
What are the symptoms of Stage 1 cervical cancer?
Signs and symptoms of stage 1 cervical cancer can include:Watery or bloody vaginal discharge that may be heavy and can have a foul odor.Vaginal bleeding after intercourse, between menstrual periods or after menopause.Menstrual periods may be heavier and last longer than normal.
How do u know if u have cervical cancer?
Signs of advanced cervical cancer may include pelvic pain, problems peeing, and swollen legs. If the cancer has spread to your nearby organs, it can affect how those organs work too. For example, a tumor might press on your bladder and make it feel like you have to pee more often.
What happens to your body when you have cervical cancer?
Cervical cancer happens when cells change in women's cervix, which connects the uterus and vagina. This cancer can affect the deeper tissues of their cervix and may spread to other parts of their body (metastasize), often the lungs, liver, bladder, vagina, and rectum.
What is the best cure for cervical cancer?
Surgery to remove the cervix and uterus (hysterectomy). Most early-stage cervical cancers are treated with a radical hysterectomy operation, which involves removing the cervix, uterus, part of the vagina and nearby lymph nodes. A hysterectomy can cure early-stage cervical cancer and prevent recurrence.
What is cervical cancer pain like?
Low Back, Pelvic or Appendix Pain A sign of cervical cancer is pelvic pain, especially continuous pain. Pelvic pain near the appendix doesn't usually occur unless the cancer is in advanced stages. There will usually be other cervical cancer red flags before pelvic pain occurs.
What is the main cause of cervical cancer?
Nearly all cervical cancers are caused by an infection with certain high-risk types of human papillomavirus (HPV). You can get HPV from: any skin-to-skin contact of the genital area. vaginal, anal or oral sex.
Does cervical cancer stop your periods?
Typically, the initial symptoms develop in tissues and organs in the pelvic region, near where the cancer originated. For instance, some noticeable signs of advanced cervical cancer include: Vaginal bleeding or spotting that occurs between menstrual periods or after menopause. Unusually heavy or irregular menstruation.
How long can you have cervical cancer without knowing?
How quickly does cervical cancer develop? Cervical cancer develops very slowly. It can take years or even decades for the abnormal changes in the cervix to become invasive cancer cells. Cervical cancer might develop faster in people with weaker immune systems, but it will still likely take at least 5 years.
Can cervical cancer go away on its own?
Cervical cancer is caused by certain types of the human papillomavirus (HPV), the most common STD. There are more than 200 kinds of HPV. Most of them aren't harmful and go away on their own. But at least a dozen types of HPV can last and sometimes lead to cancer.
How do they remove cervical cancer?
The procedure can be done in different ways: Using a surgical blade (cold knife cone biopsy) Using a laser beam (laser conization) Using a thin wire heated by electricity (the loop electrosurgical excision procedure, LEEP or LEETZ procedure).
How can you test for cervical cancer at home?
Women will be provided an at-home HPV screening kit that includes a tiny brush to swab the vagina to collect cells and a specimen container to mail the swab back to the testing facility. The study, which will be run by the NCI, will assess if the at-home test is comparable to a screening performed in a doctor's office.
Can you feel cervical cancer with your finger?
Dysplasia and cancer of the cervix The cervix can be felt with the tip of a finger inside the vagina. In cervical dysplasia, abnormal cells develop on the surface of the cervix. These abnormal cells are called lesions.
What is cervical cancer?
Cervical cancer is a type of cancer that occurs in the cells of the cervix — the lower part of the uterus that connects to the vagina. Various strains of the human papillomavirus (HPV), a sexually transmitted infection, play a role in causing most cervical cancer. When exposed to HPV, the body's immune system typically prevents ...
How to reduce cervical cancer risk?
Reduce your risk of cervical cancer by taking measures to prevent sexually transmitted infections, such as using a condom every time you have sex and limiting the number of sexual partners you have. Don 't smoke. If you don't smoke, don't start. If you do smoke, talk to your doctor about strategies to help you quit.
How does cervical cancer start?
Cervical cancer begins when healthy cells in the cervix develop changes (mutations) in their DNA. A cell's DNA contains the instructions that tell a cell what to do.
What type of cancer is squamous cell carcinoma?
Types of cervical cancer. The type of cervical cancer that you have helps determine your prognosis and treatment. The main types of cervical cancer are: Squamous cell carcinoma. This type of cervical cancer begins in the thin, flat cells (squamous cells) lining the outer part of the cervix, which projects into the vagina.
What are the risk factors for cervical cancer?
Risk factors for cervical cancer include: Many sexual partners. The greater your number of sexual partners — and the greater your partner's number of sexual partners — the greater your chance of acquiring HPV. Early sexual activity. Having sex at an early age increases your risk of HPV.
What are the two types of cells that line the surface of the cervix?
Two types of cells line the surface of the cervix, and both can become cancerous. One type (glandular cells) has a column-shaped appearance. The other type (squamous cells) is thin and flat. The boundary between the two types of cells is where cervical cancer most commonly occurs.
Does cervical cancer show symptoms?
Early-stage cervical cancer generally produces no signs or symptoms.
How do you know if you have cancer?
