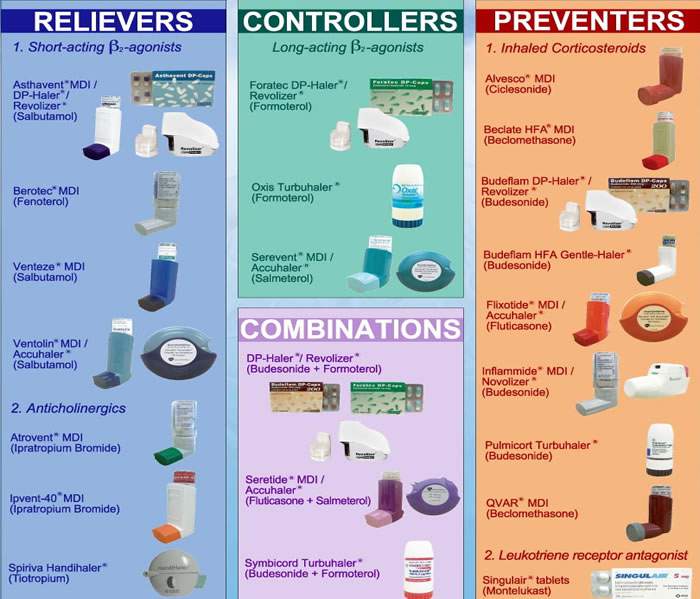
Medication
- Have asthma symptoms on 2 days a week or less.
- Use your quick-relief inhaler on 2 days a week or less.
- Have no asthma symptoms at night and do not wake up because of asthma symptoms.
- Can exercise, work, and go to school with no limitations on your activity level.
- Have a peak flow that is near your personal best (or better).
Procedures
Top 10 Herbs for Treating Asthma
- Oregano. Oregano is a powerful herb for treating asthma. ...
- Ginkgo Biloba. Ginkgo biloba contains antihistamine and anti-inflammatory properties that help treat asthma. ...
- Ginger. Another well-known herb used for treating asthma is ginger. ...
- Garlic. ...
- Slippery Elm. ...
- Licorice. ...
- Turmeric. ...
- Lemongrass. ...
- Stinging Nettle. ...
- Bishop’s Weed. ...
Self-care
“The best way to tackle health challenges is in small bits, and that goes for allergy and asthma control,” Dr. Mark Corbett, president of the American College of Allergy, Asthma and Immunology (ACAAI) says.
Nutrition
The TSG12 treatment, developed from the MT-2 protein, relaxed the airway smooth muscle cells, expanded the pulmonary airways, reduced pulmonary resistance and was more effective than current FDA-approved treatments, including bronchodilator inhalers used by almost all people with asthma.
See more
What is the ultimate goal of treatment in asthma?
What is the best natural cure for asthma?
What you can do to prevent asthma?
Which is more effective at treating asthma?
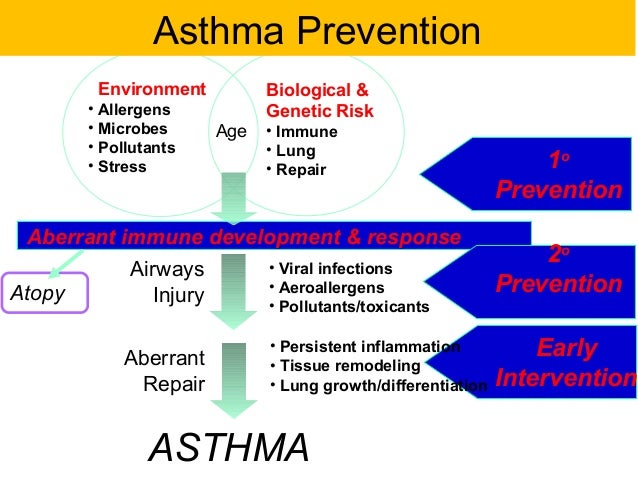
What is asthma prevention and treatment?
