Medication
The five-year relative survival rates for each group are the following:
- Localized: 90 percent. This describes cancer that remains in the part of the body where it started.
- Regional: 71 percent. This describes cancer that has spread to a different part of the body.
- Distant: 14 percent. This also describes cancer that has spread to a different part of the body but is typically referred to as “metastatic” cancer.
Procedures
Treatments may include one or more of these:
- Removing the rectal cancer with surgery
- Surgery to create a colostomy and bypass the rectal cancer (a diverting colostomy)
- Using a special laser to destroy the cancer within the rectum
- Placing a stent (hollow metal tube) within the rectum to keep it open; this does not require surgery
- Chemoradiation therapy
- Chemo alone
Therapy
Stage III rectal cancers have spread to nearby lymph nodes but not to other parts of the body. Most people with stage III rectal cancer will be treated with chemotherapy, radiation therapy, and surgery, although the order of these treatments might differ. Most often, chemo is given along with radiation therapy (called chemoradiation) first.
Nutrition
- Localized: 90%
- Regional: 71%,
- Distant: 14%
- All Stages Combined: 63%
What is the life expectancy of someone with rectal cancer?
What are the treatment options for Stage 1 rectal cancer?
Is there a cure for Stage 3 Rectal Cancer?
What are the survival rates for rectal cancer?

Is rectal cancer very treatable?
Treatments include surgery, chemotherapy and radiation therapy. Rectal cancer is curable, especially when detected early through screening methods like colonoscopy.
Does rectal cancer spread fast?
In most cases, colon and rectal cancers develop slowly over many years. Most of these cancers begin as a growth of tissue called a polyp in the inner lining of the colon or rectum. Usually polyps bulge into the colon or rectum; some are flat.
What is the latest treatment for rectal cancer?
Patients with stage IV rectal cancer are likely to receive chemotherapy for their primary and metastatic cancers—both before and after surgery. The main chemotherapy drugs, used alone or in combination, for treating stage IV rectal cancer include the following: Fluorouracil (5-FU) Leucovorin.
Can rectal cancer heal without surgery?
If the cancer can't be removed by surgery, chemo and/or targeted therapy drugs may be used. For people with certain gene changes in their cancer cells, another option might be treatment with immunotherapy. The drugs used will depend on what drugs a person has received previously and on their overall health.
What is the life expectancy of someone with rectal cancer?
They can't tell you how long you will live, but they may help give you a better understanding of how likely it is that your treatment will be successful....5-year relative survival rates for rectal cancer.SEER stage5-year relative survival rateLocalized90%Regional73%Distant17%All SEER stages combined67%Mar 1, 2022
What are signs that rectal cancer has spread?
In many cases, advanced-stage rectal cancer spreads to the liver or lungs....Metastatic rectal cancer can produce a number of symptoms, including:Pain in the rectum.Bloody or unusual stool.Changes in bowel movements.Pain when passing stool.Diarrhea and/or constipation.Fatigue.Unexplained weight loss.
How long does it take for a rectal tumor to shrink after radiation?
At the same time, if a cell doesn't divide, it also cannot grow and spread. For tumors that divide slowly, the mass may shrink over a long, extended period after radiation stops. The median time for a prostate cancer to shrink is about 18 months (some quicker, some slower).
What is the main cause of rectal cancer?
The cause of rectal cancer is unknown, but the risk of developing the disease increases with age. People with a family history of colorectal cancer or certain hereditary cancer syndromes have a higher risk. Other known risk factors for rectal cancer include: Diet.
How many cycles of chemo are needed for rectal cancer?
How often do you have it? You usually have chemotherapy every 2 to 3 weeks depending on what drugs you have. Each 2 to 3 week period is called a cycle. You may have up to 8 cycles of chemotherapy.
Can radiation cure rectal cancer?
Radiation for colon cancer It's not common to use radiation therapy to treat colon cancer, but it may be used in certain cases: Before surgery (along with chemo) to help shrink a tumor and make it easier to remove. After surgery, if the cancer has attached to an internal organ or the lining of the belly (abdomen).
