Medication
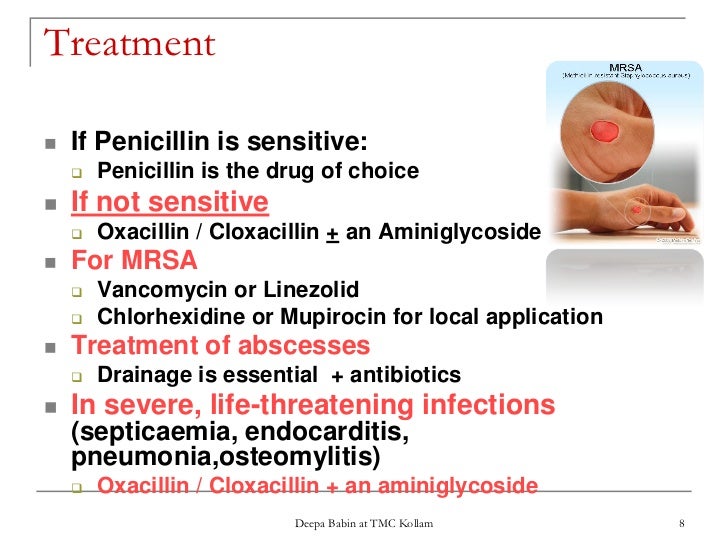
What is the strongest antibiotic for MRSA? Vancomycin is generally considered the drug of choice for severe CA- MRSA infections. Although MRSA is usually sensitive to vancomycin, strains with intermediate susceptibility, or, more rarely, resistant strains have been reported.
Procedures
What is MRSA? MRSA is methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus, a potentially dangerous type of staph bacteria that is resistant to certain antibiotics and may cause skin and other infections. As with all regular staph infections, recognizing the signs and receiving treatment for MRSA skin infections in the early stages reduces the
Nutrition
To answer your question, yes it can kill you, but mostly people on either end of the life spectrum, babies and the elderly, the immunosuppressed ... transplant patients, patients with AIDS, etc. So, again don't worry. Given enough antibiotics and time, the mrsa will be a memory.
What is the strongest antibiotic for MRSA?
Normally it takes around 10 days to get complete recovery from MRSA infection. However, the time varies from person to person and depends upon a variety of factors.
What is MRSA and how dangerous is it?
Can the disease MRSA kill you?
How long does it take for MRSA to heal?
What is the best drug to treat MRSA?
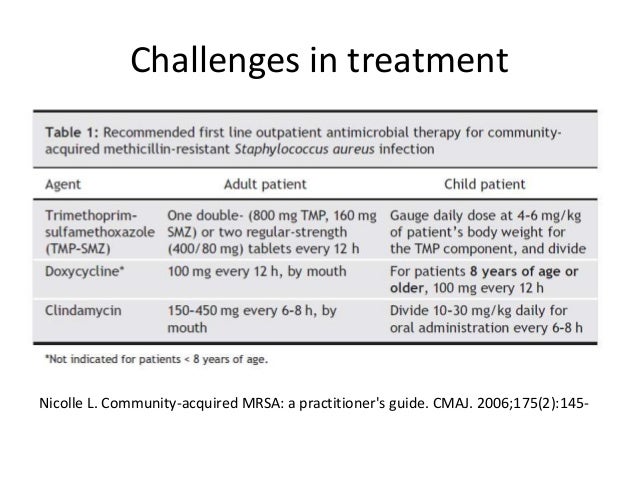
At home — Treatment of MRSA at home usually includes a 7- to 10-day course of an antibiotic (by mouth) such as trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole (brand name: Bactrim), clindamycin, minocycline, linezolid, or doxycycline.
What is the only drug of choice to treat MRSA at this time?
Common antibiotics for treatment of MRSA include sulfamethoxazole with trimethoprim, clindamycin, vancomycin, daptomycin, linezolid, tedizolid, doxycycline, minocycline, omadacycline, and delafloxacin.
