What is a multimodal approach in nursing?
Apr 01, 2019 · Multimodal Treatment (MMT) is based on the premise that humans are complex creatures who feel, act, think, sense, fantasize and interrelate. So a therapist dealing with mental and addictive disorders would have to address each of these aspects of personality since all reactions are said to be caused by the interaction of these complexities.
What are multimodal therapies for brain disorders?
Multimodal therapies are intended to optimize treatment of brain disorders by delivering different types of therapy together. The multiple modes used may include pharmacotherapy (small molecule drugs and biologics), devices, and …
What is multimodal therapy (MMT)?
Jan 25, 2022 · Multimodal therapy (MMT) is a type of holistic approach to psychotherapy, usually involving several therapeutic techniques or approaches at once. In other words, the focus tends to be on treating the whole person rather than focusing too narrowly on specific symptoms.
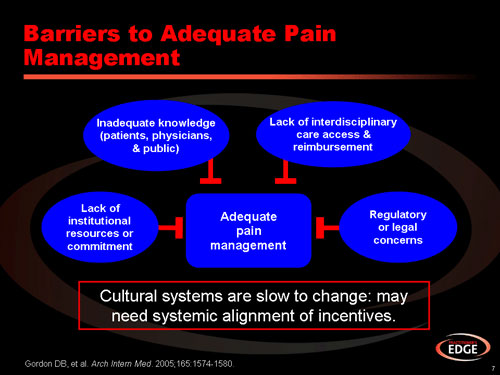
What is multimodal pain management?
Dec 18, 2021 · Multimodal therapy is a type of psychological treatment that uses multiple methods to address the problems of a person. It is an integrative approach that combines different therapies to find the best way to help a person. This can mean using different techniques within the same session or using different approaches at different times.

What is meant by a multimodal approach to treatment?
Multimodal therapies are intended to optimize treatment of brain disorders by delivering different types of therapy together. The multiple modes used may include pharmacotherapy (small molecule drugs and biologics), devices, and behavioral/psychosocial interventions (see Figure 2-1).
When is multimodal therapy used?
The goal of Multimodal Therapy is to create customized treatment for each patient depending on their psychological or behavioral problems. Not all clients will benefit from one therapy structure because everyone has a different perception of life, others and how they deal with trust or relationships.
What does multimodal mean in healthcare?
(MUL-tee-moh-DA-lih-tee TREET-ment) Therapy that combines more than one method of treatment.
What is main principle of multimodal therapy?
It emphasizes that for therapy to be comprehensive and thorough it must encompass seven discrete but interactive modalities – behavior, affect, sensation, imagery, cognition, interpersonal relationships, and drugs/biological considerations.
Who developed multimodal therapy?
Multimodal therapy is a form of psychotherapy developed by Arnold Lazarus. It focuses on reducing psychological suffering and promoting personal growth as rapidly as possible. Multimodal therapy is based on the idea that humans are biological beings that think, feel, act, sense, imagine, and interact.
What is the Lazarus technique?
Arnold Lazarus added the idea that, since personality is multi-dimensional, treatment must also consider multiple dimensions of personality to be effective. His idea of MMT involves examining symptoms on each dimension of personality in order to find the right combination of therapeutic techniques to address them all.
What is the meaning of multimodality?
Multimodality refers to the interplay between different representational modes, for instance, between images and written/spoken word. Multimodal representations mediate the sociocultural ways in which these modes are combined in the communication process (Kress & Van Leeuwen 2001, p. 20).
What is multimodal ADHD treatment?
People with ADHD can choose to use several therapies at once. Using several therapies for ADHD is called multimodal therapy. Multimodal therapy for children can include education of parent and child, behavior modification, school programs, support groups, and medication.
How do multimodal learners learn?
What is multimodal learning? Multimodal learning suggests that when a number of our senses – visual, auditory, kinaesthetic – are being engaged during learning, we understand and remember more. By combining these modes, learners experience learning in a variety of ways to create a diverse learning style.Oct 24, 2019
What is basic ID in Multimodal Therapy?
The multimodal orientation begins with the assumption that therapy must assess seven discrete but interactive modalities (abbreviated by the acronym BASIC ID, which stands for Behavior, Affect, Sensation, Imagery, Cognition, Interpersonal factors, and Drug/Biological considerations).
What are the 7 major modalities identified by Lazarus?
Lazarus hypothesized that most psychological problems are multifaceted, multi-determined, and multilayered and that comprehensive therapy calls for a careful assessment of seven reciprocally transactional dimensions or “modalities” in which individuals operate: Behavior, Affect (emotion), Sensation, Imagery, Cognition, ...Nov 30, 2019
What is bridging in Multimodal Therapy?
n. a method used in multimodal therapy in which the therapist first focuses on the client's preferred aspect of treatment (e.g., cognitions) before moving to another aspect (e.g., sensations) that the therapist believes may be more salient.
What is multimodal approach?
Multimodal approaches may enable more individualized, targeted treatment. For example, for a highly heterogeneous condition such as epilepsy, pharmacotherapy may be combined with continuous monitoring of brain electrical activity and neurostimulation to prevent seizures.
What is multimodal treatment paradigm?
In multimodal treatment paradigms, one treatment modality, such as pharmacotherapy, can be combined with other therapeutic modes, including psychosocial intervention or non-invasive neuromodulation. SOURCE: (more...)