Is rectal cancer worse than colon cancer?
The prognosis of rectal cancer was not worse than that of colon cancer. Local advanced colorectal cancer had a poorer prognosis than local regional lymph node metastasis.
How long can you live with untreated rectal cancer?
The results showed the median survival of patients to be 24 months (range 16–42). One-year survival was found to be 65% while the 2-year survival was found to be 25%. A satisfactory quality of life was also observed.
Treating Stage 0 Rectal Cancer
Stage 0 rectal cancers have not grown beyond the inner lining of the rectum. Removing or destroying the cancer is typically all that's needed. You...
Treating Stage I Rectal Cancer
Stage I rectal cancers have grown into deeper layers of the rectal wall but have not spread outside the rectum itself.This stage includes cancers t...
Treating Stage II Rectal Cancer
Many stage II rectal cancers have grown through the wall of the rectum and might extend into nearby tissues. They have not spread to the lymph node...
Treating Stage III Rectal Cancer
Stage III rectal cancers have spread to nearby lymph nodes but not to other parts of the body.Most people with stage III rectal cancer will be trea...
Treating Stage IV Rectal Cancer
Stage IV rectal cancers have spread to distant organs and tissues such as the liver or lungs. Treatment options for stage IV disease depend to some...
Treating Recurrent Rectal Cancer
Recurrent cancer means that the cancer has come back after treatment. It may come back near the area of the initial rectal tumor (locally) or in di...
What is the treatment for rectal cancer?
Treatment options include surgery, chemotherapy and radiation therapy. For the most part, treatment for rectal cancer depends on the stage of the tumor—specifically the size and location of the tumor in the rectum as well as the degree of metastasis (how far the tumor may have spread). Learn about treatment options for each ...
What tests are used to diagnose rectal cancer?
Before developing an individualized plan for rectal cancer treatment, your health care team will determine the extent of the disease using a variety of tests, which may include magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), endoscopic ultrasound, computed tomography (CT) and blood tests.
What is the procedure to remove a tumor in the lower rectum?
Local transanal resection or excision: This procedure is used to remove early stage rectal cancers in the lower rectum. It is performed using instruments that are inserted through the rectum. In addition to removing the cancer from the rectal wall, the surgeon may remove some of the surrounding rectal tissue.
What is intraoperative radiation therapy?
Intraoperative radiation therapy (IORT): During surgery, this treatment is delivered directly to the tumor site after the tumor has been removed. The treatment comes from a radioactive source fed through wires that are placed on the tumor. IORT may be used for a rectal tumor that has infiltrated muscles or bones in the pelvis. It may also be used when rectal cancer has returned after a tumor was previously treated by radiation or surgery.
How long does radiation treatment last for rectal cancer?
Radiation may shorten muscle fibers in the pelvic floor. These effects of radiation can last up to five to ten years after treatment.
How long does it take to get radiation for rectal cancer?
Radiation treatments for rectal cancer may be delivered in small doses over five to six weeks of daily treatment, or they may be delivered in higher doses over a condensed period of five days. Patients can work with their rectal cancer team to determine the ideal radiation therapy.
Is biofeedback good for rectal cancer?
In addition, biofeedback training in our cancer rehabilitation program may benefit rectal cancer patients before and after treatment.
How is rectal cancer treated?
Rectal cancer is often treated with surgery to remove the cancer cells. Which operation is best for you depends on your particular situation, such as the location and stage of your cancer, how aggressive the cancer cells are, your overall health, and your preferences.
How to deal with rectal cancer?
As you learn more about rectal cancer, you may become more confident in making treatment decisions. Keep friends and family close. Keeping your close relationships strong will help you deal with your rectal cancer.
What is the purpose of colonoscopy?
