What is treated with CAR T-cell therapy?
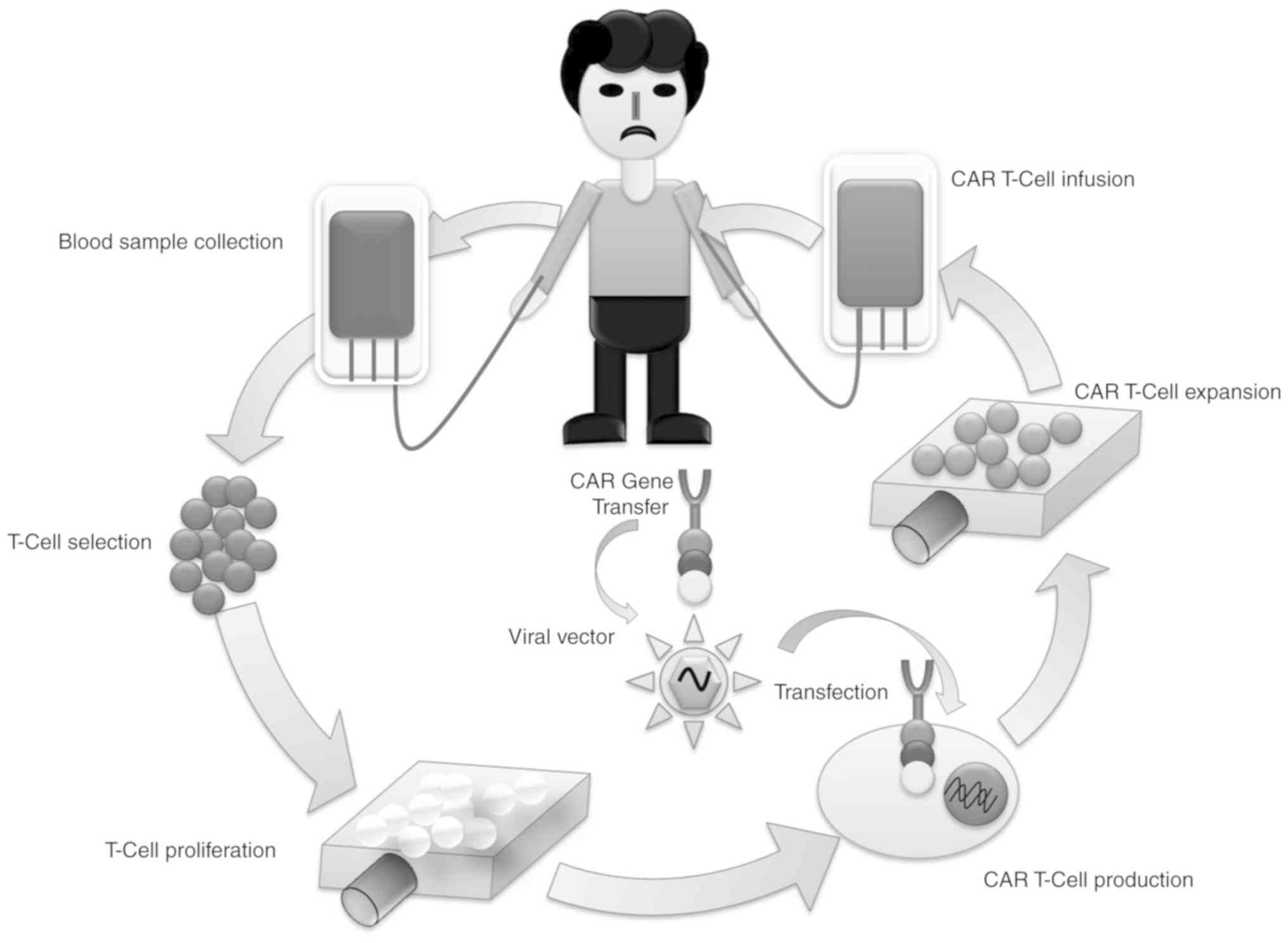
Getting CAR T-cell therapy Collecting the T cells. First, white blood cells (which include T cells) are removed from the patient’s blood using a... Making the CAR T cells. After the white cells are removed, the T cells are separated, sent to the lab, and altered by... Receiving the CAR T-cell ...
What to know about CAR T-cell therapy?
Chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy treats certain cancers by turning your T lymphocytes or T cells into more efficient cancer-fighting machines. While researchers are still collecting long-term data, CAR T-cell therapy is proving to be a very effective way of treating certain blood cancers. Your T cells are white blood cells in your immune system.
