What is the best treatment for uterine cancer?
Usually surgery for endometrial cancer includes:
- Total hysterectomy (surgical removal of the uterus)
- Bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy (removal of both ovaries and Fallopian tubes)
- Biopsy of the omentum, a fat pad in the pelvis
- Removal of lymph nodes in the pelvis and lower abdomen
How serious is invasive ductal carcinoma?
Invasive ductal carcinoma describes the type of tumor in about 80 percent of people with breast cancer. The five-year survival rate is quite high -- almost 100 percent when the tumor is caught and treated early. Once the cancer has metastasized to distant organs like the bones or liver, the five-year survival rate drops by almost three fourths.
Is no treatment the best treatment for DCIS breast cancer?
Treatment of Ductal Carcinoma in Situ (DCIS)
- Breast-conserving surgery (BCS) In breast-conserving surgery (BCS), the surgeon removes the tumor and a small amount of normal breast tissue around it.
- Mastectomy. Simple mastectomy (removal of the entire breast) may be needed if the area of DCIS is very large, if the breast has several separate areas of DCIS, or if ...
- Hormone therapy after surgery. ...
What is the best treatment for mucinous appendiceal cancer?
- TNM staging system. ...
- Staging for neuroendocrine tumors of the appendix. ...
- Staging for carcinomas of the appendix. ...
- Node (N) The "N" in the TNM system stands for lymph nodes. ...
- Metastasis (M) The "M" in the TNM system describes cancer that has spread to other parts of the body, such as the liver or lungs.

What is the usual treatment for invasive ductal carcinoma?
Surgery for IDC may include one of these procedures: Lumpectomy is removal of part of the breast. It is also known as breast-conserving surgery. Lumpectomy may be followed by radiation treatments to treat any remaining cancer cells.
How serious is invasive ductal carcinoma?
Once the cancer has metastasized to distant organs like the bones or liver, the five-year survival rate drops by almost three fourths. Invasive ductal carcinoma (also called infiltrating ductal carcinoma) is the most common type of breast cancer, accounting for about 80% of all cases of breast cancer.
Is chemo necessary for invasive ductal carcinoma?
Invasive ductal carcinoma chemotherapy may be given before breast cancer surgery to shrink tumors and destroy rapidly dividing cancer cells, or after a surgical procedure to address any residual cancer and reduce the likelihood of recurrence.
What stage is invasive ductal carcinoma?
Generally, the stage of invasive ductal carcinoma is described as a number on a scale of I through IV. Stages I, II, and III describe early-stage cancers, and stage IV describes cancers that have spread outside the breast to other parts of the body, such as the bones or liver.
What is the life expectancy of invasive ductal carcinoma?
The five-year survival rate for localized invasive ductal carcinoma is high — nearly 100% when treated early on. If the cancer has spread to other tissues in the region, the five-year survival rate is 86%. If the cancer has metastasized to distant areas of your body, the five-year survival rate is 28%.
How long does it take for invasive ductal carcinoma to spread?
Each division takes about 1 to 2 months, so a detectable tumor has likely been growing in the body for 2 to 5 years. Generally speaking, the more cells divide, the bigger the tumor grows.
What is the main cause of invasive ductal carcinoma?
The causes of invasive ductal carcinoma have not been conclusively established. Researchers have determined that cancer can form when the cells in a milk-producing duct undergo changes that cause them to grow uncontrollably, divide very rapidly or remain viable longer than they should.
Is mastectomy necessary for invasive ductal carcinoma?
A mastectomy may be required for widespread preinvasive disease, which has an excellent prognosis following surgery, and yet an aggressive, high grade invasive carcinoma, which has spread to lymph nodes, may be successfully treated with breast conserving surgery.
Which is harder on the body chemo or radiation?
Since radiation therapy is focused on one area of your body, you may experience fewer side effects than with chemotherapy. However, it may still affect healthy cells in your body.
Is a 2 cm breast lump big?
