
What is DVT and how dangerous is it?
Deep vein thrombosis occurs when a clot in the leg or pelvis breaks off and reaches the heart. Once the clot has reached the heart, the blood flow is blocked to the lungs which causes a pulmonary embolism. A pulmonary embolism may cause shortness of breath, pain in the chest, or even death depending on the size of the clot.
What should you not do with a DVT?
- Unexpected bleeding or bleeding that lasts a long time, such as: Unusual bleeding from the gums Nosebleeds that happen often Menstrual or vaginal bleeding that is heavier than normal
- Bleeding that is severe or you cannot control
- Red, pink, or brown urine
- Red or black stools (looks like tar)
- Coughing up or vomiting blood
What does a DVT feel like?
Feeling like you have a pulled muscle. Pain when walking or standing. Leg tenderness. Redness or bluish tint to the affected area. The affected area may feel warm, tender and painful as well. Unlike a pulled muscle, which gets better over time, DVT symptoms worsen. You may feel like you have a charley horse, but again, it doesn ’t go away.
What does DVT stand for in medical terms?
Try these simple tips to keep your blood circulating the way it should:
- Take care of yourself. Stop smoking, lose weight, and get active.
- Get regular checkups. And if your doctor has prescribed a medicine to control a health problem, take it as directed.
- Don’t sit for too long. If you’re traveling for 4 hours or more, take breaks to flex and stretch your lower leg muscles. ...
- Plan surgery after-care. ...
What is DVT stage?
The DVT (Design Validation Testing) phase serves the need to validate the developed product's design and start to implement DFM (design for manufacturability) along with other DF-X rules.
What is the difference between DVT and PVT?
During EVT we validate a functional scope, during DVT we stabilize and during PVT we adapt the production. During the DVT phase on, the scope is no longer touched, but errors are corrected, elements are adjusted and performance is optimized.
What is Pvt testing?
The USP Performance Verification Test (PVT) assesses the suitable performance of apparatus used in dissolution testing. This assures reliability of dissolution results that reflects the quality of the drug product and not the condition of the test equipment.
What is DVT plan in integration testing?
DVT – Design Verification Testing: Design Verification Testing (DVT) is specific product verification tests performed to deliver objective, comprehensive testing verifying the following: All products specifications. Interface standards. OEM requirements. Diagnostic commands.
Is deep vein thrombosis serious?
DVT can be very serious because blood clots in your veins can break loose, travel through your bloodstream and get stuck in your lungs. This is called a pulmonary embolism. A pulmonary embolism can be life threatening and needs treatment straight away.
Is portal vein thrombosis curable?
Portal vein thrombosis is a serious condition. If caught early, PVT can be treatable with noninvasive procedures and treatment.
What does a PCR test tell you?
PCR means polymerase chain reaction. It's a test to detect genetic material from a specific organism, such as a virus. The test detects the presence of a virus if you have the virus at the time of the test. The test could also detect fragments of the virus even after you are no longer infected.
What EVT means?
EVT (Engineering Validation Test)
What is PVT and TVT?
PVT to mean Product Verification Testing. TVT to mean Translation Verification Testing.
What is stub and driver?
Stubs are basically known as a “called programs” and are used in the Top-down integration testing. While, drivers are the “calling program” and are used in bottom-up integration testing. 3. Stubs are similar to the modules of the software, that are under development process.
Do all PE come from DVT?
Articles On DVT & Pulmonary Emobolism A pulmonary embolism (PE) usually happens when a blood clot called a deep vein thrombosis (DVT), often in your leg, travels to your lungs and blocks a blood vessel. That leads to low oxygen levels in your blood. It can damage the lung and other organs and cause heart failure, too.
Is venogram and venography the same?
A venogram, also known as venography, is an x-ray exam that is performed to examine the health of the veins — typically in your legs. During a venogram, your doctor will inject a contrast dye into the vessels to examine how blood is flowing through your veins.