How to beat cancer naturally?
Chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cell therapy is a type of cellular immunotherapy that changes T cells so they are able to recognize and attack cancer. T cells are immune system cells that play several key roles in the body’s fight against disease. They help the immune system respond to disease and directly kill abnormal cells.
How does CAR T cell therapy work?
CAR T-cell therapy is a type of treatment in which a patient's T cells (a type of immune cell) are changed in the laboratory so they will bind to cancer cells and kill …
What is CAR T cell therapy and how does it work?
What is the success rate of car T cell therapy?
How long does it take to recover from car T cell therapy?
What diseases are treated with car T therapy?
What are the side effects of CAR T-cell therapy?
- High fever and chills.
- Trouble breathing.
- Severe nausea, vomiting, and/or diarrhea.
- Feeling dizzy or lightheaded.
- Headaches.
- Fast heartbeat.
- Feeling very tired.
- Muscle and/or joint pain.
How long is the hospital stay for CAR T-cell therapy?
Is car T cell therapy better than chemotherapy?
Does CAR-T therapy require hospitalization?
Is CAR-T therapy a cure?
Does Medicare pay for car T cell therapy?
Who is eligible for T cell therapy?
What cancers does CAR-T treat?
How does T-cell transfer therapy work against cancer?
T-cell transfer therapy is a type of immunotherapy that makes your own immune cells better able to attack cancer. There are two main types of T...
What cancers are treated with T-cell transfer therapy?
T-cell transfer therapy was first studied for the treatment of metastatic melanoma because melanomas often cause a strong immune response and often...
What are the side effects of T-cell transfer therapy?
T-cell transfer therapy can cause side effects, which people experience in different ways. The side effects you may have and how serious they are w...
What is car T cell therapy?
CAR T-cell therapy is a type of cancer therapy that uses a patient’s own modified white blood cells to kill cancer cells.
How long do car T cells stay in the body?
Once attached, the T cells become activated and release toxins that kill the cancer. The CAR T cells remain in the body for a long time after the infusion, helping to fight cancer if it returns and keep the patient in remission.
How do T cells protect the body?
They protect the body by destroying abnormal cells, including cancers. Sometimes, however, T cells don’t recognize cancer cells or cannot fully destroy all of them in the body. To improve the cancer-killing ability of T cells, the next step is to genetically alter them. This is done in a special laboratory.
Can T cells destroy cancer cells?
Sometimes, however, T cells don’t recognize cancer cells or cannot fully destroy all of them in the body. To improve the cancer-killing ability of T cells, the next step is to genetically alter them. This is done in a special laboratory. The altered T cells now have special receptors on their surface.
How to improve T cells?
To improve the cancer-killing ability of T cells, the next step is to genetically alter them. This is done in a special laboratory. The altered T cells now have special receptors on their surface. These new receptors, called chimeric antigen receptors (CAR), allow the T cells to better recognize cancer cells, become activated, and kill their target.
What are the neurological events?
Neurologic events include encephalopathy (brain disease, injury, malfunction), confusion, aphasia (difficulty understand or speaking), drowsiness, agitation, seizures, loss of balance and altered consciousness.
Can low white blood cells cause anemia?
Low white blood cell count (neutropenia) Low red blood cell count ( Anemia ) Fortunately, most of the side effects can be managed with drugs or resolved on their own without the need for treatment. Ask your physician or care team about all the potential side effects.
What is car T cell therapy?
CAR T-cell therapy is the only CAR-based therapy that has been approved by the FDA. Others are in clinical trials. These include treatments that target more than one antigen on the surface of cancer cells and therapies that use natural killer (NK) cells (another type of immune system cell) instead of T cells.
Is car T cell therapy FDA approved?
CAR T-cell therapy is the only CAR-based therapy that has been approved by the FDA. Others are in clinical trials. These include treatments that target more than one antigen on the surface of cancer cells and therapies that use natural killer (NK) cells (another type of immune system cell) instead of T cells. The treatment process and side effects for these therapies are similar to FDA-approved CAR T-cell therapies.
Do T cells kill cancer cells?
They help the immune system respond to disease and directly kill abnormal cells. Unfortunately, naturally occurring T cells in patients with cancer are not good at recognizing and fighting cancer cells. CAR T-cell therapy has been extremely effective in many patients. In some cases, the treatment has eliminated all signs of cancer.
Do car T cells work?
Several CAR T-cell therapies have been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). All approved products use T cells taken from the patient. Some clinical trials use T-cells taken from donors. In both cases, the T cells are sent to a lab. There, scientists genetically modify these cells to produce a protein (called a receptor) ...
