Full Answer
What are the 5 stages of water treatment?
You might have wondered, but what is a water treatment plant? A water treatment plant is built with carefully planned machinery and runs with the help of different kinds of chemicals to make sure that impurities are being pulled out from wastewater. If it runs perfectly, it can purify wastewater to a level that is safe to drink.
What is the purpose of a water treatment plant?
The purpose of a water treatment plant in simple terms is to purify wastewater to a safe level. Wastewater that has been run through a water treatment plant can be safely released into the environment. When this treated water mixes in with the water in rivers and canals, it doesn’t decrease the water quality. In industries, the purpose of a water treatment plant is to remove …
What are the steps in the water treatment process?
WF21 is an advanced wastewater treatment (AWT) facility that reclaims secondary treatment effluent. In the beginning in 1975, the AWT plant consisted of lime clarification, ammonia stripping, recarbonation, multimedia filtration, granular activated carbon (GAC) …
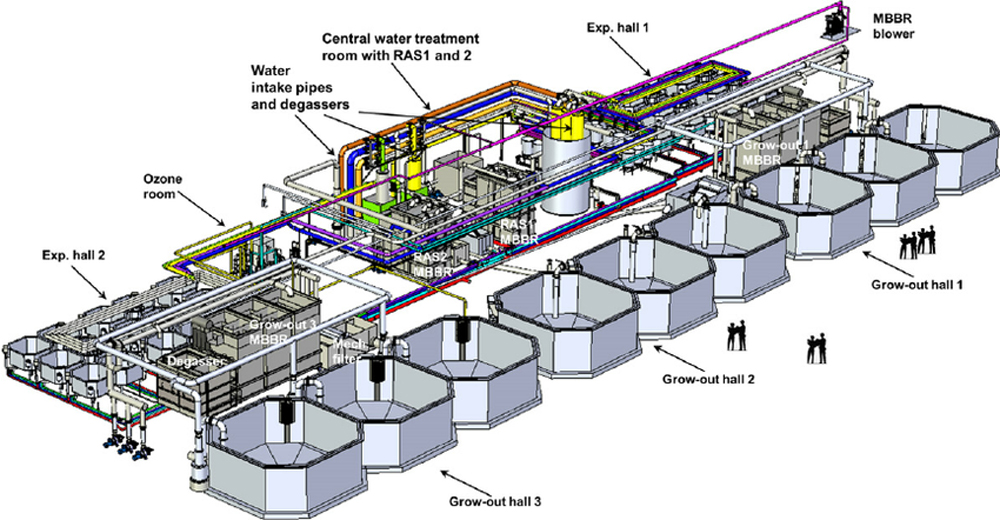
What are the components of a water treatment plant?
A number of key issues need to be addressed when converting an groundwater production facility to a water treatment plant: Physical Space Limitations - A typical groundwater production facility consists of a well, reservoir and booster pump station. The addition of treatment process equipment may exceed the physical size of the existing site.

What is a water treatment means?
Definition of water treatment noun. the act or process of making water more potable or useful, as by purifying, clarifying, softening, or deodorizing it.
What are water treatment facilities used for?
The purpose of a public or private water treatment facility is to make water potable (safe to drink) and palatable (pleasant to taste) while also ensuring that there is a sufficient supply of water to meet the community's needs.
What are the components of a water treatment facility?
The 5 major unit processes include chemical coagulation, flocculation, sedimentation, filtration, and disinfection (described below). There are chemicals added to the water as it enters the various treatment processes.
What are the types of water treatment?
Four Common Water Treatment Methods:Reverse Osmosis Water Filtration. Reverse Osmosis is a process where water pressure is employed to force water through a semi-permeable membrane. ... Ultraviolet Water Sterilization and Filtration. ... Filtration. ... Distillation.
What are the three main purposes of water treatment?
Water treatment is a process involving different types of operations (physical, chemical, physicochemical and biological), the aim of which is to eliminate and/or reduce contamination or non-desirable characteristics of water.
What are the four basic principles for water treatment?
What are the four basic principles for water treatment? Coagulation, flocculation, sedimentation – elimination of turbidity and colloid substances.Nov 25, 2021
What are the 7 methods of water treatment?
Top 7 Methods of Water TreatmentCoagulation / Flocculation. Coagulation is adding liquid aluminum sulfate or alum and/or polymer to raw or untreated water. ... Sedimentation. When water and flocs undergo the treatment process, they go into sedimentation basins. ... Filtration. ... Disinfection. ... Sludge Drying. ... Fluoridation. ... pH Correction.Nov 7, 2015
What are the 7 stages of water treatment?
