
What medications are used to treat emphysema?
Daily maintenance or controller therapy is best done using a long acting medicine that opens up the airways called a long acting bronchodilator (brawn-coe-die-lay-ters). There are two types or “classes” of the long acting bronchodilators and they work in different ways on the lungs.
What herbs help with emphysema?
Jan 13, 2020 · In this way, antibiotics can help prevent an exacerbation from getting more severe and reduce the risk for serious complications. Supplemental Oxygen Therapy Supplemental oxygen is often used to treat low blood oxygen levels, known as hypoxemia, in people with COPD.
Are there cures for emphysema?
Sometimes, people with many exacerbations may need to have medicines at home to start including antibiotics or steroids to be started according to your COPD ACTION PLAN. You may also need to increase your oxygen use. The written action plan can help you or your family or caregiver know what to do.
What are the best treatments for emphysema and COPD?
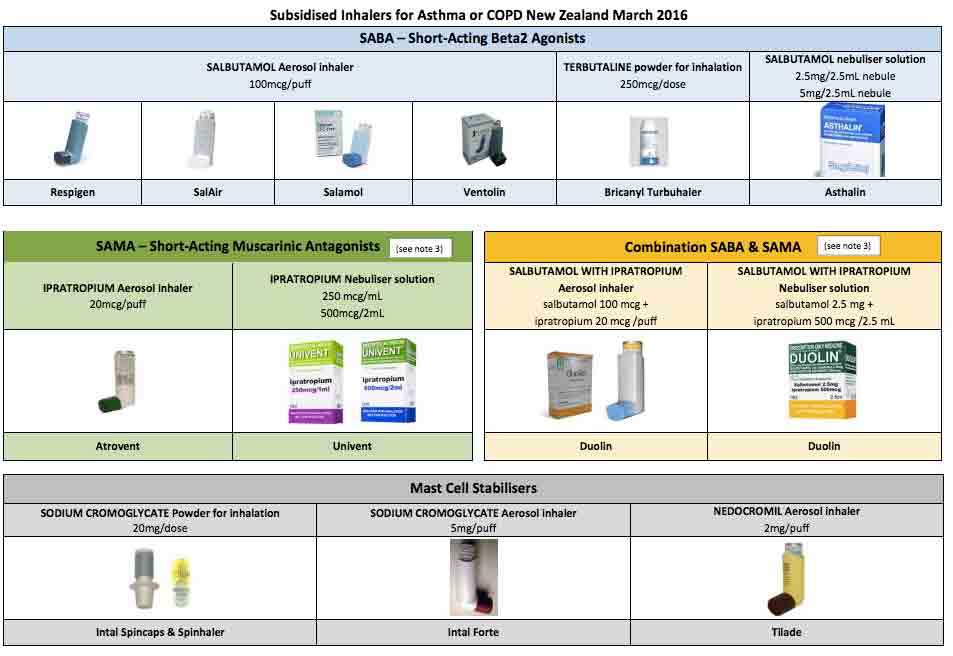
Short-acting beta-agonists are the cornerstone of drug therapy for acute exacerbations. The most widely used drug is albuterol 2.5 mg by nebulizer or 2 to 4 puffs (100 mcg/puff) by metered-dose inhaler every 2 to 6 hours.
What is the treatment for exacerbation?
Treatments options for exacerbations include bronchodilators, corticosteroids, antibiotics, oxygen therapy, and ventilation.Oct 30, 2018
What is the first line treatment for COPD exacerbation?
Key Points. Most patients with exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) require oxygen supplementation during an exacerbation. Inhaled short-acting beta-agonists are the cornerstone of drug therapy for acute exacerbations.
What is the best treatment for COPD exacerbation?
MedicationsBronchodilators. Bronchodilators are medications that usually come in inhalers — they relax the muscles around your airways. ... Inhaled steroids. ... Combination inhalers. ... Oral steroids. ... Phosphodiesterase-4 inhibitors. ... Theophylline. ... Antibiotics.Apr 15, 2020
What is the most effective treatment to minimize further exacerbation of the COPD and improving the quality of life?