Colonoscopy. Colonoscopy. During a colonoscopy, the doctor inserts a colonoscope into your rectum to check for abnormalities in your entire colon. Rectal cancer can be found during a screening test for colorectal cancer. Or it may be suspected based on your symptoms.
What is the next step in rectal cancer?
Once you're diagnosed with rectal cancer, the next step is to determine the cancer's extent (stage). The stage of your cancer helps determine your prognosis and your treatment options. Complete blood count (CBC). This test reports the numbers of different types of cells in your blood.
How does radiation therapy work?
Radiation therapy uses powerful energy sources, such as X-rays and protons, to kill cancer cells. In people with rectal cancer, radiation therapy is often combined with chemotherapy that makes the cancer cells more likely to be damaged by the radiation. It can be used after surgery to kill any cancer cells that might remain. Or it can be used before surgery to shrink a cancer and make it easier to remove.
What is the procedure to check for colon cancer?
Tests and procedures used to confirm the diagnosis include: Using a scope to examine the inside of your colon and rectum (colonoscopy). Colonoscopy uses a long, flexible tube (colonoscope) attached to a video camera and monitor to view your colon and rectum.
Can you use chemotherapy before surgery?
Chemotherapy combined with radiation therapy might also be used before an operation to shrink a large cancer so that it's easier to remove with surgery.
What is rectal cancer?
Key Points. Rectal cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the tissues of the rectum. Health history affects the risk of developing rectal cancer. Signs of rectal cancer include a change in bowel habits or blood in the stool.
How do you know if you have rectal cancer?
Signs of rectal cancer include a change in bowel habits or blood in the stool. These and other signs and symptoms may be caused by rectal cancer or by other conditions. Check with your doctor if you have any of the following: Blood (either bright red or very dark) in the stool. A change in bowel habits. Diarrhea.
Where does stage IV rectal cancer spread?
Stage IV rectal cancer. The cancer has spread through the blood and lymph nodes to other parts of the body, such as the lung, liver, abdominal wall, or ovary.
What are the risk factors for colon cancer?
Risk factors for colorectal cancer include the following: Having a family history of colon or rectal cancer in a first-degree relative (parent, sibling, or child). Having a personal history of cancer of the colon, rectum, or ovary.
How does cancer spread?
Cancer can spread through tissue, the lymph system, and the blood:
How many ways does cancer spread?
There are three ways that cancer spreads in the body.
Why do cancer tests have to be repeated?
Some tests will be repeated in order to see how well the treatment is working. Decisions about whether to continue, change, or stop treatment may be based on the results of these tests.
Why do they use chemotherapy before surgery?
For some rectal cancer patients, chemotherapy is used along with radiation therapy before surgery to shrink a tumor, so that surgeons do not have to remove too much of the tissue, blood vessels, and nerves that surround the tumor.
How long does chemotherapy last after surgery?
Chemotherapy may also be given to patients after surgery, for up to six months, to kill off any cancer cells that may have been left behind after surgery. This type of chemotherapy is sometimes called adjuvant chemotherapy. According to Nilofer Azad, M.D., an associate professor of oncology at Johns Hopkins and a medical oncologist specializing in ...
Can you use an infusion pump for chemotherapy?
For some patients, outpatient treatment with an infusion pump to provide a continuous intravenous flow of anticancer drugs is an option . Others may benefit from a chemotherapy pump surgically implanted at the tumor site to deliver anticancer drugs directly to the tumor.
Can you get chemotherapy for stage IV colon cancer?
Patients with metastatic, or stage IV rectal cancer, are also likely to receive chemotherapy for their primary and metastatic cancers, before and after surgery. These patients receive many of the same treatments as patients with metastatic colon cancer. They may also be eligible for clinical trials at Johns Hopkins that are primarily focused on colon cancer patients.
What is the best treatment for rectal cancer?
Surgery. Surgery is the most common treatment for some stages of rectal cancer. We may combine it with other therapies, such as radiation and chemotherapy, to shrink the tumor. Your care team may use several options, including: Total neoadjuvant therapy uses a precise combination of chemotherapy and radiation therapy to make tumors as small as ...
