Stylecraze.com
1. Green Tea...
2. Grape Seed Extract...
3. Juniper Oil...
4. Olive Leaf Extract...
5. Cranberry Juice...
6. Celery Seed Extract...
7. Horse Chestnut Seed Extract...
8. Pineapple Juice...
Learn More...Top10homeremedies.com
1. Apple Cider Vinegar...
2. Epsom Salt Bath...
3. Tea Tree Oil...
4. Massage...
5. Parsley...
6. Dandelion...
7. Coriander Seeds...
8. Flaxseeds...
Learn More...Homeremedyshop.com
1. Flaxseeds...
2. Lower Salt Intake...
3. Exercise...
4. Potassium...
5. Apple Cider Vinegar...
6. Elevating Limbs...
7. Tea Tree Oil...
8. Massage...
Learn More...Tinyqualityhomes.org
1. Apple Cider Vinegar...
2. Grape Seed Extract...
3. Nettle Tea...
4. Juniper Oil...
5. Cranberry Juice...
6. Horse Chestnut Seed Extract...
7. Pineapple Juice...
8. Crushed Flax Seeds...
Learn More...What is the best treatment option for corneal edema?
This includes:
- Amantedine (Gocovri), a medication used to treat patients with Parkinson’s disease
- Benzalkonium chloride, a preservative found in topical eye drops and anesthetics
- Chlorhexidine (Hibiclens), a topical antiseptic used to clean the skin in preparation for surgery or an injection
Does corneal edema go away?
Corneal edema may go away on its own if it isn’t too serious. If it doesn’t clear up over time, however, corneal edema can still go away with the proper treatment. There are both surgical and non-surgical options to treat corneal edema.
Can corneal edema get better with vitamins?
While eating healthy foods and taking vitamins as needed can improve your overall health and reduce your risk of corneal edema, there are many other underlying causes that may require more serious medical treatment.
Can edema of eye not be cured?
Macular edema cannot be cured but can be treated effectively if diagnosed early. Vision can be better preserved with early treatment of macular edema and the underlying condition causing it. Recovery from macular edema is slow and gradual and may even take months.
See more
How do you get rid of corneal edema?
Treatment of Corneal EdemaWashing, or “irrigation,” of the eye with water or saline to get rid of toxic substances.Antibiotics for bacterial infections.Bandage contact lenses for damage to the surface of the cornea.Corticosteroid medications to ease swelling after injury.More items...•
What causes edema in the cornea?
Your cornea may swell after eye surgery, injury, infection or inflammation. This is called corneal edema. It also occurs from some eye diseases. Because the cornea helps transmit and focus light as it enters your eye, this condition can affect your vision.
How long does it take for corneal edema to go away?
It is normal for the cornea to swell during the first few days after cataract surgery. Cornea swelling or corneal edema may cause some short-term blurriness. Normally, swelling will subside within a few days and vision becomes clear. Rarely, corneal swelling may not improve.
How do you treat corneal edema naturally?
There is evidence that honey may be helpful in treating dry eye disease, post-operative corneal edema, and bullous keratopathy. Furthermore, it can be used as an antibacterial agent to reduce the ocular flora.
How serious is corneal edema?
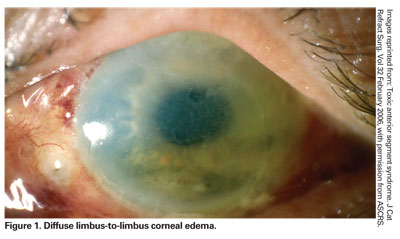
Corneal edema refers to the swelling of the cornea — the clear, dome-shaped outer surface of the eye that helps you see clearly. This condition is caused by a buildup of fluid in the cornea. When left untreated, corneal edema can lead to cloudy vision.
What medications cause corneal edema?
The use of certain drugs can also increase your risk for corneal edema:benzalkonium chloride, a preservative used in many eye drops and anesthetic drugs.chlorhexidine (Betasept, Hibiclens), an antiseptic used to disinfect the skin before surgery.amantadine (Gocovri), a drug used to treat viruses and Parkinson's disease.
How long should I use Muro 128?
Use eye drops before eye ointments to allow the drops to enter the eye. This product is recommended for use under a doctor's direction. If your condition worsens, if it persists for more than 3 days, or if you think you may have a serious medical problem, seek immediate medical attention.
Can edema cause blurry vision?
The primary symptom of macular edema is blurry or wavy vision near or in the center of your field of vision. Colors might also appear washed out or faded. Most people with macular edema will have symptoms that range from slightly blurry vision to noticeable vision loss.
What antibiotic eye drops are best?