How long does it take for car T cells to multiply?
After the T cells are collected, modifying and multiplying them for infusion usually takes a few weeks. Patients may undergo other cancer treatments during this time. When the CAR T cells are ready for use, they are sent to the hospital for infusion. Before infusion, patients are given a short course of chemotherapy.
What are the side effects of car T cells?
The most common side effect is low counts of immune system cells. This can lead to fever and infection. This is usually a mild side effect. Other mild side effects include nausea, vomiting and diarrhea.
Can car T cells cause seizures?
Other mild side effects include nausea, vomiting and diarrhea. CAR T-cell therapies can also have temporary but serious neurological effects, including confusion, slurred speech and seizures.
What is car T cell therapy?
CAR T-cell therapy is a type of treatment in which a patient's T cells (a type of immune cell) are changed in the laboratory so they will bind to cancer cells and kill them. Credit: National Cancer Institute. On This Page.
Why are car T cells used in clinical trials?
. To expand and speed up immunotherapy research, NCI has established a program to manufacture CAR T-cell therapies for use in clinical trials.
What is T cell transfer?
T-cell transfer therapy is a type of immunotherapy that makes your own immune cells better able to attack cancer. There are two main types of T-cell transfer therapy: tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (or TIL) therapy and CAR T-cell therapy.
How long does it take for T cells to grow?
The process of growing your T cells in the lab can take 2 to 8 weeks. During this time, you may have treatment with chemotherapy and, maybe, radiation therapy to get rid of other immune cells. Reducing your immune cells helps the ...
What is TIL therapy?
TIL therapy uses T cells called tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes that are found in your tumor. Doctors test these lymphocytes in the lab to find out which ones best recognize your tumor cells. Then, these selected lymphocytes are treated with substances that make them grow to large numbers quickly.
Can lymphocytes kill tumors?
The idea behind this approach is that the lymphocytes that are in or near the tumor have already shown the ability to recognize your tumor cells. But there may not be enough of them to kill the tumor or to overcome the signals that the tumor is releasing to suppress the immune system.
What is a car T cell?
CAR T cells are the equivalent of "giving patients a living drug," explained Renier J. Brentjens, M.D., Ph.D., of Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center in New York, another early leader in the CAR T-cell field.
Is car T cell research going on?
Research on CAR T cells is continuing at a swift pace, mostly in patients with blood cancers, but also in patients with solid tumors. As the biopharmaceutical industry has become more involved in the field, for instance, the number of clinical trials testing CAR T cells has expanded dramatically, from just a handful 5 years ago to more than 180 and counting.
Why are co-stimulatory signaling domains added to newer generations of CAR T cells?
Co-stimulatory signaling domains have been added to newer generations of CAR T cells to improve their ability to produce more T cells after infusion and survive longer in the circulation.
What is the FDA's T cell therapy?
In 2017, two CAR T-cell therapies were approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA), one for the treatment of children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) and the other for adults with advanced lymphomas.
What is the backbone of car T cells?
As its name implies, the backbone of CAR T-cell therapy is T cells , which are often called the workhorses of the immune system because of their critical role in orchestrating the immune response and killing cells infected by pathogens. The therapy requires drawing blood from patients and separating out the T cells .
Do car T cells work in solid tumors?
There is some skepticism that CAR T cells will have the same success in solid tumors. Dr. Rosenberg believes that finding suitable antigens to target on solid tumors—which has been a major challenge—may prove to be too difficult in most cases.
What are the cytokines released by T cells?
As part of their immune-related duties, T cells release cytokines, chemical messengers that help to stimulate and direct the immune response. In the case of CRS, there is a rapid and massive release of cytokines into the bloodstream, which can lead to dangerously high fevers and precipitous drops in blood pressure.
Does car T work for leukemia?
CAR T cell therapy has proven very effective at treating acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) in both children and adults. This type of blood cancer is usually treated successfully with chemotherapy, but in some cases conventional approaches do not work. That’s when CAR T cell therapy can be a patient’s best option.
Why are T cells used in stem cell transplants?
These cells help prevent post-transplant infections and virally caused cancers in patients, and also limit graft-versus-host disease, a dangerous side effect.
Is Esmeralda Pineda still cancer free?
When chemotherapy couldn’t get Esmeralda Pineda’s pediatric leukemia under control, doctors at Memorial Sloan Kettering turned to immunotherapy. The successful treatment wiped out all signs of her disease, and one year later, she’s still cancer free. Read Ezzy’s story
Who is the director of the Center for Cell Engineering at MSK?