Cancers of exactly 2 cm in size occupy a special niche in breast oncology. That size is the one at which breast cancer is most commonly diagnosed (the “modal size”) and 2.0 cm marks the boundary between stage i and ii for node-negative breast cancers and between stage ii and iii for node-positive breast cancers.
Does invasive ductal carcinoma return?
Invasive ductal carcinoma recurrence is possible after the completion of an initial course of treatment. In general, most physicians consider cancer to be a recurrence, rather than a progression, if a patient has exhibited no signs or symptoms for at least one year.
What is the survival rate for invasive ductal carcinoma grade 3?
Survival rates can be confusing. Remember that they don't reflect your individual circumstances. The relative 5-year survival rate for stage 3 breast cancer is 86 percent, according to the American Cancer Society . This means that out of 100 people with stage 3 breast cancer, 86 will survive for 5 years.
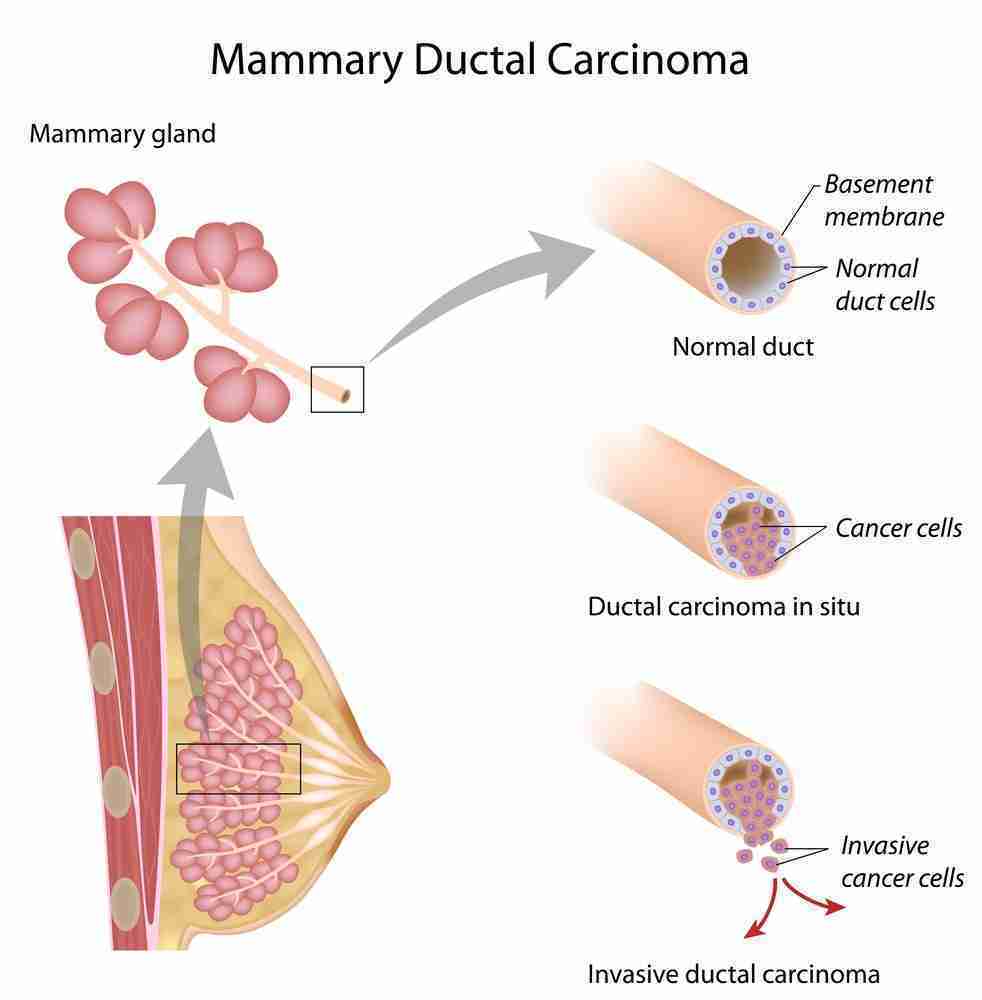
What is invasive ductal carcinoma?