As best as we can determine, the four best drugs to combat acute bacterial infection in adults are: bacitracin/polymyxin B/neomycin; tobramycin; 0.6% besifloxacin; and 1.5% levofloxacin.
What is Muro 128 eye drops used for?
This product is used to reduce swelling of the surface of the eye (cornea) in certain eye conditions. Decreasing swelling of the cornea may lessen eye discomfort or irritation caused by the swelling. This product works by drawing fluid out of the cornea to reduce swelling.
What is the best medicine for corneal edema?
The use of certain drugs can also increase your risk for corneal edema: benzalkonium chloride, a preservative used in many eye drops and anesthetic drugs. chlorhexidine (Betasept, Hibiclens), an antiseptic used to disinfect the skin before surgery. amantadine (Gocovri), a drug used to treat viruses and Parkinson’s disease.
How to treat edema in the eye?
To temporarily relieve swelling in the eye, your eye doctor may recommend concentrated saline (salt-and-water) drops or ointment.
What causes corneal edema?
Diseases that damage endothelial cells and can cause corneal edema include: 1 Fuchs’ endothelial dystrophy (or Fuchs’ dystrophy) is an inherited disease that gradually destroys endothelial cells. 2 Endotheliitis is an immune response that leads to inflammation of the endothelium. It’s caused by the herpes virus. 3 Glaucoma is a disease in which pressure builds up inside the eye. The pressure can build to the point where it damages the optic nerve and, in some cases, lead to corneal edema. This is uncommon, however. 4 Posterior polymorphous corneal dystrophy is a rare, inherited condition of the cornea. 5 Chandler’s syndrome is a rare disorder in which cells of the epithelium multiply too quickly.
How long does it take to get your eyesight back after a corneal surgery?
Mild corneal edema might not cause any symptoms or require treatment. If you have surgery to replace your entire cornea, it could take a year or longer to get your vision back fully.
What happens when you wake up with a cloudy cornea?
As the cornea swells and fluid builds up, your vision will become blurred or cloudy. You might notice that your sight is especially hazy when you first wake up in the morning, but it gets better throughout the day. Other symptoms of corneal edema include: haloes around lights. eye pain.
What is the layer of tissue that helps focus light on the back of the eye?
The cornea is made up of layers of tissue that help focus light on the back of the eye to produce clear images. Along the inner surface of the cornea is a layer of cells called the endothelium. Its job is to pump out any fluid that collects inside the eye.
Can cataract surgery cause edema?
Cataract surgery can also damage endothelial cells. Usually the damage isn’t extensive enough to cause problems, but sometimes it can cause corneal edema. Corneal edema that occurs after cataract surgery is called pseudophakic corneal edema or pseudophakic bullous keratopathy. Today, cataract surgery is much less likely to cause corneal edema ...
How to treat edema in the cornea?
Some of the more common treatment plans include. Washing, or “irrigation,” of the eye with water or saline to get rid of toxic substances. Antibiotics for bacterial infections. Bandage contact lenses for damage to the surface of the cornea.
Why does my cornea edema?
In most normal eyes, membrane called endothelium pumps fluid out of the cornea. This keeps your vision clear and your eyes working as they should. When the endothelium stops doing its job because of illness or injury, liquid builds up and your cornea swells.
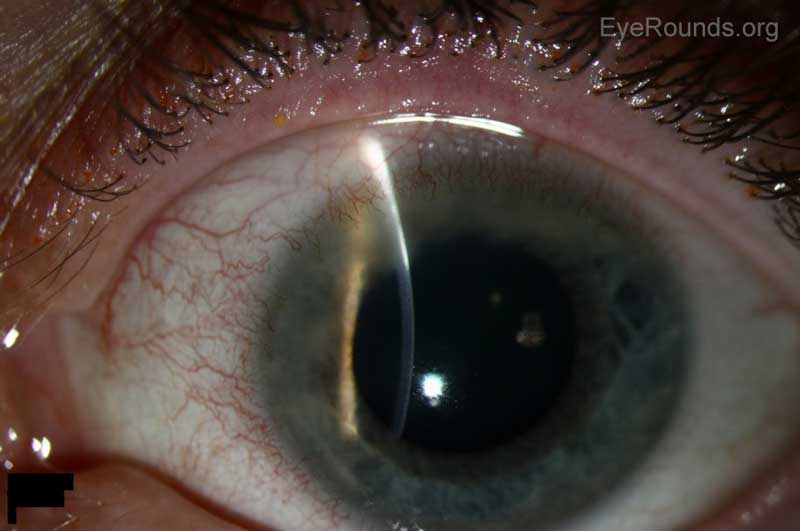
How do you know if you have corneal edema?