What is the first line treatment for MRSA?
Oral antibiotics. Some antibiotics available in oral formulations are treatment options for MRSA: First-line therapy: trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole (TMP-SMX; Bactrim DS, Septra DS. Sulfamethoprim-DS). This agent has been shown to be 95% effective.
What 3 antibiotics is MRSA resistant to?
What sets MRSA apart is that it is resistant to an entire class of antibiotics called beta-lactams. This group of antibiotics includes methicillin, and the more commonly prescribed penicillin, amoxicillin, and oxacillin among others.
Is vancomycin used for MRSA?
Because MRSA is a multidrug-resistant strain, there are tremendous difficulties in the treatment and prevention of MRSA infection in hospital. Ever since MRSA was identified in 1961, vancomycin has been the drug of choice in the treatment of MRSA infection.
Why is vancomycin used for MRSA?
aureus (MRSA) in healthcare and community settings is a major concern worldwide. Vancomycin, a glycopeptide antibiotic that inhibits cell wall biosynthesis, remains a drug of choice for treatment of severe MRSA infections.
Is doxycycline used for MRSA?
Oral antibiotics belonging to the tetracycline family, including minocycline and doxycycline, provide an effective means of treating CA-MRSA infections. As stated above, incision and drainage remains the single most important intervention against CA-MRSA infections, which present as abscess-like lesions.
What antibiotic is stronger than vancomycin?
When tested against vancomycin-resistant enterococci (VRE), the vancomycin with the three modifications was more than 6,000 times more powerful than vancomycin, meaning much less of it would need to be used.
What class of drug is vancomycin?
Vancomycin is in a class of medications called glycopeptide antibiotics. It works by killling bacteria in the intestines. Vancomycin will not kill bacteria or treat infections in any other part of the body when taken by mouth.
Can ciprofloxacin treat MRSA?
Ciprofloxacin can no longer be used in empirical therapy against MRSA infections. Use of other members of fluoroquinolone should be limited only to those strains that show laboratory confirmation of their susceptibility. Vancomycin remains the drug of choice to treat MRSA infections.
Does cephalexin treat MRSA?
Treatment with cephalexin, a traditional antimicrobial lacking activity against MRSA, resulted in 94% of children improving at 48 to 72 hours, while treatment with clindamycin, which typically is effective in these resistant infections, led to improvements in 97% (P=0.50), according to Aaron E.
Does clindamycin treat MRSA?
Reasonable antibiotics for treatment of MRSA include older agents (clindamycin, trimethoprim- sulfamethoxazole, and tetracyclines such as doxycycline or minocycline) and a newer agent, linezolid (table 1).
Linezolid (Brand Names: Zyvox, Zyvoxid Or Zyvoxam)
Approved for use in the year 2000, Linezolid is FDA approved for treating soft tissue and skin infections, including those caused by MRSA. It is of...
Mupirocin (Brand Name: Bactroban)
Commonly used as a topical cream for minor skin infections and skin lesions for Staph aureus, MRSA and Streptococcus infections. Mupirocin ointment...
Trimethoprim-Sulfamethoxazole (Brand Name: Septra Or Bactrim)
It is not FDA-approved for the treatment of Staphylococcal infections (including MRSA). However, laboratory tests have shown most CA-MRSA strains a...
Tetracyclines (Doxycycline and Minocycline)
Data suggests these drugs are effective in treatment of soft tissue and skin infections, but not for deeper or more severe infections. 1. Side Effe...
Intravenous (IV) Vancomycin
Vancomycin is often called an antibiotic of last resort for MRSA, though resistance against it has been growing. Vancomycin requires IV administrat...
Intravenous (IV) Daptomycin
Daptomycin is FDA approved for adults with Staph aureus bacteremia, some forms of endocarditis and some skin and soft tissue infections. The safety...
What is the best treatment for MRSA?