Bronchodilator therapy is considered to be one of the cornerstones of treating COPD exacerbation.
What medications are commonly prescribed to a patient admitted with exacerbation of COPD?
Hospitalized patients with exacerbations should receive regular doses of short-acting bronchodilators, continuous supplemental oxygen, antibiotics, and systemic corticosteroids.Mar 1, 2010
When do you need antibiotics for COPD exacerbation?
Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease (GOLD) guidelines recommend using antibiotics to treat exacerbations in patients with moderate or severe COPD who: have increased dyspnea, sputum volume, and sputum purulence; have 2 of these 3 symptoms if increased sputum purulence is one of the symptoms; or.
What is first line treatment for emphysema?
For most people with COPD, short-acting bronchodilator inhalers are the first treatment used. Bronchodilators are medicines that make breathing easier by relaxing and widening your airways.
What are treatments for emphysema?
TreatmentBronchodilators. These drugs can help relieve coughing, shortness of breath and breathing problems by relaxing constricted airways.Inhaled steroids. Corticosteroid drugs inhaled as aerosol sprays reduce inflammation and may help relieve shortness of breath.Antibiotics.Apr 28, 2017
How long does an emphysema exacerbation last?
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) exacerbations may last for two days or even two weeks, depending on the severity of the symptoms. Sometimes, COPD exacerbations may require antibiotics, oral corticosteroids and hospitalization.May 6, 2021
What is the newest treatment for COPD?
Bronchoscopic lung volume reduction is a Food and Drug Administration-approved treatment for patients with the emphysema phenotype of COPD that have significant hyperinflation. For selected patients, one-way endobronchial valves can be placed in the airway that cause collapse of a single lobe.Dec 3, 2021
Can a CT scan misdiagnosed emphysema?
Statistically significant correlations between emphysema and CT findings have been shown in numerous studies, but mild morphologic emphysema may be missed by CT, and occasionally CT scans give false-positive findings.
Will a COPD exacerbation go away on its own?
Warning Signs of a COPD Flare-up Signs of a COPD flare-up last 2 days or more and are more intense than your usual symptoms. The symptoms get worse and just don't go away. If you have a full-blown exacerbation, you may need to go to the hospital.Oct 1, 2019
What is the best treatment for COPD?
Most patients with exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) require oxygen supplementation during an exacerbation. Inhaled short-acting beta-agonists are the cornerstone of drug therapy for acute exacerbations. Use antibiotics if patients have acute exacerbations and purulent sputum.
What causes acute exacerbations?
The cause of an acute exacerbation is usually unknown, although some acute exacerbations result from bacterial or viral infections. Smoking, irritative inhalational exposure, and high levels of air pollution also contribute. Mild exacerbations often can be treated on an outpatient basis in patients with adequate home support. ...
How long does it take to stop prednisone?
Options include prednisone 30 to 60 mg orally once a day for 5 to 7 days and stopped directly or tapered over 7 to 14 days depending on the clinical response. A parenteral alternative is methylprednisolone 60 to 500 mg IV once a day for 3 days and then tapered over 7 to 14 days.
What is noninvasive ventilation?
Noninvasive positive-pressure ventilation (eg, pressure support or bilevel positive airway pressure ventilation by face mask) is an alternative to full mechanical ventilation. Noninvasive ventilation appears to decrease the need for intubation, reduce hospital stay, and reduce mortality in patients with severe exacerbations (defined as a pH < 7.30 in hemodynamically stable patients not at immediate risk of respiratory arrest).
How long does doxycycline last?
Trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole, amoxicillin, and doxycycline are give for 7 to 14 days. An alternative first-line antibiotic is azithromycin 500 mg orally once a day for 3 days or 500 mg orally as a single dose on day 1, followed by 250 mg once a day on days 2 through 5.
Can beta agonists be used with oxygen?
