisomy 18 has increased due to an increase in the average maternal age. The prevalence of Edward syndrome is varied by country and termination policies. In the United States, the overall prevalence of Edward syndrome is approximately 1 in 2500, and liveborn prevalence is 1 in 8600.
What type of chromosome is Edwards syndrome?
Edwards syndrome usually results from an extra copy of chromosome 18q. There are three types of Edward syndrome: Complete, partial, and mosaic trisomy 18. Complete trisomy 18 is the most common form (94%). In this type, every cell contains three complete copies of chromosome 18.
What is the extra chromosome 18?
Smith et al. confirmed the extra copy of chromosome 18 as an underlying cause for Edward syndrome.[2] Edward syndrome, also called trisomy 18 syndrome, is an autosomal chromosomal disorder due to an extra copy of chromosome 18. Edward syndrome is one of the autosomal trisomy syndrome, second in frequency only to trisomy 21.
What is ultrasonography used for?
Diagnostic imaging studies, such as ultrasonography, can be used to assess for intracranial, cardiac (echocardiogram), intraabdominal, and renal abnormalities; but circumstances will dictate the study of choice.[14] . Screening is appropriate in such patients since anomalies can be found in multiple organ systems.
What are the causes of death in Edward syndrome?
The most important causes of mortality are cardiac failure due to cardiac defects, respiratory failure due to obstructive apnea, pulmonary hypertension, hypoventilation, and central apnea. Complications. Growth: Low birth weight followed by failure to thrive is common in Edward syndrome.
When was Edward syndrome first reported?
Edward syndrome was first reported by Edwards et al. in 1960,who reported a neonate with multiple congenital malformations and cognitive deficit.[1] Smith et al. confirmed the extra copy of chromosome 18 as an underlying cause for Edward syndrome. [2]
What Treatments Are Available For Edwards Syndrome?
The treatment of Edwards syndrome is not definitive. It is often difficult for health care providers and parents to make treatment decisions for their children. The decision to provide palliative care (or comfort care) to prolong a child’s life with intensive treatment or surgery is often difficult for parents of Edward syndrome children.
How Is Edwards Syndrome Managed?
The condition is not cured by any means. Heart disease, breathing difficulties, and infections are some of the symptoms of the condition that will be treated. It is also possible that your baby will need to be fed through a feeding tube due to their difficulty swallowing.
Is Trisomy 18 A Disability?
There is an extra third copy (trisomy) of genetic material from chromosome 18 in people with Edwards syndrome, as opposed to the usual two copies. In children with this condition, intellectual disability and congenital anomalies are severe.
What Is Edwards Syndrome Mayo Clinic?
Down syndrome is the most common trisomy, followed by trisomy 18 (also known as Edwards syndrome). One in 5,000 live births is affected by this condition, which is caused by an extra chromosome 18 and similar to Down syndrome. The rate of maternal age increases more frequently than other factors.
How Long Does A Child With Edwards Syndrome Live?
Around five in ten (52 percent) babies with Edwards’ syndrome live to be at least five years old. A person may live longer than 1 week if they have a 5% chance and 12 if they have a 10% chance. The survival rate of these animals (3%) is greater than that of humans (3%).
What Are The Treatment Options For Trisomy 18?
Trisomy 18 is caused by an extra chromosome, and there are no treatments or cures for it. In the treatment of babies and children with trisomy 18, the symptoms are the most important factor.
What Happens If My Baby Has Trisomy 18?
There are many babies with trisomy 18 who have problems with their bodies in all parts. The leading cause of death is heart disease, feeding problems, and infections.
What is Edwards syndrome?
Edwards syndrome is named after John H. Edwards, a British physician and geneticist who, in 1960 and at the University of Wisconsin, described the disorder. It is an autosomal aneuploidy (a chromosomal abnormality in the non-sex chromosomes, the autosomal ones) caused by an extra copy of chromosome 18.
Causes
The causes of Edwards syndrome are very clear: having extra material from chromosome 18. It is this extra material from autosomal chromosome number 18 that causes serious physiological problems during fetal and infant development that lead to the disease.
Symptoms
Edwards syndrome is clinically manifest from birth. The presence of extra material from chromosome 18 affects the normal physiological development of the baby, with an impact on its health that will depend on how serious the chromosome abnormality is. Obviously, a total trisomy of chromosome 18 will be the most serious situation.
Treatment
Routine exams during the 18-20 weeks of pregnancy can show signs that your baby has Edwards syndrome.. When it is born, the unusually small placenta is one of the first signs that indicate the disorder.
What are the threadlike structures present in cells that help to keep genes intact?
Chromosomes are the threadlike structures present in cells that help to keep genes intact. These genes or genetic material usually carries the commands or instructions needed to make every part of a baby's body. During the formation of a zygote, when the egg and sperm join, 23 chromosomes from both the egg and sperm fuse to make a foetus which now has a total of 46 chromosomes . When either of the parents carries a wrong number of chromoso mal materials, the defect is passed on to the foetus, which now has a wrong number of chromosomes .
