
Medication
The first sign you may get is inflammation. Grade 1 can generally reverse within a few weeks to months. On average, Grade 1 May take around 2-3 months to reverse your fatty liver completely. Remember, you can only reverse your damaged liver if you follow the correct diet and corrective measures.
Procedures
To conclude, we should say that no one of us can say the number of years, for which an individual with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease will survive or experience complications. However, if a person chooses to bring lifestyle changes early, he or she may expect to avoid liver failure or liver damage.
Self-care
Your Guide to Anti-Aging Foods That Also Reverse Fatty Liver
- Red Grapes. Resveratrol is a polyphenol prevalent in a variety of plants. ...
- Green Tea. Green tea is a popular beverage that has been used for centuries in traditional Chinese medicine. ...
- Tofu. ...
- Sweet Potato. ...
- Salmon. ...
- Mushrooms. ...
- Avocado. ...
- Pomegranate. ...
- Sun-Dried Tomatoes. ...
- Kale. ...
Nutrition
What does a diet plan for fatty liver disease look like?
- 3 oz. grilled salmon
- 1 cup cooked broccoli
- 1 cup cooked quinoa
- 1 cup mixed berries
See more
How long do you live with NAFLD?
What is the life expectancy of non alcoholic liver disease?
What foods help prevent and reverse fatty liver disease?
What is the best diet to treat fatty liver disease?
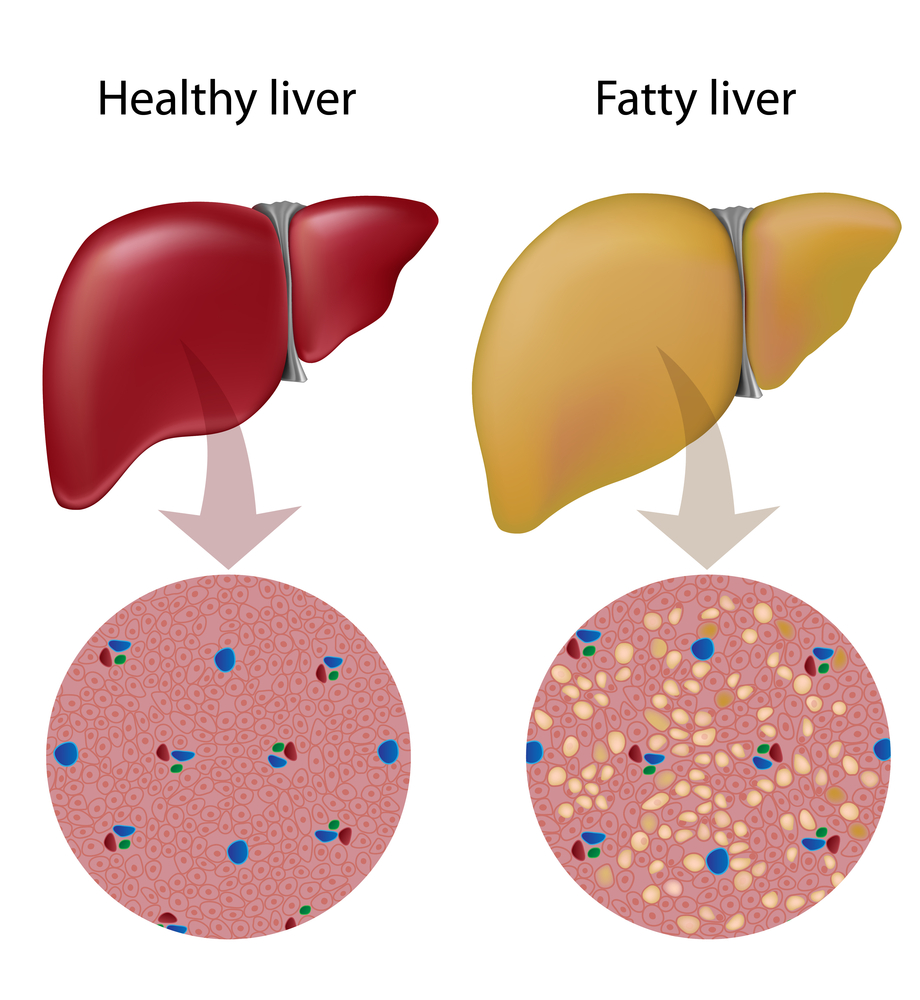
Can non-alcoholic fatty liver disease be treated?
