
How do you cure hemophilia?
The recommended treatment plan for haemophilia depends on how severe it is. There are 2 main approaches to treatment: preventative treatment, where medicine is used to prevent bleeding and subsequent joint and muscle damage; on-demand treatment, where medicine is used to treat prolonged bleeding Haemophilia is usually treated by a team at a haemophilia hospital …
Are there any cures for hemophilia?
Background: Regular treatment to prevent bleeding and consequent joint deterioration (prophylaxis) is the standard of care for persons with severe hemophilia A, traditionally based on intravenous infusions of the deficient clotting FVIII concentrates (CFCs). In recent years, extended half-life (EHL) CFCs and the non-replacement agent emicizumab, subcutaneously …
Can you cure hemophilia?
In cases of severe hemophilia, treatment may be given to stop bleeding when it occurs. Patients who have frequent... Some people with the mild or moderate form of hemophilia type A can be treated with desmopressin (DDAVP®), a synthetic... Aminocaproic acid or tranexamic acid are agents that prevent ...
How to cure hemophilia?
Get an annual comprehensive checkup at a hemophilia treatment center. Get vaccinated—Hepatitis A and B are preventable. Treat bleeds early and adequately. Exercise and maintain a healthy weight to protect your joints. Get tested regularly for blood-borne infections.

What is the best treatment for hemophilia?
The best way to treat hemophilia is to replace the missing blood clotting factor so that the blood can clot properly. This is typically done by injecting treatment products, called clotting factor concentrates, into a person's vein.
What is the treatment of choice for classical hemophilia?
Desmopressin vasopressin analog, or 1-deamino-8-D-arginine vasopressin (DDAVP), is considered the treatment of choice for mild and moderate hemophilia A.Mar 25, 2022
What is the mainstay of treatment for hemophilia?
Replacement of the congenitally deficient factor VIII or IX through plasma-derived or recombinant concentrates is the mainstay of treatment for hemophilia.Aug 30, 2010
What is prophylaxis for hemophilia A?
In haemophilia, prophylaxis can be defined as the administration of clotting factor concentrate in anticipation of or to prevent bleeding.
How is hemophilia vaccine administered?
These vaccinations are often given by their primary care physician. Most vaccinations can be given subcutaneously, or under the skin, instead of intramuscularly, or into the muscle, to reduce the risk of a muscle bleed.Sep 15, 2011
Why is FFP given in hemophilia?
In the late 1950s and much of the 1960s, fresh frozen plasma (FFP) was the mainstay of treatment for hemophilia A and hemophilia B. Each bag of FFP contained only miniscule amounts of factor VIII and factor IX, thus large volumes of intravenously administered FFP were needed to stop bleeding episodes.
What is the first line treatment for moderate to severe hemophilia A?
Treatment With Replacement Therapy. The main treatment for hemophilia is called replacement therapy. Concentrates of clotting factor VIII (for hemophilia A) or clotting factor IX (for hemophilia B) are slowly dripped or injected into a vein. These infusions help replace the clotting factor that's missing or low.
How do you stop bleeding from hemophilia?
Apply pressure to the bleeding area. Use an ice pop or piece of ice on the area. When the bleeding stops, help your child avoid hard or hot foods because they can restart the bleeding. If the bleeding does not stop within 20 minutes, call your care team.
How to prevent hemophilia?
Lifestyle and home remedies. To avoid excessive bleeding and protect your joints: Exercise regularly. Activities such as swimming, bicycle riding and walking can build up muscles while protecting joints. Contact sports — such as football, hockey or wrestling — are not safe for people with hemophilia.
How to help a child with hemophilia?
To help you and your child cope with hemophilia: Get a medical alert bracelet. This bracelet lets medical personnel know that you or your child has hemophilia, and the type of clotting factor that's best in case of an emergency. Talk with a counselor.
What is a recombinant clotting factor?
Similar products, called recombinant clotting factors, are manufactured in a laboratory and aren't made from human blood. Other therapies may include: Desmopressin. In some forms of mild hemophilia, this hormone can stimulate your body to release more clotting factor.
How to stop bleeding under the skin?
For small areas of bleeding beneath the skin, use an ice pack. Ice pops can be used to slow down minor bleeding in the mouth. Vaccinations. Although blood products are screened, it's still possible for people who rely on them to contract diseases.
What is the best way to prevent clots from breaking down?
