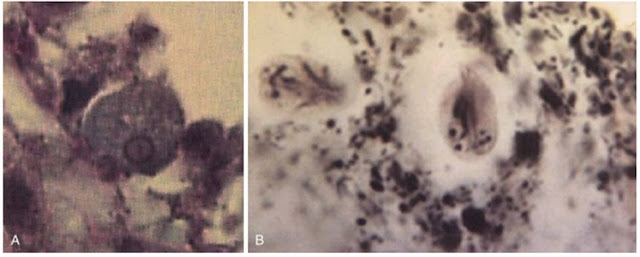
Options for protozoa and amoeba in drinking water Unlike most waterborne pathogens, such as bacteria and enteric viruses, Cryptosporidium and Giardia oocysts and cysts are very resistant to chlorine disinfection, which is commonly used to treat surface and ground waters.
What is the importance of protozoa in wastewater treatment?
Aug 23, 2019 · Options for protozoa and amoeba in drinking water Unlike most waterborne pathogens, such as bacteria and enteric viruses, Cryptosporidium and Giardia oocysts and cysts are very resistant to chlorine disinfection, which is commonly used to …
Which protozoa can survive chlorine disinfection?
Mar 12, 2018 · Cryptosporidium is one of the most resistant microorganisms in the water. According to the published data, the inactivation of Cryptosporidium has not been observed even after 18-h contact with 1.05% and 3% chlorine [ 34, 52, 53, 54 ].
What are the best books on protozoa and water industry?
Protozoa - Giardia intestinalis (also known as Giardia lamblia) Bacteria - (for example, Campylobacter, Salmonella, Shigella, E. coli) Viruses - (for example, enterovirus, hepatitis A, norovirus, rotavirus) Things to Remember When visiting places with unknown water quality, you may need to treat water to make sure it is safe to drink.
What are protozoa and why are they in my water?
* Toxoplasma and Cryptosporidium oocysts are highly resistant to chlorine disinfection. Chlorine alone should not be expected to inactivate these pathogens in drinking water. Filtering water supplies with a 1 micron absolute filter is recommended to physically remove the oocysts before chlorination if these pathogens are of concern.
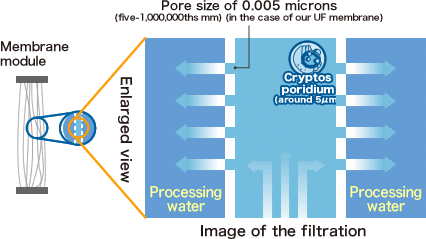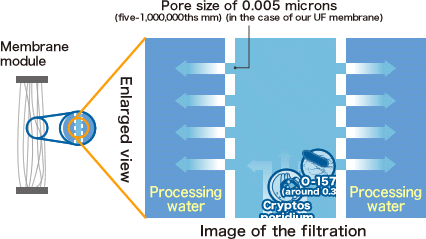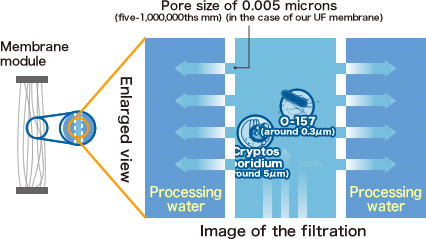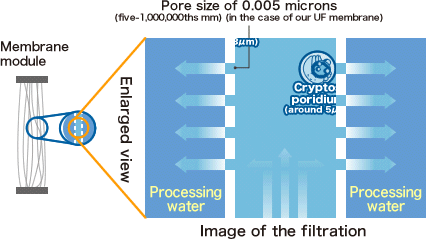
Which protozoa is resistant to chlorine?
CryptosporidiumToxoplasma and Cryptosporidium oocysts are highly resistant to chlorine disinfection. Chlorine alone should not be expected to inactivate these pathogens in drinking water.
Is protozoa resistant to disinfection?
Microbes, however, differ greatly in their sensitivity to disinfectants. Specific protozoa, viruses and bacteria are known to be highly resistant to chemical agents and pose a unique challenge to the water treatment industry.Apr 15, 2002
Which is the protozoa found in polluted water?
The pathogenic protozoan parasites, Cryptosporidium and Giardia, are significant microbial contaminants in the U.S. and have been found in surface waters and filtered drinking water supplies.Aug 23, 2019
Why are protozoa resistant to chlorine?
Protozoan cysts and oocysts are bigger than bacteria or viruses. They have a hard shell that helps them survive a long time in the environment and protects them against chlorine.
What microorganisms are most resistant to disinfectants?
