- Surgery to remove the tumor. This is a highly effective treatment for acoustic neuromas. ...
- Stereotactic radiosurgery. This form of radiation therapy delivers precisely targeted radiation to the tumor while avoiding the surrounding healthy tissue. ...
- Observation.
When should an acoustic neuroma be removed?
You may be a candidate for suboccipital acoustic neuroma surgery if you have: A medium or large acoustic neuroma that is causing symptoms, especially balance problems caused by brainstem compression. Serviceable hearing in the affected ear. Neurofibromatosis type 2 (NF-2)
What is the treatment of choice for acoustic neuromas?
As discussed below, the therapeutic options for acoustic neuromas include observation, surgery and radiosurgery. The optimal treatment varies according to whether the tumor is large or small, whether it has caused neurologic damage prior to treatment and on patient factors.
What is the survival rate for acoustic neuroma?
Multivariate analyses revealed that postoperative mortality following acoustic neuroma excision was 0.5%, with adverse discharge disposition of 6.1%. The odds ratio for mortality in African Americans compared with Caucasians was 8.82 (95% confidence interval = 1.85–41.9, P = . 006).Aug 19, 2011
How do you shrink an acoustic neuroma?
Using the Gamma Knife system, the neurosurgeon can target your acoustic neuroma precisely, shrinking and destroying the tumor while sparing nearby structures. This procedure reduces the risk of permanent hearing damage or other risks that are associated with surgery.
What happens if acoustic neuroma goes untreated?
Left untreated, an acoustic neuroma can block the flow of cerebrospinal fluid and cause hydrocephalus, which can in turn lead to severe vision problems and difficulty breathing and swallowing. Fortunately, most patients seek treatment long before an acoustic neuroma reaches this stage.
At what size should an acoustic neuroma be removed?
11, 27 Observation alone may be the best option for tumors up to 1.5 cm in size. If they grow, they can undergo low-morbidity surgery providing this is done promptly, before the tumor reaches the critical size of 1.5 cm.
Can you live a long life with acoustic neuroma?
The patient may choose to live with the acoustic neuroma as long as it is not a life-threatening condition rather than risk further hearing loss that can potentially occur from therapy. If an acoustic neuroma eventually causes symptoms, then radiation therapy or microsurgery may be necessary.
How serious is an acoustic neuroma?
Even if acoustic neuroma is not growing, it can cause worsening hearing loss and balance function. If a growing acoustic neuroma is left untreated, it can cause a dangerous buildup of fluid in the brain or it can compress the cerebellum and brain stem, which can be life threatening.
Is acoustic neuroma fatal?
Untreated acoustic neuroma can be fatal An acoustic neuroma is usually benign, but it can still be fatal if left untreated. This is because the tumour will keep growing. Once it runs out of space inside the small canal that links the inner ear to the brain, it begins to grow into the skull cavity.
Can acoustic neuroma return?
An acoustic neuroma can occasionally return after treatment. This is thought to happen to around 1 in every 20 people who have had surgical removal. You'll probably continue having regular MRI scans after any treatment to check if the tumour is growing again or coming back.
What causes an acoustic neuroma to grow?
Cause of Acoustic Neuroma For most acoustic neuromas, the cause at the cellular level is the failure of a "governor" gene to suppress the growth of Schwann cells—those cells responsible for coating nerve fibers with insulation. Without suppression, these cells grow like a wart to produce the neuroma.
How fast does acoustic neuroma grow?
Although most acoustic neuromas grow slowly, some grow quite quickly and can double in volume within 6 months to a year. Although some tumors adhere to one or another of these growth patterns, others appear to alternate between periods of no or slow growth and rapid growth.
Neuroma Can Include Surgery vs. Radiosurgery
As discussed below, the therapeutic options for acoustic neuromas include observation, surgery and radiosurgery. The optimal treatment varies accor...
Considerations in Choice of Treatment
Controversy exists regarding the optimal form of treatment for the acoustic neuromas. Small tumors that do not pose a risk to brain function and do...
Microsurgical Resection of Acoustic Neuromas Can Be Accomplished Using One of Three Operative Approaches.