Symptoms of Corneal Edema. The first thing you might notice is blurry vision. Often, it might be the worst first thing in the morning and then get better throughout the day. You might also have: Eye pain or discomfort in light. Pain or tenderness when you touch your eye. A scratchy feeling in your eye.
How to check for scars on cornea?
Look for scars or cloudiness on your cornea. Use magnifiers like a slit lamp or an ophthalmoscope to see details of your eye. They might also measure the thickness of your cornea using a device called a pachymeter. Your doctor may use ultrasound to get a better look at your eye.
What causes a swollen eye?
Injury to your eye from a blow or a puncture. Inflammation due to problems like rheumatoid arthritis or specific eye issues like iritis or keratitis. Eye surgery. Poisonous substances that inflame, irritate, or damage parts of your eye.
What is the name of the fluid in the back of the eye?
Corneal Edema: Symptoms, Causes, and Treatments. Corneal edema, also called corneal swelling, is a buildup of fluid in your cornea, the clear lens that helps focus light onto the back of your eye.
Why does my cornea edema?
Corneal edema can happen when the cornea becomes inflamed (known as keratitis) due to medical conditions like herpes simplex viral infections. Or it can develop after the use of certain medications or from wearing irritating contact lenses too often.
What is the condition called when the cornea is swollen?
Corneal edema is a condition that is characterized by the swelling of the eye’s cornea. The cornea is the clear tissue layer of the eye that transmits and focuses light so that you can see. It’s made up of five important layers:
Why do I get edema after cataract surgery?
You can also develop corneal edema after eye surgery, such as cataract surgery. This is because intraocular procedures can damage the cornea. While corneal edema may be due to an underlying cause, most commonly, it happens when there’s a buildup of fluid in your eye. The endothelium of the cornea controls the build-up and release of fluid.
What is the endothelium of the cornea?
The endothelium of the cornea controls the build-up and release of fluid. You can damage the endothelium of your cornea and develop corneal edema a few ways: Fuchs’ endothelial dystrophy (a disease that affects the endothelial cells) Endotheliitis (an immune response to herpes) Other endothelial dystrophies.
Why do I get headaches when I have edema?
Corneal edema can cause headaches for some people. Because of the swelling and your impaired vision, you may find yourself straining your eyes more often so that you can see more clearly. Increased sensitivity to light and foreign particles may also induce headaches.
Can corneal edema go away?
Corneal edema may go away on its own if it isn’t too serious. If it doesn’t clear up over time, however, corneal edema can still go away with the proper treatment. There are both surgical and non-surgical options to treat corneal edema.
Can a 50 year old develop corneal edema?
While corneal edema occurs most often in people who are 50 years old or older, anyone at any age can develop the eye condition. Jump to topic.
What is the best treatment for corneal edema?
Stromal edema, in the lower layers of corneal cells, is harder to treat with eye drops . Another agent used in a similar situation is polyoxyethylene, which pulls water out ...
What is corneal edema?
Corneal edema, or swelling of the cornea, is typically a symptom of an underlying problem. This could be trauma from surgery or an injury, inflammation from an infection, a genetic or congenital disease, or harm from a toxic chemical. ( Learn More)
Why does my cornea swell?
Corneal edema is one progressive symptom of these issues. Inflammatory causes: Conditions that can inflame the cornea can cause it to swell with more water as a reaction to physical damage. These are the most common causes of inflammation: Primary endotheliitis. Uveitis.
Why is my cornea thicker?
Your cornea may become thicker too, which changes how light is refracted to your retina. These problems can cause blind spots, blurry vision, discomfort in your eyes, or double vision.
What part of the eye is the cornea?
The cornea is a clear, multilayered structure on the front of your eye, over the pupil. This part of your eye focuses light onto the retina, a cluster of photoreactive cells at the back of your eye. The retina sends signals through the optical nerve to the brain, where these signals are interpreted as images.
Why do you need corticosteroid drops for your eyes?
Inflammation and infection: Your eye doctor will prescribe corticosteroid eye drops to reduce inflammation, either because of a viral infection or after corneal surgery.
Can laser surgery help with corneal edema?
Chronic forms of corneal edema, along with severe and acute corneal edema, may require surgery. Laser eye surgeries that relieve intraocular pressure can help to reduce corneal edema indirectly. If there is a serious problem with the cornea itself that leads to swelling, you may need to have your cornea, or some layers of your cornea, replaced.
What drugs can help with corneal edema?
Other drugs that might contribute indirectly to the resolution of corneal edema include alpha 2-adrenergic agonists and beta-adrenergic blockers. These drugs lower intraocular pressure and reduce the production of aqueous humor or increase its outflow.
Why does corneal edema occur?