7-9 The most resistant to disinfectants are believed to be the prions,” followed by coccidia, with bacterial spores and mycobacteria being the most resistant types of bacteria (Fig. l).
Is Giardia a protozoan?
Causal Agent. Giardia duodenalis is a protozoan flagellate (Diplomonadida). This protozoan was initially named Cercomonas intestinalis by Lambl in 1859. It was renamed Giardia lamblia by Stiles in 1915 in honor of Professor A.
What are 2 examples of protozoa?
Examples of protozoa are Amoeba, Paramoecium, Trypanosoma, Plasmodium, etc.
What is protozoa in drinking water?
Protozoa are a diverse group of microorganisms. Most are free-living organisms that can reside in fresh water and pose no risk to human health. Some enteric protozoa are pathogenic and have been associated with drinking water related outbreaks. The main protozoa of concern in Canada are Giardia and Cryptosporidium.Oct 28, 2016
What are 3 types of protozoa?
Protozoa are divided into four major groups based on the structure and the part involved in the locomotion:Mastigophora or Flagellated protozoans: They are parasites or free-living. ... Sarcodina or Amoeboids: They live in the freshwater, sea or moist soil. ... Sporozoa or Sporozoans: ... Ciliophora or Ciliated protozoans:
Which is waterborne infection caused by protozoan?
The waterborne parasites Giardia lamblia, Naegleria fowleri, Acanthamoeba spp., Entamoeba histolytica, Cryptosporidium parvum, Cyclospora cayetanesis, Isospora belli, and the microsporidia are reviewed.Jan 1, 1997
How can protozoa be detected in water?
The most widely used method for detecting protozoans has been the indirect immunofluorescent assay. While Method 1623 has improved upon the utility of the immunofluorescent assays for Giardia and Cryptosporidium, the procedure is still labor intensive and highly dependent on the skill of the microscopist.
What kills protozoan cysts?
Protozoan cysts have been removed up to 90%–95% by the application of polyelectrolyte coagulant.
What is the best way to kill pathogens in drinking water?
If boiling water is not possible, a combination of filtration and chemical disinfection is the most effective pathogen reduction method in drinking water for backcountry or travel use. Manufacturer’s instructions must be followed. Other treatment methods can be effective against some of the above pathogens: Ultraviolet Light (UV Light) can be used ...
How effective is boiling for removing cryptosporidium?
Boiling (Rolling boil for 1 minute) has a very high effectiveness in killing Cryptosporidium; Filtration has a high effectiveness in removing Cryptosporidium when using an absolute less than or equal to 1 micron filter (NSF Standard 53 or 58 rated “cyst reduction / removal” filter);
What are the factors that affect the effectiveness of disinfecting?
However, contact time, disinfectant concentration, water temperature, water turbidity (cloudiness), water pH, and many other factors can impact the effectiveness of chemical disinfection.
How long should you boil water to kill pathogens?
Boiling can be used as a pathogen reduction method that should kill all pathogens. Water should be brought to a rolling boil for 1 minute. At altitudes greater than 6,562 feet (greater than 2000 meters), you should boil water for 3 minutes.
What is the best way to kill giardia?
Methods that may remove some or all of Giardia from drinking water are: Boiling (Rolling boil for 1 minute) has a very high effectiveness in killing Giardia;
What are the health effects of drinking water contaminated with bacteria?
Potential health effects from ingestion of water contaminated with bacteria are: Gastrointestinal illness (for example, diarrhea, vomiting, cramps). Sources of bacteria in drinking water are: Human and animal fecal waste. Methods that may remove some or all of bacteria from drinking water are:
Does Miox use chlorine?
Manufacturer’s instructions must be followed. MIOX® systems use a salt solution to create mixed oxidants, primarily chlorine. Chlorine has a low to moderate effectiveness in killing Giardia, and a high effectiveness in killing bacteria and viruses. Manufacturer’s instructions must be followed.
Is cyst removal a barrier to protozoa?
These studies have demonstrated that protozoan cyst removal throughout all stages of the conventional treatment is largely influenced by the effectiveness of coagulation pretreatment, which along with clarification constitutes the first treatment barrier against protozoan breakthrough.
Is there a treatment for giardia in drinking water?
Drinking water treatment processes for removal of Cryptosporidium and Giardia. Major waterborne cryptosporidiosis and giardiasis outbreaks associated with contaminated drinking water have been linked to evidence of suboptimal treatment. Cryptosporidium parvum oocysts are particularly more resistant than Giardia lamblia cysts to removal ...
What is the role of protozoa in aquatic ecosystems?
