Can the brain help treat mental illness?
Such knowledge will support the field in prioritizing novel and refined treatment strategies to improve interventions for people burdened by some of the most disabling effects of mental illness. Of course, the brain is not the ultimate solution for developing and optimizing mental health treatments.
What is the best treatment for mental health conditions?
Treatment for mental health conditions is not a one size fits all approach. Treatment can include private doctors, community mental health centers, emergency rooms, hospitalization and substance abuse centers. Knowing where to look and what to expect can help reduce confusion and stress.
How can neuroscience be used to promote mental health treatment?
Cognitive neuroscience has perhaps gained the most traction in promoting mental health treatment through the identification of neural targets for intervention.
What are brain stimulation treatments for depression?
Brain-stimulation treatments are sometimes used for depression and other mental health disorders. They're generally reserved for situations in which medications and psychotherapy haven't worked. They include electroconvulsive therapy, repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation, deep brain stimulation and vagus nerve stimulation.

Is electro shock therapy still used today?
But electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) is still being used -- more in Europe than the United States -- and it may be the most effective short-term treatment for some patients with depressive symptoms, a newly published review in the journal The Lancet suggests.
What is the new ECT?
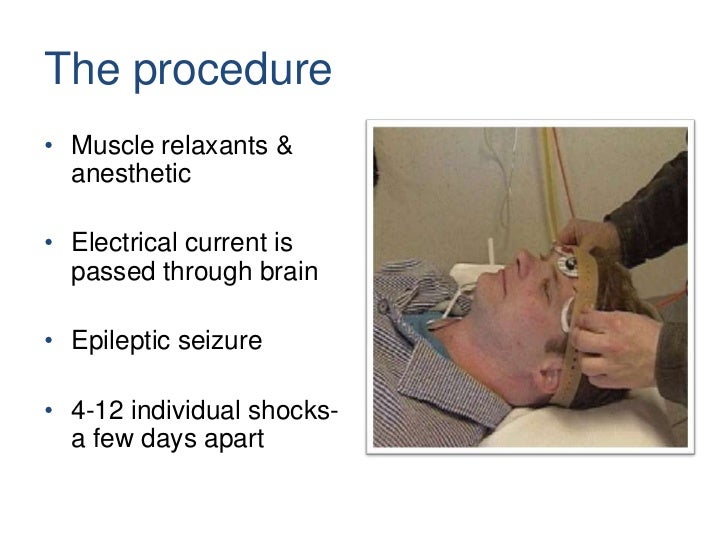
Electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) is a medical treatment most commonly used in patients with severe major depression or bipolar disorder that has not responded to other treatments. ECT involves a brief electrical stimulation of the brain while the patient is under anesthesia.
What are some of the newer methods of stimulating the brain?
These include:vagus nerve stimulation (VNS)repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (rTMS)magnetic seizure therapy (MST)deep brain stimulation (DBS)
What is the therapy for brain?
Electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) has been around for more than 80 years. It's the most-researched type of brain stimulation therapy. It's typically used for severe, treatment-resistant depression or bipolar disorder. Studies show ECT is safe and works well.
Is shock therapy still used in 2021?
July 19, 2021, at 8:14 a.m. MONDAY, July 19, 2021 (HealthDay News) -- "Shock" therapy often helps lift severe depression, but fear and stigma can deter patients from getting it. Now a large new study is confirming the treatment's safety.
Which is better TMS or ECT?
TMS is more affordable (covered by most insurance and Medicare), and elicits fewer side effects than ECT. It has also been proven to be an effective treatment for depression. However, it appears to be less effective than ECT and requires more sessions.
What does a deep brain stimulator do?
Deep brain stimulation (DBS) involves implanting electrodes within certain areas of the brain. These electrodes produce electrical impulses that regulate abnormal impulses. Or the electrical impulses can affect certain cells and chemicals within the brain.
Who is a good candidate for deep brain stimulation?