Microsurgical resection of acoustic neuromas can be accomplished through three different operative approaches to the tumor. Traditionally the suboc...
The Surgery of Acoustic Neuroma Has been Aided by Technological Advances.
Intraoperative monitoring of brain and nerve function is now routinely performed with all surgical procedures for the resection of acoustic neuroma...
Surgery For Acoustic Neuromas: Surgical Results
Most modern surgical series report complete tumor removal with both anatomic and functional preservation of the facial nerve in over 90% of patient...
What is the treatment for acoustic neuromas?
The options for the treatment of the acoustic neuromas include surgery and radiosurgery. Our approach to surgery for acoustic neuromas is based on the Johns Hopkins experience of nearly 100 years of surgery of the brain. Experience with this type of surgery appears to be essential in minimizing the risk of complications as acoustic neuromas.
How long does radiation last?
Few studies to date have documented the effects of radiation beyond 5 years. Moreover, there now exist several reports of malignancies (cancers) developing within the field of radiation treatment for acoustic neuroma.
Is acoustic neuroma slow growing?
Because acoustic neuromas are usually slow-growing, immediate intervention is not always necessary.
What is intraoperative monitoring?
Otolaryngologists work with neurosurgeons on each case. Intraoperative monitoring is used to avoid damaging auditory, facial and other cranial nerves. "We think it's important to take out all of the tumor. But sometimes we do a less than complete resection to keep the facial nerve intact," Dr. Link says.
Where is the Mayo Clinic?
Over the past 26 years, it has been used at Mayo Clinic's campus in Minnesota to treat approximately 1,000 acoustic neuromas. In addition, Mayo Clinic neurosurgeons have surgically removed thousands of acoustic neuromas.
What is the treatment for acoustic neuroma?
The treatments for acoustic neuroma, in fact, include surgical removal, radiation therapy, regular monitoring and more. MRI and monitoring: this is beneficial since there is some acoustic neuroma that does not grow. Thus, continuous monitoring is a must. Radiosurgery: it delivers radiation straight through the tumor.
How do you know if you have acoustic neuroma?
Some other symptoms of an acoustic neuroma include: Confusion. Unsteadiness or clumsiness. Headaches. Hoarseness and difficulty in swallowing. Taste changes. Facial weakness. Facial numbness as well as tingling which can be constant or may come and go. The feeling like the world is spinning or vertigo.
What nerve connects the inner ear to the brain?
Acoustic neuroma is actually a non-cancerous growth, which develops on the eighth cranial nerve. This is also known as the vestibular nerve, which connects the inner ear with the brain. Furthermore, it has two different parts, the one is transmitting sound, and the other helps in sending balance information from the inner ear to the brain.
What is the name of the nerve that causes tinnitus?
It is also known as the neurolemmomas or vestibular schwannoma. Moreover, the branches of the vestibular nerve that gets affected because of the condition have branches of its own. And these branches directly influence the balance as well as the hearing. Not only that, the pressure that comes from the acoustic neuroma may also cause tinnitus or ...
What does it feel like to be spinning?
The feeling like the world is spinning or vertigo. Problems with balance. It is very important to see your doctor if you already have these symptoms. Furthermore, mental confusion, as well as clumsiness, may be an indication of more serious problems which may require urgent treatments.
What percentage of acoustic neuroma cases are not known?
the exact cause of the condition is not yet clear even up to this date. In fact, according to a certain research, there is about 95 percent of the cases that have no known cause. However, there are some factors that may increase the risk of acoustic neuroma. These include:
Can acoustic neuroma cause ringing in ears?
Not only that, the pressure that comes from the acoustic neuroma may also cause tinnitus or the ringing in the ear, unsteadiness, as well as hearing loss. Usually, the condition arises from the Schwann cells, which covers the nerve. Furthermore, it also grows in slow motion or even not at all.
What Is The Best Treatment for Acoustic Neuroma?
Due to its slow-growing and non-malignant properties, these tumors do not require any form of treatment for them. The growth sometimes becomes so slow that people often survive a lifetime without even experiencing any symptoms and tumor is detected after death during the autopsy.
