Medication
Treatment for heart arrhythmias may include medications, therapies such as vagal maneuvers, cardioversion, catheter procedures or heart surgery. Medications used to treat heart arrhythmias depend on the type of arrhythmia and potential complications.
Procedures
Arrhythmia is a heart rhythm problem caused by a glitch in the electrical impulses to the heart. It can cause symptoms such as heart palpitations, a fast or slow heartbeat, shortness of breath, and chest pain.
Therapy
Choose a Treatment for Arrhythmia that will help you live a healthier, longer life. Eat a healthy diet. A heart-healthy diet includes plenty of fresh fruits and vegetables, and lean protein (such as chicken, fish and beans).
Self-care
Sometimes, a heart doctor (cardiologist) uses the electrodes to stimulate the heart to beat at rates that may trigger — or stop — an arrhythmia. Doing this helps the doctor determine the location of the arrhythmia, its possible causes and the best treatment options.
Nutrition
What are the treatments for heart arrhythmias?
What is arrhythmia and what causes it?
How can I live a longer life with arrhythmia?
How do doctors use electrodes to diagnose arrhythmia?

How do you memorize antiarrhythmic drugs?
Mnemonic. To recall all class I antiarrhythmic medications, think of ordering a burger at a restaurant: “Double Quarter Pounder with Lettuce, Mayo, Pickles, and Fries, Please!”
How do I remember amiodarone?
1:352:41Amiodarone Vimonics (Visual mnemonics ... - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipAnd the mnemonic. Is potassium channel blocker makes liver and now phototoxic.MoreAnd the mnemonic. Is potassium channel blocker makes liver and now phototoxic.
What are the 4 classes of antiarrhythmic drugs?
Antiarrhythmic drug classes:Class I - Sodium-channel blockers.Class II - Beta-blockers.Class III - Potassium-channel blockers.Class IV - Calcium-channel blockers.Miscellaneous - adenosine. - electrolyte supplement (magnesium and potassium salts) - digitalis compounds (cardiac glycosides)
How do I remember the side effects of amiodarone?
Amiodarone Lung Toxicity One way to remember that amiodarone affects the thyroid is to recall how important iodine is to thyroid function. AmIODarone, as the name indicates, has a large amount of iodine. About 3% to 5% of patients on amiodarone develop hyperthyroidism and about 5% develop hypothyroidism.
How do you remember tachycardia and bradycardia?
1:162:33Bradycardia IDEA Nursing Mnemonics, Nursing School Study TipsYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipSo the mnemonic is idea I DEA. So I have an idea for how to treat this bradycardia. And hypotension.MoreSo the mnemonic is idea I DEA. So I have an idea for how to treat this bradycardia. And hypotension. So that I is for isoproterenol isoproterenol the D is for dopamine a is for epinephrine.
How do you remember atropine and adenosine?
1:368:02Adenosine Mnemonic for NCLEX - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipThis fast moving push cart reminds me of the ultra. Fast action of adenosine. As such we need toMoreThis fast moving push cart reminds me of the ultra. Fast action of adenosine. As such we need to administer adenosine extra fast via rapid iv push. Get it a fast push cart for rapid iv push.
Is a beta blocker an antiarrhythmic?
For this reason, β-blockers are widely utilized clinically as antiarrhythmics. In this review, the molecular mechanisms of β-adrenergic action in the heart, the cellular and tissue level cardiac responses to β-adrenergic stimulation, and the clinical use of β-blockers as antiarrhythmic agents are reviewed.
What is the best drug for arrhythmia?
Flecainide, sotalol (also a beta blocker) and amiodarone are also commonly prescribed for arrhythmias. They have the ability to terminate an arrhythmia and are usually given to prevent the abnormal rhythm from occurring or reduce its frequency or duration.
Do beta blockers stop arrhythmias?
Beta blockers are used to control the irregular heart rhythm in people with atrial fibrillation (AF). By slowing the heart rate, the symptoms caused by AF, particularly palpitations and fatigue, are often improved.
How do you remember diltiazem?
The “-Pine” and “-Zem” Drugs An easy way to identify calcium channel blockers is to remember drugs ending in “-pine.” Most of the calcium channel blockers like Amlodipine (Norvasc), Nifedipine (Procardia), or the most popular, Diltiazem or Cardizem which is another popular drug used in hospitals.