Avoid Allergens/Irritants Reduce occupational and environmental exposures to allergens, irritants, and physical conditions known to worsen asthma symptoms. If relevant, initiate a smoking cessation Smoking has been associated with difficulty maintaining adequate asthma control.
What is the treatment of asthma?
Quick-relief inhalers (bronchodilators) quickly open swollen airways that are limiting breathing. In some cases, allergy medications are necessary. Long-term asthma control medications, generally taken daily, are the cornerstone of asthma treatment.
What are 4 treatments for asthma?
Types of asthma medicationsInhaled corticosteroids.Leukotriene modifiers.Long-acting beta agonists (LABAs)Theophylline.Combination inhalers that contain both a corticosteroid and a LABA.
What are 5 treatments for asthma?
These are the most common long-term control medications for asthma. These anti-inflammatory drugs include fluticasone (Flovent HFA), budesonide (Pulmicort Flexhaler), beclomethasone (Qvar RediHaler), ciclesonide (Alvesco, Omnaris) and mometasone (Asmanex HFA).
How do you prevent asthma?
PreventionFollow your asthma action plan. ... Get vaccinated for influenza and pneumonia. ... Identify and avoid asthma triggers. ... Monitor your breathing. ... Identify and treat attacks early. ... Take your medication as prescribed. ... Pay attention to increasing quick-relief inhaler use.
What is the first line treatment for asthma?
Thus, inhaled corticosteroids are recommended as first-line therapy in all patients with persistent asthma.
How is asthma treated in adults?
Anti-inflammatories: This is the most important type of medication for most people with asthma. Anti-inflammatory medications, such as inhaled steroids, reduce swelling and mucus production in the airways. As a result, airways are less sensitive and less likely to react to triggers.
How to treat asthma in 2016?
March 7, 2016. The main treatment for asthma is using asthma control medicine on a regular basis. Asthma control drugs reduce inflammation in the airways. When the airways are less inflamed, they become less sensitive, or hyperresponsive. This reduces your risk of having an asthma attack. You may need 1 or more drugs to get your asthma ...
What is the best medicine for asthma?
Oral corticosteroids reduce inflammation. These drugs may be used short-term at the start of an asthma attack or after an attack. Common names of oral steroids include methylprednisolone, prednisolone, and prednisone. 1
What is a long acting beta agonist?
Long-acting beta agonists (LABAs) relax the muscles that surround the airways. LABAs are used together with inhaled corticosteroids to treat people with moderate to severe asthma. LABAs reduce asthma symptoms, asthma attacks, and rescue medication use. 1
How long does it take for asthma to go down?
This may mean increasing the dose or adding another drug. If your asthma is well controlled for at least 3 months, you may go down 1 step.
Do steroids help with asthma?
Inhaled steroids make the airways less inflamed and less sensitive. This leads to less severe asthma symptoms and better lung function. You are less likely to have an asthma attack or need to visit the emergency room if you take inhaled corticosteroids. 1,2.
Can LTRAs be used for asthma?
These are pills taken by mouth. 1,2. LTRAs can be used instead of inhaled steroids for people with mild to moderate asthma (Step 2). Leukotriene modifiers can also be used in addition to inhaled corticosteroids for moderate asthma (Steps 3 and 4).
How to help asthma?
Regular exercise can strengthen your heart and lungs, which helps relieve asthma symptoms. If you exercise in cold temperatures, wear a face mask to warm the air you breathe. Maintain a healthy weight. Being overweight can worsen asthma symptoms, and it puts you at higher risk of other health problems.
How to stop asthma attacks?
Treatment. Prevention and long-term control are key to stopping asthma attacks before they start. Treatment usually involves learning to recognize your triggers, taking steps to avoid triggers and tracking your breathing to make sure your medications are keeping symptoms under control.
How is asthma classified?