Antibiotics are commonly prescribed as a treatment for MRSA skin infections, either by themselves or along with draining of the infection by a healthcare professional. Antibiotics are also the standard medical therapy for internal MRSA infections. Antibiotic therapy is often prescribed for the following types of infections:
What is the best antibiotic for MRSA?
1. Clindamycin. It has been successfully and widely used for the treatment of soft tissue and skin infections as well as bone, joint and abscesses caused by Staph and MRSA.
What is the name of the cream that is used to treat staph aureus?
3. Mupirocin (Brand Name: Bactroban) Commonly used as a topical cream for minor skin infections and skin lesions for Staph aureus, MRSA and Streptococcus infections. Mupirocin ointment is applied to reduce or eliminate MRSA colonization in the nose (see also “MRSA carriers”).
What is a broad spectrum antibiotic?
Oftentimes a broad-spectrum antibiotic is used in conjunction with the following antibiotics. Most options below use intravenous methods of delivering antibiotics into the body. A picc line may be used for prolonged treatment. 1. Intravenous (IV) Vancomycin.
What type of infection is treated with antibiotics?
Antibiotic therapy is often prescribed for the following types of infections: Skin infections, such as boils or abscesses, that do not respond to incision and drainage. Systemic or internal infections such as bone, implant or lung infections. Severe local symptoms.
What is Linezolid used for?
Approved for use in the year 2000, Linezolid is FDA approved for treating soft tissue and skin infections, including those caused by MRSA. It is often prescribed for CA-MRSA pneumonia and in particular, HA-MRSA pneumonia.
Is MRSA resistant to Zyvox?
Because MRSA is becoming more resistant, and it’s more common for antibiotic treatments to fail, and treatment may require the use of newer antibiotics, such as the “glycopeptides” which includes Vancomycin and Zyvox. Unfortunately, there are newer strains of MRSA that are becoming resistant to these two drugs.
What is the best treatment for MRSA?
Vancomycin or daptomycin are the agents of choice for treatment of invasive MRSA infections [1]. Alternative agents that may be used for second-line or salvage therapy include telavancin, ceftaroline, and linezolid. Recent studies of treatment of MRSA bacteremia are reviewed. Vancomycin.
How much daptomycin should I take for MRSA?
This is reflected in the Infectious Diseases Society of America guidelines for treatment of MRSA infections, where daptomycin dosing is recommended at 8 to 10 mg/kg for complicated bacteremia and in combination with other agents if there has been prior vancomycin treatment failure [1].
What is the fifth generation of cephalosporin?
Ceftaroline. Ceftaroline is a fifth-generation cephalosporin with bactericidal activity against MRSA and VISA as well as Gram-negative pathogens [14]. Ceftaroline fosamil, the pro-drug of ceftaroline, received approval by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 2010.
When was telavancin approved?
Telavancin was approved in November 2009 in the United States for the treatment of acute bacterial skin and skin structure infections (ABSSSI), and in June 2013 in US for hospital-acquired pneumonia (HAP) caused by gram-positive pathogens including MRSA where alternative treatments are not suitable.
Is telavancin effective for MRSA?
Telavancin may prove effective for treatment of MRSA bacteremia. In a phase 2 trial of telavancin for treatment of bacteremia including 17 patients, cure rates were comparable for telavancin and standard therapy (88 vs 89%) [8].
Is vancomycin bactericidal?
aureus. Furthermore, vancomycin is slowly bactericidal, which may be partly responsible for reported clinical failures in treatment of bacteremia and endocarditis.
Is vancomycin good for MRSA?
Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus(MRSA) is a significant cause of health care-associated infections. Vancomycin remains an acceptable treatment option. There has been a welcome increase in the number of agents available for the treatment of MRSA infection.
Drugs used to treat Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus Infection
The following list of medications are in some way related to, or used in the treatment of this condition.
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
How to diagnose MRSA?
Doctors diagnose MRSA by checking a tissue sample or nasal secretions for signs of drug-resistant bacteria. The sample is sent to a lab where it's placed in a dish of nutrients that encourage bacterial growth. But because it takes about 48 hours for the bacteria to grow, newer tests that can detect staph DNA in a matter ...