How do you treat a tumor?
How we treat you depends on several factors, including: 1 the tumor’s size and location 2 whether it has spread to the lymph nodes or other organs
Does MSK help with rectal cancer?
MSK has helped pioneer watch-and-wait therapy (also known as nonoperative management) for rectal cancer. Our researchers have demonstrated that for some people with rectal cancer, chemotherapy and radiation may destroy the tumor, eliminating the need for surgery.
Can chemotherapy be used before surgery?
Chemotherapy may be used in combination with radiation before surgery to shrink a tumor or after surgery to kill any remaining cancer cells.
Can you get surgery for rectal cancer?
If the rectal cancer has spread, surgery may not be the best option. Chemotherapy, sometimes combined with radiation therapy, may allow treatment to start throughout your entire body without delay.
What is the difference between colon cancer and rectal cancer?
The management of rectal cancer varies somewhat from that of colon cancer because of the increased risk of local recurrence and a poorer overall prognosis. Differences include surgical technique, the use of radiation therapy, and the method of chemotherapy administration.
Why should rectal cancer be screened?
Evidence supports screening for rectal cancer as a part of routine care for all adults aged 50 years and older, especially for those with first-degree relatives with colorectal cancer, for the following reasons: Incidence of the disease in those 50 years and older. Ability to identify high-risk groups.
What is the purpose of colonoscopy?
Colonoscopy: Complete colonoscopy to rule out cancers elsewhere in the bowel. [ 5]
How long does pelvic radiation last?
The acute side effects of pelvic radiation therapy for rectal cancer are mainly the result of gastrointestinal toxicity, are self-limiting, and usually resolve within 4 to 6 weeks of completing treatment .
What are the most important risk factors for colorectal cancer?
Increasing age is the most important risk factor for most cancers. Other risk factors for colorectal cancer include the following:
How accurate is endorectal ultrasound?
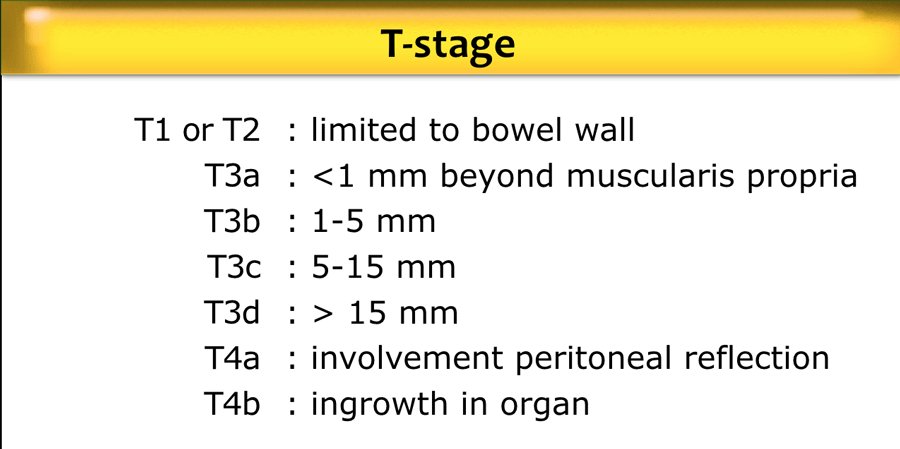
In the tumor (T) staging of rectal carcinoma, several studies indicate that the accuracy of endorectal ultrasound ranges from 80% to 95% compared with 65% to 75% for CT and 75% to 85% for MRI. The accuracy in determining metastatic nodal involvement by endorectal ultrasound is approximately 70% to 75% compared with 55% to 65% for CT and 60% to 70% for MRI. [ 2] In a meta-analysis of 84 studies, none of the three imaging modalities, including endorectal ultrasound, CT, and MRI, were found to be significantly superior to the others in staging nodal (N) status. [ 8] Endorectal ultrasound using a rigid probe may be similarly accurate in T and N staging when compared with endorectal ultrasound using a flexible scope; however, a technically difficult endorectal ultrasound may give an inconclusive or inaccurate result for both T stage and N stage. In this case, further assessment by MRI or flexible endorectal ultrasound may be considered. [ 4, 9]
What is the impact of the distance of the tumor from the anal sphincter musculature?