Beta-agonists and anticholinergics, with or without corticosteroids, should be started concurrently with oxygen therapy (regardless of how oxygen is administered) with the a im of reversing airway obstruction. Methylxanthines, once considered essential to treatment of acute COPD exacerbations, are no longer used; toxicities exceed benefits.
What are some examples of antibiotics?
Examples of antibiotics that are effective are. Trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole 160 mg/800 mg orally twice a day. Amoxicillin 250 to 500 mg orally 3 times a day. Doxycycline 50 to 100 mg orally twice a day.
How to stop COPD?
Quitting smoking. The most essential step in any treatment plan for COPD is to quit all smoking. Stopping smoking can keep COPD from getting worse and reducing your ability to breathe. But quitting smoking isn't easy. And this task may seem particularly daunting if you've tried to quit and have been unsuccessful.
What is the best medication for COPD?
Theophylline. When other treatment has been ineffective or if cost is a factor, theophylline (Elixophyllin, Theo-24, Theochron), a less expensive medication, may help improve breathing and prevent episodes of worsening COPD.
What is a spirometer?
A spirometer is a diagnostic device that measures the amount of air you're able to breathe in and out and the time it takes you to exhale completely after you take a deep breath. COPD is commonly misdiagnosed. Many people who have COPD may not be diagnosed until the disease is advanced. To diagnose your condition, ...
How to diagnose COPD?
To diagnose your condition, your doctor will review your signs and symptoms, discuss your family and medical history, and discuss any exposure you've had to lung irritants — especially cigarette smoke. Your doctor may order several tests to diagnose your condition.
What tests are done to determine if you have a pulmonary disease?
Your doctor may order several tests to diagnose your condition. Tests may include: Lung (pulmonary) function tests. These tests measure the amount of air you can inhale and exhale, and whether your lungs deliver enough oxygen to your blood.
How does pulmonary rehabilitation help COPD?
Pulmonary rehabilitation after episodes of worsening COPD may reduce readmission to the hospital, increase your ability to participate in everyday activities and improve your quality of life.
Do bronchodilators help with shortness of breath?
This can help relieve coughing and shortness of breath and make breathing easier . Depending on the severity of your disease, you may need a short-acting bronchodilator before activities, a long-acting bronchodilator that you use every day or both.
What is the best way to treat COPD?
Bronchodilators. If you have COPD, you should have an action plan from your doctor. An action plan is a written statement of steps to take in the event of a flare-up. Your action plan will most often direct you to your quick-acting inhaler. The inhaler is filled with a medication called a quick-acting bronchodilator.
How to prevent COPD flare ups?
In addition to avoiding your triggers, keep a healthy lifestyle to help prevent flare-ups. Follow a low-fat, varied diet, get plenty of rest, and try gentle exercise when you’re able. COPD is a chronic condition, but proper treatment and management can keep you feeling as good as possible.
How to know if you have a symtom?
If you have any of these symptoms, call your doctor right away: 1 chest pain 2 blue lips 3 unresponsiveness 4 agitation 5 confusion
What is COPD in the lung?
COPD overview. COPD, or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, is a common form of lung disease. COPD causes inflammation in your lungs, which narrows your airways. Symptoms can include shortness of breath, wheezing, tiredness, and frequent lung infections such as bronchitis.
What is the best treatment for shortness of breath?
As part of your ongoing treatment, your doctor may prescribe oxygen therapy . Oxygen therapy helps relieve the shortness of breath that occurs during a flare-up. If you have advanced lung disease, you may need oxygen therapy all the time. If not, you may only need the extra help during a flare-up.
How to avoid a flare up?
To avoid a flare-up, know and avoid your triggers. A trigger is an event or situation that often causes a flare-up of your COPD symptoms. Each person with COPD has different triggers, so everyone’s prevention plan will be different. Here are some tips for avoiding common triggers:
What to do if you have a flare up?
If you have any of these symptoms, call your doctor right away: If your symptoms are severe or you think you’re having a medical emergency, call 911 or go to the nearest emergency room .