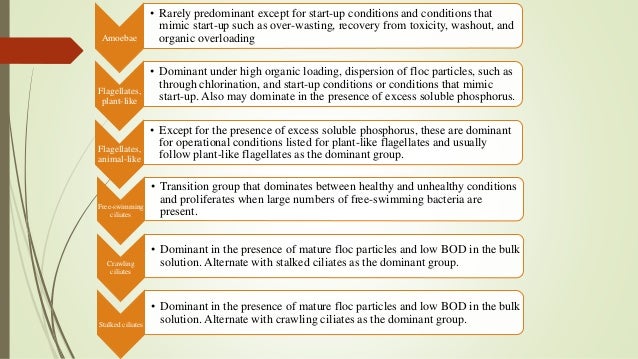
Protozoa not only play an important ecological role in the self-purification and matter cycling of natural ecosystems, but also in the artificial system of sewage treatment plants.
What are protozoans used for?
Protozoans are valuable indicators of the wastewater biological treatment process and are used in a variety of water resource recovery facilities (WRRF). The aim of this study was to determine the applicability of the Sludge Biotic Index (SBI) as an indicator of activated sludge purification efficiency during different influent loadings: municipal wastewater (M) and municipal wastewater combined with industrial wastewater from a sugar refinery (M + S). Despite the higher organic load during the M + S period, purification efficiency was higher for BOD5, compared with the M period. SBI values were high during both periods, indicating stable sludge, excellent biological activity, and good to very good performance. According to the share of indicator taxa, better conditions of activated sludge were found during the M + S period. Protozoan abundance differed between the two study periods, as well as purification efficiency for some parameters. Certain taxa showed a significant correlation with purification efficiency for specific parameters. Although SBI is a useful tool for estimating activated sludge health, it should be used in combination with additional indicator metrics and/or a species‐specific approach. Practitioner points • Activated sludge can have high purification efficiency during the co‐treatment of industrial and municipal wastewater. • The Sludge Biotic Index is applicable as an indicator of activated sludge condition during the treatment of municipal and sugar refinery wastewaters. • A combination of indicators and a species‐specific approach can give better estimation of the health of activated sludge.
What is the colonization of surfaces by bacteria?
colonization o f surfaces by bacteria is a widespread p rocess in the environment. In natural biotopes, bacteria favor the colonization of suspended particles and. sediment. By far the majority (99 %) of all bacteria in the environment adhere. to surfaces such as stones, sedimen t, and soil.
What is wastewater treatment?
Wastewater treatment process is designed in a manner to allow the process of natural breakdown of pollutants in controlled conditions. The physical and chemical processes include removal of solids materials. The one method which all wastewater treatment processes have in common is the biological method. This process relies on the use of some microorganisms to convert organic contaminants into environmentally beneficial product. A wastewater treatment plant itself is a microbial zoo containing bacteria, protozoa, metazoa, and various micro life. During the course of their processing in wastewater treatment plant, the amount and share of the microbial community in wastewater will continue to change. The type of technology used for wastewater treatment significantly affects the microbial content of treated wastewater.
How much of the eukaryotic biomass is made up of protozoa?
protozoa made up over 90 % of the total eukaryotic biomass of two municipal. wastewater treatment plants. Acc ording to Aescht and Foissner [61], protozoa. made up 99 – 100 % of the eukaryotes in a pharmaceutical plant with a bacterial. nutrient load.
Is sludge biosolids safe for agriculture?
Sludge biosolids for agricultural application represent a valuable fertilizer but also a health risk unless pathogens are effectively reduced, and recontamination controlled. The Post Anaerobic Digestion Thermal Hydrolysis Process (Post-AD THP) is gaining interest due to improved dewaterability, reducing the volume and thus transportation costs of biosolids. However, Post-AD THP results in sterile biosolids easily exposed to recontamination by pathogens due to the lack of microbial competitors. In theory, this could be suppressed by establishing a competing community of harmless bacteria. The theory was tested by monitoring the abundance of Escherichia coli (viable counts) and gene abundance (ddPCR) in wastewater recontaminated Post-AD THP biosolids, with and without addition of compost. Respiration, total bacterial population and bacterial diversity (16S rRNA amplicon sequencing) were used to monitor the microbial community. Biosolids from the regulatory approved methods thermophilic AD (TAD) and Pre-AD THP were tested in parallel for comparison. The results demonstrated that regulatory requirements can be reached by storing the TAD and Pre-AD THP biosolids for 3 days after recontamination and the Post-AD THP biosolids for more than 13 days. However, addition of compost suppressed growth of E. coli in Post-AD THP biosolids, reducing the time to comply with regulative requirements. In conclusion, pathogen growth in Post-AD THP biosolids can be controlled by inoculation with compost. Graphical abstract