What is the best antiviral drug for VZV?
Vidarabine (adenine arabinoside) was the first intravenous antiviral drug accepted for widespread clinical use and was shown to be effective for VZV infections in immunocompromised patients. Vidarabine has now been replaced by more effective and less toxic antiviral drugs. Interferon
When should antiviral therapy be used to treat varicella-zoster virus (VZV) infection?
A switch to oral antiviral therapy (acyclovir, valacyclovir, or famciclovir) can be considered when the patient is afebrile and new lesion formation has ceased. When feasible, the dosage of immunosuppressive medications should be temporarily reduced in immunosuppressed patients with varicella.
Is acyclovir effective in the treatment of VZV infection?
Prophylactic (or pre-emptive) therapy with acyclovir for a pregnant woman after VZV exposure may be effective, but is an unproven approach. Immunocompromised (including HIV-seropositive) patients
What is the role of systemic antiviral therapy in the treatment of HZO?
Systemic antiviral therapy has largely replaced topical antiviral preparations for treatment of the ocular complications of HZO.
What drug treats varicella zoster virus?
Acyclovir has 2 limitations—bioavailability and the existence of some resistant strains of varicella-zoster virus (VZV). Other medications, including valacyclovir, penciclovir, and famciclovir, are also available. They may have an increasing role in the treatment of typical zoster.
Does ganciclovir cover VZV?
Ganciclovir has activity against CMV, HSV, VZV, and HHV-6, HHV-7, and HHV-8. However, one of the other nucleoside analogues (eg, famciclovir, penciclovir, acyclovir) is preferred to treat VZV and herpes simplex infections.
Can varicella be given to HIV patients?
Live viral vaccines, including measles-mumps-rubella (MMR), varicella, and zoster, can be considered for at-risk HIV patients who are clinically stable and have low level immunosuppression (CD4 ≥200 cells/mm3).
What should be the best treatment for varicella in this case?
If you or your child are at high risk of complications, your doctor may suggest an antiviral drug such as acyclovir (Zovirax, Sitavig). This medication might lessen the severity of chickenpox when given within 24 hours after the rash first appears.
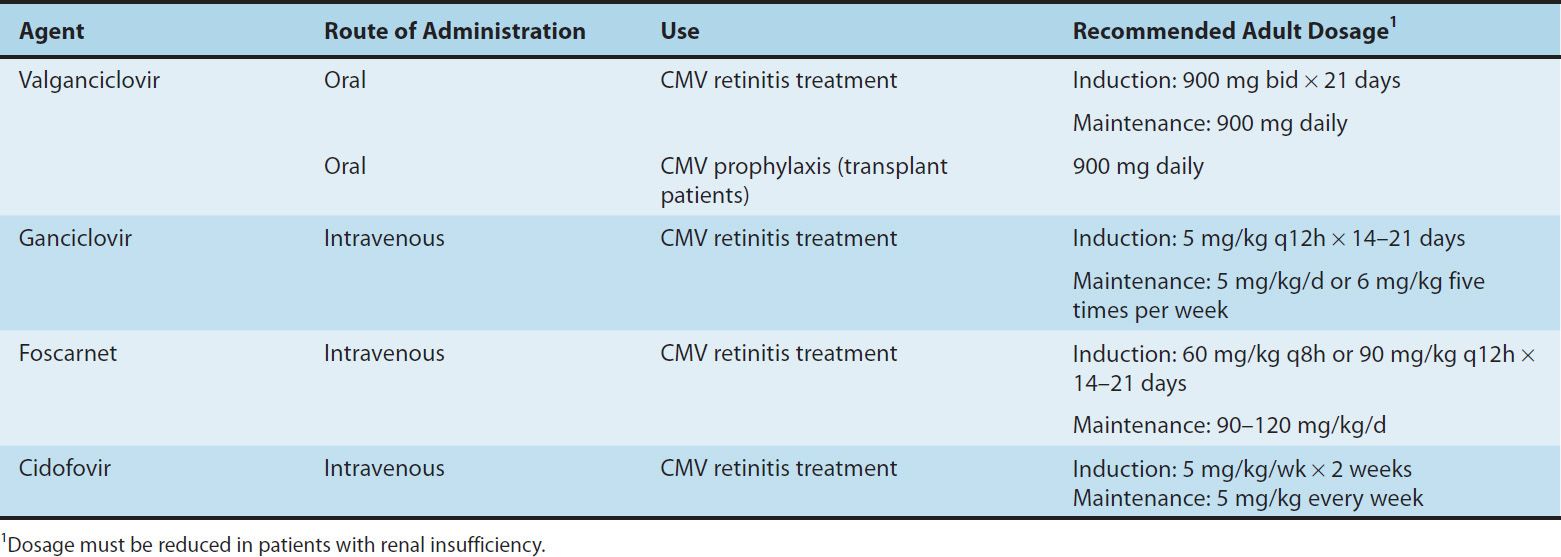
What is foscarnet used to treat?
