Medications
Treatment options include:
- Anticoagulation medicines (blood thinners): They are the most common treatment for a blood clot in the lungs. ...
- Thrombolytic therapy (“the clot busters” or “clot dissolvers”) to dissolve the existing clots.
- Surgery may be needed to remove a very large, life-threatening clot.
Surgical and other procedures
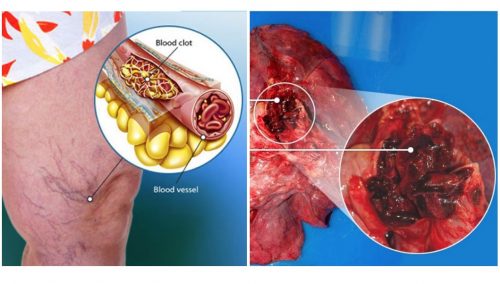
A clot on the lung is serious because when one forms or gets stuck inside a blood vessel, it can clog the vessel and prevent blood from moving through the body where it needs to go. If a blood clot occurs in the lungs, it may be difficult to breathe, the lungs can become damaged, and it can even lead to death. A clot on the lung can be dangerous.
Ongoing care
It can harm part of the lung due to restricted blood flow, reduce oxygen levels in the blood, and affect other organs too. Big or multiple blood clots can be fatal. The blockage can be dangerous. According to the Mayo Clinic, it results in the death of one-third of people who go undiagnosed or without treatment.
Anticoagulants
Blood Clot Prognosis. A part of a clot can also break away form the main clot and travel to the lung or brain where it causes another blockage or embolism. The condition may be treated with anticoagulants or blood thinners, which decrease the clot's ability to cause blockage as well as preventing its growth.
Clot dissolvers – thrombolytics
How dangerous are blood clots in the lungs?
How serious is a blood clot in the lung?
How serious is blood clots in your lungs?
What is the prognosis for a blood clot in the lung?

Can blood clots in lungs be cured?
Pulmonary embolism is serious but very treatable. Quick treatment greatly reduces the chance of death. Symptoms may include: Sudden shortness of breath -- whether you've been active or at rest.
How long does it take to get rid of a blood clot in the lung?
A pulmonary embolism (PE) is caused by a blood clot that gets stuck in an artery in your lungs. That blockage can damage your lungs and hurt other organs if they don't get enough oxygen. It's a serious condition, and recovery can take weeks or months. Once you've had one, your chances of another go up.
What is the survival rate of a pulmonary embolism?
A pulmonary embolism (PE) is a blood clot in the lungs, which can be serious and potentially lead to death. When left untreated, the mortality rate is up to 30% but when treated early, the mortality rate is 8%. Acute onset of pulmonary embolism can cause people to die suddenly 10% of the time.
What are the chances of surviving a blood clot in the lung?
Pulmonary embolism can be life-threatening. About one-third of people with undiagnosed and untreated pulmonary embolism don't survive. When the condition is diagnosed and treated promptly, however, that number drops dramatically.
How serious is blood clots in the lungs?
A blood clot in the lung is a very serious issue and a leading cause of death. There are almost a million cases of this every year in the US. One in three blood clots in the lung will eventually result in death. A blood clot in the lung can result in lower life expectancy and decreased quality of life.
Can you live a normal life with pulmonary embolism?
Most patients with PE make a full recovery within weeks to months after starting treatment and don't have any long-term effects. Roughly 33 percent of people who have a blood clot are at an increased risk of having another within 10 years, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC).
Can you fully recover from a pulmonary embolism?
Most patients with DVT or PE recover completely within several weeks to months without significant complications or long-term adverse effects. However, long-term problems can occur, with symptoms ranging from very mild to more severe.
Is death from a pulmonary embolism quick?
A PE, particularly a large PE or many clots, can quickly cause serious life-threatening problems and, even death. Treatment of a PE often involves anti-coagulation medicines or blood thinners.
How long does it take for a blood clot to dissolve on blood thinners?
Blood clots can take weeks to months to dissolve, depending on their size. If your risk of developing another blood clot is low, your doctor may prescribe you 3 months of anticoagulant medication, as recommended by the American Heart Association . If you're at high risk, your treatment may last years or be lifelong.
How long does it take for a blood clot to resolve?
It takes about 3 to 6 months for a blood clot to go away. During this time, there are things you can do to relieve symptoms. Elevate your leg to reduce swelling. Talk to your doctor about using compression stockings.
Will I ever feel normal after pulmonary embolism?
The exact amount of time that it takes to recover from a PE can vary from person to person. Many people can completely recover and return to their normal level of activity after a period of several weeks or months . It's possible that some of your symptoms will ease as you receive treatment and your body heals.