It can be injected slowly into a vein or provided as a nasal spray. Clot-preserving medications. These medications help prevent clots from breaking down. Fibrin sealants. These medications can be applied directly to wound sites to promote clotting and healing. Fibrin sealants are especially useful in dental therapy.
How to treat internal bleeding?
If internal bleeding has caused severe damage, you may need surgery. First aid for minor cuts. Using pressure and a bandage will generally take care of the bleeding. For small areas of bleeding beneath the skin, use an ice pack.
How to prevent tooth extractions?
Practice good dental hygiene. The goal is to prevent tooth extraction, which can lead to excessive bleeding. Protect your child from injuries that could cause bleeding. Kneepads, elbow pads, helmets and safety belts all may help prevent injuries from falls and other accidents.
What is the treatment for haemophilia A?
Haemophilia A. Preventative treatment for haemophilia A involves regular injections of a medicine called octocog alfa (Advate). Read about octocog alfa (Advate) on the European Medicines Agency's website. This medicine is an engineered version of clotting factor VIII (8), the clotting factor people with haemophilia A do not have enough of.
How to treat haemophilia in children?
Preventative treatment. Most cases of haemophilia are severe and need preventative treatment. This involves regular injections of clotting factor medicine. If your child has haemophilia, you'll be trained to give them the injections when they're young.
What is the name of the drug that makes blood clotting factor less effective?
Inhibitors . Some people who take blood clotting factor medicine develop antibodies in their immune system, called inhibitors, which make the medicine less effective. People having treatment for haemophilia should be regularly tested for inhibitors. Inhibitors can be treated with immune tolerance induction (ITI).
What is preventative treatment?
preventative treatment, where medicine is used to prevent bleeding and subsequent joint and muscle damage. on-demand treatment, where medicine is used to treat prolonged bleeding. Haemophilia is usually treated by a team at a haemophilia hospital department.
How often should I take octocog alfa?
This medicine is an engineered version of clotting factor VIII (8), the clotting factor people with haemophilia A do not have enough of. Injections every 48 hours are often recommended. Side effects of octocog alfa are uncommon but can include: an itchy skin rash. redness and soreness at the site of the injection.
Can ITI be given to people with haemophilia?
ITI is usually offered to people with severe haemophilia A. People with haemophilia B may be offered ITI, but it's less effective and there's a risk of severe allergic reaction. People with mild or moderate haemophilia A who develop inhibitors may be offered either bypass therapy or immunosuppressants.
Do you need to find veins for every injection?
This port is connected to a blood vessel near the heart, so you do not need to try to find a vein for every injection. People who have preventative treatment will need regular follow-up appointments with their care team so their progress can be monitored. Preventative treatment is usually continued for life.
How is hemophilia managed?
In most cases a child with severe hemophilia is managed at home by his parents, with the administration of factor on a prophylactic schedule. As the child gets older, he is taught how to self-administer his factor on schedule or when an acute bleed occurs.
What is the most common type of hemophilia?
There are two main types of inherited hemophilia: Type A , the most common type, is caused by a deficiency of factor VIII, one of the proteins that helps blood to form clots. This type is known as classic hemophilia. Type B hemophilia is caused by a deficiency of factor IX. This type is also called Christmas disease.
Why does hemophilia occur?
The disorder occurs because certain blood clotting factors are missing or do not work properly. Because a clot does not form, extensive bleeding can be caused from a cut or wound.
How many people have hemophilia A?
Hemophilia A affects 1 in 5,000 to 10,000 males. Hemophilia B is less common, affecting 1 in 25,000 to 30,000 males. Around 60% to 70% of people with hemophilia A have the severe form of the disorder and about 15% have the moderate form. The rest have mild hemophilia.
What causes hemophilia in a daughter?
In about 20% of all cases of hemophilia, the disorder is caused by a spontaneous gene mutation. In such cases there is no family history of abnormal bleeding.
What is the chance that any of her sons will inherit the gene and be born with hemophilia?
There is a 50% chance that any of her sons will inherit the gene and will be born with hemophilia. There is also a 50% chance that any of her daughters will be carriers of the gene without having hemophilia themselves.
What is the cause of hemophilia?
Hemophilia is caused by mutations in either the factor VIII or factor IX genes on the X chromosome. If a woman carries the abnormal gene on one of her X chromosomes (females have a pair of X chromosomes), she will not have hemophilia herself, but she will be a carrier of the disorder.
