Medication
Self-care
Nutrition
What is the success rate of the measles vaccine?
One dose of MMR vaccine is 93% effective against measles, 78% effective against mumps, and 97% effective against rubella.
What are the chances of surviving measles?
Measles has a low death rate in healthy children and adults, and most people who contract the measles virus recover fully. The risk of complications is higher in the following groups: children under 5 years old. adults over 20 years old.
How effective is the measles virus?
Since then, widespread use of measles virus-containing vaccine has led to a greater than 99% reduction in measles cases compared with the pre-vaccine era.
Is measles easily treated?
There's no specific treatment for measles. Unlike bacterial infections, viral infections aren't sensitive to antibiotics. The virus and symptoms typically disappear in about two or three weeks. There are some interventions available for people who may have been exposed to the virus.
Is measles very serious?
Measles can be serious. Children younger than 5 years of age and adults older than 20 years of age are more likely to suffer from complications. Common complications are ear infections and diarrhea. Serious complications include pneumonia and encephalitis.
What was death rate of measles before vaccine?
Pre-vaccine era In the first decade of reporting, an average of 6,000 measles-related deaths were reported each year. In the decade before 1963 when a vaccine became available, nearly all children got measles by the time they were 15 years of age.
Do measles still exist?
As of April 2019, there have been 695 cases of measles reported in 22 states. This is the highest number of measles cases since it was declared eradicated in 2000. From 1 January, to 31 December 2019, 1,282 individual cases of measles were confirmed in 31 states.
How effective was the first measles vaccine?
One dose is about 93% effective while two doses of the vaccine are about 97% effective at preventing measles.
Why measles is coming back?
The director of the National Institutes of Health wrote in 2016 that parents refusing to vaccinate their children were leading to outbreaks of preventable diseases, including measles. The World Health Organization also reported that the rise in measles is a direct result of anti-vaccination movements.
What is the effective treatment for measles?
There is no specific treatment for measles, and symptoms usually go away within 7 to 10 days. If there are no complications, the doctor will recommend rest and plenty of fluids to prevent dehydration. If there is a risk of complications, the doctor may recommend spending time in the hospital.
Which drug can cure measles?
There's no specific treatment for a measles infection once it occurs. Treatment includes providing comfort measures to relieve symptoms, such as rest, and treating or preventing complications....Treatment for a measles infection may include:Fever reducers. ... Antibiotics. ... Vitamin A.
Can kids get Covid twice?
To be safe, all children with cold symptoms should stay home and isolate based on CDC criteria and get tested for COVID-19 as soon as possible. Can children get the virus twice in the same season? Yes, we have seen children with re-infections, though this still occurs rarely at this time.
Signs and Symptoms
Who Is at Risk?
Transmission
Treatment
Specialist to consult
Prevention
Measles Virus
- Unvaccinated young children are at highest risk of measles and its complications, including death. Unvaccinated pregnant women are also at risk. Any non-immune person (who has not been vaccinated or was vaccinated but did not develop immunity) can become infected. Measles is still common in many developing countries – particularly in parts of Africa and Asia. The overwhelmi…
Pathogenesis
- Measles is one of the world’s most contagious diseases. It is spread by coughing and sneezing, close personal contact or direct contact with infected nasal or throat secretions. The virus remains active and contagious in the air or on infected surfaces for up to 2 hours. It can be transmitted by an infected person from 4 days prior to the onset of the rash to 4 days after the r…
Clinical Features
- No specific antiviral treatment exists for measles virus. Severe complications from measles can be reduced through supportive care that ensures good nutrition, adequate fluid intake and treatment of dehydration with WHO-recommended oral rehydration solution. This solution replaces fluids and other essential elements that are lost through diarrhoea or vomiting. Antibiot…
Epidemiology
- Routine measles vaccination for children, combined with mass immunization campaigns in countries with high case and death rates, are key public health strategies to reduce global measles deaths. The measles vaccine has been in use for nearly 60 years. It is safe, effective and inexpensive. It costs approximately one US dollar to immunize a child against measles. The mea…
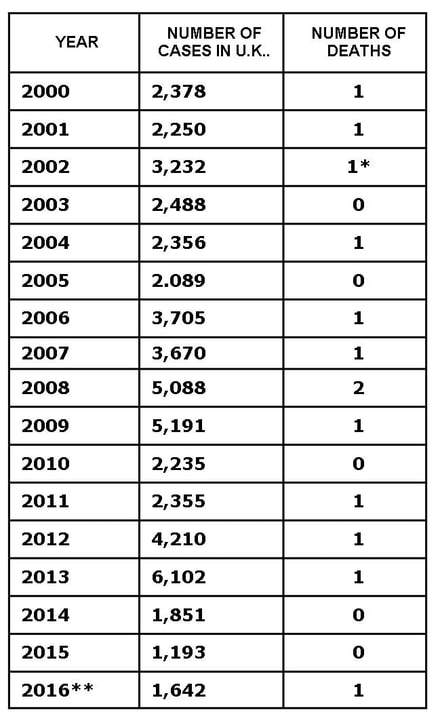
Secular Trends in The United States
Measles Vaccine
Vaccination Schedule and Use
- If you or your child has measles, keep in touch with your doctor as you monitor the progress of the disease and watch for complications. Also try these comfort measures: 1. Take it easy.Get rest and avoid busy activities. 2. Sip something.Drink plenty of water, fruit juice and herbal tea to replace fluids lost by fever and sweating. 3. Seek respira...
Contraindications and Precautions to Vaccination
Vaccine Safety
- Measles is a systemic infection. The primary site of infection is alveolar macrophages or dendritic cells. Two to three days after replication in the lung, measles virus spreads to regional lymphoid tissues followed by a systemic infection. Following further viral replication in regional and distal reticuloendothelial sites, a second viremia occurs 5 to 7 days after initial infection. During this p…
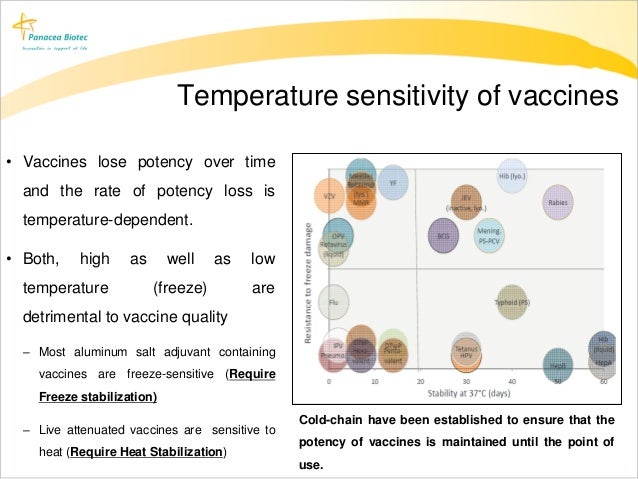
Vaccine Storage and Handling
- The incubation period of measles from exposure to prodrome averages 11 to 12 days. The time from exposure to rash onset averages 14 days, with a range of 7 to 21 days. The prodrome lasts 2 to 4 days, with a range of 1 to 7 days. It is characterized by fever, which increases in a stepwise fashion often peaking as high as 103°F to 105°F, cough, coryz...