How long does it take for blood to return to normal after blood thinners?
If blood Coumadin levels are in the therapeutic range, in most people the effects are gone within 3-4 days of stopping the medicine.
Causes of Pulmonary Embolism
Embolism can form for a range of reasons. Pulmonary embolisms are frequently caused by deep vein thrombosis, a condition where blood clots form in...
Who Is Under Risk to Have Blood Clots in lungs?
Factors that increase your risk of establishing deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism consist of: 1. weight problems 2. a family history of e...
Symptoms of Blood Clots in Lung
Symptoms of a pulmonary embolism depend on the size of the clot and where it lodges in the lung.The most common symptom of a pulmonary embolism is...
Blood Clots in Lung Treatment
Your treatment for a pulmonary embolism depends upon the size and location of the embolism. If the issue is small and captured early, your doctor m...
How to prevent blood clots from forming?
Blood-thinning medications are commonly used to prevent blood clots from forming or getting bigger. Thrombolytic medications can break up existing clots. Catheter-directed treatments, such as percutaneous transcatheter treatment, are done by inserting a catheter into a blood vessel in the groin.
Where is a thrombectomy tube used?
Surgical thrombectomy, in which the clot is surgically removed from the vein or artery, is often used in arms or legs, but can be used elsewhere in the body.
Can blood clots cause shortness of breath?
Blood clots can be very serious, so symptoms of blood clots should be evaluated by a doctor immediately. If not treated, a clot can break free and cause a pulmonary embolism—where the clot gets stuck in a blood vessel in the lung, causing severe shortness of breath and even sudden death.
What is the best treatment for deep vein thrombosis?
This is typically deep vein thrombosis. You’ll most likely start taking anticoagulant medications, such as heparin and warfarin, to prevent blood clots from returning. You may also have to use compression stockings (they resemble actually tight socks) or another device to prevent clots from forming in your legs.
How do you know if you have blood clots in your lungs?
Other symptoms of blood clots in lungs include: lightheadedness. fast heartbeat. fainting . weak pulse. stress and anxiety. chest pain that may extend into your arm, jaw, neck, and shoulder.
What is pulmonary embolism?
A pulmonary embolism is a blood clot that takes place in the lungs. What is blood clots in lungs? It can harm part of the lung due to restricted blood flow, reduce oxygen levels in the blood, and affect other organs too. Big or multiple blood clots can be fatal. The blockage can be dangerous.
What is the best treatment for a small embolism?
Some drugs can break up little embolisms. Drugs your doctor may recommend include: anticoagulants: Also called blood slimmers, the drugs heparin and warfarin prevent new embolisms from forming in your blood.
What is the difference between lung angiography and MRI?
MRI: This scan uses radio waves and an electromagnetic field to produce comprehensive images. lung angiography: This test involves making a little cut so your doctor can direct specialized tools through your veins. Your doctor will inject a special dye so that the blood vessels of the lung can be seen.
Where do blood clots start?
The blood clots that usually cause lung embolisms begin in the legs or pelvis. Blood clots in the deep veins of the body can have numerous various causes, consisting of: Medical conditions: Some health conditions cause blood to thicken too easily, which can lead to pulmonary embolism. Treatments for medical conditions, ...
Why does my embolism happen?
Inactivity: During long periods of lack of exercise, gravity causes blood to stagnate in the lowest areas of your body, which may result in an embolism. This might happen if you’re sitting for a prolonged journey or if you’re lying in bed recovering from a health problem.
What is the treatment for pulmonary embolism?
Treatment of pulmonary embolism is aimed at keeping the blood clot from getting bigger and preventing new clots from forming. Prompt treatment is essential to prevent serious complications or death.
Where to get pulmonary embolism evaluated?
Preparing for your appointment. Pulmonary embolism is often initially evaluated in hospitals, emergency rooms or urgent care centers. If you think you might have a pulmonary embolism, seek immediate medical attention.
What is a blood clot tracer?
The tracer maps blood flow (perfusion) and compares it with the airflow to your lungs (ventilation) and can be used to determine whether blood clots are causing symptoms of pulmonary hypertension.
How accurate is a pulmonary embolism test?
This test provides a clear picture of the blood flow in the arteries of your lungs. It's the most accurate way to diagnose pulmonary embolism, but because it requires a high degree of skill to administer and has potentially serious risks, it's usually performed when other tests fail to provide a definitive diagnosis.
Why is it important to keep on blood thinners?
Because you may be at risk of another deep vein thrombosis or pulmonary embolism, it's important to continue treatment, such as remaining on blood thinners, and be monitored as often as suggested by your doctor. Also, keep regular doctor visits to prevent or treat complications.
What does a blood test measure?