What is the difference between pulmonary embolism and thromboembolism?
Pulmonary embolism (PE) occurs when clots break off from vein walls and travel through the heart to the pulmonary arteries. The broader term venous thromboembolism (VTE) refers to DVT, PE, or to a combination of both.
Is a pulmonary embolism the same as a blood clot?
A pulmonary embolism (PE) is a blood clot that develops in a blood vessel elsewhere in the body (often the leg), travels to an artery in the lung, and suddenly forms a blockage of the artery.
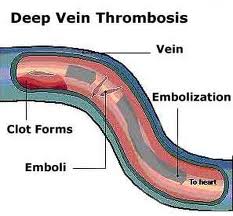
What is a DVT?
Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a condition in which a blood clot (thrombus) forms in one or more of the deep veins, usually in the legs. Blood clots can break free and travel with blood causing life-threatening condition like pulmonary embolism (PE) or a stroke due to paradoxical embolism in people with patent foramen ...
How to treat DVT?
reduce chances of repeated DVT. Deep vein thrombosis treatment options include: Anticoagulants (popularly called blood thinners): These drugs decrease blood’s ability to clot.
How tall is a VTE?
Short (height <1.6 m; 5 ft, 3 in) and very tall (height >1.9 m; 6 ft, 3 in) air passengers appear to be at an additional risk due to fixed seats, which cannot be adjusted to their height.
What is paradoxical embolism?
Paradoxical embolism is called a condition in which a travelling blood clot passes to the arterial circulation instead of being lodged or filtered out in pulmonary circulation.
What are the preexisting risks of DVT?
Pre-existing risks for DVT include: Estrogen use (hormonal contraceptives or hormone replacement therapy) Thrombophilia (an abnormally increased tendency to create clots ) Most individuals who developed travel-related VTE (75–99.5 percent) of those have more than one preexisting risk factor.
How long does it take for a venous thromboembolism to resolve?
Most air travel-related venous thromboembolism (VTE) occurs within the first two weeks after the flight and resolves within eight weeks. Many cases of DVT are asymptomatic and resolve spontaneously.
What are the symptoms of DVT?
Symptoms may include: Swelling in the affected leg, ankle and foot. Pain in calf that spreads to the ankle and foot. Warmth over the affected area. Skin color change to pale, red or blue.
What causes DVT in the body?
Damage to a vein from surgery or trauma and inflammation due to infection or injury are some of the most common causes of DVT.
What are the symptoms of DVT?
Physical indicators of DVT include swelling and inflammation of the lower leg and calf, redness, and warmth to the touch.
What is the term for a blood clot in the lower leg?
Deep venous thrombosis or deep vein thrombosis (DVT) occurs when a blood clot forms in one or more deep veins, usually in a person’s lower leg and thigh. The clot may interfere with circulation in this area, and it may break off and travel through the bloodstream, or embolize. The embolus could lodge in the brain, lungs, heart, or other areas, causing severe damage to that organ. When DVT breaks off and travels into a lung, it is called a pulmonary embolism (PE) and is often fatal.
What is it called when blood clots do not go away?
Eventually, a clot forms a protective scab over a healing wound. When this blood clot does not go away, it is called a thrombus. When clots are in the deep veins like that of the leg, a dangerous condition called deep vein thrombosis (DVT) can occur.
What is the term for a vein that is swollen and red?
Superficial venous thrombosis (SVT) occurs when the veins just below the skin of the legs, arms, or groin have minor clotting. The skin in these areas becomes red, swollen, or painful after a slight injury and may require treatment. However, these types of clots do not usually travel to the lungs unless they reach the deep veins.
What is the name of the vein that clots the skin below the skin?
Superficial venous thrombosis (SVT) occurs when the veins just below the skin of the legs, arms, or groin have minor clotting. The skin in these areas becomes red, swollen, or painful after a slight injury and may require treatment.