Conclusion
Waiting approach is usually applied in non-symptomatic patients of acoustic neuroma. Initial treatment would be supportive with the target towards symptomatic relief to the patients. Hearing ability can a by the use of hearing aids in the management of early symptoms or after the operation.
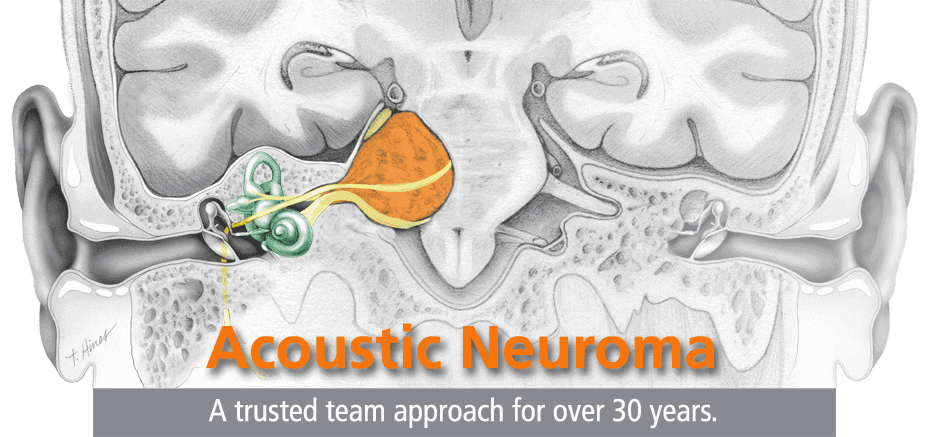
What is acoustic neuroma?
Acoustic (bilateral) neuroma is a benign tumor that develops in the auditory nerve, which is also called an acoustic nerve. The acoustic nerve is responsible for transmitting the acoustic information to the brain and it is located in the inner ear. The incidence rate of acoustic neuroma is two cases per 200,000 population. This tumor occupies 11 - 12% of all brain cancers. Generally the disease is more likely to appear among the individuals between 35 and 45 years. There has never been cases of acoustic neuroma among children and teenagers.
What is the hearing test?
Hearing test is a diagnostic procedure of the acoustic (bilateral) neuroma that measures hearing in both ears. Electronystagmography is a test, during which the cold and warm water are poured into the ear canal and the results of dizziness and of eye movements are recorded and analyzed.
How many departments does University Hospital Ulm have?
The hospital is famous for its numerous discoveries and the world-class achievements in medicine and pharmaceuticals. The medical facility has 29 specialized departments a
When was the University Hospital Tuebingen founded?
According to the prestigious medical publication Focus, the University Hospital Tuebingen ranks among the top five German hospitals! The hospital was founded in 1805, therefore it is proud of its long history, unique experience, and outstanding achievements in the field of medical care, as well as research and teaching activitie
What is the University Hospital Marburg?
The University Hospital Marburg UKGM offers patients modern diagnostics and comprehensive therapy at the international level. As a maximum care hospital, the medical facility specializes in all fields of modern medicine ranging from ophthalmology to traumatology and dentistry. The main areas of specialization of the hospital are
Is University Hospital Hamburg Eppendorf a top ten hospital in Germany?
According to the Focus magazine, the University Hospital Hamburg-E ppendorf ranks among the top ten hospitals in Germany! Since its foundation in 1889, the hospital has taken a leading position in the European medical arena and still occupies it until today. A highly competent medical team of more than 11,000 employees takes care
Is University Hospital Würzburg a German hospital?
According to the Focus magazine in 2019, the University Hospital Würzburg ranks among the top national German hospitals! The hospital is one of the oldest medical facilities in Germany. The centuries-old traditions of first-class treatment are combined with the very latest achievements of modern evidence-based medicine and
What is the best treatment for acoustic neuroma?
Doctors may also recommend radiation therapy to treat older patients. Radiosurgery.
What is the most common type of acoustic neuroma?
There are 2 types of acoustic neuromas: Unilateral acoustic neuromas. This type affects only one ear. It is the most common type of acoustic neuroma. This tumor may develop at any age.
