What is the best procedure to unblock a carotid artery?
Once the doctor confirms that you have carotid artery disease, the treatment will depend on the degree of narrowing and if you are having symptoms. Carotid Endarterectomy (CEA) Carotid …
How to clean out a carotid artery blockage?
For otherwise healthy men with a 50% or greater narrowing of the carotid artery, recent studies have shown that they may benefit from surgery. This procedure is called carotid …
What percent of carotid artery blockage requires surgery?
Medical treatment for carotid artery disease may include: Lifestyle changes. Quit smoking. Quitting smoking can reduce the risk for carotid artery disease and cardiovascular disease. All …
How to treat carotid artery naturally?
Oct 04, 2018 · Treatment of carotid artery disease usually involves a combination of lifestyle changes, medication and sometimes surgery. Symptoms In its early stages, carotid artery …
What percentage of carotid artery blockage requires surgery?
How do they clear a blocked carotid artery?
How serious is carotid artery surgery?
How long can you live with blocked carotid artery?
How long is the hospital stay for carotid artery surgery?
How serious is a blocked artery in the neck?
Is carotid artery surgery painful?
Are you awake during carotid artery surgery?
What is the success rate for carotid artery surgery?
Do cardiologists treat carotid artery blockage?
When a primary care physician or cardiologist suspects that a patient may have carotid stenosis, they will refer them to a vascular surgeon, who will typically perform an ultrasound.
What happens if one carotid artery is blocked?
How can I naturally unblock my carotid artery?
- Add more good fats to your diet. Good fats are also called unsaturated fats. ...
- Cut sources of saturated fat, such as fatty meat and dairy. Choose lean cuts of meat, and try eating more plant-based meals.
- Eliminate artificial sources of trans fats. ...
- Increase your fiber intake. ...
- Cut back on sugar.
How to treat carotid stenosis?
Treatment for severe carotid stenosis involves eliminating the artery blockage. The most common way to do that is with a surgery called “ carotid endarterectomy .”. It’s performed by making an incision along the front of the neck, opening the carotid artery and removing the plaque.
What is a TCAR stent?
With TCAR, a stent can be placed to open the artery and relieve the blockage, while the brain is protected from any debris that could lead to a stroke.
What is a TCAR procedure?
There is a new treatment, however, called transcarotid arterial revascularization, or TCAR, that uses a different approach to opening a blocked carotid artery. The risk of a stroke during that procedure may be lower than it would be with other methods.
How do you treat carotid artery disease?
Carotid artery disease can be treated medically, interventionally or surgically. Once the doctor confirms that you have carotid artery disease, the treatment will depend on the degree of narrowing and if you are having symptoms.
What is the most common procedure for carotid artery disease?
Carotid endarterectomy is the most commonly performed surgical treatment for carotid artery disease. During carotid endarterectomy, the surgeon reduces the risk of stroke from the operation by shunting (using a plastic tube to re-route blood flow to the brain) and monitoring the patient carefully.
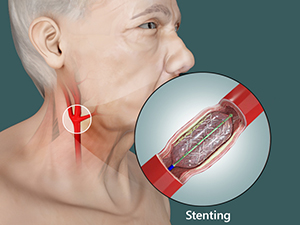
What is carotid stenting?
For patients who meet certain eligibility criteria, carotid stenting offers an alternative approach to repairing the blockage in the artery. Carotid stenting is approved as a carotid artery disease surgical treatment for patients who are experiencing symptoms, have a carotid artery that is blocked 70 percent or more, and for whom surgery would be high risk. Some examples of patients who might benefit from this approach as opposed to carotid endarterectomy include patients who have had prior surgery or radiation surgery in the neck.
Why do doctors vary in quality?
Doctors vary in quality due to differences in training and experience; hospitals differ in the number of services available. The more complex your medical problem, the greater these differences in quality become and the more they matter.