What should I check before giving amiodarone?
Before taking amiodarone, tell your doctor: If you have a history of lung, liver, heart or thyroid disease. Periodic blood work will need to be done to test your liver and thyroid function. You may also be asked to perform a breathing test to measure your pulmonary (lung) function.
What happens if you give amiodarone too fast?
Infusing amiodarone too fast may result in serious side effects such as severe lowering of the blood pressure. Your dosage and infusion rate may be adjusted depending upon your medical condition and response to therapy.
What herbs are used to treat sinus rhythm?
Examples are American Valerian, garden heliotrope or valerian, skullcap, hawthorn and corydalis.
What is the best way to reduce cholesterol?
Eat a healthy diet. A heart-healthy diet includes plenty of fresh fruits and vegetables, and lean protein (such as chicken, fish and beans). Avoid fatty foods, including saturated fats, trans-fats, and cholesterol.
What drugs can you take to treat arrhythmia?
Street drugs such as cocaine, marijuana and “speed” or methamphetamines. If you're being treated for arrhythmia and use any of these substances, be sure to discuss this with your doctor.
How to prevent AFIB?
Especially for people with AFib, prevent blood clots from forming to reduce stroke risk. Control your heart rate within a relatively normal range. Restore a normal heart rhythm, if possible. Treat heart disease/condition that may be causing arrhythmia. Reduce other risk factors for heart disease and stroke.
What are the causes of irregular heartbeats?
Certain substances can contribute to an abnormal/irregular heartbeat, including: Caffeine. Tobacco. Alcohol. Cold and cough medications. Appetite suppressants. Psychotropic drugs (used to treat certain mental illnesses) Antiarrhythmics (paradoxically, the same drugs used to treat arrhythmia can also cause arrhythmia.
How to count the number of beats in one minute?
Put the second and third fingers of one hand on the inside of the wrist of the other hand, just below the thumb OR on the side of your neck, just below the corner of your jaw. Feel for the pulse. Count the number of beats in one full minute.
How to treat arrhythmias?
Cardioversion — delivers an electrical shock to “reset” the heart by converting an irregular or fast heart rhythm to a normal heart rhythm. Ablation therapy — a minimally invasive procedure to remove or destroy (ablate) the abnormal tissue responsible for the arrhythmia.
What tests are needed to diagnose arrhythmia?
An assessment of your symptoms. In particular, the doctor will listen to your heart with a stethoscope. Following your exam, your doctor may order additional tests to help confirm an arrhythmia diagnosis. These tests may include: Blood tests.
What is a Holter monitor?
A Holter monitor. An event recorder. An electrophysiology (EP) study. If your doctor detects an arrhythmia, he or she will work with you to determine the best cardiac arrhythmia treatment. Testing results. Your doctor or nurse will tell you when to expect your test results and will call you when they're available.
What is the cause of heart palpitations?
Arrhythmia is a heart rhythm problem caused by a glitch in the electrical impulses to the heart. It can cause symptoms such as heart palpitations, a fast or slow heartbeat, shortness of breath, and chest pain.
Do you need to have regular checkups for arrhythmia?
Treatment. Arrhythmia Treatment. Some less serious types of arrhythmia do not require treatment, but you should have regular checkups. If you do require treatment, most often your doctor will prescribe heart arrhythmia medications to control your irregular heartbeat.
Monitor your pulse
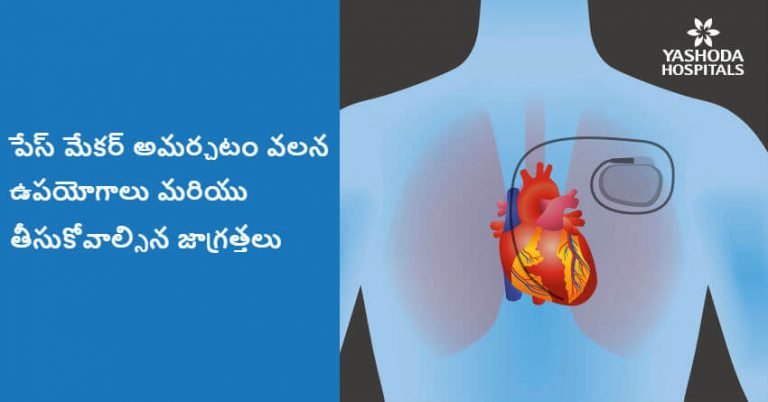
You should know how to take your pulse – especially if you have an artificial pacemaker.