What are the two types of thrombosis?
Understanding how blood flows throughout the human body can help you differentiate between the two main types of thrombosis: venous thrombosis and arterial thrombosis.
How to get rid of DVT?
Do seated leg stretches. Raise and lower your heels while keeping your toes on the floor. Raise and lower your toes while keeping your heels on the floor. Tighten and release your leg muscles. If you’re at risk for a DVT, talk with your doctor about taking medication or wearing graduated compression stockings.
What happens if you leave a DVT untreated?
When a DVT is left untreated, a part of the clot can break off and travel to the lungs, causing a blockage called a pulmonary embolism (PE ). A PE can be deadly by preventing blood from reaching the lungs.
What happens when blood clots straddle the junction where the main pulmonary artery supplies blood to the?
This occurs when one or more blood clots straddle the junction where the main pulmonary artery, which supplies blood to the lungs, branches off into the right and left pulmonary arteries, causing right heart strain and, potentially, sudden death.
What are the risk factors for blood clots?
Other risk factors, such as limited movement due to extended travel or bed rest, a personal or family history of blood clots, or injury to a vein, can increase a person’s chance of developing a blood clot. Learn more about the risk factors.
How to get blood flow in legs?
Improve blood flow in your legs when sitting for long periods of time, following bed rest, or when traveling for more than 4 hours by moving your legs as much as possible and exercising your calf muscles. Get up and walk around every 2–3 hours if you are able to and if space allows. Do seated leg stretches.
Can a blood clot cause cancer?
Although anyone can be affected by a blood clot, certain risk factors, such as hospitalization, pregnancy, cancer, and some types of cancer treatments, can increase a person’s chance of developing one. Other risk factors, such as limited movement due to extended travel or bed rest, a personal or family history of blood clots, or injury to a vein, ...
Is it possible to get a blood clot early?
It’s important to be aware of the signs and symptoms of a blood clot so that you can alert your doctor or seek medical treatment immediately. If discovered early, a blood clot is treatable.
What are the risks of blood clots?
Some cancers pose a greater risk for blood clots, including cancers involving the pancreas, stomach, brain, lungs, uterus, ovaries, and kidneys. Certain blood cancers, such as lymphoma and myeloma, also increase risk. Treatments for these cancers involving hospitalization, surgery, chemotherapy, hormonal therapy, ...
What is the CDC's goal for blood clot awareness?
Since 2014, CDC has funded the National Blood Clot Alliance#N#external icon#N#(NBCA) to increase general awareness of blood clots by working to develop educational materials on the public health issue of VTE. In 2019, new content has focused on the risk for blood clots among people with cancer for a digital public health education campaign called Stop the Clot, Spread the Word®#N#external icon#N#. This campaign was one of many CDC resources recognized in 2017 as an important asset in a collection of VTE educational resources published by The Joint Commission.#N#pdf icon#N#[PDF – 3.24 MB]#N#external icon#N#The Commission accredits and certifies nearly 21,000 healthcare organizations in the United States.
What are the factors that increase the risk of blood clots?
Several other factors may also increase the risk for a blood clot in a person being treated for cancer, such as. Family history of blood clots or inherited clotting disorder. Hospitalization for illness or major surgery, particularly those involving the pelvis, abdomen, hip, or knee. Severe physical trauma, such as a motor vehicle accident.
How to protect yourself from blood clots?
Take Steps to Protect Yourself from Blood Clots During Your Cancer Treatment. Know the signs and symptoms of blood clots. Discuss your risks with your cancer doctor. A blood clot occurring in the legs or arms is called deep vein thrombosis (DVT). Signs and symptoms of a DVT include.
What states have VTE?
populations: 1) Oklahoma County, Oklahoma and 2) three Duke-affiliated hospitals.
What are the symptoms of a pulmonary embolism?
This is called a pulmonary embolism (PE), and can be life threatening. Signs and symptoms of a PE include. Difficulty breathing.