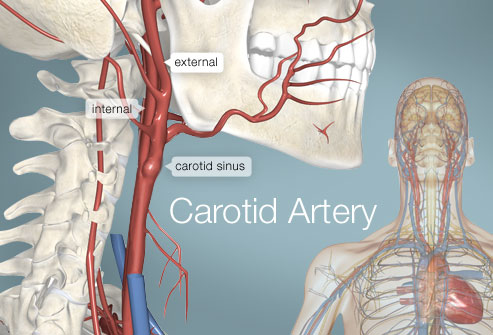
What is the narrowing of the carotid artery?
The narrowing of the carotid artery is known as carotid stenosis. The plaque in the artery is common in people who smoke, have diabetes, a family history of this problem, uncontrolled high blood pressure and high cholesterol. Carotid artery narrowing may cause a temporary loss of sight in one eye that lasts only several minutes.
Can a 50% narrowing of the carotid artery cause stroke?
Studies of patients with carotid stenosis but no symptoms have shown that as little as a 50% narrowing of the artery may increase the patient's risk for stroke. For otherwise healthy men with a 50% or greater narrowing of the carotid artery, recent studies have shown that they may benefit from surgery.
Why do carotid arteries become narrow?
For many reasons, these major arteries may become narrow, decreasing the blood flow to the brain and increasing the risk of stroke. The most common reason why these arteries become narrow or blocked is atherosclerotic disease.
Why do my arteries get narrow?
The most common reason why these arteries become narrow or blocked is atherosclerotic disease. This is a condition where cholesterol sticks to the wall of the artery. (This is called plaque.) In other cases, the walls of the artery may split. (This is called a dissection. ) When this happens, blood can travel between the layers of the artery wall.
Where is a stent placed?
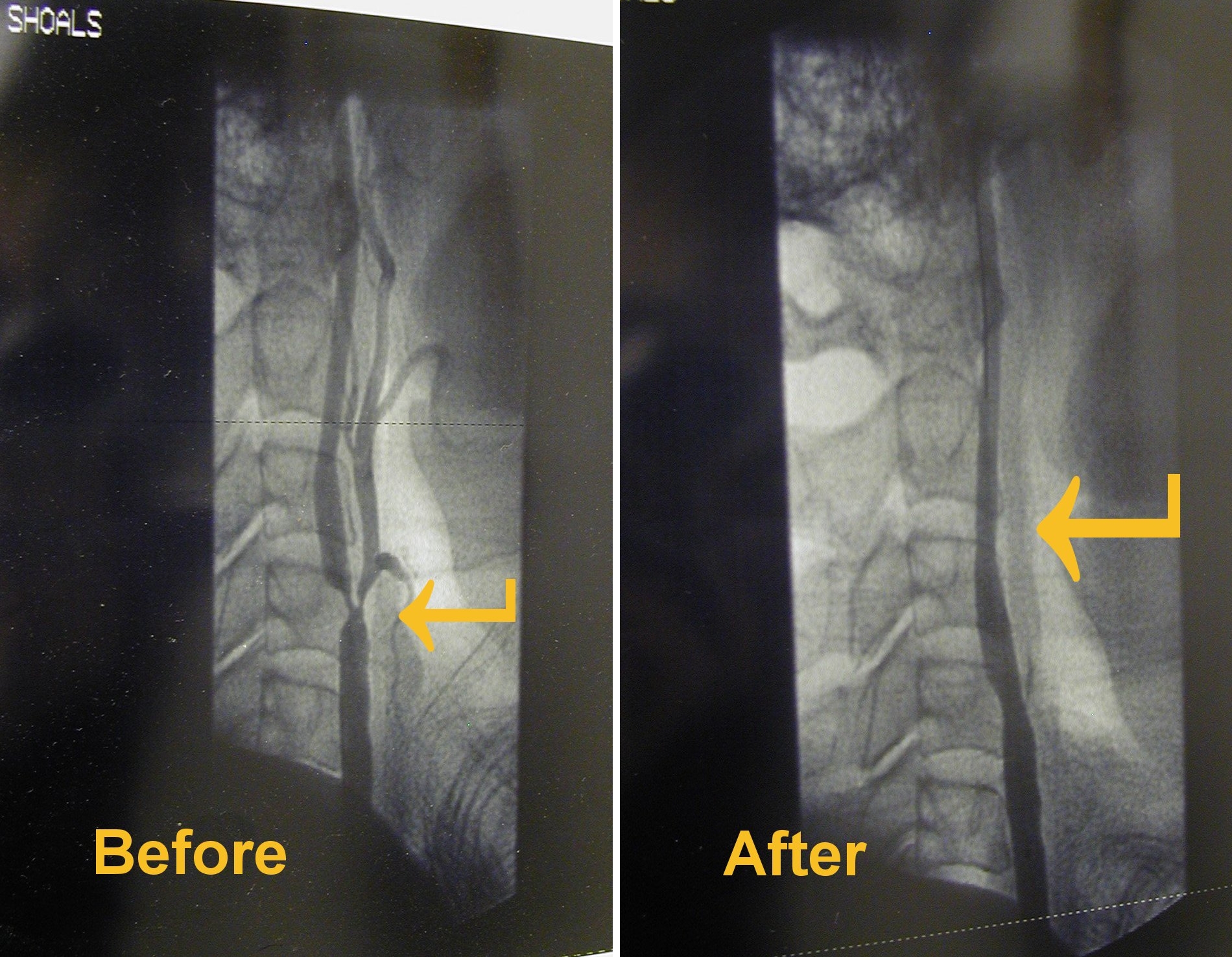
In these cases, a stent can be placed in the carotid artery. In this procedure, the patient has an angiogram. A small tube is placed in an artery in the groin. The tube is fed up through the artery to the point where the narrowing is. Then, a small alloy metal tube known as a stent is threaded through the first tube and placed in the narrow spot ...
Can a stent be placed in the neck?
It can also happen is the narrow portion of the artery is too high up the neck to reach with surgery. In these cases, a stent can be placed in the carotid artery. In this procedure, the patient has an angiogram. A small tube is placed in an artery in the groin.
What is the sound of a carotid artery?
For this test, your doctor places a stethoscope over the carotid artery to listen for a sound called a bruit (pronounced brew-ee). This sound is made when blood passes through a narrowed artery. A bruit can be a sign of atherosclerosis. But, an artery may be diseased without producing this sound.