What is a vestibular schwannoma?
It grows slowly from an overproduction of Schwann cells and is also called a vestibular schwannoma. The tumor then presses on the hearing and balance nerves in the inner ear. Schwann cells normally wrap around and support nerve fibers. A large tumor can press on the facial nerve or brain structures.
How does MRI work?
MRI uses magnetic fields and radio waves, rather than x-rays, and computers to create detailed pictures of the brain. It shows visual “slices” of the brain that can be combined to create a three-dimensional picture of the tumor. A contrast dye is injected into the patient.
Where is the hearing aid implanted?
The bone-anchored hearing aid (Baha) speech processor is a hearing aid that doctors surgically implant under the skin near the ear. The device grows into the skull bone and enhances the bone’s natural transmission of sound.
What is the first test for neuroma?
Hearing test (audiometry): A test of hearing function, which measures how well the patient hears sounds and speech, is usually the first test performed to diagnose acoustic neuroma. The patient listens to sounds and speech while wearing earphones attached to a machine that records responses and measures hearing function. The audiogram may show increased " pure tone average " (PTA), increased " speech reception threshold " (SRT) and decreased " speech discrimination " (SD).
How do cochlear implants work?
Cochlear implants work by bypassing the damaged portions of the ear and directly stimulating the hearing nerve. They generate signals from the auditory nerve to the brain, which recognizes the signals as sound. Cerebrospinal fluid leak is a common problem after surgical removal of an acoustic neuroma.
How To Diagnose Acoustic Neuroma?
It is not easy to detect acoustic neuroma in the early stages as symptoms are gradual in development. Its symptoms also resemble the symptoms of other ailments of the middle and inner ear. Physical examination of the inner ear is first stepping to find out acoustic neuroma. Your physician may ask a few questions regarding your symptoms.
What Is The Best Medicine For Acoustic Neuroma?
Surgery is considered the best treatment for acoustic neuroma. The tumors are surgically incised from the nerve through a window from the skull. Its main aim is to preserve the facial nerve. However, if the symptoms of this tumor are asymptomatic, then the physician may decide to wait and monitor the tumor regularly.
Conclusion
Acoustic neuroma is detected after careful evaluation of the symptoms, physical examination, audiometry (hearing test), CT scan and MRI scan. The best medicine for acoustic neuroma is the surgical incision of the tumor on the eighth cranial nerve. It is sometimes followed by radiation therapy.

Overview
- An acoustic neuroma (also known as vestibular schwannoma or acoustic neuroma) is a benign (nonmalignant), usually slow-growing tumor that develops from the balance and hearing nerves supplying the inner ear. The tumor comes from an overproduction of Schwann cellsthe cells that normally wrap around nerve fibers to help support and insulate nerves.
- An acoustic neuroma is a tumor that grows from the nerves responsible for balance and hearing. These tumors grow from the sheath covering the vestibulocochlear nerve. Acoustic neuromas are benign (not cancer) and usually grow slowly. Over time the tumor can cause gradual hearing loss, ringing in the ear, and dizziness. Because of their slow growth, not all acoustic neuromas need t…
Treatment
- Your acoustic neuroma treatment may vary, depending on the size and growth of the acoustic neuroma, your overall health, and if you're experiencing symptoms. To treat acoustic neuroma, your doctor may suggest one or more of three potential treatment methods: monitoring, surgery or radiation therapy.