These include: (1) Collection ; (2) Screening and Straining ; (3) Chemical Addition ; (4) Coagulation and Flocculation ; (5) Sedimentation and Clarification ; (6) Filtration ; (7) Disinfection ; (8) Storage ; (9) and finally Distribution.
What is the process of water treatment?
Water TreatmentCoagulation. Coagulation is often the first step in water treatment. ... Flocculation. Flocculation follows the coagulation step. ... Sedimentation. Sedimentation is one of the steps water treatment plants use to separate out solids from the water. ... Filtration. ... Disinfection.
What are the 3 parts of water treatment?
There are three main stages of the wastewater treatment process, aptly known as primary, secondary and tertiary water treatment. In some applications, more advanced treatment is required, known as quaternary water treatment.Dec 6, 2018
Which type of water is generally used in treatment of water?
Which type of water is generally used in the treatment of water? Explanation: Water treatment plant generally uses raw water which is obtained from different sources containing various impurities. It is not recommended to be used directly without treatment and hence it is supplied to the treatment plant for treatment.
Why do people use water treatment units?
Even though EPA regulates and sets standards for public drinking water, many Americans use a home water treatment unit to: Remove specific contaminants. Take extra precautions because a household member has a compromised immune system. Improve the taste of drinking water.
How does a water treatment unit work?
Even though EPA regulates and sets standards for public drinking water, many Americans use a home water treatment unit to: 1 Remove specific contaminants 2 Take extra precautions because a household member has a compromised immune system 3 Improve the taste of drinking water
What is the process of boiled water?
Distillation is a process in which impure water is boiled and the steam is collected and condensed in a separate container, leaving many of the solid contaminants behind. Disinfection. Disinfection is a physical or chemical process in which pathogenic microorganisms are deactivated or killed.
What are the steps of water treatment?
Today, the most common steps in water treatment used by community water systems (mainly surface water treatment) include: Coagulation and flocculation are often the first steps in water treatment. Chemicals with a positive charge are added to the water.
Why is surface water more contaminated than ground water?
Typically, surface water requires more treatment and filtration than ground water because lakes, rivers, and streams contain more sediment and pollutants and are more likely to be contaminated than ground water. Some water supplies may also contain disinfections by-products, inorganic chemicals, organic chemicals, and radionuclides.
What is a water softener?
Water Softeners. A water softener is a device that reduces the hardness of the water. A water softener typically uses sodium or potassium ions to replace calcium and magnesium ions, the ions that create “hardness.”. Distillation Systems.
What is the most common type of water treatment system?
The most common types of household water treatment systems consist of: Filtration Systems. A water filter is a device which removes impurities from water by means of a physical barrier, chemical, and/or biological process. Water Softeners. A water softener is a device that reduces the hardness of the water.
What is centralized water treatment?
Centralized water treatment plants are based on coagulation, flocculation and disinfection processes and found to be most cost-effective in treating large quantities of water.
What is water treatment automation?
Automation of water treatment plant involves the control system opening and closing valves and starting and stopping equipment in predefined sequences to complete specific tasks or to provide the desired process plant output. To achieve these results the automation system relies on signals from correctly selected and placed instruments, devices such as actuators and motor control circuits and reliable control logic. The degree of automation to be used is fundamental to developing an automation system.
What is the water district in Orange County?
Orange County Water District (OCWD). OCWD located between Los Angeles and San Diego counties in southern California manages the groundwater basin that supplies about 3.0 × 10 8 m 3 per year potable water to a population of more than 2 million.
What is the water used in CMF-S?
Raw (surface) water is pre-screened, and dosed with lime and carbon dioxide in a contact reactor to control alkalinity and corrosion. Next, water is dosed with a coagulant, liquid aluminium chlorohydrate (ACH) prior to entering the CMF-S plant to remove colour, some organic content, and dissolved metals.
What is the Bendigo water treatment plant?
I. Bendigo water treatment plant (BWTP). The 12.54 × 10 4 m 3/day (33 MGD) BWTP has been producing drinking water for nearly 1 million people in central Victoria, Australia since 2002. It is one of the largest if not the largest MF plant in the world. The plant combines submerged microfiltration (CMF-S), ozonation and biological activated carbon (BAC) to treat a variable and difficult raw water. Raw (surface) water is pre-screened, and dosed with lime and carbon dioxide in a contact reactor to control alkalinity and corrosion. Next, water is dosed with a coagulant, liquid aluminium chlorohydrate (ACH) prior to entering the CMF-S plant to remove colour, some organic content, and dissolved metals. The coagulant dosage is typically 5–6 mg/l. The coagulant precipitate is removed by MF. The coagulant/CMF-S process removes up to 15% of the dissolved organic carbon.64
What is make up water treatment?