What causes a narrowing of the arteries?
The narrowing is caused by atherosclerosis. This is the buildup of fatty substances, calcium, and other waste products inside the artery lining. Carotid artery disease is similar to coronary artery disease, in which buildup occurs in the arteries of the heart and can cause a heart attack. Carotid artery disease reduces the flow ...
What is the name of the blood vessel that carries oxygen to the brain?
The carotid arteries are the main blood vessels that carry blood and oxygen to the brain. When these arteries become narrowed, it’s called carotid artery disease. It may also be called carotid artery stenosis. The narrowing is caused by atherosclerosis. This is the buildup of fatty substances, calcium, and other waste products inside ...
What is a CTA test?
Computed tomography angiography (CTA). This test uses X-rays and computer technology along with contrast dye to make horizontal, or axial, images (often called slices) of the body. A CTA shows pictures of blood vessels and tissues and is helpful in identifying narrowed blood vessels. Angiography.
Can a stroke cause paralysis?
A stroke may result in long-term problems, such as weakness in an arm or leg. It may cause paralysis, loss of speech, or even death. The symptoms of carotid artery disease may look like other medical conditions or problems. Always see your doctor for a diagnosis.
What are statins used for?
Statins are a group of cholesterol-lowering medicines . They include simvastatin and atorvastatin. Studies have shown that certain statins can decrease the thickness of the carotid artery wall and increase the size of the opening of the artery. Blood pressure-lowering medicines.
What is a CAS catheter?
Carotid artery angioplasty with stenting (CAS). This is an option for people who are unable to have carotid endarterectomy. It uses a very small hollow tube, or catheter, that is thread through a blood vessel in the groin to the carotid arteries.
How to prevent carotid artery disease?
Prevention. To prevent or slow the progression of carotid artery disease, consider these suggestions: Don't smoke. Within a few years of quitting, a former smoker's risk of stroke is similar to a nonsmoker's. Maintain a healthy weight.