The roots of CAR T therapy stretch back nearly 30 years, to the work of a young immunologist named Michel Sadelain, who is now the Director of the Center for Cell Engineering at MSK.
What is bone marrow used for?
Bone marrow transplants used in cancer treatment . MSK scientists use bone marrow stem cells from an unrelated donor to replenish a patient’s blood cells after intensive chemotherapy. T cells from the donor kill cancer cells in the recipient. Many consider this to be one of the first successful immunotherapies .
Who is the scientist who created the T cell?
T cell engineering begins. As a postdoctoral student at the Whitehead Institute at MIT, immunologist Michel Sadelain begins using newly developed genetic engineering tools, specifically retroviral vectors, to introduce genes into T cells, with the goal of making souped-up cancer fighters.
Who is Michel Sadelain?
As a postdoctoral student at the Whitehead Institute at MIT, immunologist Michel Sadelain begins using newly developed genetic engineering tools, specifically retroviral vectors, to introduce genes into T cells, with the goal of making souped-up cancer fighters. This idea would bear fruit in the coming years.
What is car T cell therapy?
CAR -T cell therapy is a kind of immunotherapy. It involves harnessing the power of a person's own immune system by engineering T cells to recognize and destroy cancer cells.
What is a car T cell?
What is chimeric antigen receptor (CAR)-T cell therapy? CAR -T cell therapy is a kind of immunotherapy. It involves harnessing the power of a person's own immune system by engineering T cells to recognize and destroy cancer cells.
What time does Mayo Clinic have appointments?
Patient appointments are scheduled Monday through Friday from 8 a.m. to 5 p.m. local time at each campus. Consultations with Mayo doctors are also available during these hours. Minnesota: Have your doctor call the Hematology Department directly at 507-284-8707 to request an appointment for a consultation.
Does insurance cover car T?
CAR -T cell therapy is a newer type of cancer treatment that may be more expensive than other therapies. Not all insurance policies cover CAR -T cell therapy. The out-of-pocket cost for CAR -T cell therapy varies, depending on your insurance coverage for services at Mayo Clinic as well as for CAR -T cell therapy itself.
What does a caregiver do?
The caregiver provides physical and emotional support and, sometimes, acts as an advocate for you. Some tasks a caregiver might do for you: Oversee your daily needs such as keeping track of medications, nutrition and monitoring for changes in your health. Help you to stay organized and manage details.
What is Car T cell therapy?
Chimeric antigen receptor (CAR)-T cell therapy is a revolutionary new pillar in cancer treatment. Although treatment with CAR-T cells has produced remarkable clinical responses with certain subsets of B cell leukemia or lymphoma, many challenges limit the therapeutic efficacy of CAR-T cells in solid tumors and hematological malignancies.
Is Car T cell therapy a first line treatment?
Although CAR-T cell therapy has been a revolutionary cancer treatment tool, high rates of toxicities with some fatalities have prevented CAR-T cell therapy from becoming first-line treatment. Critical factors that likely determine the incidence and severity of CRS, HLH/MAS, and/or ICANS are the design of the CAR, the specific target, ...
What is a chimer antigen receptor?
Chimeric antigen receptor (CAR)-T cell therapy has been revolutionary as it has produced remarkably effective and durable clinical responses1. CARs are engineered synthetic receptors that function to redirect lymphocytes, most commonly T cells, to recognize and eliminate cells expressing a specific target antigen.
What are the components of a car?
CAR Structure. CARs are modular synthetic receptors that consist of four main components: (1) an extracellular target antigen-binding domain, (2) a hinge region, (3) a transmembrane domain, and (4) one or more intracellular signaling domains. Here we will discuss the current principles underlying CAR design.
What is the function of the transmembrane domain?
The major function of the transmembrane domain is to anchor the CAR to the T cell membrane, although evidence suggests that the transmembrane domain can also be relevant for CAR-T cell function19,20.
Can tumor cells downregulate antigens?
Tumor cells can downregulate antigens due to the selective pressure of the CAR-T cells. Even with appropriate antigen targeting, on-target off-tumor effects can occur and cause associated toxicity. In solid tumors, getting CAR-T cells to traffic to and infiltrate the tumor is a challenge.
What are antigen binding domains?
Historically, the antigen-binding domains are derived from the variable heavy (VH) and light (VL) chains of monoclonal antibodies, connected via a flexible linker to form a single-chain variable fragment (scFv).
