Nutrition
- Mild cases. The guidelines suggested that patients who have mild cases of Covid-19 to isolate themselves, monitor their temperature and oxygen saturation level and stay in contact of a physician.
- Moderate cases. The guidelines said that patients suffering from moderate cases of the disease should be admitted to a hospital.
- Severe cases. ...
What medications are used to treat tuberculosis?
Treatment of tuberculosis with antibiotics
- Antibiotics for tuberculosis in adults. ...
- Antibiotic effective in the treatment of tuberculosis. ...
- Sensitivity of tuberculosis to antibiotics. ...
- Titles. ...
- Antibiotics for the prevention of tuberculosis. ...
- Antibiotics for pulmonary tuberculosis. ...
What antibiotic is used for TB treatment?
They include:
- Antibiotics called fluoroquinolones
- An injectable antibiotic, such as amikacin ( Amikin ), and streptomycin
- Newer antibiotic treatments, such as bedaquiline ( Sirturo ), ethionamide ( Trecator ), and para-amino salicylic acid. These are given in addition to other medications. ...
What antibiotics are used to treat tuberculosis?
With latent TB:
- You cannot spread TB to other people.
- In some people, the bacteria can become active. If this happens, you may become sick, and you can pass the TB germs to someone else.
- Even though you do not feel sick, you need to take medicines to treat latent TB for 6 to 9 months. ...
Why should I take antibiotics for TB?
What is isoniazid used for?
How to take antacids?
Does isoniazid work for viral infections?
About this website
What are the side effects of INH?
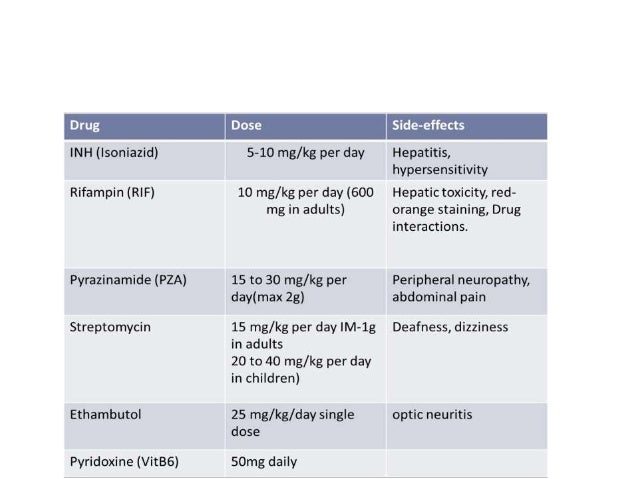
What Are Side Effects of Isoniazid?numbness and tingling in the extremities,hepatitis (symptoms include loss of appetite, nausea, vomiting, fatigue, malaise, and weakness),nausea,vomiting,upset stomach,fever, or.rash.
How long do you take INH for TB?
If you have TB infection, you will probably just take INH (Isoniazid) for 6 to 9 months, or you may take INH and Rifapentine (RPT) for 3 months. Together, you and your doctor will decide which medicine is right for you.
What is INH solution?
Isoniazid is used with other medications to treat active tuberculosis (TB) infections. It is also used alone to prevent active TB infections in people who may be infected with the bacteria (people with positive TB skin test). Isoniazid is an antibiotic and works by stopping the growth of bacteria.
How is INH taken?
The ideal time to take your tablets each day is half an hour before breakfast. If you forget, then take the tablets two hours after breakfast or wait until half an hour before your next meal. This is because isoniazid is absorbed better when your stomach is empty.
Can isoniazid cause liver damage?
Even with monitoring, isoniazid remains a major cause of acute liver failure due to idiosyncratic reactions, and is associated with several instances of acute liver failure and death or emergency liver transplanation in the United States each year.
Does INH cure latent TB?
As of 2018, there are four CDC-recommended treatment regimens for latent TB infection that use isoniazid (INH), rifapentine (RPT), and/or rifampin (RIF). All the regimens are effective.
What does INH stand for?
InhAcronymDefinitionInhI Need HelpInhInstitute for Nutrisciences and Health (Canada)InhInheems (Dutch)InhInfectious Necrotic Hepatitis8 more rows
What is full name INH?
Isoniazid, also known as isonicotinic acid hydrazide (INH), is an antibiotic used for the treatment of tuberculosis. For active tuberculosis it is often used together with rifampicin, pyrazinamide, and either streptomycin or ethambutol.
Can isoniazid cause seizures?
The ingestion of toxic amounts of isoniazid causes recurrent seizures, profound metabolic acidosis, coma and even death. In adults, toxicity can occur with the acute ingestion of as little as 1.5 g of isoniazid. Doses larger than 30 mg per kg often produce seizures.