Blood tests also can measure the amount of oxygen and carbon dioxide in your blood. A clot in a blood vessel in your lungs may lower the level of oxygen in your blood. In addition, blood tests may be done to determine whether you have an inherited clotting disorder.
Can a chest X-ray show pulmonary embolism?
Although X-rays can't diagnose pulmonary embolism and may even appear normal when pulmonary embolism exists , they can rule out conditions that mimic the disease.
What is the best treatment for a blood clot in the lungs?
Anticoagulation medicines (blood thinners): They are the most common treatment for a blood clot in the lungs. Although blood thinners do not make your blood thin. They slow the process of new clots forming and prevent the already formed ones from getting bigger. Blood thinners include:
What is it called when a blood clot is inside the lungs?
When a blood clot occurs inside the arteries to the lungs, the condition is called pulmonary embolism (PE). The terms ‘embolus’ (plural: emboli) and ‘embolism’ refer to a blood clot or a part of a blood clot that forms at one site in ...
What is PE in pulmonary thrombosis?
Pulmonary Embolism (Blood Clot in the Lung) A pulmonary embolism (PE) occurs when a piece of a blood clot from deep vein thrombosis (DVT) breaks off and travels to an artery in the lung where it blocks the artery and damages the lung.
What is the term for a blood clot that forms at one site in the body and travels to another
The terms ‘embolus’ (plural: emboli) and ‘embolism’ refer to a blood clot or a part of a blood clot that forms at one site in the body and travels to another site. Pulmonary embolism is a condition in which this traveling clot lodges itself in the arteries of the lungs.
What causes a blood clot in the deep veins?
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a blood clot in the deep veins, and can be caused by broken bones, trauma to a limb, immobility, medications, smoking, cancer, genetic predisposition, and cancer. Symptoms of a deep vein thrombosis in a leg are swelling, tenderness, redness, warmth, and pain. Treatments for DVT include medications and surgery.
What is the term for the rupture of the air sacs in the lungs?
Barotrauma is a condition in which the alveoli (air sacs of the lungs) rupture with a subsequent entry of air into the surrounding extra alveolar space. Barotrauma mainly occurs either due to the rupture of the air sacs (alveolus) of lungs or a direct injury.
What are the symptoms of pulmonary embolism?
The most common symptoms of a pulmonary embolism are shortness of breath, chest pain, and a rapid heart rate. Causes of pulmonary embolism include prolonged immobilization, certain medications, smoking, cancer, pregnancy, and surgery. Pulmonary embolism can cause death if not treated promptly.
How to reduce risk of blood clots?
obesity. To lower their risk of further blood clots, people can take the following steps: quitting smoking. reaching or maintaining a moderate weight by following a balanced diet and addressing any underlying causes of excess body weight. exercising regularly.
How long does it take for a blood clot to heal in the lungs?
Recovery from blood clots in the lungs can vary from person to person. Many people recover in several months. During this time, they may need to keep taking medication to prevent additional blood clots. Sometimes, people need to take medication indefinitely.
What to do after pulmonary embolism?
Exercise. People will need to speak with their doctor about when it is safe for them to exercise again after experiencing a pulmonary embolism and what types of exercise are best. According to the National Blood Clot Alliance, gentle exercise, such as swimming and walking, can be a suitable choice.
How long do people with pulmonary embolism stay in hospital?
While 19% of people with pulmonary embolism stayed in the hospital for 5 days or less, 17% of patients had treatment at home. A 2018 study suggests some people with low risk pulmonary embolism may not require hospitalization. The study looked at 200 adults with acute low risk pulmonary embolism.
How long do you have to stay in the hospital for a blood clot?
Recovery tips. Prevention. Complications. When to seek help. Summary. The recovery time for a blood clot in the lungs, or pulmonary embolism, can vary. People may need to stay in the hospital and take medications to prevent further clots for 3 months or more.
How long after a blood clot can you travel?
If people need to travel after experiencing a blood clot, they may need to wait a few weeks. A doctor can help decide when it is safe to travel again.
How long does it take to recover from a pulmonary embolism?
The time it takes to completely recover from a pulmonary embolism can be several months or years, depending on the circumstances. However, people typically start to notice improvements in their symptoms once treatment begins. Usually, people can resume normal activities few days after starting medication.
What is it called when a blood clot breaks loose and travels to the lungs?
When a blood clot breaks loose and travels to the lungs, it is known as a pulmonary embolism. Some people who experience a pulmonary embolism die immediately, while others may die a short time afterwards when the body is unable to get needed oxygen.
How long does it take for pulmonary embolism to thin?
Hospitalization for a few days to make sure the blood is thinned adequately may be required. Medication for thinning the blood may need to be taken for six months or even longer ...