What causes a carotid artery to narrow?
A carotid artery may become so narrowed by atherosclerosis that not enough blood is able to reach portions of your brain. Ruptured plaques. A piece of a plaque may break off and flow to smaller arteries in your brain.
Where are the carotid arteries located?
Overview. The carotid arteries are a pair of blood vessels located on both sides of your neck that deliver blood to your brain and head. Carotid artery disease occurs when fatty deposits (plaques) clog the blood vessels that deliver blood to your brain and head (carotid arteries).
Can carotid artery disease cause stroke?
In its early stages, carotid artery disease often doesn't produce any signs or symptoms. The condition may go un noticed until it's serious enough to deprive your brain of blood , causing a stroke or TIA.
How many strokes are caused by carotid artery disease?
Carotid artery disease causes about 10 to 20 percent of strokes. A stroke is a medical emergency that can leave you with permanent brain damage and muscle weakness. In severe cases, a stroke can be fatal. Carotid artery disease can lead to stroke through: Reduced blood flow.
Can TIA cause a stroke?
You may have experienced a TIA, an important sign that you're at risk of a full-blown stroke. Talk to your doctor if you have risk factors for carotid artery disease. Even if you don't have any signs or symptoms, your doctor may recommend aggressive management of your risk factors to protect you from stroke.
What causes a buildup of plaque in the arteries?
Causes. Carotid artery disease is caused by a buildup of plaques in arteries that deliver blood to your brain. Plaques are clumps of cholesterol, calcium, fibrous tissue and other cellular debris that gather at microscopic injury sites within the artery. This process is called atherosclerosis.
Diagnosing carotid artery disease
Through proper evaluation, a specialist can tell you if you are developing carotid artery disease and do something about it.
If the artery is 80 to 99 percent blocked
First, we look at whether or not you have symptoms resulting from stroke or mini-strokes. This includes slurred speech, visual deficit in one eye, weakness on one side of the body, or any facial asymmetry such as a droopy mouth.
If the artery is 100 percent blocked
What happens when a carotid artery is 100 percent blocked? It’s bad, but it’s not the end of the world. You’ve still got three other arteries supplying blood flow to the brain. The question then is what do we do about it? Should we try to clear or remove the blockage?
Treating advanced disease
Despite the known challenges, there are many cases where we can successfully treat advanced carotid artery disease and free patients from the potential of devastating strokes.
Treatment
Overview
- Carotid stenosis occurs when fatty deposits, or plaques, block the carotid arteries the blood vessels that deliver blood to your brain and head. The blockage increases stroke risk. A stroke is a medical emergency that occurs when the blood supply to the brain is interrupted or significantly reduced. Stroke is the leading cause of permanent disability in the U.S.
Pathophysiology
- Carotid stenosis is particularly dangerous because as plaque builds up inside a carotid artery, the plaque becomes increasingly unstable, and the plaque blockage bursts, releasing pieces of plaque into the bloodstream. Those pieces are carried up into the brain, where they can become lodged in a blood vessel and lead to a stroke.
Risks
- During both procedures, there is a risk that a stroke could occur if, as the surgeon is working, plaque is dislodged and travels to the brain. During angioplasty, theres also a risk that blood clots may form on the catheter or plaque may break loose and travel to the brain, possibly leading to a stroke.
Mechanism
- The new TCAR technique is a hybrid of the two techniques. It involves making a tiny incision at the base of the neck and, from there, inserting a stent into the carotid artery. While the stent is being placed, blood flow through the carotid artery is reversed temporarily. This is accomplished by inserting a small device into the carotid artery that removes the blood and reroutes it to a vein in …
Purpose
- That external circuit contains a pump to move the blood and a filter to remove any plaque that may break free from the artery during the procedure. With TCAR, a stent can be placed to open the artery and relieve the blockage, while the brain is protected from any debris that could lead to a stroke.