Foscarnet is principally used for the treatment of ganciclovir-resistant cytomegalovirus (CMV) infections in patients with the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS) or in transplant recipients.
What is the difference between acyclovir and ganciclovir?
Ganciclovir is a nucleoside analog of 2-deoxyguanosine, similar to acyclovir. Despite its structural similarities with acyclovir, ganciclovir is much more active in vitro against CMV than acyclovir. Ganciclovir inhibits all herpesviruses, including CMV, by preventing DNA elongation.
Is acyclovir good for chickenpox?
Acyclovir is a safe treatment that reduces the duration and severity of chickenpox in normal children when therapy is initiated during the first 24 hours of rash.
Can you take acyclovir for chickenpox?
The approved dose of oral acyclovir for chickenpox is 200 mg/kg (up to a maximum of 800 mg) 4–5 times daily for 5 days. Adults with herpes zoster can be treated with oral acyclovir at a dose of 800 mg five times daily.
Is Valtrex used for chickenpox?
Valacyclovir is used to treat infections caused by certain types of viruses. In children, it is used to treat cold sores around the mouth (caused by herpes simplex) and chickenpox (caused by varicella zoster). In adults, it is used to treat shingles (caused by herpes zoster) and cold sores around the mouth.
What is the treatment for HIV infection?
Because disease-related complications can occur in untreated patients with high CD4 counts and because less toxic drugs have been developed, treatment with antiretroviral therapy (ART) is now recommended for nearly all patients.
Why is antiretroviral therapy recommended for all patients?
Because disease-related complications can occur in untreated patients with high CD4 counts and because less toxic drugs have been developed , treatment with antiretroviral therapy (ART) is now recommended for nearly all patients. The benefits of ART outweigh the risks in every patient group and setting that has been carefully studied.
What are the classes of antiretrovirals used in ART?
Multiple classes of antiretrovirals are used in ART (see table Antiretroviral Drugs ). Two classes inhibit HIV entry, and the others inhibit one of the 3 HIV enzymes needed to replicate inside human cells; 3 classes inhibit reverse transcriptase by blocking its RNA-dependent and D NA-dependent DNA polymerase activity.
What are the effects of antiretroviral drugs?
b All classes of antiretroviral drugs may contribute to chronic metabolic adverse effects, which include elevated cholesterol and triglycerides, insulin resistance, and centripetal redistribution of body fat. Adverse effects listed for drug class can occur when any drug in that class is used.
What are some examples of CCR-5 inhibitors?
For example, CCR-5 inhibitors block the CCR-5 receptor. Post-attachment inhibitors bind to the CD4 receptor and prevent HIV (that also binds to the CD4 receptor) from entering the cell. Integrase inhibitors prevent HIV DNA from being integrated into human DNA.
How many drugs are needed to suppress HIV replication?
Combinations of 2, 3, or 4 drugs from different classes are usually necessary to fully suppress replication of wild-type HIV. The specific drugs are chosen based on the following: Anticipated adverse effects. Simplicity of regimen. Concomitant conditions (eg, hepatic or renal dysfunction)
What is the most common sexually transmitted disease?
Human papillomavirus (HPV) infection is the most common sexually transmitted infection and can cause skin warts, genital warts, or certain cancers. Of the many different strains of HPV, which of the following is most likely to cause visible genital warts?