How asthma is classified. To classify your asthma severity, your doctor will consider how often you have signs and symptoms and how severe they are. Your doctor will also consider the results of your physical exam and diagnostic tests. Determining your asthma severity helps your doctor choose the best treatment.
What test is used to diagnose asthma?
Other tests to diagnose asthma include: Methacholine challenge. Methacholine is a known asthma trigger. When inhaled, it will cause your airways to narrow slightly. If you react to the methacholine , you likely have asthma. This test may be used even if your initial lung function test is normal. Imaging tests.
How to reduce asthma triggers?
Taking steps to reduce your exposure to asthma triggers is a key part of asthma control. To reduce your exposure, you should: Use your air conditioner. Air conditioning reduces the amount of airborne pollen from trees, grasses and weeds that finds its way indoors.
What is the best bronchodilator for asthma?
Like other bronchodilators, ipratropium (Atrovent HFA) and tiotropium (Spiriva, Spiriva Respimat) act quickly to immediately relax your airways, making it easier to breathe. They're mostly used for emphysema and chronic bronchitis, but can be used to treat asthma. Oral and intravenous corticosteroids.
What is the test for lung function?
Lung function tests often are done before and after taking a medication to open your airways called a bronchodilator (brong-koh-DIE-lay-tur), such as albuterol. If your lung function improves with use of a bronchodilator, it's likely you have asthma.
How to control asthma?
You can control your asthma and avoid an attack by taking your medicine exactly as your doctor or other medical professional tells you to do and by avoiding things that can cause an attack. Not everyone with asthma takes the same medicine. Some medicines can be inhaled, or breathed in, and some can be taken as a pill.
Can you take long term control if you have asthma?
If you need to use your quick-relief medicines more and more, you should visit your doctor or other medical professional to see if you need a different medicine. Long-term control medicines help you have fewer and milder attacks, but they don’t help you if you’re having an asthma attack.
Can asthma medicine be taken with a doctor?
Asthma medicines can have side effects, but most side effects are mild and soon go away. Ask your doctor or other medical professional about the side effects of your medicines. The important thing to remember is that you can control your asthma. With your doctor’s or other medical professional’s help, make your own asthma action plan ...
How to help someone with asthma?
If you think that someone you know is having an asthma attack, tell them to sit them upright and assist them in using their rescue inhaler or nebulizer. Two to six puffs of medication should help ease their symptoms.
How to stop asthma attacks?
Activity can trigger an asthma attack, but regular exercise may actually help reduce the risk of breathing problems. Managing stress . Stress can be a trigger for asthma symptoms. Stress can also make stopping an asthma attack more difficult.
What are the symptoms of asthma?
The most common symptom of asthma is wheezing, a squealing or whistling sound made when you breathe. Other asthma symptoms may include: coughing, especially at night, when laughing, or during exercise. tightness in the chest. shortness of breath. difficulty talking. anxiousness or panic.
What are the causes of asthma?
The list of possible causes and triggers is extensive. Triggers include: Illness. Respiratory illnesses such as viruses, pneumonia, and the flu can trigger asthma attacks. Exercise. Increased movement may make breathing more difficult.
How long does it take for asthma to show symptoms?
The symptoms may begin within minutes or hours. These patients also typically have nasal polyps. About 9 percent of people with asthma have AIA.
How does asthma affect the lungs?
Asthma symptoms occur when the lining of your airways swell and the muscles around them tighten. Mucus then fills the airways, further reducing the amount of air that can pass through.
Why is it so hard to breathe with asthma?
It becomes increasingly difficult to breathe because your airways are swollen and your bronchial tubes have narrowed. The symptoms of an exacerbation may include: hyperventilation.
How to treat asthma?
Four fundamental steps for achieving these goals are: 2 1 Using long-term control medications 2 Avoiding asthma triggers 3 Treating co-existing medical conditions 4 Monitoring changes in your symptoms or lung function
How does asthma medication help?