No alternative medicine treatments are proved to cure nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. But researchers are studying whether some natural compounds could be helpful, such as: Vitamin E.
What is the best medicine for non-alcoholic fatty liver?
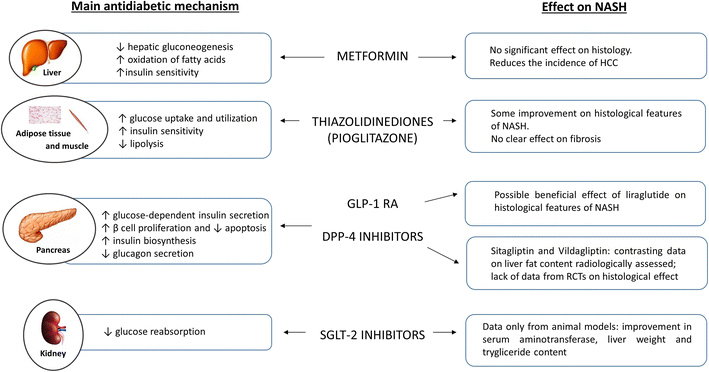
Currently, insulin sensitizers (thiazolidinediones) and antioxidants (vitamin E) seem to be the most promising therapeutic agents for NAFLD/NASH, and lipid-lowering drugs, pentoxifylline, angiotensin receptor blockers, and n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids also have promise.
How do you fix non-alcoholic liver disease?
exercise regularly – aim to do at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity activity, such as walking or cycling, a week; all types of exercise can help improve NAFLD, even if you do not lose weight. stop smoking – if you smoke, stopping can help reduce your risk of problems such as heart attacks and strokes.
What are the treatment options for fatty liver disease?
Unfortunately, there are no FDA-approved medications for fatty liver disease. So far, the two best drug options affirmed by the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases for biopsy-proven NASH are vitamin E (an antioxidant) and pioglitazone (used to treat diabetes).
What is the fastest way to cure a fatty liver?
Lifestyle and dietary changes are currently the most effective options for managing NAFLD. Losing weight, being physically active, cutting back on sugar, eating a nutrient-dense diet, and drinking coffee (if you can tolerate it) are some of the methods that may help improve symptoms associated with NAFLD.
What are the 3 signs of a fatty liver?
SymptomsAbdominal swelling (ascites)Enlarged blood vessels just beneath the skin's surface.Enlarged spleen.Red palms.Yellowing of the skin and eyes (jaundice)
What causes non-alcoholic fatty liver disease?
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease tends to develop in people who are overweight or obese or have diabetes, high cholesterol or high triglycerides. Rapid weight loss and poor eating habits also may lead to non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.
How long can you live with nonalcoholic cirrhosis of the liver?
Survival and mortality The median survival was 24.2 (range 0.2-26.1) years in the NAFLD group and 19.5 (range 0.2-24.2) years in the AFLD group (p = 0.0007). Median follow-up time for the non-alcoholic group was 9.9 years (range 0.2-26 years) and 9.2 years (0.2-25 years) for the alcoholic group.
How long does it take to heal a fatty liver?
Alcoholic fatty liver disease Fatty liver disease rarely causes any symptoms, but it's an important warning sign that you're drinking at a harmful level. Fatty liver disease is reversible. If you stop drinking alcohol for 2 weeks, your liver should return to normal.
What is the best medicine for liver disease?
A number of alternative medicines have been used to treat liver diseases. Milk thistle (silymarin) is the most widely used and best studied.
What medications should be avoided with liver disease?
The 10 Worst Medications for Your Liver1) Acetaminophen (Tylenol) ... 2) Amoxicillin/clavulanate (Augmentin) ... 4) Amiodarone (Cordarone, Pacerone) ... 5) Allopurinol (Zyloprim) ... 8) Azathioprine (Imuran) ... 9) Methotrexate. ... 10) Risperidone (Risperdal) and quetiapine (Seroquel)
What is the medical name for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease?
Medications for Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Other names: Fatty Liver; Idiopathic Fatty Liver; NAFLD; NASH; Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis; Steatohepatitis; Steatosis. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) describes a range of conditions that affect people who drink little or no alcohol.
Is there a lack of accepted safety for use under medical supervision?
Has a high potential for abuse. Has a currently accepted medical use in treatment in the United States or a currently accepted medical use with severe restrictions. Abuse may lead to severe psychological or physical dependence.