What are the black box warnings of INH?
A recent report suggests an increased risk of fatal hepatitis associated with isoniazid among women, particularly black and Hispanic women. The risk may also be increased during the post partum period. More careful monitoring should be considered in these groups, possibly including more frequent laboratory monitoring.
Can you drink while taking INH?
Avoid alcohol while taking isoniazid. Alcohol may increase the risk of damage to the liver during isoniazid treatment. Alcohol can also cause isoniazid side effects to get worse. Contact your doctor if you experience flushing, chills, headache, nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea.
What foods should be avoided while taking isoniazid?
Patients should be advised to avoid foods containing tyramine (e.g., aged cheese, cured meats such as sausages and salami, fava beans, sauerkraut, soy sauce, beer, or red wine) or histamine (e.g., skipjack, tuna, mackerel, salmon) during treatment with isoniazid.
How long should you take rifampin?
You must complete the full course of treatment (unless your doctor tells you otherwise), or your infection may come back. If you are taking rifampicin for TB, a course of treatment usually lasts for around six months.
Can latent TB be cured in 3 months?
A course of antibiotic medicine will treat latent TB. You may be given Rifampicin and Isoniazid for three months (which may be together in a tablet called Rifinah) or Isoniazid by itself for six months. Your doctor or TB specialist nurse will talk you through the treatment and answer any questions you may have.
What happens when you stop taking isoniazid?
Skipping doses may also increase your risk of further infection that is resistant to antibiotics. Isoniazid will not treat a viral infection such as the flu or a common cold. Your liver function may need to be checked every month while you are taking this medicine.
Why tuberculosis treatment is long?
A fundamental problem in the treatment of tuberculosis (TB) is the long duration of therapy required for cure. The recalcitrance of Mycobacterium tuberculosis (MTB) to eradication is thought to result from its achieving a nonreplicating (dormant) state in the host.
What You Need to Know About Your Medicine for Latent Tuberculosis ...
CS234967G National Center for HIV/AIDS, Viral Hepatitis, STD, and TB Prevention Division of Tuberculosis Elimination What You Need to Know About Your Medicine
Deciding When to Treat Latent TB Infection | Treatment | TB | CDC
People with latent TB infection do not have symptoms, and they cannot spread TB bacteria to others. However, if latent TB bacteria become active in the body and multiply, the person will go from having latent TB infection to being sick with TB disease.
List of drugs/medicine used for Tuberculosis (Tuberculosis)
View list of generic and brand names of drugs used for treatment of Tuberculosis(Tuberculosis ). You can find more information including dosage, side effects of the Tuberculosis(Tuberculosis ).
Tuberculosis (TB) - Treatment - NHS
Treatment for tuberculosis (TB) usually involves taking antibiotics for several months. While TB is a serious condition that can be fatal if left untreated, deaths are rare if treatment is completed.
Isoniazid Side Effects: Common, Severe, Long Term - Drugs.com
For Healthcare Professionals. Applies to isoniazid: intramuscular solution, oral syrup, oral tablet. General. The most commonly reported side effects included mild and transient elevation of serum transaminase levels, peripheral neuropathy, and hepatitis. [Nervous system
Tuberculosis - Diagnosis and treatment - Mayo Clinic
Treatment. If you have latent TB, your doctor might recommend treatment with medication if you're at high risk of developing active TB.For active tuberculosis, you must take antibiotics for at least six to nine months. The exact drugs and length of treatment depend on your age, overall health, possible drug resistance and where the infection is in your body.
How long does it take to treat TB?
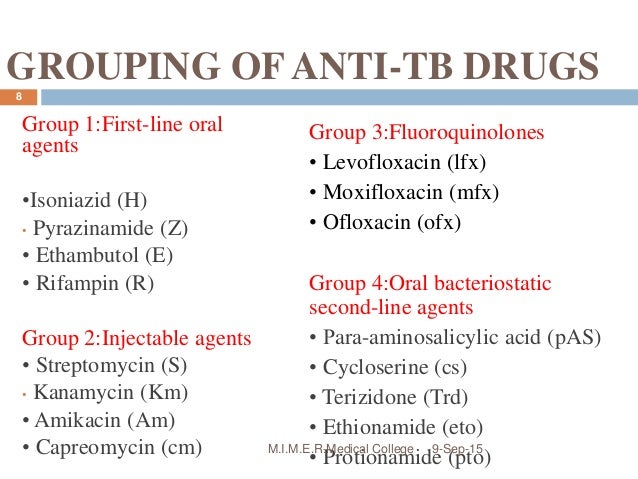
TB disease can be treated by taking several drugs for 6 to 9 months. There are 10 drugs currently approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for treating TB. Of the approved drugs, the first-line anti-TB agents that form the core of treatment regimens are: isoniazid (INH) rifampin (RIF)
What is it called when TB bacteria multiply?