Is a blood clot preventable?
Related Pages. If you are currently being treated for cancer, it is important to know that you are at increased risk for developing a blood clot. The good news, though, is blood clots may be preventable and treated if discovered early.
What is a blood clot in the leg?
Know the Lingo About Blood Clots. Deep vein thrombosis (DVT): Blood clot located in a deep vein, usually in a leg or arm. Pulmonary embolism (PE): Blood clot that has traveled from a deep vein to a lung.
What are the symptoms of a blood clot?
Difficulty breathing. Faster than normal or irregular heartbeat. Chest pain or discomfort, which usually worsens with a deep breath or coughing. Coughing up blood. Very low blood pressure, lightheadedness, or fainting. What You Can Do to Prevent Death or Complications of a Blood Clot.
What are the factors that increase the risk of blood clots?
Some Factors Can Increase This Risk. Hospitalization and Surgery – One-half of blood clots occur during or soon after a hospital stay or surgery. Being Immobile – Not moving for long periods of time (for example, extended bed rest or extended travel). Other Risk Factors. Older age.
Can you have a blood clot before surgery?
Blood clots can be safely treated by your doctor. Before any surgery, talk with your doctor about blood clots. Tell your doctor if you have risk factors for blood clots. For more information, please visit: cdc.gov/ncbddd/dvt/index.html. Top of Page. Page last reviewed: February 7, 2020.
How old was Caroline Kelly when she had DVT?
Caroline Kelly, now a 33-year-old model and entrepreneur from San Diego, was a soccer-playing 19-year-old when she had DVT for the first time. Dana Pellegrino, a New York City-based lawyer, was 29 and worked out at least three times a week when it happened to her.
What happens if a blood clot doesn't dissolve?
Support helps. When you have a blood clot that hasn’t dissolved, the concern is that it will break off and travel to your heart or your lungs. The clots in McCartney’s arms were dangerously close to her heart. “Every night I kissed my son, not knowing whether I’d wake up the next day,” she says.
Can you get blood clots in your veins?
Blood clots may sound like a problem for older people or those who don’t get up and move around much. But potentially life-threatening clots that form in the veins deep within your body can happen to anyone. Even young and active people can get deep vein thrombosis (DVT). People who’ve had it have some things they want you to know:
Did Caroline Kelly have a clotting disorder?
Still, 3 years after her first clot, she took a long flight to Hawaii and had another clot. Caroline Kelly. Though she doesn’t have a clotting disorder , thicker blood runs in her family.
Does smoking cause blood clots?
Smoking can interfere with circulation and raise the risk for blood clots. Jones, the personal trainer, also learned she had an inherited clotting disorder, thrombophilia, which causes the blood to clot unnecessarily. Birth control that uses hormones to prevent pregnancy, such as the pill, can raise your risk too.
Can a doctor check for DVT?
Doctors might not check for DVTs at first, especially in people who are young and healthy. Doctors might think your symptoms are caused by something else. Both Kelly and Pellegrino were sent home the first time they went to see a doctor about the leg pain they later learned was a DVT clot.
Where is DVT most commonly found?
Are you at an increased risk for deep vein thrombosis (DVT?) What exactly is a deep vein thrombosis? At its most basic definition, a DVT is a blood clot or thrombus that forms in a deep vein in the body, most commonly in the lower extremities like the calf or the thigh.
Why do blood clots form?
Blood clots may form when blood flow moves too slowly through the veins due to plaque buildup, hardening of the arteries, injury, or long periods of immobility. A blood clot like a DVT can contribute to dangerous health issues, and sometimes, even death.
Why does dehydration cause blood clots?
Adequate amounts of water consumed on a daily basis keeps blood thinner and moving through the circulatory system. Dehydration adds to the thick ness or viscosity of blood, so it takes longer and has to work harder to make its way through the arteries and veins.
