
Coding Answer: A simple simulation (77280) on the first day can be charged for an electron boost to verify patient setup including the block location, block design, gantry clearance and isocenter. The electron cutout documentation should include a hard copy or electronically archived images, or a photograph.
What is a boost in radiation therapy?
Simulation is a critical preparation step before radiation treatment. It is performed at the simulation room equipped with a dedicated big-bore CT scanner. During the simulation, the treatment setup will be simulated by positioning the patient on the flat couch immobilized by specially designed devices. The patient will then be aligned to the reference low-energy lasers …
What is simulation in radiation therapy?
During simulation, your radiation oncologist and radiation therapists will place you on the CT scanner in the exact position you will be in during the actual treatment. Certain measurements may be taken, and once the correct position is determined the radiation therapist may place permanent ink tattoos on your skin. When needed, these marks ...
What is a a boost to the tumour bed?
After radiation therapy to the whole breast, you may have more radiation (called a boost) to the part of the breast that had the tumor. This boost increases the amount of radiation given to the area at highest risk for breast cancer recurrence. Your boost radiation session is similar to a regular session.
What is the difference between radiation and radiation boost?
Jan 01, 2020 · Before you begin radiation treatment, your radiation therapy team carefully plans your treatment in a process called radiation simulation. Treatment planning usually involves positioning your body, making marks on your skin and taking imaging scans. Your radiation therapy team determines whether you'll lie on your back, stomach or side during treatment.
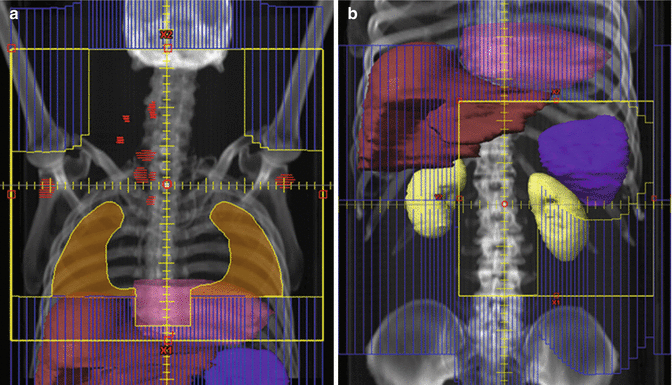
What do they do at radiation simulation?
What does simulation mean in radiotherapy?
What is boost in radiation therapy?
How long after simulation does radiation start?
Why is simulation important in radiotherapy?
What should I do after radiation therapy?
Is boost radiation stronger?
Is boost radiation necessary?
What should you avoid during radiation?
What is the success rate of radiation therapy?
Do you wear clothes during radiation treatment?
Can you take Tylenol during radiation?
What is radiation simulation?
This planning process is referred to as “simulation” because it simulates the treatment position and allows for acquisition of your unique anatomy to be used ...
Can a radiation oncologist put tattoos on your skin?
During simulation, your radiation oncologist and radiation therapists will place you on the CT scanner in the exact position you will be in during the actual treatment. Certain measurements may be taken, and once the correct position is determined the radiation therapist may place permanent ink tattoos on your skin.
What is hypofractionated breast irradiation?
This is called hypofractionated whole-breast irradiation. It’s like standard whole-breast radiation therapy except it uses a slightly higher dose of radiation per session (hypofractionation). This reduces the number of treatment sessions, making the overall course shorter. For most women with early breast cancer, ...
How to contact Komen for breast cancer?
Transportation, lodging, child care and elder care assistance 1 If you or a loved one needs more information about breast health or breast cancer, call the Komen Breast Care Helpline at 1-877 GO KOMEN (1-877-465-6636). All calls are answered by a trained specialist or oncology social worker in English and Spanish, Monday through Friday from 9:00 a.m. to 10:00 p.m. ET. You can also email the helpline at [email protected]. 2 We offer an online support community through our closed Facebook Group – Komen Breast Cancer group. The Facebook group provides a place where those with a connection to breast cancer can discuss each other’s experiences and build strong relationships to provide support to each other. Visit Facebook and search for “Komen Breast Cancer group” to request to join the closed group. 3 Our fact sheets, booklets and other education materials offer additional information.
What is radiation therapy for breast cancer?
Radiation therapy is planned specifically for your breast cancer, the shape of your body and your internal anatomy. This is why sessions can’t be split between different treatment centers. Your treatment plan is based on: The tumor size, type and location. The number of lymph nodes with cancer. The type of breast surgery (and lymph node surgery) ...
What is a boost breast?