Make up water treatment. Treated raw water is mixed with potable water and pumped to the boiler feedwater treatment system. The system is designed to remove 99% of the dissolved minerals and provide high-purity water to the boiler.
What is raw water pretreatment?
The raw water pretreatment plant is designed principally for solids removal from the incoming Hanover county sewage effluent (grey water), backwash water and wastewater from the oily water collection system. Raw water enters a coagulation/flocculation chamber followed by a clarifier and dual media depth filters. Backwash water from the filters is periodically returned to the clarifier. Clarifier sludge is dosed with polymer before being thickened and then sent to the filter press for dewatering. The cake is sent to landfill and the recovered water returned to the clarifier.
Why is water treatment important?
Water treatment is performed in order to improve water quality. The processes employed for water treatment depend on the quality of the water supply. In all cases, water has to be disinfected in order to deactivate any existing microorganisms present in water. So far, this technique was proved to be the most important for the protection ...
What is MF water treatment?
MF is used to remove turbidity and larger microorganisms. Water treatment in existing installations uses immersed membrane modules that are simply placed in water tanks where a vacuum at the permeate side drives the collection of purified water.
What are the most important problems in water?
If the water originates from a surface water supply such as a river, lake, or dam, then the suspended particles are the most important problem. Different techniques to remove suspended particles include the addition of coagulants and the use of membranes.
What is membrane technology?
The development of large-scale modules with lower-energy consumption reduced costs significantly. Especially in the water industry, membrane technology has grown much more than coagulation and ozonation, since membranes require minimal addition of aggressive chemical reagents and produce no by-products.
What is the most effective method of removing bacteria and viruses from raw water prior to conventional treatment?
zooplankton) and macro-invertebrate filter feeders also reduce pathogen numbers. Apart from pre-chlorination, storage is the most effective method of removing bacteria and viruses from raw water prior to conventional treatment.
What is biological waste water treatment?
Biological waste water treatment is the primary method of preparing food-processing waste water flows for return to the environment. Increasing waste water loads on existing plants and more stringent government discharge requirements have put considerable pressure on the food-processing industry to refine and understand better the design and management of biological waste water treatment processes. Though activated sludge and other biological treatment processes are still frequently operated by general guidelines and ‘rules of thumb,’ facility design and operation must be guided by consideration of both the physical and biological aspects of waste water treatment. Various modifications and combinations of aerobic and anaerobic biological treatment processes are commonly used in the food-processing industry.
How to improve the taste of water?
1. Understand the treatment need: For many consumers, simply improving the taste of the water is their primary treatment need. For some, there may be health contaminants that must be treated. And others may have very hard water, causing issues with lime scale around fixtures and possibly damaging appliances. 2.
What is water treatment?
Water treatment is any process that improves the quality of water to make it appropriate for a specific end-use. The end use may be drinking, industrial water supply, irrigation, river flow maintenance, water recreation or many other uses, including being safely returned to the environment. Water treatment removes contaminants ...
Why is water treatment important?
This treatment is crucial to human health and allows humans to benefit from both drinking and irrigation use.
What is the treatment for flocculation?
Also referred to as "Conventional" Treatment. Coagulation for flocculation. Coagulant aids, also known as polyelectrolytes – to improve coagulation and for more robust floc formation. Polyelectrolytes or also known in the field as polymers, usually consist of either a positive or negative charge.
What is chemical treatment?
Chemical treatments are techniques adopted to make industrial water suitable for use or discharge. These include chemical precipitation, chemical disinfection, chemical oxidation, advanced oxidation, ion exchange, and chemical neutralization.
What is water cooling?
Water cooling is a method of heat removal from components of machinery and industrial equipment. Water may be a more efficient heat transfer fluid where air cooling is ineffective. In most occupied climates water offers the thermal conductivity advantages of a liquid with unusually high specific heat capacity and the option that of evaporative cooling. Low cost often allows rejection as waste after a single use, but recycling coolant loops may be pressurized to eliminate evaporative loss and offer greater portability and improved cleanliness. Unpressurized recycling coolant loops using evaporative cooling require a blowdown waste stream to remove impurities concentrated by evaporation. Disadvantages of water cooling systems include accelerated corrosion and maintenance requirements to prevent heat transfer reductions from biofouling or scale formation. Chemical additives to reduce these disadvantages may introduce toxicity to wastewater. Water cooling is commonly used for cooling automobile internal combustion engines and large industrial facilities such as nuclear and steam electric power plants, hydroelectric generators, petroleum refineries and chemical plants .