When this happens, the most common symptoms are: Abnormal vaginal bleeding, such as bleeding after vaginal sex, bleeding after menopause, bleeding and spotting between periods, or having (menstrual) period s that are longer or heavier than usual.
Can cervical cancer cause blood in urine?
Problems urinating or having a bowel movement. Blood in the urine. These signs and symptoms can also be caused by conditions other than cervical cancer. Still, if you have any of these symptoms, see a health care professional right away.
What tests are done to determine if you have cervical cancer?
Your cancer's stage is a key factor in deciding on your treatment. Staging exams include: Imaging tests.
What is the test for cervical cancer?
A Pap test can detect abnormal cells in the cervix, including cancer cells and cells that show changes that increase the risk of cervical cancer. HPV DNA test.
What tests can be done to check if you have cancer?
Tests such as X-ray, CT, MRI and positron emission tomography (PET) help your doctor determine whether your cancer has spread beyond your cervix. Visual examination of your bladder and rectum. Your doctor may use special scopes to see inside your bladder and rectum.
Does palliative care help with cancer?
When palliative care is used along with all of the other appropriate treatments, people with cancer may feel better and live longer.
Can you remove cancer from a small cervix?
Surgery to cut away the cancer only. For a very small cervical cancer, it might be possible to remove the cancer entirely with a cone biopsy. This procedure involves cutting away a cone-shaped piece of cervical tissue, but leaving the rest of the cervix intact.
Can you use chemotherapy for cervical cancer?
Sometimes both methods are used. For locally advanced cervical cancer, low doses of chemotherapy are often combined with radiation therapy, since chemotherapy may enhance the effects of the radiation . Higher doses of chemotherapy might be recommended to help control symptoms of very advanced cancer.
Does Mayo Clinic help with cervical cancer?
Our caring team of Mayo Clinic experts can help you with your cervical cancer-related health concerns Start Here
What is cervix cancer?
Cervical cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the tissues of the cervix.
Where does cervical cancer form?
Cervical cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the tissues of the cervix. The cervix is the lower, narrow end of the uterus (the hollow, pear-shaped organ where a fetus grows). The cervix leads from the uterus to the vagina (birth canal). Anatomy of the female reproductive system.
How big is stage 2 cervical cancer?
Stage II cervical cancer. In stages IIA1 and IIA2, cancer has spread from the cervix to the upper two-thirds of the vagina but has not spread to the tissue around the uterus. In stage IIA1, the cancer is 4 centimeters or smaller. In stage IIA2, the cancer is larger than 4 centimeters.
What is the risk factor for cervical cancer?
Human papillomavirus (HPV) infection is the major risk factor for cervical cancer. Anything that increases your chance of getting a disease is called a risk factor. Having a risk factor does not mean that you will get cancer; not having risk factors doesn't mean that you will not get cancer.
Can cervical cancer be treated during pregnancy?
The patient’s age. Treatment of cervical cancer during pregnancy depends on the stage of the cancer and the stage of the pregnancy. For cervical cancer found early or for cancer found during the last trimester of pregnancy, treatment may be delayed until after the baby is born.
Can cervical cancer be detected early?
There are usually no signs or symptoms of early cervical cancer but it can be detected early with regular check- ups. Early cervical cancer may not cause signs or symptoms. Women should have regular check-ups, including tests to check for human papillomavirus (HPV) or abnormal cells in the cervix.
Can cervical cancer spread to children?
Over time, the abnormal cells may become cancer cells and start to grow and spread more deeply into the cervix and to surrounding areas. Cervical cancer in children is rare. See the following PDQ summaries for more information about cervical cancer: Cervical Cancer Prevention. Cervical Cancer Screening.
What are the symptoms of cervical cancer?
Any of the following could be signs or symptoms of cervical cancer: Blood spots or light bleeding between or following periods. Menstrual bleeding that is longer and ...
What is cervical cancer palliative care?
If cervical cancer is diagnosed, relieving symptoms remains an important part of cancer care and treatment. This may be called palliative care or supportive care. It is often started soon after diagnosis and continued throughout treatment.
Can precancerous cells be prevented?
If these symptoms appear, it is important to talk with your doctor about them even if they appear to be symptoms of other, less serious conditions. The earlier precancerous cells or cancer is found and treated, the better the chance that the cancer can be prevented or cured.
Does precancer cause symptoms?
Precancer often does not cause any signs or symptoms. Symptoms do typically appear with early-stage cervical cancer. With advanced cancer or cancer that has spread to other parts of the body, the symptoms may be more severe depending on the tissues and organs to which the disease has spread. The cause of a symptom may also be a different medical ...
What are the treatments for cervical cancer?
Common types of treatments for cervical cancer include: Surgery for Cervical Cancer. Radiation Therapy for Cervical Cancer. Chemotherapy for Cervical Cancer. Targeted Therapy for Cervical Cancer. Immunotherapy for Cervical Cancer.
What do people with cancer need?
People with cancer need support and information, no matter what stage of illness they may be in. Knowing all of your options and finding the resources you need will help you make informed decisions about your care.
What are the best doctors for cancer?