Corneal edema is caused by disease of the inner cell layer, trauma to the eye, surgical trauma, certain types of glaucoma, or infections due to contact lens . The epithelial cells of the cornea are arranged in a single layer. These cells rarely divide, therefore, when they are damaged they are not replaced.
What is a bandage lens?
The bandage contact lenses used in treating corneal edema are thin, high-water content contact lenses. These lenses are permeable to oxygen and so are well tolerated. Bandage contact lenses are intended to help reduce the pain and discomfort of corneal edema.
Why does my cornea swell?
The endothelium cells of the cornea pump out fluid to keep vision clear. When these cells stop working, it creates water retention, which leads to swelling in the cornea. This condition is also known as corneal edema . Corneal edema is caused by disease of the inner cell layer, trauma to the eye, surgical trauma, certain types of glaucoma, ...
What is it called when you have blisters on your cornea?
In some cases, the corneal epithelium may develop very painful blisters. This condition is known as bullous keratopathy. The eye doctor may use a soft bandage contact lens on the affected cornea to reduce discomfort.
How to reduce edema in the conjunctiva at night?
To help reduce the edema even at night, 5% sodium chloride ointment is recommended to be applied to the conjunctiva at night. Hypertonic solutions can also be applied in the morning to help remove the fluid built up in the cornea during the night.
How to treat bullous keratopathy?
Another method of alleviating the symptoms of complex corneal edema is to embed tissue over the cornea. Yet another treatment option is Anterior Stroma Puncture.
What causes corneal swelling?
One common cause of swelling is Fuch’s endothelial dystrophy, a heredity condition that causes a gradual loss of endothelial cells and often becomes noticeable when patients are in their 50’s.
What are the symptoms of corneal swelling?
Many patients seek treatment for this condition after noticing that their vision is becoming blurred. Other common symptoms include:
How is corneal swelling diagnosed?
Diagnostic tests for corneal scars are completed in an outpatient setting. Your ophthalmologist will talk with you about your medical history and symptoms. Then, he or she will conduct an eye exam. During the exam, your ophthalmologist will look for clouding of your cornea.
How is corneal swelling treated?
In formulating your treatment plan, your ophthalmologist will consider the severity and underlying cause of your corneal swelling. Treatment options may include:
Our providers
Getting the care you need starts with seeing one of our ophthalmologists.
What causes corneal edema?
Fuchs’ dystrophy is a disease that affects the endothelium, which can cause corneal edema. Endotheliitis, an immune response of herpes, is another cause of inflammation of the endothelium. Certain drugs can also increase the risk of developing corneal edema, including benzalkonium chloride and chlorhexidine.
What is the number to call for corneal edema?
If you believe you or a loved one is dealing with corneal edema, the doctors at the Dean McGee Eye Institute can help provide lasting relief! Call 405.271.1095 or 800.787.9017 today to make an appointment and see why DMEI is the leading provider of eye care in the state.
How do you know if you have edema?
Symptoms of a Corneal Edema. Buildup of fluid in the cornea causes vision to blur and become clouded. These effects are at their worst when first waking up in the morning, but will fade throughout the day as the cornea dries from the eyes being open. Other symptoms of corneal edema may include: Rings or halos around light sources. Pain in the eye.
What is the swelling of the cornea?
Corneal edema refers to the swelling of the cornea — the clear, dome-shaped outer surface of the eye that helps you see clearly. This condition is caused by a buildup of fluid in the cornea. When left untreated, corneal edema can lead to cloudy vision.
What is the layer of the cornea that is responsible for pumping out fluid?
Along the inner surface of the cornea is a layer of cells called the endothelium. Its job is to pump out any fluid that collects inside the eye. Damage to this layer results in excess fluid building up, clouding up the cornea and affecting vision. Fuchs’ dystrophy is a disease that affects the endothelium, which can cause corneal edema.
Can a corneal transplant be used for edema?
Mild cases of corneal edema may not need any treatment. If there is swelling, your ophthalmologist may recommend saline eye drops. If swelling becomes severe enough to cause significant vision issues, surgery may be required to either replace the cornea with a corneal transplant, or DSEK surgery, which replaces just the endothelial layer.
Corneal edema causes
Corneal edema is essentially caused by fluid buildup in the cornea. This can be the result of a number of factors, including:
Corneal edema treatment
While options can involve eye drops, hair dryers and surgery, the best treatment for corneal edema depends on the underlying cause of the condition.
Beyond treatment
It’s important to care for your eye health, whether or not you experience a condition that may lead to corneal edema. Though it is not life-threatening, it’s critical to contact an eye doctor as soon as you notice any signs of corneal edema.
Notes and References
Corneal edema. Bascom Palmer Eye Institute, University of Miami Health System. Accessed June 2021.