Benefits
- Research has shown that the temporary reversal of blood flow during TCAR is safe. And the treatment has been shown to have a lower stroke risk than traditional stenting or surgery. Although its not the best option for everyone, TCAR can be an attractive treatment alternative for many people who have severe carotid stenosis and are at high risk for stroke. Dr. Andrew Olden…
Treatment
Causes
Definition
- A blockage doesnt necessarily mean that a patient is going to have a stroke, says Dr. Lanzino. A partial blockage (greater than 60 percent) in patients without symptoms carries a risk of stroke of about 2 percent each year. That increased risk needs to be weighed against the risk and benefits of treatment.
Research
- Dr. Lanzino worked with Mayo Clinic neurologists Alejandro Rabinstein, M.D., and Robert D. Brown, M.D., to review the most current studies dealing with the medical, surgical, and endovascular treatment of carotid artery stenosis. Their findings, published in April 2009, included:
Symptoms
- Symptoms of carotid artery stenosis include transient blindness in one eye, weakness or numbness of an arm, leg or the face, or the temporary inability to speak or to understand conversation.
Medical uses
- Angioplasty and stenting is an option for higher risk symptomatic patients: Patients with symptoms of carotid artery stenosis who have other health risks precluding surgery may be good candidates for angioplasty and stenting.
Diagnosis
- Differentiating symptomatic and asymptomatic patients is critical: Patients often are diagnosed with carotid artery stenosis after seeing a doctor for dizziness, blurry vision, floaters in the vision or generalized weakness. These are not considered symptoms of carotid artery stenosis even when imaging shows a blockage is present.
Risks
- Age matters when determining treatment: For patients 75 and older, especially those with other health conditions, the risk of treating carotid artery stenosis may exceed the benefit. For patients age 80 and older, angioplasty and stenting has a higher risk of stroke than surgery (carotid endarterectomy).
Consequences and Complications
Risk Factors For Blockage in Carotid Arteries
- Hypertension: High blood-pressure puts pressure on the arterial walls, weakening them and increasing the risk of a rupture.
- Tobacco use and abuse; Smoking increases heart rate and blood pressure. Further Nicotine can irritate the inner lining of arteries.
- Diabetes lowers the body’s ability to process fat efficiently, which increases the risk of hypert…
- Hypertension: High blood-pressure puts pressure on the arterial walls, weakening them and increasing the risk of a rupture.
- Tobacco use and abuse; Smoking increases heart rate and blood pressure. Further Nicotine can irritate the inner lining of arteries.
- Diabetes lowers the body’s ability to process fat efficiently, which increases the risk of hypertension and atherosclerosis.
- High blood-fat levels: High levels of LDL (bad cholesterol) and triglycerides increase the risk of plaque formation.
Signs and Symptoms of Blocked Carotid Artery
- Just for you to be aware, strokes can be caused by many reasons other than carotid artery stenosis. But when it comes to symptoms, for all practical purposes, symptoms of carotid artery stenosis are same as that of a stroke. This includes: 1. Sudden numbness, weakness or tingling in the face, hands or legs, on only one side of the body 2. Sudden trouble in speaking (slurred spee…
Diagnosis
- Various tests are conducted to confirm (or rule out) the condition, and its severity. 1. Physical exam: The doctor uses a stethoscope to listen to an abnormal sound (called bruit – ‘bro-ee’) in the carotid artery. 2. Carotid ultrasound: A standard or Doppler ultrasound that uses ultrasound waves to get a clear picture of the carotid artery and blood flow in the same. 1. CT scan: A CT scan of t…
Treatment
- Three primary options for treatment are available and the doctor will decide if one or more of these must be employed and if so, when. 1. Lifestyle changes: The doctor will recommend reducing weight, salt intake, sugar intake and alcohol consumption. He/she will advise the patient to quit smoking, exercise more and consume a healthy diet low in fat...
Outlook
- The worst part of Carotid Artery Stenosis is that there are no symptoms till an actual stroke occurs. The transient attack of mini-stroke is a warning sign that something is wrong. But waiting till a stroke occurs is risky as there can be complications later. That is why, it’s important that all adults above 30 years of age must mandatorily have a comprehensive health checkup once a ye…