Doctors on your cancer treatment team may include: 1 A gynecologist: a doctor who treats diseases of the female reproductive system 2 A gynecologic oncologist: a doctor who specializes in cancers of the female reproductive system who can perform surgery and prescribe chemotherapy and other medicines 3 A radiation oncologist: a doctor who uses radiation to treat cancer 4 A medical oncologist: a doctor who uses chemotherapy and other medicines to treat cancer
Why is it important to communicate with your cancer care team?
Communicating with your cancer care team is important so you understand your diagnosis, what treatment is recommended, and ways to maintain or improve your quality of life.
What kind of doctor treats cancer?
Doctors on your cancer treatment team may include: A gynecologist: a doctor who treats diseases of the female reproductive system. A gynecologic on cologist: a doctor who specializes in cancers of the female reproductive system who can perform surgery and prescribe chemotherapy and other medicines. A radiation on cologist: a doctor who uses radiation ...
What are the services offered by the American Cancer Society?
These might include nursing or social work services, financial aid, nutritional advice, rehab, or spiritual help. The American Cancer Society also has programs and services – including rides to treatment, lodging, and more – to help you get through treatment.
What to talk to your cancer care team about?
Be sure to talk to your cancer care team about any method you are thinking about using. They can help you learn what is known (or not known) about the method, which can help you make an informed decision.
What are the symptoms of cervical cancer?
For early screening and detection of cervical cancer, women should look out for a number of cervical cancer signs and symptoms: 1. Abnormal pain or bleeding: Irregular bleeding is considered the most common symptom in women with cervical cancer. Bleeding or pain may occur between menstrual periods, ...
How to confirm cervical cancer?
Your doctor can often confirm cervical cancer using a number of diagnostic methods. A colposcopy and cervical biopsy will help determine the location of cancer cells on the cervix. An endocervical biopsy will detect whether cancer cells are on the cervical canal.
What is a red flag for HPV?
Genital warts: Small genital warts can be considered a red warning flag for HPV, which can significantly increase the risk of cervical cancer in women. There are many different types of HPV, but HPV-6 and HPV-11 are known to cause 90% of every form of genital warts. 5.
What is the procedure to find cervical cancer?
Also, a loop electrosurgical excision procedure (LEEP) or a cone biopsy may be performed to examine cervical tissue with a microscope. Other tests that may find cervical cancer include a chest X-ray of the lungs, a CT scan, an ultrasound, an MRI, a PET scan, or a biopsy of fine-needle aspiration.
What test is used to detect cervical cancer?
For instance, the Pap test is considered the routine test to screen for cervical cancer and detect abnormal cell changes in the cervix.
How many women died from cervical cancer in 2015?
As a result, about 4,100 women will die from the cancer.
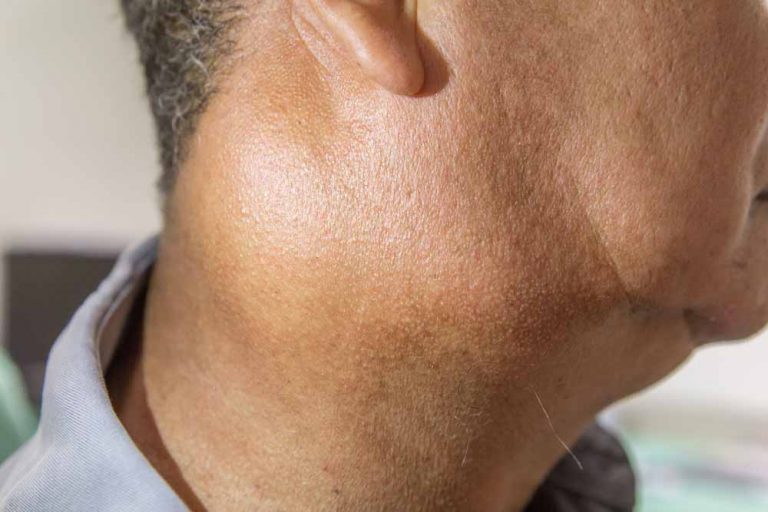
Can cervical cancer cause a bladder to be compressed?
6. Lack of urinary control: When the cervix swells, the bladder and kidneys may be compressed. As a result, urine flow is obstructed and you may not be able to control your bladder. Women with cervical cancer will have that sudden urge to urinate.
What is cervical cancer?
This diagram shows different parts of a woman’s reproductive system. Cancer is a disease in which cells in the body grow out of control. Cancer is always named for the part of the body where it starts, even if it spreads to other body parts later.
Where is the cervix located?
The cervix connects the vagina (birth canal) to the upper part of the uterus. The uterus (or womb) is where a baby grows when a woman is pregnant. All women are at risk for cervical cancer. It occurs most often in women over age 30.
Diagnosis
Treatment
- Early-stage cervical cancer generally produces no signs or symptoms. Signs and symptoms of more-advanced cervical cancer include: 1. Vaginal bleeding after intercourse, between periods or after menopause 2. Watery, bloody vaginal discharge that may be heavy and have a foul odor 3. Pelvic pain or pain during intercourse
Clinical Trials
Coping and Support
Preparing For Your Appointment