Invasive ductal carcinoma treatment is designed to address cancer cells that initially form in a milk duct and then grow beyond the walls of the duct into the surrounding breast tissue.
How to contact Moffitt for ductal carcinoma?
If you’d like to learn more about invasive ductal carcinoma treatment option at Moffitt, call 1-888-663-3488 or complete a new patient registration form online. No referrals are required.
How to treat a large tumor?
Additionally, to treat a large tumor (measuring more than 1 centimeter in diameter) or cancer that has spread beyond the breast tissue and lymph nodes, a physician might recommend a systemic treatment, such as chemotherapy or hormonal therapy, to destroy cancerous cells or shrink the tumor prior to surgery.
What is the best treatment for cancer?
Hormonal therapy – If a cancer tests positive for hormone receptors (special proteins that tell the cancer cells when to grow and divide in response to the presence of certain hormones, such as estrogen and progesterone), hormonal therapy may be used to lower the amount of hormones in the body that can potentially signal cancer cell growth. ...
What is a lumpectomy?
Lumpectomy – A surgeon removes a breast tumor along with some surrounding healthy tissue.
Nanotechnology In Breast Cancer
The field of nanotechnology has rapidly evolved as evidenced by the fact that there are more than 150 ongoing clinical trials investigating the efficacy of nanotechnology based drug delivery carriers targeting cancer.
Treatment For Triple Negative Breast Cancer
Treatment for triple negative breast cancer usually involves surgery , radiotherapy if breast conserving surgery was performed, and chemotherapy. If you would like to read more about the main types of breast cancer surgery, visit the surgery section of this website.
Is Infiltrating Ductal Carcinoma Curable
All together, invasive ductal carcinoma refers to cancer that has broken through the wall of the milk duct and begun to invade the tissues of the breast. Over time, invasive ductal carcinoma can spread to the lymph nodes and possibly to other areas of the body. Invasive ductal carcinoma also affects men.
What Does It Mean To Have Invasive Ductal Carcinoma
Invasive Ductal Carcinoma About 80% of all breast cancers are invasive ductal carcinomas. Invasive means that the cancer has invaded or spread to the surrounding breast tissues. Ductal means that the cancer began in the milk ducts, which are the pipes that carry milk from the milk-producing lobules to the nipple.
What Can I Expect If I Have Invasive Ductal Carcinoma
If youve been diagnosed with invasive ductal carcinoma, your healthcare provider will discuss your treatment options with you in detail. For best results, youll want to begin treatment as soon as possible.
Breast Cancer Survival By Age
Five-year survival for female breast cancer shows an unusual pattern with age: survival gradually increases from 85% in women aged 15-39 and peaks at 92% in 60-69 year olds survival falls thereafter, reaching its lowest point of 70% in 80-99 year-olds for patients diagnosed with breast cancer in England during 2009-2013.
What Is Stage 1 Breast Cancer
Stage 1 breast cancer is the earliest stage of invasive breast cancer. The breast cancer has spread from its original location to the surrounding tissue but it is still contained in a relatively small area.
What is a DCIS?
Treatment of Ductal Carcinoma in Situ (DCIS) Ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) means the cells that line the milk ducts of the breast have become cancer, but they have not spread into surrounding breast tissue. DCIS is considered non-invasive or pre-invasive breast cancer.
What is BCS in surgery?
Breast-conserving surgery (BCS) In breast-conserving surgery (BCS), the surgeon removes the tumor and a small amount of normal breast tissue around it. Lymph node removal is not always needed with BCS, but it may be done if the doctor thinks the area of DCIS might also contain invasive cancer.
What hormones are used after breast surgery?
Hormone therapy after surgery. If the DCIS is hormone receptor-positive (estrogen or progesterone), treatment with tamoxifen (for any woman) or an aromatase inhibitor (for women past menopause) for 5 years after surgery can lower the risk of another DCIS or invasive cancer developing in either breast. If you have hormone receptor-positive DCIS, ...
Does DCIS have invasive cancer?