Can antibiotics help with MRSA?
Treatment. Both health care-associated and community-associated strains of MRSA still respond to certain antibiotics. Doctors may need to perform emergency surgery to drain large boils (abscesses), in addition to giving antibiotics. In some cases, antibiotics may not be necessary.
What antibiotics are used for MRSA?
These antibiotics include: Clindamycin, Linezolid (Zyvox), Mupirocin, Septra or Bactrim for generalized skin infections.
Why is it difficult to know which antibiotic is best for MRSA?
Because MRSA bacteria are so resistant to many drug therapies, many people may find their prescribed antibiotic does not work.
What antibiotics are used for skin infections?
These antibiotics include: Clindamycin, Linezolid (Zyvox), Mupirocin, Septra or Bactrim for generalized skin infections. For more severe infections, antibiotics can include Vancomycin, Zyvox, Daptomycin and Clindamycin. Even though the above antibiotics are current therapies in 2012, it does not mean they will work for all strains of MRSA.
Can you take antibiotics for MRSA?
If you’ve been diagnosed with any type of MRSA, chances are your doctor will want you to start you on antibiotics. They may prescribe oral antibiotics you take by mouth or by IV antibiotics if the infection is more severe. Figuring out which antibiotic is best is a difficult question to answer. Because MRSA bacteria are so resistant ...
How long does it take to treat MRSA?
The duration of therapy for treatment of MRSA SSTIs may range from 5 to 14 days depending on the extent of infection and response to treatment .
What are the steps to prevent MRSA?
Prevention and control of MRSA infections include necessary infection-control steps like strict hand hygiene and adequate contact precautions. Hand hygiene means washing hands with soap and water or an alcohol-based cleanser before and after contact with patients who have MRSA infection.
What is the MIC of Methicillin in S. aureus?
Last Update: July 18, 2021. Continuing Education Activity. Based on the antibiotic susceptibilities, Methicillin resistance in S. aureus is defined as an oxacillin minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) of greater than or equal to 4 micrograms/mL. MRSA infection is one of the leading causes of hospital-acquired infections ...
What is the MIC of Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus?
Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus - StatPearls - NCBI Bookshelf. Based on the antibiotic susceptibilities, Methicillin resist ance in S. aureus is defined as an oxacillin minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) of greater than or equal to 4 micrograms/mL. MRSA infection is one of the leading causes of hospital-acquired infections ...
How does methicillin resistance occur?
Methicillin resistance has occurred in S. aureusby mutation of a penicillin-binding protein, a chromosome-encoded protein. This type of resistance is transferred between S. aureusorganisms by bacteriophages. This is one of the only medically relevant examples of chromosome-mediated drug resistance by phage transduction.
What is the MIC of Methicillin?
Based on the antibiotic susceptibilities, Methicillin resistance in S. aureus is defined as an oxacillin minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) of greater than or equal to 4 micrograms/mL.
What is a positive Gram stain?
A positive Gram stain with cocci in clusters is suggestive of S. aureus. DNA polymerase chain reaction (PCR) of MRSA is the most sensitive test and gold standard test if cultures are inconclusive. DNA PCR of MRSA from nares is a frequently employed diagnostic test to rule out MRSA colonization.
How long does it take for MRSA to develop?
It is important to discuss a follow-up plan with your patients in case they develop systemic symptoms or worsening local symptoms, or if symptoms do not improve within 48 hours.
What is the purpose of obtaining specimens for culture and susceptibility testing?
Obtaining specimens for culture and susceptibility testing is useful to guide therapy , particularly for those with more severe infections and those who fail to respond adequately to initial management.
Is a spider bite a S. aureus infection?
A patient’s presenting complaint of “spider bite” should raise suspicion of an S. aureus infection. Recent data suggest that MRSA as a cause of skin infections in the general community remains at high probability.