When TB bacteria become active (multiplying in the body) and the immune system can’t stop the bacteria from growing, this is called TB disease. TB disease will make a person sick. People with TB disease may spread the bacteria to people with whom they spend many hours.
What is XDR TB?
Extensively drug-resistant TB (XDR TB) is a rare type of MDR TB that is resistant to isoniazid and rifampin, plus any fluoroquinolone and at least one of three injectable second-line drugs (i.e., amikacin, kanamycin, or capreomycin). Treating and curing drug-resistant TB is complicated.
Can TB be treated?
It is very important that people who have TB disease are treated, finish the medicine, and take the drugs exactly as prescribed. If they stop taking the drugs too soon, they can become sick again; if they do not take the drugs correctly, the TB bacteria that are still alive may become resistant to those drugs.
How long do you have to take antibiotics for tuberculosis?
For active tuberculosis, you must take antibiotics for at least six to nine months. The exact drugs and length of treatment depend on your age, overall health, possible drug resistance and where the infection is in your body.
What test is used to test for tuberculosis?
The most commonly used diagnostic tool for tuberculosis is a skin test, though blood tests are becoming more commonplace. A small amount of a substance called tuberculin is injected just ...
How long does ethambutol last?
If you have drug-resistant TB, a combination of antibiotics called fluoroquinolones and injectable medications, such as amikacin or capreomycin (Capastat), are generally used for 20 to 30 months. Some types of TB are developing resistance to these medications as well.
What is the test for TB?
Sputum tests. If your chest X-ray shows signs of tuberculosis, your doctor might take samples of your sputum — the mucus that comes up when you cough. The samples are tested for TB bacteria. Sputum samples can also be used to test for drug-resistant strains of TB.
Can a TB test be wrong?
Results can be wrong. The TB skin test isn't perfect. Sometimes, it suggests that people have TB when they don't. It can also indicate that people don't have TB when they do. You can have a false-positive result if you've been vaccinated recently with the bacille Calmette-Guerin (BCG) vaccine.
Can TB drugs cause liver damage?
Serious side effects of TB drugs aren't common but can be dangerous when they do occur. All tuberculosis medications can be toxic to your liver. When taking these medications, call your doctor immediately if you have any of the following:
What is the name of the drug that is used to treat TB?
Isoniazid (INH) Rifapentine (RPT) Rifampin (RIF) These medications are used on their own or in combination, as shown in the table below. CDC and the National Tuberculosis Controllers Association (NTCA) preferentially recommend short-course, rifamycin-based, 3- or 4-month latent TB infection treatment regimens over 6- or 9-month isoniazid ...
What should a clinic decide on TB treatment?
Clinicians should choose the appropriate treatment regimen based on drug susceptibility results of the presumed source case (if known), coexisting medical conditions (e.g., HIV. ), and potential for drug-drug interactions. Consultation with a TB expert is advised if the known source of TB infection has drug-resistant TB.
Is 6H or 9H better for TB?
Although effective, 6H and 9H have higher toxicity risk and lower treatment completion rates than most short-term treatment regimens. All treatment must be modified if the patient is a contact of an individual with drug-resistant TB disease.
Is 3HP a short course?
Short-course treatment regimens, like 3HP and 4R, are effective, safe, and have higher completion rates than longer 6 to 9 months of isoniazid monotherapy (6H/9H). Shorter, rifamycin-based treatment regimens generally have a lower risk of hepatotoxicity than 6H and 9H.
Where is TB common?
From countries where TB is common, including Mexico, the Philippines, Vietnam, India, China, Haiti, and Guatemala, or other countries with high rates of TB. (Of note, people born in Canada, Australia, New Zealand, or Western and Northern European countries are not considered at high risk for TB infection, unless they spent time in a country ...
Why is latent TB important?
Treatment of latent TB infection is essential to controlling TB in the United States because it substantially reduces the risk that latent TB infection will progress to TB disease.
How many people have latent TB?
In the United States, up to 13 million people may have latent TB infection. Without treatment, on average 1 in 10 people with latent TB infection will get sick with TB disease in the future. The risk is higher for people with HIV, diabetes, or other conditions that affect the immune system.
What is a TST reaction?