- As discussed below, the therapeutic options for acoustic neuromas include observation, surgery and radiosurgery. The optimal treatment varies according to whether the tumor is large or small, whether it has caused neurologic damage prior to treatment and on patient factors. Because acoustic neuromas are usually slow-growing, immediate intervention is not always necessary. F…
- There are three ways to treat acoustic neuromas — observation, radiation and surgery.At least 10% of acoustic neuromas do not show signs of growth after they are found. Since the tumor is very slow-growing and benign, having a follow-up MRI scan and an audiogram in 6 and 12 months is a safe alternative to immediate intervention. If no changes are found, yearly checkups afterwa…
- Early diagnosis of an acoustic neuroma is key to preventing its serious consequences. The three treatment options are surgical removal, radiation, and monitoring. Typically, the tumor is surgically removed. The exact type of operation involved depends on the size of the tumor and the level of hearing remaining in the affected ear. As an alternative to conventional surgical techniques, radi…
Diagnosis
- Acoustic neuroma is often difficult to diagnose in the early stages because signs and symptoms may be subtle and develop gradually over time. Common symptoms such as hearing loss are also associated with many other middle and inner ear problems.After asking questions about your symptoms, your doctor will conduct an ear exam. Your doctor may order the following tests: 1. …
- To review complications that occur during the course of acoustic neuroma surgery a retrospective case review was published (Otol Neurotol 2001 Nov;22(6):895-902 Perioperative morbidity of acoustic neuroma surgery. Slattery WH 3rd, Francis S, House KC). A series of 1,687 patients undergoing acoustic neuroma surgery between 1987 and 1997 included 822 male and 865 fema…
- Because the symptoms of acoustic neuroma are often subtle and slow to develop, they can be missed easily in their early stages. Gradual hearing loss, especially if it occurs only in one ear, always should be checked by a physician.If your doctor suspects that you have an acoustic neuroma, he or she will examine you to look for other conditions that can cause similar sympto…
- Other CPA tumours include meningiomas, epidermoids, lower cranial nerve schwannomas and arachnoid cysts.
Symptoms
- Acoustic neuromas generally grow slowly so the symptoms develop gradually and are easy to miss or misinterpret. The earliest and most common symptoms of an acoustic neuroma are: 1. Loss of hearing in one ear — This usually is gradual, but can occur suddenly in 10% of cases. 2. Tinnitus, a ringing, buzzing or noisy sound in the ear when there is no external sound present. Le…
Prognosis
- Once resected the tumors were evaluated for their cellular architecture. Viable tumor was present in all cases. Despite the scarring of the areas surrounding the tumor, there was no significant scarring or other changes within the tumor. That is, for unknown reasons, these tumors appeared unaffected by the prior radiation treatment. It may be that \"pockets\" of the tumor evaded the ef…
- Acoustic neuromas are not cancerous (malignant) and do not spread to other parts of the body. Timely diagnosis and proper treatment can minimize the losses that they cause and prevent any shortening of one's lifespan.
- If the tumor is very small, hearing function may be preserved and accompanying symptoms may improve. As the tumor grows larger, however, surgical removal becomes more complicated because the tumor may have damaged the nerves that control facial movement, hearing, and balance, and may also have affected structures of the brain. When the tumor has affected these …
Clinical Trials
- Explore Mayo Clinic studies testing new treatments, interventions and tests as a means to prevent, detect, treat or manage this disease.
- Clinical trials are research studies in which new treatments—drugs, diagnostics, procedures, and other therapies—are tested in people to see if they are safe and effective. Research is always being conducted to improve the standard of medical care. Information about current clinical trials, including eligibility, protocol, and locations, are found on the Web. Studies can be sponsored by t…
Management
- The growth pattern of acoustic neuromas is variable. As many as 75% of tumours have been reported to show no growth. However, there are no reliable predictors of tumour behaviour.There are three treatment options: microsurgery (the technique of choice), stereotactic radiosurgery and observation.When assessing the most appropriate management for each individual patient, con…
Future
- Currently, long-term follow-up after treatment that documents a high cure rate is only available for surgical removal, and only when the vast majority of the tumor is completely resected. (There is a suggestion that small \"flecks\" of tumor may be left without risk of regrowth, but significant portions of the tumor left behind present a significant risk of regrowth). In some cases, however…
Pathophysiology
- A recent study based at Johns Hopkins documented the experience of removing acoustic neuromas that grow after radiation therapy (Lee, Westra, Staecker, Long, Niparko: Clinical and histopathological features of recurrent acoustic neuroma following stereotactic radiosurgery. Otology & Neurotology, in press, 2003). As stereotactic radiosurgery for acoustic neuroma entail…
When To Call A Professional
- See your physician if you develop new hearing loss or tinnitus, particularly if the hearing loss or tinnitus is only on one side.