The chances an area of DCIS contains invasive cancer goes up with tumor size and how fast the cancer is growing. If lymph nodes are removed, this is usually done as a sentinel lymph node biopsy (SLNB ). If BCS is done, it is usually followed by radiation therapy. This lowers the chance of the cancer coming back in the same breast ...
Is DCIS invasive or noninvasive?
DCIS is considered non-invasive or pre-invasive breast cancer. DCIS can’t spread outside the breast, but it still needs to be treated because it can sometimes go on to become invasive breast cancer (which can spread).
Can you get BCS without radiation?
BCS without radiation therapy is not a standard treatment, but it might be an option for certain women who had small areas of low-grade DCIS that were removed with large enough cancer-free surgical margins.
Can a BCS remove DCIS?
Simple mastectomy (removal of the entire breast) may be needed if the area of DCIS is very large, if the breast has several separate areas of DCIS, or if BCS cannot remove the DCIS completely (that is, the BCS specimen and re-excision specimens still have cancer cells in or near the surgical margins).
What is DCIS on a mammogram?
DCIS is most often discovered during a mammogram used to screen for breast cancer. If your mammogram shows suspicious areas such as bright white specks (microcalcifications) that are in a cluster and have irregular shapes or sizes, your radiologist likely will recommend additional breast imaging. You may have a diagnostic mammogram, which takes ...
What to write down for breast cancer?
Write down your medical history, including any benign breast conditions with which you've been diagnosed. Also mention any radiation therapy you may have received, even years ago. Note any family history of breast cancer, especially in a first-degree relative, such as your mother or a sister.
What is lumpectomy surgery?
A lumpectomy involves removing the cancer and some of the healthy tissue that surrounds it. This illustration shows one possible incision that can be used for this procedure, though your surgeon will determine the approach that's best for your particular situation.
Does DCIS have a high chance of success?
Treatment of DCIS has a high likelihood of success, in most instances removing the tumor and preventing any recurrence.
Can alternative medicine cure DCIS?
Alternative medicine. No alternative medicine treatments have been found to cure DCIS or to reduce the risk of being diagnosed with an invasive breast cancer. Instead, complementary and alternative medicine treatments may help you cope with your diagnosis and the side effects of your treatment, such as distress.
Is radiation needed after lumpectomy?
Radiation is typically used after lumpectomy. But it might not be necessary if you have only a small area of DCIS that is considered low grade and was completely removed during surgery.
Can you have a lumpectomy alone?
If you have other serious health conditions, you might consider other options, such as lumpectomy plus hormone therapy, lumpectomy alone or no treatment.
What Is Invasive Ductal Carcinoma?
Invasive Ductal Carcinoma (IDC) is an invasive cancer where abnormal cancer cells that began forming in the milk ducts have spread beyond the ducts into other parts of the breast tissue. Invasive cancer cells can also spread to other parts of the body. It is also sometimes called infiltrative ductal carcinoma.
What is the most common type of breast cancer?
IDC is the most common type of breast cancer, making up nearly 70- 80% of all breast cancer diagnoses.
What is the difference between DCIS and IDC?
DCIS means the cancer is still contained in the milk duct and has not invaded any other area. IDC is cancer that began growing in the duct and is invading the surrounding tissue.
What is invasive ductal carcinoma?
Invasive ductal carcinoma stages provide physicians with a uniform way to describe how far a patient’s cancer may have spread beyond its original location in a milk duct. This information can be helpful when evaluating treatment options, but it is not a prognostic indicator in and of itself. Many factors can influence a patient’s outcome, so ...
What test is used to determine if ductal carcinoma is spread?
If, based on the initial test results, a physician believes that the cancer may have spread to other parts of the body, further testing may be ordered, such as a bone scan, positron emission tomography (PET) scan or liver function test. Invasive ductal carcinoma is usually described through a numeric scale ranging from 1 (the earliest stage) ...
What is stage 1 breast cancer?
Stage 1 – A breast tumor is smaller than 2 centimeters in diameter and the cancer has not spread beyond the breast.