People with a tuberculin skin test (TST) reaction of 5 or more millimeters who are: HIV-infected persons. Recent contacts to a patient with active TB disease. Persons with fibrotic changes on chest radiograph consistent with old TB. Organ transplant recipients.
Can TB be treated with LTBI?
Persons with no known risk factors for TB may be considered for treatment of LTBI if they have either a positive IGRA result or if their reaction to the TST is 15 mm or larger. However, targeted TB testing programs should only be conducted among high-risk groups.
Can TB spread to others?
People with latent TB infection do not have symptoms, and they cannot spread TB bacteria to others. However, if latent TB bacteria become active in the body and multiply, the person will go from having latent TB infection to being sick with TB disease.
How long does it take to treat TB in children?
Children over 2 years of age can be treated for latent TB infection with once-weekly isoniazid-rifapentine for 12 weeks. Alternative treatments for latent TB infection in children include 4 months of daily rifampin or 9 months of daily isoniazid.
Why is treatment recommended for children with latent TB?
Treatment is recommended for children with latent TB infection to prevent them from developing TB disease. Infants, young children, and immunocompromised children with latent TB infection or children in close contact with someone with infectious TB disease, require special consideration because they are at increased risk for getting TB disease.
How long does it take for TB to go away?
TB disease is treated by taking several anti-TB medicines for 6 to 9 months. It is important to note that if a child stops taking the drugs before completion, the child can become sick again. If drugs are not taken correctly, the bacteria that are still alive may become resistant to those drugs.
Why is TB so common in adults?
In comparison to children, TB disease in adults is usually due to past TB infection that becomes active years later, when a person’s immune system becomes weak for some reason (e.g., HIV infection, diabetes).
Can children take TB medicine?
It is very important that children or anyone being treated for latent TB infection or TB disease take the drugs exactly as instructed by the doctor and finish the medicine.
How to treat latent TB?
Go to your planned clinic visits. Discuss any alcohol use with your doctor. Alcohol use may cause side effects. Tell your doctor about all other medicines you are taking. Be sure to tell your other doctors that you are being treated for latentTB infection.
How to take a pill?
Tips to Help You Take Your Medicine: 1 Take your medicine at the same time every day. 2 Set an alarm reminder for the time you should take your medicine. 3 Ask a family member or friend to remind you. 4 Use a pillbox. 5 Put a reminder note on your mirror or refrigerator. 6 Use a calendar to check off the day when you take your medicine.
What is isoniazid used for?
Isoniazid is an antibiotic that fights bacteria. Isoniazid is used to treat and to prevent tuberculosis (TB). You may need to take other TB medicines in combination with isoniazid. When treating active TB, isoniazid must be used with other TB medicines.
Can you drink alcohol while taking isoniazid?
Avoid drinking alcohol. It may increase your risk of liver damage while you are taking isoniazid. You may need to avoid certain foods while you are taking isoniazid. This includes red wine, aged cheese, dried meats, and tuna or other types of fish.
Can you take isoniazid if you have liver disease?
You should not use isoniazid if you have active liver disease, or if you have taken isoniazid in the past and it caused liver problems, fever, chills, joint pain, or severe allergic reaction.
Can Isoniazid be used for a viral infection?
Skipping doses may also increase your risk of further infection that is resistant to antibiotics. Isoniazid will not treat a viral infection such as the flu or a common cold.
Does isoniazid cause hives?
Isoniazid side effects. Get emergency medical help if you have signs of an allergic reaction ( hives, difficult breathing, swelling in your face or throat) or a severe skin reaction (fever, sore throat, burning in your eyes, skin pain, red or purple skin rash that spreads and causes blistering and peeling).
What is isoniazid used for?
Isoniazid is used with other medications to treat active tuberculosis (TB) infections. It is also used alone to prevent active TB infections in people who may be infected with the bacteria (people with positive TB skin test ). Isoniazid is an antibiotic and works by stopping the growth of bacteria.This antibiotic treats only bacterial infections. It will not work for viral infections (such as common cold, flu ). Using any antibiotic when it is not needed can cause it to not work for future infections.
How to take antacids?
Take this medication by mouth on an empty stomach (1 hour before or 2 hours after meals) as directed by your doctor. If you are using the liquid form of this medication, carefully measure the dose using a special measuring device/spoon. Do not use a household spoon because you may not get the correct dose. If you also take antacids that contain ...
Does isoniazid work for viral infections?
Isoniazid is an antibiotic and works by stopping the growth of bacteria.This antibiotic treats only bacterial infections. It will not work for viral infections (such as common cold, flu ). Using any antibiotic when it is not needed can cause it to not work for future infections.