Abstract
Alcoholic liver disease (ALD) and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) are serious health problems worldwide. These two diseases have similar pathological spectra, ranging from simple steatosis to hepatitis to cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma.
INTRODUCTION
Alcoholic liver disease (ALD) and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) are serious health issues whose incidences are on the rise with each passing decade. Alcohol is responsible for approximately 4% of all deaths annually and 5% of all disabilities worldwide [ 1 ].
ALD TREATMENT
For the last 50 years, abstinence has remained the primary therapy for ALD treatment. However, serious symptoms develop with the abrupt cessation of alcohol. Treating the alcohol withdrawal syndrome is thus extremely important and requires administration of fluid, calories, vitamins and minerals.
NAFLD TREATMENT
Like ALD there is no effective treatment to date for NAFLD. In the absence of a proven effective therapy, we must follow a multi-disciplinary approach in NAFLD treatment, where a combination of drugs and factors are taken into consideration to counter multiple pathological risk factors involved in NAFLD.
CONCLUSION
Both ALD and NAFLD are chronic liver diseases with similar spectrums from simple steatosis to cirrhosis with basic differences only in their etiology. Despite understanding much of the pathophysiology of both diseases, there is still no effective treatment for either disease.
Contributor Information
Sukhpreet Singh, Research Service, Veterans Affairs Nebraska-Western Iowa Health Care System, Omaha, NE 68105, United States.
How to treat non-alcoholic fatty liver?
Here are the most common non-alcoholic fatty liver disease natural remedies: 1. Exercise . Weight loss is considered the most effective approach in the treatment of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.
How much aerobic exercise is needed for fatty liver disease?
A minimum of 40 minutes of moderat e to intense aerobic exercise for five days week ly can help benefit NAFLD patients.
How to treat fatty liver with dandelion root tea?
Enjoy dandelion root tea to obtain the full effects of fatty liver disease. Add a teaspoon of dried dandelion root to a cup of boiling hot water. Next, cover and steep for up to 10 minutes. Strain the decoction.
What foods cause fatty liver disease?
The elimination of high-glycemic-index (GI) foods is vital for the prevention and treatment of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. High GI foods that increase blood sugar levels include potatoes, watermelon, brown rice, and processed foods like chocolate bars, sweetened cereals, and beer. It is interesting to note that a 2008 study published in the Canadian Journal of Gastroenterology found that 80% of NAFLD patients drank enough juices and soft drinks that equaled 12 teaspoons of sugar; they also noted that sugar-laden drinks can cause NAFLD.
What is it called when you don't drink alcohol?
However, people who don’t drink a lot of alcohol are also at risk of the liver disease called non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). The condition often ranges in severity. When there is inflammation of the liver, it is known as nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH). This stage is serious where things may advance to cirrhosis ...
How to treat NAFLD?
To make licorice root tea, simply pour boiling water over a teaspoon of licorice root powder, and let it steep for about 10 minutes. Let it strain, and enjoy the tea. It is a good idea to consume the licorice root tea once or twice daily.
What is the best herb for liver disease?
Cilantro or coriander ( Coriandrum sativum) is another important herbal remedy for liver protection. Cilantro is also useful for conditions related to NAFLD, especially diabetes. The cooking herb contains antioxidant and antihyperglycemic effects, according to studies of diabetic rats.
What is the most common chronic liver disease?
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease ( NAFLD) has become the most frequently encountered chronic liver disease. NAFLD is associated with increased liver-related morbidity and mortality, but also contributes to cardiovascular disease, diabetes and non-liver-related malignancy.
What is the most severe subtype of NAFLD?
Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) is considered the more severe subtype of NAFLD that drives most of these adverse outcomes. Lifestyle modification and associated weight loss can improve NASH but are not always sufficient and sustained results are difficult to obtain.
What is the most common form of liver cancer?
Liver cancer begins in the cells of the liver. The most common form of liver cancer begins in cells called hepatocytes and is called hepatocellular carcinoma. The main complication of NAFLD and NASH is cirrhosis, which is late-stage scarring in the liver. Cirrhosis occurs in response to liver injury, such as the inflammation in NASH.
What is the most common form of NAFLD?
NAFLD is increasingly common around the world, especially in Western nations. In the United States, it is the most common form of chronic liver disease, affecting about one-quarter of the population. Some individuals with NAFLD can develop nonalcoholic ...
What is the name of the vein that carries blood from the intestine to the liver?