What is hemophilia clotting?
Table of Contents. Hemophilia is usually an inherited bleeding disorder in which the blood does not clot properly. This can lead to spontaneous bleeding as well as bleeding following injuries or surgery. Blood contains many proteins called clotting factors that can help to stop bleeding. People with hemophilia have low levels ...
How is hemophilia determined?
The severity of hemophilia that a person has is determined by the amount of factor in the blood. The lower the amount of the factor, the more likely it is that bleeding will occur which can lead to serious health problems. In rare cases, a person can develop hemophilia later in life. The majority of cases involve middle-aged or elderly people, ...
What is the effect of hemophilia on blood clotting?
About 15-20 percent of people with hemophilia develop an antibody (called an inhibitor) that stops the clotting factors from being able to clot the blood and stop bleeding. Treatment of bleeding episodes becomes extremely difficult, and the cost of care for a person with an inhibitor can skyrocket because more clotting factor or a different type of clotting factor is needed. People with inhibitors often experience more joint disease and other problems from bleeding that result in a reduced quality of life.
What tests are done to determine if a newborn has hemophilia?
To make a diagnosis, doctors would perform certain blood tests to show if the blood is clotting properly. If it does not, then they would do clotting factor tests, also called factor assays, to diagnose the cause of the bleeding disorder.
What is an HTC?
Often the best choice for care is to visit a comprehensive Hemophilia Treatment Center (HTC). An HTC not only provides care to address all issues related to the disorder, but also provides health education that helps people with hemophilia stay healthy. Learn more about treatment.
How do you know if you have hemophilia?
Signs and Symptoms. Common signs of hemophilia include: Bleeding into the joints. This can cause swelling and pain or tightness in the joints; it often affects the knees, elbows, and ankles. Bleeding into the skin (which is bruising) or muscle and soft tissue causing a build-up of blood in the area (called a hematoma).
What is a female with one X chromosome?
A female with one affected X chromosome is a “carrier” of hemophilia. Sometimes a female who is a carrier can have symptoms of hemophilia. In addition, she can pass the affected X chromosome with the clotting factor gene mutation on to her children. Learn more about the inheritance pattern for hemophilia.
What is the treatment for hemophilia?
The treatment of hemophilia may involve prophylaxis, management of bleeding episodes, treatment of factor VIII (FVIII) inhibitors, and treatment and rehabilitation of hemophilia synovitis. Use of factor replacement products and other medications, including pain medications, is typically required.
What is an inhibitor in hemophilia?
Inhibitors are antibodies that neutralize factor VIII (FVIII) and can render replacement therapy ineffective. They are found more commonly in patients with moderate to severe hemophilia (up to 30% of those with severe disease) who have received significant amounts of replacement therapy.
What is nonautologous gene therapy?
Nonautologous gene therapy, in which cells modified to secrete FVIII are packaged in immunoprotected devices and implanted into recipients. Preclinical studies in mice and dogs with hemophilia have resulted in long-term correction of the bleeding disorders and, in some cases, a permanent cure.
Why is prophylaxis not accepted?
Prophylaxis is not universally accepted, with only about half the children with hemophilia A receiving this treatment modality in the United States. Reasons cited for the lack of acceptance include need for venous access, factor availability, repeated venipunctures, and cost, among others.
What is the purpose of FVIII concentrate?
Various purification techniques are used in plasma-based FVIII concentrates to reduce or eliminate the risk of viral transmission, including heat treatment, cryoprecipitation, and chemical precipitation. These techniques inactivate viruses such as hepatitis B virus, hepatitis C virus, and HIV.
When was emicizumab approved?
In November 2017 , following a priority review, the FDA approved emicizumab for routine prophylaxis of bleeding episodes in adult and pediatric patients (including newborns) with hemophilia A who have FVIII inhibitors. Approval was based on the HAVEN 1 and 2 clinical trials.
Is Desmopressin vasopressin effective for hemophilia?
Desmopressin vasopressin analog, or 1-deamino-8-D-arginine vasopressin (DDAVP), is considered the treatment of choice for mild and moderate hemophilia A. It is not effective in the treatment of severe hemophilia. DDAVP stimulates a transient increase in plasma FVIII levels. Other possible mechanisms of action are noted.
What is a hemlibra?