What are the two main processes of water treatment?
Processes. Two of the main processes of industrial water treatment are boiler water treatment and cooling water treatment . A large amount of proper water treatment can lead to the reaction of solids and bacteria within pipe work and boiler housing. Steam boilers can suffer from scale or corrosion when left untreated.
What to do when living away from drinking water?
Living away from drinking water supplies often requires some form of portable water treatment process . These can vary in complexity from the simple addition of a disinfectant tablet in a hiker's water bottle through to complex multi-stage processes carried by boat or plane to disaster areas.

Community Water Treatment
Water Fluoridation
- Community water fluoridation prevents tooth decay safely and effectively. Water fluoridation has been named one of 10 great public health achievements of the 20th century 1. For more information on the fluoridation process and to find details on your water system’s fluoridation, visit CDC’s Community Water Fluoridationpage. Top of Page
Consumer Confidence Reports
- Every community water supplier must provide an annual report, sometimes called a Consumer Confidence Report, or “CCR,” to its customers. The report provides information on your local drinking water quality, including the water’s source, contaminants found in the water, and how consumers can get involved in protecting drinking water. 1. View the CDC’s guide to Understandi…
Household Water Treatment
- Even though EPA regulates and sets standards for public drinking water, many Americans use a home water treatment unit to: 1. Remove specific contaminants 2. Take extra precautions because a household member has a compromised immune system 3. Improve the taste of drinking water Household water treatment systems are composed of two categories: point-of-us…
Overview
Water treatment is any process that improves the quality of water to make it appropriate for a specific end-use. The end use may be drinking, industrial water supply, irrigation, river flow maintenance, water recreation or many other uses, including being safely returned to the environment. Water treatment removes contaminantsand undesirable components, or reduces their concentration so that the water becomes fit for its desired end-use. This treatment is cruci…
Regulation
The Safe Drinking Water Act requires the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) to set standards for drinking water quality in public water systems (entities that provide water for human consumption to at least 25 people for at least 60 days a year). Enforcement of the standards is mostly carried out by state health agencies. States may set standards that are more stringent than the federal standards.
Drinking water treatment
Water contamination is primarily caused by the discharge of untreated wastewater from enterprises. The effluent from various enterprises, which contains varying levels of contaminants, is dumped into rivers or other water resources. The wastewater may have a high proportion of organic and inorganic contaminants at the initial discharge. Industries generate wastewater as a result of fabrication processes, processes dealing with paper and pulp, textiles, chemicals, and fro…
Heavy Metals
Heavy metals in wastewater have become a serious environmental issue in recent years, owing to the high damage they pose to ecosystems and human health even at extremely low concentrations. Heavy metal pollution is a substantial environmental burden due to its flexibility, accumulation, non-biodegradability, and persistence. Its effluent is discharged into the environment by industries such as paper, Insecticides, tanneries, metal plating, mining operations, …
Water Treatment Technologies
Elimination of hazardous chemicals from the water, many treatment procedures have been applied. The selection of wastewater treatment systems is contingent on a number of factors: (1)The degree to which a method is necessary to raise the waste water quality to a permissible level; (2) The control method's flexibility; (3) The process's cost; and (4) The process's environmental compatibility.
Standards
Many developed countries specify standards to be applied in their own country. In Europe, this includes the European Drinking Water Directive and in the United States the United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) establishes standards as required by the Safe Drinking Water Act. For countries without a legislative or administrative framework for such standards, the World Health Organizationpublishes guidelines on the standards that should be achieved. China …
Industrial water treatment
Two of the main processes of industrial water treatment are boiler water treatment and cooling water treatment. A large amount of proper water treatment can lead to the reaction of solids and bacteria within pipe work and boiler housing. Steam boilers can suffer from scale or corrosionwhen left untreated. Scale deposits can lead to weak and dangerous machinery, while additional fuel is required to heat the same level of water because of the rise in thermal resistance. Poor q…
Developing countries
Appropriate technology options in water treatment include both community-scale and household-scale point-of-use (POU) or self-supply designs. Such designs may employ solar water disinfection methods, using solar irradiation to inactivate harmful waterborne microorganisms directly, mainly by the UV-A component of the solar spectrum, or indirectly through the presence of an oxide photocatalyst, typically supported TiO2 in its anatase or rutile phases. Despite progress in SODISte…