What are the treatments for COPD?
COPD treatments include both medicines and other important therapies such as pulmonary rehabilitation, smoking/vaping cessation support and immunizations. If you were asked about COPD medicines you would probably think about your inhalers and you’d probably say, "they open up my lungs".
How to prevent fires in a home?
Maintenance (Controllers-Prevention): As a responsible person, you do your best to prevent fires by maintaining your home, keeping the electrical wires operating safely, turning off the stove when you’re not using it and putting hot matches in a fireproof container or in water.
What is a nebulizer?
A nebulizer is a device that changes liquid medicine into a fine mist that can be inhaled into the lungs. This mist can be breathed in through a mouthpiece or face mask. There are different types of nebulizers: jet, vibrating mesh and ultrasonic nebulizers. Sometimes the vibrating mesh and ultrasonic types are lumped together under "electronic" nebulizers.
How does the nervous system work?
This is the job of the parasympathetic nervous system. If you touch something hot, a message is sent through your nerves to pull your hand away. How does this work in the lungs? In our lungs, messages are sent to squeeze down the airways in response to things like “bad air” like smoke or cold or other pollution or in response to things that might cause an infection or irritation to the lung. You can think of this as trying to prevent unhealthy things from coming into the lungs. This squeezing down of the airways also called bronchoconstriction (brawn-co-con-stric-shun), causes feelings of chest tightness and shortness of breath. Anticholinergic medicines block these messages from being produced or getting through to the airways and helping keep your airways open. Yes, this is pretty amazing!
Can you use an inhaler with ICS?
However, some people may still use an inhaler with just the ICS. Currently approved ICS only medicines include the following commercial brand names for ciclesonide, fluticasone furoate, mometasone furoate, fluticasone furoate, budesonide and beclomethasone dipropionate. Alvesco® (I)*. Arunity Ellipta® (I)*.
What is volume reduction surgery?
Lung Volume Reduction Surgery is surgical procedure for carefully selected patients with severe emphysema struggling despite maximal medical therapy. Currently, the surgery is almost always done with a minimally invasive approach called VATs, video assisted thoracoscopy. During the operation, the surgeon removes the worst area of emphysema. By doing this, the healthier portions of the lung are able to work more efficiently. This surgery also reduces pressure on the diaphragm, making it easier to breathe.
How long does a lama last?
Different brands of LAMAs can last for 12 or up to 24 hours and so are usually taken once or twice a day by inhaler or nebulizer. Currently approved LAMAs include these commercial brand names for umeclidinium bromide, tiotropium bromide, aclidinium bromide, and glycopyrrolate:
What is the best treatment for COPD?
Supplemental Oxygen Therapy. Supplement al oxygen is often used to treat low blood oxygen levels, known as hypoxemia, in people with COPD. People with chronic hypoxemia often need to use oxygen every day, but oxygen therapy is also used to treat temporary hypoxemia caused by COPD exacerbations.
What to do if your COPD flares up?
There's a good chance that your COPD action plan will tell you to take extra medication when your symptoms flare up. It might, for example, tell you to take more of your usual medication (e.g. use your rescue inhaler more often) or it might tell you to start a new course of medication like steroids or antibiotics.
How to tell if you have COPD?
Here are some of the signs of a COPD Exacerbation: 1 Increased shortness of breath 2 Increased coughing or more sputum 3 Increased fatigue 4 Morning headaches 5 Noisier breaths or wheezing sounds when you breathe 6 Fever 7 Symptoms of a cold or another respiratory illness 8 Change in the color of your mucus or sputum 9 Swollen ankles 10 Confusion
Why are action plans important?
While action plans are important for daily COPD management, they are perhaps even more useful for managing exacerbations. They tell you exactly what to do as soon as you notice your symptoms flare up, which gives you the opportunity to respond to a potential exacerbation quickly so you can start self-treatment at home.
What are the symptoms of a flare up?
