Explore
Negative myoclonus (NM) is a motor phenomenon characterized by involuntary jerky movements due to a brief, sudden interruption of muscular activity. This motor disturbance can be observed in a variety of clinical conditions, that can range from physiological NM, occurring when falling asleep or afte … Negative myoclonus Clin Neurosci.
What is negative myoclonus?
Most of the time, however, the underlying cause can't be cured or eliminated, so treatment is aimed at easing myoclonus symptoms, especially when they're disabling. There are no drugs specifically designed to treat myoclonus, but doctors have borrowed from other disease treatment arsenals to relieve myoclonic symptoms.
Is there a cure for myoclonus?
A person may experience myoclonus as a side effect of medication. Myoclonus is the medical term for a sudden jerking of a muscle or group of muscles. This is involuntary — the person is not in control of the movement. Muscle jerks can happen at random or in response to a trigger. They may repeat in a pattern.
What is myoclonus a side effect of medication?
Clonazepam is used for subcortical–nonsegmental myoclonus, but other treatments, depending on the syndrome, have been used for this physiological type of myoclonus. Segmental myoclonus is difficult to treat, but clonazepam and botulinum toxin are used.
Which medications are used to treat subcortical–nonsegmental myoclonus?

How do you treat myoclonus?
Treatment of myoclonus focuses on medications that may help reduce symptoms. The drug of first choice is clonazepam, a type of tranquilizer. Many of the drugs used for myoclonus, such as barbiturates, phenytoin, and primidone, are also used to treat epilepsy.
What causes negative myoclonus?
Negative myoclonus NM occurs when there is sudden interruption of ongoing muscle contraction (Figure 1). Clinically, it appears as a shock- like involuntary jerk that causes postural lapses. When trunk or lower limbs are involved, as for example in Lance–Adams syndrome, NM will cause a person to fall.
What is negative myoclonus?
Negative myoclonus (NM) is a motor phenomenon characterized by involuntary jerky movements due to a brief, sudden interruption of muscular activity.
How do you treat myoclonus naturally?
Exercise is the solution. Exercise can contribute to further muscle twitching, but it also gives your brain an excuse for that twitching so that it doesn't assume it's disease related. It is possible to trick the brain, and by exercising often the muscle twitches you experience will not be as worrisome.
Does myoclonus need treatment?
Treatment of myoclonus is most effective when a reversible underlying cause can be found that can be treated — such as another condition, a medication or a toxin.
Does myoclonus ever go away?
The condition usually appears in adults and can last indefinitely. People with palatal myoclonus may note a “clicking” sound in the ear when the muscles in the soft palate contract. This can be idiopathic or secondary to injury in the brain stem or adjacent cerebellum. Spinal myoclonus originates in the spinal cord.
What drugs can cause myoclonus?
The most frequently reported classes of drugs causing myoclonus include opiates, antidepressants, antipsychotics, and antibiotics.
How do you stop myoclonus jerks?
Anti-seizure drugs that treat epilepsy can relieve myoclonus. If a person experiences mild myoclonic seizures, which last for a few seconds, they may not need treatment. If medication is ineffective, a doctor may recommend Botox injections to relieve the muscle jerks, as Botox causes muscles to relax.
What triggers myoclonus?
Essential myoclonus occurs on its own, usually without other symptoms and without being related to any underlying illness. The cause of essential myoclonus is often unexplained (idiopathic) or, in some cases, hereditary.
What vitamin is good for seizures?
Nutrients that may reduce seizure frequency include vitamin B6, magnesium, vitamin E, manganese, taurine, dimethylglycine, and omega-3 fatty acids.
Can myoclonus lead to seizures?
Progressive myoclonic epilepsy (PME) is a group of rare conditions, rather than a single disorder. They cause myoclonic seizures and other seizure types, often GTC seizures.
Which Magnesium is best for seizures?
Most patients were well maintained on MgO 420 mg twice a day, or in 2 cases, Mg Lactate, without significant adverse effects, the most frequent being diarrhea (4/22). Discussion: These results suggest that oral Mg supplementation may prove to be a worthwhile adjunctive medication in treating drug intractable epilepsy.