Criteria for Deep Brain Stimulation Surgery An ideal candidate for DBS surgery is under 70 years old and is in good health. Patients who fluctuate between “on” and “off” medication states are usually good surgical candidates, as are those who have troublesome dyskinesias.
What is the difference between electroshock therapy and electroconvulsive therapy?
Electroshock therapy, also known as electroconvulsive therapy (ECT), is a treatment for severe major depression, bipolar depression, and other mental health conditions. Psychiatrists may recommend ECT when a person does not respond well to other treatments.
What is brain recovery?
Brain rehabilitation therapy helps people relearn functions lost as a result of a brain injury. These might include daily activities such as eating, dressing, walking or speech. Brain injuries can affect people in many different ways.
How is Neurotherapy done?
Neurotherapy only involves placing electrodes on the scalp to monitor your brain activity. Electrodes only read what's happening inside your brain. They don't transmit any type of signal to your brain. Provides long-lasting effects.
Is there brain surgery for depression?
The neurosurgical treatment of treatment-resistant depression (TRD) has entered a new era with more and more patients being treated with deep brain stimulation (DBS) via surgically implanted intracerebral electrodes.
How has ECT changed?
In the 1950s and 1960s, the widening adoption of modified ECT—which includes the use of a muscle relaxant and general anesthesia—helped bolster acceptance of the treatment. The muscle relaxants eliminated the convulsions associated with seizures and therefore greatly reduced the risk of injuries.
Does ECT destroy brain cells?
The review of literature and present evidence suggests that ECT has a demonstrable impact on the structure and function of the brain. However, there is a lack of evidence at present to suggest that ECT causes brain damage.
What is the difference between unilateral and bilateral ECT?
Depending on the location of the electrodes, ECT is defined as bilateral or uni- lateral. In bilateral ECT, one electrode is placed on the left side of the head, the other on the right side. In unilateral ECT, one electrode is placed at the top (vertex) of the head and the other typically on the right side.
How does ECT work?
Overview. Electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) is a procedure, done under general anesthesia, in which small electric currents are passed through the brain, intentionally triggering a brief seizure. ECT seems to cause changes in brain chemistry that can quickly reverse symptoms of certain mental health conditions.
Which type of therapy is the best studied brain stimulation therapy?
While these types of therapies are less frequently used than medication and psychotherapies, they hold promise for treating certain mental disorders that do not respond to other treatments. Electroconvulsive therapy is the best studied brain stimulation therapy and has the longest history of use.
How does brain stimulation work?
Brain stimulation therapies involve activating or inhibiting the brain directly with electricity. The electricity can be given directly by electrodes implanted in the brain, or noninvasively through electrodes placed on the scalp. The electricity can also be induced by using magnetic fields applied to the head.
What is DBS treatment?
Deep brain stimulation (DBS) was first developed as a treatment for Parkinson's disease to reduce tremor, stiffness, walking problems and uncontrollable movements. In DBS, a pair of electrodes is implanted in the brain and controlled by a generator that is implanted in the chest.
How long does it take for ECT to work?
But after about an hour, the patient usually is alert and can resume normal activities. A typical course of ECT is administered about three times a week until the patient's depression improves (usually within 6 to 12 treatments).
What is the treatment for a rTMS?
repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (rTMS) magnetic seizure therapy (MST) deep brain stimulation (DBS) A treatment plan may also include medication and psychotherapy. Choosing the right treatment plan should be based on a person's individual needs and medical situation, and under a doctor's care.
What is ECT therapy?
Electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) uses an electric current to treat serious mental disorders. This type of therapy is usually considered only if a patient's illness has not improved after other treatments (such as antidepressant medication or psychotherapy) are tried, or in cases where rapid response is needed (as in the case of suicide risk and catatonia, for example).
What is the first area of the brain targeted by DBS?
In the case of depression, the first area of the brain targeted by DBS is called Area 25, or the subgenual cingulate cortex. This area has been found to be overactive in depression and other mood disorders. But later research targeted several other areas of the brain affected by depression.
How to improve mental health?