Hemlibra (emicizumab-kxwh) Emicizumab is a humanized, bispecific, monoclonal antibody that binds to FIX / FIXa and FX / FXa, thereby standing in for the missing FVIII to prevent or reduce the occurrence of bleeding in patients with hemophilia A.
How does rFVIII work?
Some rFVIII concentrates have been bioengineered to modulate functional properties of the molecule. This includes strategies which alter the pharmacokinetic properties of the molecule. For example, a recombinant factor molecule is fused to another protein, such as human albumin or the Fc fragment of human IgG1. The fusion is accomplished by adding the gene for the partner protein to the gene for factor VIII or IX before the factor gene is inserted into a cell line for production of the recombinant factor-fusion protein molecule. The purpose of adding the fusion protein is to prolong the half-life of the infused factor in the circulation. Another approach to prolonging half-life is to conjugate the factor protein to another molecule such as PolyEthylene Glycol (PEG) which delays degradation of the factor, thus prolonging the half-life in the circulation.
How long after emicizumab can you take FEIBA?
In particular, in those using emicizumab prophylaxis, concomitant FEIBA should be avoided during and up to six months after emicizumab use, as residual emicizumab levels may persist in the plasma (MASAC Document #255). Treatment of Patients with Acquired Hemophilia A.
What is desmopressin acetate?
Desmopressin acetate is a synthetic analogue of the natural pituitary antidiuretic hormone, 8-arginine vasopressin. When given to persons who have the capability of producing some FVIII or VWF, the drug effects a rapid, transient increase in FVIII and VWF. It can be given intravenously, subcutaneously, or by intranasal spray.
What antibody binds to FIXA?
A humanized bispecific monoclonal antibody that binds to FIXa and FX to bypass a FVIII inhibitor to prevent or reduce the frequency of bleeding episodes in patients with hemophilia A and FVIII inhibitor. (Table IV.C.)
What is rVWF concentrate?
Recombinant V WF (rVWF) concentrate is available to treat patients with type 2B and type 3 VWD; it can also be used in patients with types 1, 2A, 2M, and 2N VWD who are not responsive to DDAVP and in children under 2 years of age regardless of VWD type.
How long does a ribastap stay heated?
Fibrinogen Concentrate (Human) (RiaSTAP) is heated in aqueous solution (pasteurized) at 60°C for 20 hours. Fibrinogen (Human) (FIBRYNA, also called FIBRYGA) undergoes solvent/detergent treatment and nanofiltration. Both products can be used to treat patients with congenital hypo-fibrinogenemia and afibrinogenemia.
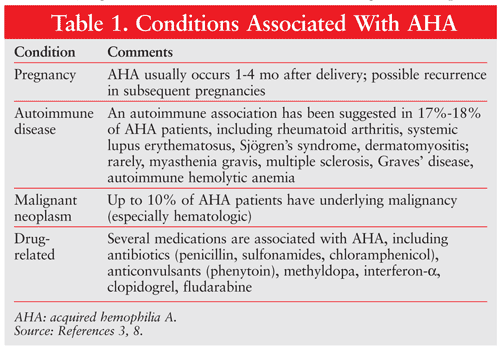
Diagnosis
Treatment
- The main treatment for severe hemophilia involves replacing the clotting factor you need through a tube in a vein. This replacement therapy can be given to treat a bleeding episode in progress. It can also be given on a regular schedule at home to help prevent bleeding episodes. Some people receive continuous replacement therapy. Replacement clotti...
Clinical Trials
- Explore Mayo Clinic studiestesting new treatments, interventions and tests as a means to prevent, detect, treat or manage this condition.
Lifestyle and Home Remedies
- To avoid excessive bleeding and protect your joints: 1. Exercise regularly.Activities such as swimming, bicycle riding and walking can build muscles while protecting joints. Contact sports — such as football, hockey or wrestling — are not safe for people with hemophilia. 2. Avoid certain pain medications.Drugs that can make bleeding worse include aspirin and ibuprofen (Advil, Motr…
Coping and Support
- To help you and your child cope with hemophilia: 1. Get a medical alert bracelet.This lets medical personnel know that you or your child has hemophilia, and the type of clotting factor that's best in case of an emergency. 2. Talk with a counselor.Striking the right balance between keeping your child safe and encouraging as much activity as possible can be tricky. A social worker or therapi…
Preparing For Your Appointment
- If you or your child has signs or symptoms of hemophilia, you might be referred to a doctor who specializes in blood disorders (hematologist).