Change in the color of your mucus or sputum. Swollen ankles. Confusion. These changes can happen suddenly without much warning, so you should always be on the lookout for flare-ups; even small up-tick in symptoms need to be carefully monitored for change.
How long does a COPD flare up last?
One of the biggest culprits of symptom flare-ups are COPD exacerbations, which are periods of elevated symptoms that can last for days, weeks, or more. In some cases, they can even lead to permanent lung damage and quicker lung function loss, which is why managing exacerbations is a vital aspect of treating COPD.
Why do doctors prescribe antibiotics?
However, sometimes doctors prescribe antibiotics before an infection is known, in order to control bacteria in the lungs and prevent a more serious infection from taking hold.
What is an exacerbation of COPD?
An exacerbation (x-saa-cer-bay-shun) is a flare-up or episode when your breathing gets worse than usual and may continue to get worse without extra treatment. With COPD you may have the same daily symptoms with the same activities for weeks or months. Then suddenly you may have a flare-up where the cough, shortness of breath, or mucus may increase, ...
How to count your breathing rate?
Counting Your Breathing Rate (Respirations): Place your hand on your upper chest to feel it rise and fall. Each rise and fall counts as one breath. Look at your watch. Count the number of breaths in one minute and this is your breathing or respiratory rate. Or just count for 30 seconds and multiply this number by two.
Why do I have a cough and shortness of breath?
Then suddenly you may have a flare-up where the cough, shortness of breath, or mucus may increase, often caused by a lung infection. This can be very serious, causing you to go to the emergency room or have to stay in the hospital for a few to several days.
How to know if you have a flare up?
Important Early Warning Signs are: Increases in cough. Increase or changes in mucus. More shortness of breath with the same or less activity. Other common signs and symptoms of an exacerbation or flare up are: Low grade fever that doesn’t go away. Increased use of rescue or quick relief inhaler or nebulizer medicines.
What causes a bad day?
Some things that might cause you to have a bad day are: weather, a "cold" or start of a lung infection, low pressure, emotions like stress or anxiety or depression, allergies, higher altitude, ...
How to know if you have COPD?
Know Your Heart Rate and Rate of Your Breathing plus. As a person with COPD, it is important that you know what your heart and breathing rates are when you are feeling good. These are called your "baseline" rates. When you start to feel a flare-up coming on, take your heart rate and breathing rate.
What are the symptoms of low oxygen?
More wheezing. In addition, an exacerbation may come with signs of lower oxygen in your blood: Morning headaches, dizzy spells, and restlessness. A need to increase your oxygen, if you are on oxygen. Rapid breathing.
What is the best treatment for COPD?
Most patients with exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) require oxygen supplementation during an exacerbation. Inhaled short-acting beta-agonists are the cornerstone of drug therapy for acute exacerbations. Use antibiotics if patients have acute exacerbations and purulent sputum.
What causes acute exacerbations?
The cause of an acute exacerbation is usually unknown, although some acute exacerbations result from bacterial or viral infections. Smoking, irritative inhalational exposure, and high levels of air pollution also contribute. Mild exacerbations often can be treated on an outpatient basis in patients with adequate home support. ...
How long does it take to stop prednisone?
Options include prednisone 30 to 60 mg orally once a day for 5 to 7 days and stopped directly or tapered over 7 to 14 days depending on the clinical response. A parenteral alternative is methylprednisolone 60 to 500 mg IV once a day for 3 days and then tapered over 7 to 14 days.
When was the Merck Manual first published?
The Merck Manual was first published in 1899 as a service to the community. The legacy of this great resource continues as the Merck Manual in the US and Canada and the MSD Manual in the remainder of the world. Learn more about our commitment to Global Medical Knowledge.
What is noninvasive ventilation?
Noninvasive positive-pressure ventilation (eg, pressure support or bilevel positive airway pressure ventilation by face mask) is an alternative to full mechanical ventilation. Noninvasive ventilation appears to decrease the need for intubation, reduce hospital stay, and reduce mortality in patients with severe exacerbations (defined as a pH < 7.30 in hemodynamically stable patients not at immediate risk of respiratory arrest).