Manage your risk factors
Just having certain arrhythmias increases your risk of heart attack, cardiac arrest and stroke. Work with your healthcare team and follow their instructions to control other risk factors:
Take it one day at a time
Researchers continue to investigate arrhythmias, and they're making progress. The best thing you can do is to follow your treatment plan and take things one day at a time. Sometimes you may feel that you don't get the support you need and that the people around you aren't very understanding.
Monitor your pulse
You should know how to take your pulse – especially if you have an artificial pacemaker.
Manage your risk factors
Just having certain arrhythmias increases your risk of heart attack, cardiac arrest and stroke. Work with your healthcare team and follow their instructions to control other risk factors:
Take it one day at a time
Researchers continue to investigate arrhythmias, and they're making progress. The best thing you can do is to follow your treatment plan and take things one day at a time. Sometimes you may feel that you don't get the support you need and that the people around you aren't very understanding.
What is the atrial flutter?
Atrial flutter is an abnormal rhythm that occurs in the atria of the heart. Atrial flutter has an atrial rhythm that is regular but has an atrial rate of 250 to 400 beats/minute. It has sawtooth appearance. QRS complexes are uniform in shape but often irregular in rate.
What is the term for a disturbance in the normal cardiac rhythm of the heart?
Arrhythmia or dysrhythmia are disturbances in the normal cardiac rhythm of the heart which occurs as a result of alterations within the conduction of electrical impulses. These impulses stimulate and coordinate atrial and ventricular myocardial contractions that provide cardiac output. Interpreting EKG. Sinus Tachycardia.
What causes a ventricular rate of greater than 150 BPM?
Causes includes heart failure, tricuspid valve or mitral valve diseases, pulmonary embolism, cor pulmonale, inferior wall MI, carditis and digoxin toxicity. Management if the patient is unstable with ventricular rate of greater than 150 bpm, prepare for immediate cardioversion.
What is the heart rate of a person with a heart rate of 60 beats per minute?
Sinus Bradycardia. Sinus bradycardia is a heart rate less than 60 beats per minute and originates from the sinus node (as the term “sinus” refers to sinoatrial node). It has the following characteristics. Rate is less than 60 beats per minute.
What causes sinus tachycardia?
Causes of sinus tachycardia may include exercise, anxiety, fever, drugs, anemia, heart failure, hypovolemia and shock. Sinus tachycardia is often asymptomatic. Management however is directed at the treatment of the primary cause. Carotid sinus pressure (carotid massage) or a beta blocker may be used to reduce heart rate.
What is premature atrial contraction?
Premature Atrial Contraction are ectopic beats that originates from the atria and they are not rhythms. Cells in the heart starts to fire or go off before the normal heartbeat is supposed to occur. These are called heart palpitations and has the following characteristics:
What is the most common diagnostic tool for heart disease?
One of the most useful and commonly used diagnostic tools is electrocardiography (EKG) which measures the heart’s electrical activity as waveforms. An EKG uses electrodes attached to the skin to detect electric current moving through the heart. These signals are transmitted to produce a record of cardiac activity.

Diagnosis
Treatment
Clinical Trials
Lifestyle and Home Remedies
Specialist to consult
Preparing For Your Appointment
- To diagnose a heart arrhythmia, the doctor will usually do a physical exam and ask questions about your medical history and symptoms. Tests may be done to confirm an irregular heartbeat and look for conditions that can cause arrhythmias, such as heart disease or thyroid disease. Te…
Mayo Clinic Heart Rhythm Program
- Treatment for heart arrhythmias depends on whether you have a fast heartbeat (tachycardia) or slow heartbeat (bradycardia). Some heart arrhythmias do not need treatment. Your doctor may recommend regular checkups to monitor your condition. Heart arrhythmia treatment is usually only needed if the irregular heartbeat is causing significant symptoms, or if the condition is putti…