The distance of the tumor from the anal sphincter musculature has implications for the ability to perform sphincter-sparing surgery. The bony constraints of the pelvis limit surgical access to the rectum, which results in a lesser likelihood of attaining widely negative margins and a higher risk of local recurrence.
Who treats colorectal cancer?
Based on your treatment options, you might have different types of doctors on your treatment team. These doctors could include:
What is systemic treatment for colorectal cancer?
These are called systemic treatments because they can reach cancer cells throughout almost all the body. Depending on the type of colorectal cancer, different types of drugs might be used, such as: Chemotherapy for Colorectal Cancer. Targeted Therapy for Colorectal Cancer. Immunotherapy for Colorectal Cancer.
What is the difference between a radiation oncologist and a cancer oncologist?
A colorectal surgeon: a doctor who uses surgery to treat diseases of the colon and rectum. A radiation oncologist: a doctor who treats cancer with radiation therapy. A medical oncologist: a doctor who treats cancer with medicines such as chemotherapy ...
Why do we do clinical trials?
Clinical trials are carefully controlled research studies that are done to get a closer look at promising new treatments or procedures . Clinical trials are one way to get state-of-the art cancer treatment. In some cases they may be the only way to get access to newer treatments. They are also the best way for doctors to learn better methods to treat cancer. Still, they're not right for everyone.
Why is it important to communicate with your cancer care team?
Communicating with your cancer care team is important so you understand your diagnosis, what treatment is recommended, and ways to maintain or improve your quality of life.
Why is it important to discuss treatment options with your doctor?
Making treatment decisions. It’s important to discuss all of your treatment options, including their goals and possible side effects, with your doctors to help make the decision that best fits your needs. It’s also very important to ask questions if there's anything you’re not sure about.
What is a medical oncologist?
A medical oncologist: a doctor who treats cancer with medicines such as chemotherapy or targeted therapy. You might have many other specialists on your treatment team as well, including physician assistants (PAs), nurse practitioners (NPs), nurses, psychologists, nutritionists, social workers, and other health professionals.
What is the cancer in the colon?
The cancer had blocked (obstructed) the colon. The cancer caused a perforation (hole) in the wall of the colon.
How long does it take for colon cancer to heal?
Chemotherapy may also be used after surgery (called adjuvant treatment ). Most adjuvant treatment is given for about 6 months.
What is stage 1 colon cancer?
Stage I colon cancers have grown deeper into the layers of the colon wall, but they have not spread outside the colon wall itself or into the nearby lymph nodes. Stage I includes cancers that were part of a polyp. If the polyp is removed completely during colonoscopy, with no cancer cells at the edges (margins) ...
What to do if cancer spreads too much?
If the cancer has spread too much to be treated with surgery, chemo and/or targeted therapies may be used. Possible treatment schedules are the same as for stage IV disease.
What is the treatment for stage IV cancer?
Most people with stage IV cancer will get chemo and/or targeted therapies to control the cancer. Some of the most commonly used regimens include:
Where does stage IV colon cancer spread?
Stage IV colon cancers have spread from the colon to distant organs and tissues. Colon cancer most often spreads to the liver, but it can also spread to other places like the lungs, brain, peritoneum (the lining of the abdominal cavity), or to distant lymph nodes. In most cases surgery is unlikely to cure these cancers.
What does it mean when cancer comes back?
Recurrent cancer means that the cancer has come back after treatment. The recurrence may be local (near the area of the initial tumor), or it may be in distant organs.
Diagnosis
Treatment
Clinical Trials
Coping and Support
Specialist to consult
Preparing For Your Appointment