What are the challenges of multimodal therapies?
In addition to the technical and scientific challenges of developing multimodal therapies, companies face commercial challenges in bringing those therapies to market, particularly because multimodal approaches often involve multiple companies as well as multiple modalities, said Califf.
Why are companies reluctant to develop multimodal therapies?
For example, companies or investors may be reluctant to pursue development of multimodal therapies because of concern about treatment interactions. If multiple treatments are to be evaluated in a single trial, a company may refrain because they fear their treatment will lose out to an alternative.
What are the consequences of multimodal approaches?
Multimodal approaches are also often necessary for conditions such as traumatic brain injury (TBI), which has multiple consequences, including cognitive disability, psychological injury, behavioral disorders, sensory disturbances, and pain; it is also accompanied by other visceral and orthopedic injuries (see Figure 2-2).
What is the FDA doing with CNS?
The FDA, with the cooperation of industry, is moving toward using existing data from clinic al trials and common data standards to increase the scale of studies of multimodal therapies for central nervous system (CNS) disorders, as is already being done in oncology (Califf, Potter).
What are some examples of multiple modes of treatment?
For example, in coronary artery disease, the multiple modes used may include a drug-eluting stent; multiple pharmacologic therapies, including blood thinners, statins, antihypertensives, and biologics; and behavioral interventions, such as diet and exercise. Multimodal approaches (as well as some combinations of multiple drugs) ...
What Is Multimodal Therapy?
Multimodal therapy (MMT) is a type of holistic approach to psychotherapy, usually involving several therapeutic techniques or approaches at once. 1 In other words, the focus tends to be on treating the whole person rather than focusing too narrowly on specific symptoms.
Types of Multimodal Therapy
A variety of different types of treatments may be employed in multimodal therapy. Below is a list of some of the most common types of therapy that may be used concurrently in a multimodal therapy treatment program.
Techniques of Multimodal Therapy
MMT is a type of treatment that uses several different approaches to increase the likelihood that behavior change will take place. As such, the techniques that are used in MMT are drawn from a wide variety of cognitive, behavioral, and psychodynamic strategies.
What Multimodal Therapy Can Help With
Multimodal therapy can be used in the treatment of emotional and psychological problems, including depression, anxiety, schizophrenia, personality disorders, bipolar disorder, ADHD (attention deficit hyperactivity disorder), autism spectrum disorders, substance abuse, eating disorders, and psychotic symptoms.
Benefits of Multimodal Therapy
Below are some of the specific potential benefits of multimodal therapy:
Effectiveness of Multimodal Therapy
The effectiveness of MMT can vary depending on how it is implemented; however, research indicates that multimodal therapy is likely to be effective for many different conditions including depression and anxiety. 5
How to Get Started With Multimodal Therapy
If you are interested in starting multimodal therapy, ask your therapist whether they typically use techniques from different modalities or if they prefer to focus on one approach at a time. You may also want to explore the approach that they favor so you can decide if it will be most beneficial for you.
What is bridging in therapy?
Bridging: The therapist starts from the patient’s preferred modality in BASIC I.D., then moves to other more efficient dimensions. For example, if the therapist finds it appropriate to start from emotional modality, if the patient prefers to start from cognitive modality, it is done so. This provides a smooth transition to other modalities in the future without making the patient feel unclear.
How many models are there in Lazarus?
Multimodal therapy of Lazarus is made up of 7 different and also interrelated models. These models are known as BASIC-ID with the abbreviation of English names formed by their initials.
Q. What is the MTA?
A. The MTA was a multisite study designed to evaluate the leading treatments for ADHD, including behavior therapy, medications, and the combination of the two. The study included nearly 600 children, ages 7-9, who were randomly assigned to one of four treatment modes:
Q. Why is the MTA important?
A. While previous studies have examined the safety and compared the effectiveness of medication and behavior therapy for ADHD, they generally were short-term—no more than four months.
Q. What are the major findings of the MTA?
A. The MTA primary results were published in December 1999 in the Archives of General Psychiatry. Combination treatment and medication management alone were both significantly superior to intensive behavioral treatment alone and to routine community care in reducing ADHD symptoms.
Q. What did the MTA tell us about the safety of stimulant medication?
A. Of the 289 children randomized to medication, 4 percent had adverse effects severe enough to prompt them to discontinue the medication. Adverse effects included loss of appetite, sleep problems, crying spells, and repetitive movements. Medication also slowed the physical growth of children during the 14 months of treatment.
Q. What is the role of behavioral therapy in treating ADHD?
A. Research has shown that behavioral therapies are very effective in treating children with ADHD. However, the MTA study demonstrated that, on average, carefully monitored medication with monthly follow-up is more effective than intensive behavioral treatment alone, for up to 14 months.
Q. Which treatment is right for my child?
A. Parents must consult with their child's doctor to determine the best course of treatment for their child. No single treatment is best for all children with ADHD. Families should consider side effects of medications, or other circumstances that might render certain treatments inappropriate for their child.
Q. Why do many social skills improve with medication?
A. Previously, it was thought that children with ADHD could only learn new social skills if they were explicitly taught. However, the MTA study findings suggest that many children can acquire these skills on their own when given the opportunity.