How long does doxycycline last?
Trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole, amoxicillin, and doxycycline are give for 7 to 14 days. An alternative first-line antibiotic is azithromycin 500 mg orally once a day for 3 days or 500 mg orally as a single dose on day 1, followed by 250 mg once a day on days 2 through 5.
Can beta agonists be used with oxygen?
Beta-agonists and anticholinergics, with or without corticosteroids, should be started concurrently with oxygen therapy (regardless of how oxygen is administered) with the a im of reversing airway obstruction. Methylxanthines, once considered essential to treatment of acute COPD exacerbations, are no longer used; toxicities exceed benefits.
What is the best way to recover from COPD?
Pulmonary rehabilitation programs typically combine education, exercise training, nutrition advice and counseling.
How to treat a syphilis?
By taking the right medicine at the right time, you can: 1 Breathe better 2 Do more of the things you enjoy 3 Have fewer flare-ups or exacerbations
What is clinical trial?
Clinical trials are research studies that test how well new medical approaches work in people. Each study answers scientific questions and tries to find better ways to prevent, screen for, diagnose or treat a disease. People who take part in clinical trials for COPD have an opportunity to contribute to knowledge of and progress against COPD. They also receive up-to-date care from experts. Learn more about clinical trials for COPD »
What is supplemental oxygen?
Supplemental Oxygen. Your body needs oxygen to do everything from digesting food, daily household chores, to going to the grocery store. Sometimes with COPD, you require extra or supplemental oxygen (also called oxygen therapy). Learn how supplemental oxygen works and get safety tips ».
What is complementary therapy?
Complementary therapies refer to the many therapies, philosophies and practices that are not considered conventional or standard medical care in the United States. Some examples of complementary therapy included massage, yoga and acupuncture. These techniques can't treat COPD, but may be able to improve symptoms and quality of life. Always discuss these techniques with your care team before you participate »
Is there a medicine for COPD?
A variety of medicines are used to treat COPD and there is no "best" medicine for all people. Each person's COPD is different and your doctor and healthcare team will work with you to set up the best plan to address your symptoms and needs. Learn more about your treatment options ».
What is palliative care?
Palliative care is a specialty in medicine focused on treating the symptoms, pain and stress that accompany serious illnesses like COPD. It is available to you from the moment you are diagnosed and through the entire course of your illness.
What is an exacerbation of COPD?
What is a COPD exacerbation? A COPD exacerbation, or flare-up, occurs when your COPD respiratory symptoms become much more severe. While everyone experiences exacerbations differently, there are a number of possible warning signs — and you may feel as if you can’t catch your breath. Exacerbations can last for days or even weeks, ...
How long does a COPD exacerbation last?
Exacerbations can last for days or even weeks, and may require antibiotics, oral corticosteroids, and even hospitalization. As your lung function declines in the later stages of COPD, exacerbations tend to increase in frequency.
What are the symptoms of low oxygen levels?
Call 911 if you experience these dangerous warning signs, such as: Severe shortness of breath or chest pain. Blue color in lips or fingers.
What to include in an emergency contact list?
A list of your healthcare providers. Include names, phone numbers, and all relevant contact information.
What are the signs of a syringe?
Call 911 if you experience these dangerous warning signs, such as: 1 Severe shortness of breath or chest pain 2 Blue color in lips or fingers 3 Confusion, disorientation, or difficulty speaking in full sentences
Diagnosis
- To determine if you have emphysema, your doctor will ask about your medical history and do a physical exam. Your doctor may recommend a variety of tests.
Treatment
Clinical Trials
Lifestyle and Home Remedies
Coping and Support
Preparing For Your Appointment
- Many people with COPDhave mild forms of the disease for which little therapy is needed other than smoking cessation. Even for more advanced stages of disease, effective therapy is available that can control symptoms, slow progression, reduce your risk of complications and exacerbations, and improve your ability to lead an active life.