Esophage al varices. Esophage al varices. Esop hageal varices are enlarged veins in the esophagus. They're often due to obstructed blood flow through the portal vein, which carries blood from the intestine, pancreas and spleen to the liver.
What is the name of the disease where the body doesn't take up sugar?
Insulin resistance, in which your cells don't take up sugar in response to the hormone insulin. High blood sugar (hyperglycemia), indicating prediabetes or type 2 diabetes. High levels of fats, particularly triglycerides, in the blood. These combined health problems appear to promote the deposit of fat in the liver.
Where is the liver located?
About the size of a football, it's located mainly in the upper right portion of your abdomen, beneath the diaphragm and above your stomach.
What is the complication of NAFLD?
The main complication of NAFLD and NASH is cirrhosis, which is late-stage scarring in the liver. Cirrhosis occurs in response to liver injury, such as the inflammation in NASH. As the liver tries to halt inflammation, it produces areas of scarring (fibrosis).
What is the best vitamin for liver damage?
Vitamin E. This vitamin, which is an antioxidant, theoretically works by reducing or neutralizing the damage caused by inflammation. Some evidence suggests vitamin E supplements may be helpful for people with liver damage due to NAFLD and NASH.
How to treat NAFLD?
The first line of treatment for NAFLD and NASH is weight loss, done through a combination of calorie reduction, exercise, and healthy eating. Weight loss can reduce fat and inflammation in the liver. The following lifestyle changes are important in managing your disease. 1.
What are the best foods to eat to reduce a fatty stomach?
Replace them with monounsaturated fats (olive, canola, and peanut oils) and polyunsaturated fats (corn, safflower, soybean oils, and many types of nuts).
How does bariatric surgery work?
Alternatively, there are weight-loss (bariatric) surgical procedures and endoscopic therapies that work by either physically limiting the amount of food your stomach can hold, or reducing the amount of nutrients and calories your body absorbs. Talk to your doctor about which option may be best for you. 2.
How to keep your triglycerides and cholesterol levels down?
Healthy eating combined with exercise – and taking cholesterol-lowering medications if prescribed by your doctor – will help keep your cholesterol and triglyceride levels where they need to be. 4. Protect your liver. Don’t do things that put extra stress on your liver.
What is the best way to reduce a person's risk of a syphilis?
Eating a healthy diet that’s rich in fruits and vegetables, whole grains and low in saturated fats. Limit animal-based foods, like red meat which is high in saturated fats, and eat more plant-based foods like beans, legumes, and nuts. Use good fats like olive oil.
Does coffee help with fatty liver?
In the meantime, there a few alternative treatments that could be helpful, although none have been proven to cure nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Coffee. In studies of people with NAFLD, those who drank coffee had less liver damage than those who drank little or no coffee.
Alcohol Withdrawal Treatment
The most crucial step for beginning treatment for alcoholic liver disorder (ALD is to quit drinking completely. Unfortunately, because the body has become dependent on alcohol, the sudden cessation of alcohol may cause painful withdrawal symptoms.
Alcoholic Liver Disease Treatment: Nutritional Support
If you have ALD, you may be also malnourished. A loss of appetite and nausea may have prevented you from ingesting enough nutrients. Providing sufficient calories with nutritional supplements is very crucial to your recovery and healing of your liver inflammation.
Alcoholic Liver Disease Treatment: Liver Transplantation
In severe cases, patients’ condition may deteriorate further and develop liver failure. At that point, liver transplantation is the only cure.
Treating Complications of Alcoholic Liver Disease
There are a number of complications that may arise in patients with ALD. Your medical team will help you manage these complications.
Cirrhosis of the Liver
Cirrhosis is a result of chronic liver disease. It occurs when the disease has destroyed normal liver tissue, leaving nonfunctioning scar tissue in its place. Cirrhosis is rarely reversible.
Portal Hypertensive Bleeding
Because of the liver scarring resulting from ALD, your blood cannot circulate easily throughout your body. Portal hypertension is when you develop varices (varicose veins) in your esophagus or stomach, as a result of high blood pressure in your portal vein. The varices can be examined during an endoscopy.
Ascites
Ascites is a condition when excess fluid accumulate in your abdomen due to high blood pressure in the liver. Low salt diet in combination with diuretics (water pills) will help to remove the fluid in majority of patients. If not, you may need an abdominal paracentesis.
Diagnosis
Treatment
Clinical Trials
Lifestyle and Home Remedies
Specialist to consult
Preparing For Your Appointment