The most frequently used asthma control medications reduce inflammation in your airways. 2 When the airways are less inflamed, they become less sensitive (“ hyperresponsive ”). This reduces your risk of having an asthma attack. 2.
How to treat asthma flare ups?
Your plan should describe who and when to call based on your peak expiratory flow measurements and the type of symptoms you are having. In general, treatment begins at home. 2 You will be instructed on how to take your rescue inhaler. The next steps depend on how your symptoms respond to your rescue medication.
How often do you need to use beta agonist?
Asthma does not wake you up or cause difficulty with sleeping. You do not use your short-acting beta agonist (SABA) more than twice a week. Your activities are not limited due to asthma complications. Four fundamental steps for achieving these goals are: 2.
What are the triggers of asthma?
You and your provider can work together to identify your triggers. Common triggers include pet dander, dust mites, cockroaches, pollen, mold, and viruses. Exercise, cold air, and pollution can also trigger symptoms.
Does homeopathy work for asthma?
Herbal remedies and homeopathy have not been studied well enough to know whether they work. The National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute does not recommend acupuncture to treat asthma. 2 Their position is based on several randomized, clinical trials that showed acupuncture was not effective.
Is peak flow monitoring good for asthma?
Peak flow monitoring may be better for people with severe asthma, a history of sudden attacks, or difficulty noticing worsening symptoms . Monitoring your asthma helps you to notice the start of an asthma attack early. By starting treatment right away, you may be able to avoid having a severe asthma attack.
How to manage asthma?
For people with asthma, having an asthma management plan is the best way to prevent symptoms. An asthma management plan is something developed by you and your doctor to help you control your asthma, instead of your asthma controlling you. An effective plan should allow you to: 1 Be active without having asthma symptoms 2 Fully take part in exercise and sports 3 Sleep all night, without asthma symptoms 4 Attend school or work regularly 5 Have the clearest lungs possible 6 Have few or no side effects from asthma medicines 7 Have no emergency visits or stays in the hospital
How to control asthma?
The key to controlling your asthma is taking your medicine at the earliest possible sign of worsening. There is a simple, pocket-sized device called a peak flow meter that can help detect narrowing in your airways hours, or even days, before you feel symptoms.
How do you inhale asthma medicine?
Asthma medicines are usually inhaled through a machine called a nebulizer, through a small device called a metered dose inhaler (also called an inhaler, puffer or MDI) or through a dry powder inhaler (DPI). For inhalers to work well, you must use them correctly.
What are the parts of asthma management?
Four Parts of Your Asthma Management Plan: 1. Know your asthma triggers and minimize contact with them . Avoiding your triggers is the best way to reduce your need for medicines and to prevent asthma episodes. But first, you have to learn what those triggers are.
How to be active without asthma?
An effective plan should allow you to: Be active without having asthma symptoms. Fully take part in exercise and sports. Sleep all night, without asthma symptoms. Attend school or work regularly. Have the clearest lungs possible. Have few or no side effects from asthma medicines.
Can you use an inhaler properly?
But more than half of all people who use inhalers don’t use them properly. Ask your doctor or nurse to watch you and check your technique. If it is still difficult to use, you have two choices. Ask them to recommend a spacer or holding chamber.
Can you use a spacer for asthma?
Everyone can benefit from using a spacer or holding chamber, especially children. Or, ask about using a “breath-actuated” inhaler, which automatically releases medicine when you inhale. Unless your asthma is very mild, chances are you have prescriptions for at least two different medicines. That can be confusing.
How to manage asthma?
Taking an active role in managing your asthma treatment will help you maintain better long-term asthma control, prevent asthma attacks and avoid long-term problems. Create a written asthma action plan with your doctor. This written plan will serve as an asthma treatment guide tailored to your specific needs. It will help you follow these three ...
How to prevent asthma attacks?
Following your plan will help you avoid asthma attacks and minimize the disruptions caused by asthma symptoms. Meet with your doctor regularly to review your treatment.
How to write asthma symptoms?