What does it mean when a baby has 3 copies of the chromosome 18?
A trisomy usually signifies that the baby chiefly has an extra chromosome in one or more body cells. In case of Trisomy 18 or Edward’s syndrome, the baby has 3 copies of the chromosome 18 which may ultimately lead to several abnormalities.
What is Edward's syndrome?
Edward’s Syndrome, termed medically as Trisomy 18 is a type of birth defect caused due to the presence of added genetic material i. e. a third copy of the chromosome 18 instead of the natural 2 copies.
What is the difference between partial trisomy and partial trisomy 18?
Partial Trisomy 18: In partial trisomy, the baby has only one part of the chromosome 18, i.e. the extra part of the chromosome 18 is attached to any other chromosome of the egg or sperm.
How many chromosomes are in a zygote?
During the formation of a zygote, when the egg and sperm join, 23 chromosomes from both the egg and sperm fuse to make a foetus which now has a total of 46 chromosomes. When either of the parents carries a wrong number of chromosomal materials, the defect is passed on to the foetus, which now has a wrong number of chromosomes.
How rare is Hirschsprung?
Named after the English geneticist John Hilton Edwards, who first described the syndrome in 1960, the Trisomy 18 is quite a rare type of defect, i.e. about 1 in every 5000 babies and is more commonly seen in case of a girl child.
What tests can be done to confirm abnormality?
Tests such as Amniocentesis and Chorionic villus sampling (CVS) tests are generally considered safe and can help in the prenatal genetic diagnosis of the foetus.
What are the symptoms of Edwards syndrome?
Some of the symptoms are as follows: Structural malfunctions of heart, brain, genitals, kidneys, digestive tract; causing problems in breathing, feeding, etc.
How long does Edwards syndrome last?
If necessary, use of nasogastric tube alternatives for children with feeding problem. Giving emotional support to parents, as only some children affected by Edwards’s syndrome survive beyond 1 year.
How long do children with a syphilis disease live?
Almost 1/2 the number of children affected by this disorder do not live beyond seven days. Only some patients live till the teenage years, along with all associated deformities and disorders.
How many chromosomes are in an egg?
A good egg is made of individual chromosomes, each one of which contribute to the twenty-three pairs of chromosomes required to develop a cell with forty-six chromosomes. The process of egg development can lead to formation of an additional chromosome, increasing its number from twenty-three to twenty-four.
What happens when chromosome 18 is obstructed?
Still, specialists feel that it obstructs in the interaction of different genes, thereby leading to mutilations.
What is it called when a part of chromosome 18 is translocated?
Mild cases of Edwards’ syndrome may also occur when only few of the cells in the body have an additional copy of chromosome 18. This condition is referred to as mosaic Edwards’ syndrome. Sometimes, a part of chromosome 18 becomes translocated before or after conception.
What is trisomy in sperm?
Insemination by sperm or fertilization of eggs that has an additional chromosome causes trisomy, which means 3 prints of a chromosome instead of 2. A meiotic nondisjunction event causes this syndrome. With nondisjunction, an egg cell or a sperm cell is created with an additional copy of chromosome 18. The resultant egg cell or sperm cell therefore ...
What is Edward's syndrome?
Edwards Syndrome (also known as Trisomy 18 (T18) or Trisomy E) is a genetic disorder caused by the presence of all or part of an extra 18th chromosome. The majority of people with the syndrome die during the fetal stage; infants who survive experience serious defects and commonly live for short periods of time.
Who is Edwards Syndrome named after?
It is named after John H. Edwards, who first described the syndrome in 1960. The syndrome occurs in about one out of every five-thousand births. Edward's syndrome affects more girls than boys - around 80 percent of those affected are female.
How many copies of chromosomes do children with Edwards syndrome have?
Children with the syndrome inherit three (referred to as a, 'trisomy'), instead of two, copies of chromosome eighteen . Ninety-five percent of children with Edward's syndrome have what is referred to as, 'full-trisomies,' while two-percent are due to trans-locations where only a portion of an extra chromosome is present.
What percentage of children with Edward's syndrome have mosaic tristomies?
Three-percent of children with Edward's syndrome have what is referred to as, 'mosaic tristomies,' where the extra chromosome is there, but not in every one of the child's cells.
What is the extra material from chromosome eighteen?
The extra material from chromosome eighteen, obtained after the egg is fertilized, is responsible for causing Edward's syndrome. Children with Edward's syndrome have an incorrect number of chromosomes. Children with the syndrome inherit three (referred to as a, 'trisomy'), instead of two, copies of chromosome eighteen.
How many children with Edward's syndrome survive?
Approximately five to ten-percent of children with Edward's syndrome survive beyond their first year of life, requiring treatments that are appropriate for the various and chronic effects that are associated with the syndrome.
How many discrete defects are there in Edwards syndrome?
Edwards' syndrome is associated with a broad spectrum of abnormalities which consist of greater than one-hundred and thirty discrete defects involving the brain, heart, craniofacial structures, kidneys and stomach.