What triggers the body's responses in forming a clot to stop bleeding and start healing processes?
Injury to a vein or any blood vessel – which automatically triggers the body’s responses in forming a clot to stop bleeding and start healing processes
Where does a blood clot get stuck?
Unfortunately, that clot can get stuck anywhere along the way, most commonly in a pulmonary vein (inside the lung), where it is now known as a pulmonary embolism (PE).
What is the D-dimer in blood?
One of those leftovers is called D-dimer. It’s part of a protein. Normally, with a little time, it goes away. But you can get high levels of D-dimer in your blood if you have a major clot like with deep vein thrombosis ( DVT ). With DVT, you have a clot deep in one of your veins, usually in your legs, and it can lead to serious problems.
What is DIC test?
To test for Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation:D-dimer can also be used to help test for what’s called disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC), in which blood clots form in small blood vessels throughout your body while also causing bleeding. It can be life-threatening.
What is a PE in a pulmonary embolism?
Pulmonary embolism, or PE, a blood clot that has traveled to your lungsthat may lead to trouble breathing, fast heartbeat, pain in your chest, and coughing
Why do you need a D-dimer test?
To rule out DVT and other conditions: The D-dimer test is most useful when your doctor thinks something else is causing your symptoms and wants to quickly rule out these causes: DVT, which may give you swelling, pain, or redness in your leg.
Can a positive D-dimer test show a blood clot?
In this case, the test is only helpful if you’re not too likely to have blood clots. A positive D-dimer test doesn’t mean you have a blood clot. Other tests will be needed to check for that. If your odds of having a clot are higher, you’ll need different tests. You have higher odds of a clot with:

Why Are People with Cancer at Risk For Developing A Blood clot?
- Some cancers pose a greater risk for blood clots, including cancers involving the pancreas, stomach, brain, lungs, uterus, ovaries, and kidneys. Certain blood cancers, such as lymphoma and myeloma,...
- Treatments for these cancers involving hospitalization, surgery, chemotherapy, hormonal therapy, and catheters (small tubes placed in veins to administer treatments) may also incre…
- Some cancers pose a greater risk for blood clots, including cancers involving the pancreas, stomach, brain, lungs, uterus, ovaries, and kidneys. Certain blood cancers, such as lymphoma and myeloma,...
- Treatments for these cancers involving hospitalization, surgery, chemotherapy, hormonal therapy, and catheters (small tubes placed in veins to administer treatments) may also increase your risk for...
Take Steps to Protect Yourself from Blood Clots During Your Cancer Treatment
- Know the signs and symptoms of blood clots. Discuss your risks with your cancer doctor.
- A blood clot in the legs or arms can break off and travel to the lungs. This is called a pulmonary embolism (PE), and can be life threatening. Signs and symptoms of a PE include
- Talk with your cancer doctor and other healthcare providers about factors that might increase your risk for a blood clot. Let them know if you or anyone else in your family has ever had a bl…
- Know the signs and symptoms of blood clots. Discuss your risks with your cancer doctor.
- A blood clot in the legs or arms can break off and travel to the lungs. This is called a pulmonary embolism (PE), and can be life threatening. Signs and symptoms of a PE include
- Talk with your cancer doctor and other healthcare providers about factors that might increase your risk for a blood clot. Let them know if you or anyone else in your family has ever had a blood clot.
CDC’s Work in Blood Clots and Cancer
- In 2018, CDC funded the Association of University Centers on Disabilities (AUCD) to determine the number of people with cancer newly diagnosed with VTE in two U.S. populations: 1) Oklahoma County, Oklahoma and 2) three Duke-affiliated hospitals. AUCD provided funding to researchers at Duke University and the University of Oklahoma Health Science Center to evaluate, analyze, and …
Campaign Video
- This video shares important information about blood clot signs and symptoms, as well as the risk factors for blood clots for people who are being treated for cancer.