What is myoclonus treatment?
Focal and segmental myoclonus, irrespective of its origin, may be treated with botulinum toxin injections, with variable success. Keywords: classification, clinical approach, myoclonus, treatment. Definition. Myoclonus is a movement disorder, which presents itself with sudden, brief, shock-like jerks.
What is the best treatment for myoclonus?
A single pharmacological agent rarely control myoclonus and therefore polytherapy with a combination of drugs, often in large dosages, is usually needed. Generally, antiepileptic drugs such as valproate, levetiracetam and piracetam are effective in cortical myoclonus, but less effective in other forms of myoclonus.
What is progressive myoclonic ataxia?
Progressive myoclonic ataxias, also known as Rumsey–Hunt syndrome, include conditions with prominent myoclonus and ataxia, but little in the way of epilepsy or progressive dementia. PMA include coeliac disease, some cases of mitochondrial diseases, vitamin E deficiency and some cases of Unverricht–Lundborg disease.
What is the most common form of myoclonus?
Cortical myoclonus is the most common form of myoclonus, seen in both outpatient and inpatient clinical settings. Cortical myoclonus mainly affects the distal upper limbs and face, which reflects the largest cortical representations of these body areas [Caviness, 2009].
What is myoclonus classified as?
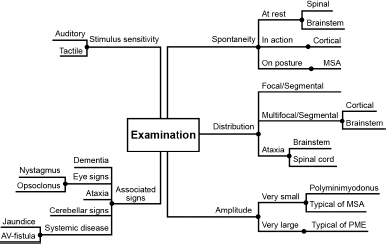
By distribution, myoclonus is classified as focal, multifocal or generalized and by provoking factors as spontaneous and reflex. Myoclonus can also be divided in cortical, subcortical, spinal or peripheral, based on the presumed source of its generation.
What is the first step in neurophysiology assessment of myoclonus?
Neurophysiologic assessment. Electrophysiology is very helpful to detect whether myoclonus is cortical, subcortical or spinal/segmental. Polymyography is the first step in the neurophysiologic assessment of myoclonus and includes recording of duration, distribution and stimulus sensitivity of muscle jerks.
What is the most practical classification of myoclonus?
Physiological classification of myoclonus is the most practical, since the presumed source of myoclonus (cortical, subcortical, spinal or peripheral) guides the physician towards the most effective treatment.
What tests can be done to diagnose myoclonus?
After an initial physical examination, a doctor also may request any of the following tests: electroencephalography (EEG) to record the electrical activity of the brain. MRI or CT scan to determine whether structural problems or tumors are present.
What are the different types of myoclonus?
The following are some of the most common types: Action myoclonus is the most severe form. It may affect the arms, legs, face, and voice.
What causes myoclonus and seizures?
System degenerations cause action myoclonus, seizures, and irregular balance and walking. Reticular reflex myoclonus is a form of epilepsy that starts in the brain stem. Spasms usually affect the whole body, causing reactions with muscles on both sides.
How do you know if you have myoclonus?
One region of the body or all muscle groups can be affected. The nature of the symptoms will depend on the underlying condition. Typically, signs of myoclonus include jerks or spasms that are: unpredictable. sudden.
What is myoclonus muscle spasm?
What is myoclonus? Myoclonus is a sudden muscle spasm. The movement is involuntary and can’t be stopped or controlled. It may involve one muscle or a group of muscles. The movements may occur in a pattern or randomly. Myoclonus is usually a symptom of an underlying disorder rather than a condition itself.
Why does myoclonus cause muscle jerking?
The muscular jerking is made worse by attempts at controlled, voluntary movement. It’s often caused by a lack of oxygen or blood flow to the brain. Cortical reflex myoclonus originates in the outer layer of the brain tissue. It’s thought to be a form of epilepsy.
Can sleep myoclonus be treated?
Surprise may intensify the sensitivity of an affected person. Sleep myoclonus occurs as a person is falling asleep. Treatment may not be needed. However, it may indicate a more significant sleep disorder such as restless leg syndrome. Symptomatic (secondary) myoclonus is a common form.