Write down your symptoms in an asthma diary each day. Recording symptoms can help you recognize when you need to make treatment adjustments according to your asthma action plan. Use your asthma diary to record: 1 Shortness of breath or whistling sounds when you exhale (wheezing). 2 Disturbed sleep caused by shortness of breath, coughing or wheezing. 3 Chest tightness or pain. 4 Quick-relief (rescue) inhaler use — record when you need to use your quick-relief inhaler, such as albuterol (Proventil HFA, Ventolin HFA, ProAirHFA), and write down how many puffs you take. 5 Disruptions to work, school, exercise or other day-to-day activities caused by asthma symptoms. 6 Asthma symptoms during exercise. 7 Changes in color of phlegm you cough up. 8 Hay fever symptoms such as sneezing and runny nose. 9 Anything that seems to trigger asthma flare-ups.
What is the measurement of air in the lungs called?
This measurement is called forced expiratory volume (FEV1) . Your FEV1 measurement is compared with the typical FEV1 for people who don't have asthma.
What is a quick relief inhaler?
Quick-relief inhalers contain a fast-acting medication such as albuterol. These medications are sometimes called rescue inhalers. They're used as needed to quickly open your airways and make breathing easier. Knowing when to use these medications can help prevent an impending asthma attack.
How to keep a record of asthma?
It will help you follow these three important steps and keep a good record of your asthma treatment: 1. Track your symptoms. Write down your symptoms in an asthma diary each day. Recording symptoms can help you recognize when you need to make treatment adjustments according to your asthma action plan. Use your asthma diary to record:
How much of your personal best is asthma?
60 to 80% of your predicted personal best. Less than 60% of your predicted personal best. There are two main types of medications used to treat asthma: Long-term control medications such as inhaled corticosteroids are the most important medications used to keep asthma under control.
What is the best treatment for asthma?
If your doctor finds that you have allergies, allergy shots (immunotherapy) may help prevent allergy symptoms and keep your asthma from getting worse. With allergy shots, the doctor injects small doses of allergens under your skin on a regular schedule.
What to do when you have asthma?
When you have an asthma attack, check the diary to see which thing, or combination of things, might have led to it. Some common asthma triggers, like molds and cockroaches, aren’t always obvious. Ask your asthma specialist about tests to find the allergens you respond to. Then take steps to avoid them.
How to prevent asthma in 2021?
Tips for Asthma Prevention. Medically Reviewed by Renee A. Alli, MD on June 01, 2021. If you have asthma, you need to do what you can to cut your exposure to asthma triggers. That starts by knowing what causes you to cough, wheeze and grasp for breath. While there’s no cure, there are steps you can take to keep your asthma in control ...
Why is it important to keep your distance from allergens?
If you have allergies and asthma, it’s important to keep your distance from allergens (things you’re allergic to). Allergen exposure can increase the inflammation in your airways for a while, making an attack more likely.
How to make asthma worse?
Smoking always makes asthma worse. 4. Prevent Colds. Do what you can to stay well. Avoid close contact with people who have a cold or the flu, because catching it will make your asthma symptoms worse. Wash your hands well if you handle items that someone with a respiratory infection may have touched.
Is smoking bad for asthma?
Smoke and asthma are a bad mix. Limit exposure to all sources of smoke, including tobacco, incense, candles, fires, and fireworks. Don’t allow smoking in your home or car, and avoid public places that permit it. If you smoke cigarettes, get help to quit. Smoking always makes asthma worse.

Diagnosis
Treatment
Clinical Trials
Lifestyle and Home Remedies
Specialist to consult
Alternative Medicine
Coping and Support
- Prevention and long-term control are key to stopping asthma attacks before they start. Treatment usually involves learning to recognize your triggers, taking steps to avoid triggers and tracking your breathing to make sure your medications are keeping symptoms under control. In case of an asthma flare-up, you may need to use a quick-relief inhaler.
Preparing For Your Appointment