Even light physical activity can make a difference. Make healthy choices. Maintaining a regular schedule that includes sufficient sleep, healthy eating and regular physical activity are important to your mental health.
What is brain stimulation?
Brain-stimulation treatments are sometimes used for depression and other mental health disorders. They're generally reserved for situations in which medications and psychotherapy haven't worked. They include electroconvulsive therapy, repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation, deep brain stimulation and vagus nerve stimulation.
What is the DSM-5?
The defining symptoms for each mental illness are detailed in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5), published by the American Psychiatric Association. This manual is used by mental health professionals to diagnose mental conditions and by insurance companies to reimburse for treatment.
What is the difference between psychotherapy and talk therapy?
Psychotherapy, also called talk therapy, involves talking about your condition and related issues with a mental health professional. During psychotherapy, you learn about your condition and your moods, feelings, thoughts and behavior. With the insights and knowledge you gain, you can learn coping and stress management skills.
What are the different classes of mental illness?
Classes of mental illness. The main classes of mental illness are: Neurodevelopmental disorders. This class covers a wide range of problems that usually begin in infancy or childhood, often before the child begins grade school.
Can mental illness get better?
In most cases, a mental illness won't get better if you try to treat it on your own without professional care. But you can do some things for yourself that will build on your treatment plan: Stick to your treatment plan. Don't skip therapy sessions. Even if you're feeling better, don't skip your medications.
Can psychiatric medications help with mental health?
Although psychiatric medications don't cure mental illness, they can often significantly improve symptoms. Psychiatric medications can also help make other treatments, such as psychotherapy, more effective. The best medications for you will depend on your particular situation and how your body responds to the medication.
What is the medical term for a doctor who specializes in treating mental health?
A medical doctor (M.D. ) who specializes in treating mental diseases. A psychiatrist evaluates a person's mental health along with his or her physical health and can prescribe medications. psychiatry. The branch of medicine that deals with identifying, studying, and treating mental, emotional, and behavioral disorders.
What is mental illness?
A mental illness can be defined as a health condition that changes a person's thinking, feelings, or behavior (or all three) and that causes the person distress and difficulty in functioning. As with many diseases, mental illness is severe in some cases and mild in others.
What is the term for a person who has five or more symptoms nearly every day for a two week period?
A depressive disorder commonly referred to as depression. Depression is more than simply being sad; to be diagnosed with depression, a person must have five or more characteristic symptoms nearly every day for a two-week period. mania. Feelings of intense mental and physical hyperactivity, elevated mood, and agitation.
How important is it to choose the right treatment for mental health?
Choosing the right mix of treatments and supports that work for you is an important step in the recovery process. Treatment choices for mental health conditions will vary from person to person. Even people with the same diagnosis will have different experiences, needs, goals and objectives for treatment.
How can education help with mental health?
Education about how to manage a mental health condition along with other medical conditions can provide the skills and supports to enrich the unique journey toward overall recovery and wellness.
What are the innovations in the range of evidence based medications, therapy and psychosocial services?
Innovations in the range of evidence based medications, therapy and psychosocial services such as psychiatric rehabilitation, housing, employment and peer supports have made wellness and recovery a reality for people living with mental health conditions.
What is the term for a person who speaks with a trained therapist in a safe and confidential environment?
Psychotherapy , also known as “talk therapy ,” is when a person speaks with a trained therapist in a safe and confidential environment to explore and understand feelings and behaviors and gain coping skills.
What is a crisis response system?
A well-designed crisis response system can provide backup to community providers, perform outreach by connecting first-time users to appropriate services and improve community relations by providing reassurance that the person’s needs are met in a mental health crisis.
What do mental health professionals do?
Mental health professionals check the medical case history, analyze the symptoms, conduct tests and assessments and speak to family members to be able to diagnose the illness accurately and then decide on the type of treatment. The patient and caregivers are kept informed about the entire process.
What is cognitive behavioral therapy?
Cognitive therapy focuses on a person's thoughts and beliefs and their influence on a person's mood and actions, and aims to change a person's thinking to be more adaptive and healthy.