After radiation therapy to the whole breast, you may have more radiation (called a boost) to the part of the breast that had the tumor. This boost increases the amount of radiation given to the area at highest risk for breast cancer recurrence. Your boost radiation session is similar to a regular session.
What is a komen group?
We offer an online support community through our closed Facebook Group – Komen Breast Cancer group. The Facebook group provides a place where those with a connection to breast cancer can discuss each other’s experiences and build strong relationships to provide support to each other. Visit Facebook and search for “Komen Breast Cancer group” to request to join the closed group.
What is brachytherapy in cancer?
Brachytherapy uses targeted radiation placed inside the tumor bed. Implanted radiation “seeds” (interstitial radiation therapy) or a single small balloon device (intracavitary radiation therapy) can be used to deliver the radiation. External beam radiation therapy uses standard external beam radiation therapy, but only targets the tumor bed.
Why do you hold your breath during a radiation plan?
You may be asked to hold your breath during the planning session. This is one way to minimize radiation exposure to the heart.
What is radiation simulation?
Before you begin radiation treatment, your radiation therapy team carefully plans your treatment in a process called radiation simulation . Treatment planning usually involves positioning your body, making marks on your skin and taking imaging scans.
How long should you hold your back during radiation?
It's crucial to find a position that optimizes your treatment, but is comfortable enough to hold for 15 to 45 minutes.
How does one bill for respiratory gating during treatment?
Coding Question: How does one bill for respiratory gating during treatment?#N#Coding Answer : CPT ® code +77293 was added to the radiation oncology code set as an add-on code. CPT code +77293 is utilized to capture the work associated with respiratory motion management and is billed once on the same date of service as treatment planning code 77295 or 77301. If the patient receives treatment utilizing respiratory gating or other respiratory motion tracking, HCPCS code G6017 or CPT code 77387 should be used. G6017 or 77387 may be used daily when respiratory motion tracking is used as part of the treatment process, depending on the requirements of the individual payer.
What modifier is used for a second simulation?
Certain payers may prefer modifier 59 (distinct procedure) on the second simulation code, or may require that the verification simulation be charged with two units. Physicians are encouraged to contact individual payers to confirm how they want this reported.
What is 77280 coding?
Coding Answer: A simple simulation (77280) on the first day can be charged for an electron boost to verify patient setup including the block location, block design, gantry clearance and isocenter. The electron cutout documentation should include a hard copy or electronically archived images, or a photograph. All documentation, including any images of treatment devices, must contain the physician signature and evidence of physician participation.
Can a 4D CT be used to detect a tumor?
Coding Answer: Yes, at times the respiratory movement of the tumor is minimal and respiratory gating may not be indicated. However, 4-D CT evaluation is indicated to confirm that the tumor is not mobile and should be reported with appropriate documentation of medical necessity.
What is computerized radiation planning?
During treatment planning, the technologists also perform special calculations to help assure that the proper radiation dose will be delivered. Computerized treatment planning may facilitate these calculations. Computers have become extremely sophisticated in planning radiation therapy delivery. Some computers are even capable of extremely complex three-dimensional representation of the treatment area and surrounding normal tissues. If such computerized planning is necessary, the patient may be asked to have a special CT scan (a special type of x-ray device with a donut shaped opening).
What is a tattoo in radiation?
Once the aspects of the treatment fields are set, the technologist will take special simulation x-rays representing the treatment fields. In most centers, the patient is given multiple “tattoos,” which mark the treatment fields and replace the marks previously made with magic markers. These tattoos are not elaborate and consist of no more than pinpricks followed by ink, appearing like a small freckle. Tattoos enable the radiation technologists to set up the treatment fields each day with precision, while allowing you to wash and bathe without worrying about obscuring the marks that indicate where treatment will be delivered.
What is a radiation oncologist consultation?
The consultation is an important visit that allows both you and the radiation oncologist to gain more information. During the consultation, the radiation oncologist will obtain a medical history and perform a physical examination. Many patients find it helpful to prepare for the consultation by bringing x-rays, medical records, a list of medications, insurance information, and referral forms.
What is the next session of radiation oncology?
After the initial consultation and decision to use radiation treatment, the next session is usually a planning session, which is called a simulation . Simulation is used to determine the radiation treatment fields and most of the treatment planning. Of all the visits to the radiation oncology facility, the simulation session may actually take the most time.
Why are simulation sessions necessary?
Sometimes several simulation sessions are necessary in order to optimize treatment and are often performed prior to planned “boost” or “reduced field” treatments as part of the overall treatment plan.
How many degrees does the radiation table rotate?