What is CBT used for?
CBT can be used to treat several mental illnesses such as depression, anxiety, eating disorder, and bipolar disorder. Interpersonal Therapy (IPT): Intended to improve communication and the way a person interacts with other people.
What is ECT therapy?
Electroconvulsive therapy (ECT): A therapy where electric current is passed through the brain, to treat symptoms of certain mental illnesses. Read more about why and when ECT is prescribed as a treatment. Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS): A procedure where magnetic fields are used to stimulate nerve cells in the brain to improve symptoms ...
What is the purpose of a bipolar med?
This medication is used to treat bipolar disorder and helps prevent the return of manic and depressive episodes in bipolar disorder. In some cases, this medication is also used to treat severe depression, or.
Why is medication important?
Medication helps improve or control symptoms and promote recovery. In most cases, medication is considered the first line of treatment. The impact of medication depends on the severity of the illness, and on how the person's body responds to medication.
What does a therapist do?
The therapist encourages the person to speak about their symptoms and related issues, and helps them analyze and understand their moods, feelings, thought patterns and behavior. With this insight and understanding about oneself, the person is in a better position to learn how to cope with their condition and recover.
When did coma therapy start?
The coma-therapy trend began in 1927 . Viennese physician Manfred Sakel accidentally gave one of his diabetic patients an insulin overdose, and it sent her into a coma. But what could have been a major medical faux pas turned into a triumph. The woman, a drug addict, woke up and declared her morphine craving gone.
When did the STD cure?
There was no cure for the STD until the early 1900s, when Viennese neurologist Wagner von Jauregg got the idea to treat syphilis sufferers with malaria-infected blood. Predictably, these patients would develop the disease, which would cause an extremely high fever that would kill the syphilis bacteria.
Is hydrotherapy a psychiatric treatment?
If the word "hydrotherapy" conjures up images of Hollywood stars lazily soaking in rich, scented baths, then you probably weren't an early 20th-century psychiatric patient. Building off the idea that a dip in the water is often calming, psychiatrists of yore attempted to remedy various symptoms with corresponding liquid treatments. For instance, hyperactive patients got warm, tiring baths, while lethargic patients received stimulating sprays.
Can seizures help with schizophrenic symptoms?
To this day, no one is quite clear on why seizures can help ease some schizophrenic symptoms, but many scientists believe the convulsions release chemicals otherwise lacking in patients' brains. Ultimately, the side effects (including fractured bones and memory loss) turned away both doctors and patients. 8.
How does mental illness affect the brain?
As the organ most responsible for our behavior, decision making, and emotions, our brain is directly impacted by mental illness.
What is the most common mental illness in the United States?
Depression . Depression is one of the most common forms of mental illness in the United States, with more than 17 million adults struggling with depression each year, according to NAMI. Depression is characterized by: Lack of motivation or interest in the outside world.
What are some examples of neurotransmitters?
For example, in the case of bipolar disorder, scientists believe that a combination of dopamine, serotonin, and norepinephrine contribute to the development of particular symptoms.
What are the neurotransmitters that affect mental health?
Researchers do believe, however, that neurotransmitters like dopamine, serotonin, and GABA play a critical role in understanding why mental illness affects some people and not others. One example where scientists see neurotransmitters affecting our mental health is in the brains of people with depression.
How does lack of norepinephrine affect the brain?
Researchers believe that a lack of norepinephrine may affect different regions of the brain that are responsible for making decisions, staying organized, paying attention, regulating emotions, and processing information. In many cases, a combination of neurotransmitters affects our mental health.
What are the effects of dopamine on mental health?
Changing levels of dopamine have been linked to a variety of mental health challenges, often associated with cravings, reward-seeking or addictive behaviors, and even hallucinations. Among the findings that scientists have discovered about dopamine include:
What is the difference between mental illness and mental health?
According to the APA, one key distinction of mental illness is that the term refers to mental health challenges that are “diagnosable,” that is, conditions that can be defined and understood by mental health professionals. This also means that if mental illness can be diagnosed, it can also be treated.