The machine and treatment table may rotate up to 360 degrees if the treatment requires the radiation to hit the tumor from all angles. The technologists will not be in the room during the treatment, but they will be monitoring the treatment via a video camera and an audio connection with the treatment room. You will not feel the radiation as it is being delivered.
How often is radiation given?
Radiation therapy is generally given once a day, five days a week, usually at the same time each day. Occasionally, treatment is given less frequently or twice a day. The number of treatments depends on multiple factors and varies from 5-10 to 40 or more, which means that treatment may last anywhere from one to eight weeks or more. Radiation treatments are generally given as outpatient treatments and involve relatively little time each day. While the first few visits might last for an hour or more, typically a daily radiation treatment will take about 15-30 minutes in the treatment room and the actual treatment only lasts a few minutes. It is important not to miss treatments. Extending treatments beyond the recommended time period may reduce the chance of controlling the cancer.
How does radiation therapy work?
During simulation, your radiation oncologist and radiation therapist place you on the simulation machine in the exact position you will be in during the actual treatment. Your radiation therapist, under your doctor’s supervision, then marks the area to be treated directly on your skin or on immobilization devices. Immobilization devices are molds, casts, headrests or other devices that help you remain in the same position during the entire treatment. The radiation therapist marks the immobilization devices and/or your skin with either a bright, temporary paint or a set of small, permanent tattoos. Often, a special treatment planning CT scan is done to help with the simulation and treatment planning. This CT scan is in addition to your diagnostic CT scan. Your radiation oncologist may request that special blocks or shields be made for you. These blocks or shields are put in the external beam therapy machine before each of your treatments and are used to shape the radiation to your tumor and keep the rays from normal tissue. Multi-leaf collimators, shaping devices located in the head of the linear accelerator itself, may also be used to shape the beam and achieve safe delivery of your radiation treatment.
What is the name of the doctor who oversees radiation therapy?
Radiation Oncologists. Radiation oncologists are the doctors who will oversee your radiation therapy treatments. These physicians work with the other members of the radiation therapy team to develop and prescribe your treatment plan and make sure that each treatment is given accurately. Your radiation oncologist will also track your progress ...
What is a radiation therapist?
Radiation therapists work with radiation oncologists to give the daily radiation treatment under the doctor’s prescription and supervision. They maintain daily records and regularly check the treatment machines to make sure they are working properly.
How often do you get chemotherapy and radiation?
In some cases, a patient may receive chemotherapy and radiation therapy at the same time. The chemotherapy may be delivered weekly, every three weeks or at some schedule determined by the medical oncologist together with the radiation oncologist.
What is the role of a medical physicist?
Medical physicists work directly with the radiation oncologist during treatment planning and delivery. They oversee the work of the dosimetrist and help ensure that complex treatments are properly tailored for each patient. Medical physicists develop and direct quality control programs for equipment and procedures.
What is radiation oncology nursing?
Radiation oncology nurses work with every member of the treatment team to care for you and your family before, during and after treatment. They will explain the possible side effects you may experience and will describe how you can manage them.
Why do you need a special CT scan?
Often, a special treatment planning CT scan is done to help with the simulation and treatment planning. This CT scan is in addition to your diagnostic CT scan. Your radiation oncologist may request that special blocks or shields be made for you.

What Is A Radiation Boost?
Effectiveness
- A radiation boost can reduce the risk of local recurrence, especially for higher-risk individuals, although less so for those with positive margins of less than 2 millimeters.3 More research is needed to further explore just how effective radiation boosts are in reducing the risk of recurrence.
Side Effects
- As with any treatment, side effects from a radiation boost may occur. There are short-term side effects and long-term side effects. Talk with your healthcare provider about the risks and benefits, and what you should watch for. Short-term side effects can include:7 1. Fatigue 2. Breast swelling 3. Skin redness, itching, and discoloration Higher doses of total radiation due to the boost have …
Summary
- After radiation therapy is completed, sometimes an extra dose, or a boost, is recommended. This recommendation is based on guidelines developed based on age, margin status, and cancer grade. Studies have shown that a radiation boost reduces breast cancer recurrence, especially for people with a DCIS diagnosis before age 50. But the boost hasn't proven to increase long-term s…
A Word from Verywell
- While receiving an extra dose of radiation may seem scary or unnecessary, you can take comfort knowing that the goal of this boost is to minimize the chances of your breast cancer returning. If your healthcare provider suggests one, but you are uncertain about moving ahead with it, have an open discussion about your concerns and ask the specific reasons behind the recommendation …