Why do people with schizophrenia have different brain structures?
People with schizophrenia may have different brain structure for two reasons#N#1. The illness itself. These changes are not associated with taking medications.#N#2. The antipsychotic medications used to treat the illnesses. These changes can explain why the medicines work or could be a side-effect of the medication.
Who described schizophrenia as a tremor?
Kraepelin, in 1919, described patients with rigidity and bradykinesia as well as those with a tremor (Kraepelin, 1919). Similarly, in 1926, Reiter described patients with schizophrenia with a “well-defined parkinsonian syndrome, which overshadows all other symptoms” (Reiter, 1926).
What is the role of glial proliferation and hypertrophy of the prefrontal cortex?
Glial proliferation and hypertrophy of the prefrontal cortex is reported to be “a common response to antipsychotic drugs” and may “play a regulatory role in adjusting neurotransmitter levels or metabolic processes.”
How to assess electrophysiological function in schizophrenia?
The most common way to assess electrophysiological function in individuals with schizophrenia is with an electroencephalogram (EEG). EEGs have been used for psychiatric research since the early 1930s. Between 1941 and 1954, five EEG studies of individuals with schizophrenia were carried out in which normal control groups were also included. An additional study by Colony and Willis (1956) is not included in this analysis because it is unclear whether or not the patients with schizophrenia were being medicated and also because the “control” group consisted of other psychiatrically hospitalized patients, including those diagnosed with schizoid personalities and paranoid states.
Do antipsychotics cause brain changes?
The findings that antipsychotic drugs produce structural brain changes should not be a surprise. Schizophrenia and bipolar disorder are known to produce structural brain changes as part of the disease process, so it is reasonable to expect drugs that are effective in treating these diseases to do likewise. Some opponents of the use of antipsychotic medication misunderstand such research, arguing that brain changes prove that antipsychotic drugs are dangerous and should not be used. On the contrary, this research is very important and may eventually led to better and more effective medications.
Is schizophrenia a brain disease?
As such, schizophrenia is a disease of the brain in the same sense that Parkinson’s disease and multiple sclerosis are diseases of the brain. Amariah Brigham (1844), a founding member of the American Psychiatric Association, expressed this clearly in 1844:

Diagnosis
- To determine a diagnosis and check for related complications, you may have: 1. A physical exam.Your doctor will try to rule out physical problems that could cause your symptoms. 2. Lab tests.These may include, for example, a check of your thyroid function or a screening for alcohol and drugs. 3. A psychological evaluation.A doctor or mental health professional talks to you about your symptoms, thoughts, feelings and behavior patterns. You ma…
Treatment
- Your treatment depends on the type of mental illness you have, its severity and what works best for you. In many cases, a combination of treatments works best. If you have a mild mental illness with well-controlled symptoms, treatment from your primary care provider may be sufficient. However, often a team approach is appropriate to make sure all your psychiatric, medical and social needs are met. This is especially important for severe mental i…
Lifestyle and Home Remedies
- In most cases, a mental illness won't get better if you try to treat it on your own without professional care. But you can do some things for yourself that will build on your treatment plan: 1. Stick to your treatment plan.Don't skip therapy sessions. Even if you're feeling better, don't skip your medications. If you stop, symptoms may come back. A...
Coping and Support
- Coping with a mental illness is challenging. Talk to your doctor or therapist about improving your coping skills, and consider these tips: 1. Learn about your mental illness.Your doctor or therapist can provide you with information or may recommend classes, books or websites. Include your family, too — this can help the people who care about you understand what you're going through and learn how they can help. 2. Join a support group.Connecting with …
Preparing For Your Appointment
- Whether you schedule an appointment with your primary care provider to talk about mental health concerns or you're referred to a mental health professional, such as a psychiatrist or psychologist, take steps to prepare for your appointment. If possible, take a family member or friend along. Someone who has known you for a long time may be able to share important information, with your permission.