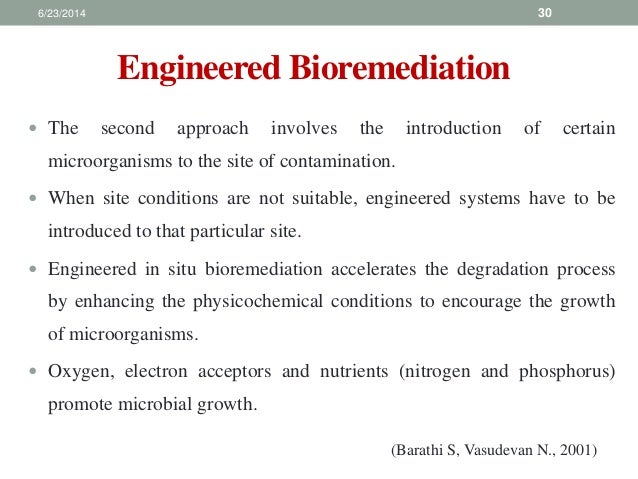
What are the methods of PCB wastewater treatment?
PCB wastewater treatment is mainly divided into the chemical method and physical method. Chemical method is to convert pollutants in wastewater into the easily separable physical state (solid or gaseous), including chemical precipitation method, redox method, ion exchange method, and electrolysis method.
What is a PCB?
PCBs belong to a broad family of man-made organic chemicals known as chlorinated hydrocarbons. PCBs were domestically manufactured from 1929 until manufacturing was banned in 1979.
What will happen if the PCB wastewater is polluted?
If the PCB wastewater is allowed to polluted, the consequences will be unimaginable. China PCB fabrication industry value has accounted for more than 25% of the world's total output value, becoming the world's first PCB fabrication site, but the rapid development also has exacerbated the wastewater emissions during PCB fabrication process.
What is risk-based PCB remediation?
Risk-based cleanup and disposal (40 CFR section 761.61 (c)) The risk-based option allows for a site-specific approval to sample, cleanup, or dispose of PCB remediation waste in a manner other than the self-implementing or the performance-based disposal options.

What is PCB wastewater?
Polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) are a toxic manmade chemical found nearly everywhere in the environment. Historically, PCBs were primarily used in coolants and lubricants in electrical equipment, such as transformers and capacitors. In the United States, PCBs were largely sold under the trade name Aroclor.
What does PCBs stand for?
Polychlorinated biphenylsPolychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) are a group of manmade chemicals. They are oily liquids or solids, clear to yellow in color, with no smell or taste.
What does PCB and DDT stand for?
The human health effects of DDT (dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane) and PCBS (polychlorinated biphenyls) and an overview of organochlorines in public health.
What does PCB stand for EPA?
Polychlorinated BiphenylsPolychlorinated Biphenyls (PCBs) | US EPA.
How do you remove PCBs from water?
The good news is that PCBs can be removed from water effectively with PCBs water filters that use activated carbon as part of their active filtration medium. The best water treatment solution for removing polychlorinated biphenyls from drinking water is by using the granular activated carbon (GAC).
What are PCBs and why are they toxic?
PCBs belong to a broad family of man-made organic chemicals known as chlorinated hydrocarbons. PCBs were domestically manufactured from 1929 until manufacturing was banned in 1979. They have a range of toxicity and vary in consistency from thin, light-colored liquids to yellow or black waxy solids.
What is PCBs pesticide?
Background. Polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) and organochlorine pesticides (OCPs) are persistent organic pollutants that have been linked to many health concerns involving the liver, skin, reproductive, endocrine, neurological and immune system[1–4].
Are PCBs still used today?
Unfortunately, the legacy of PCBs for humans, birds, fish, wildlife, and habitat has been a lasting one. As NOAA's National Ocean Service notes: Even with discontinued use, PCBs, or polychlorinated biphenyls, are still present in the environment today because they do not breakdown quickly.
Why is PCBs bad for the environment?
Environmental Impacts: The PCBs accumulate in the food chain when bigger fish consume contaminated smaller fish or organisms. The contamination is passed up the food chain and can reach levels thousands of times higher than the actual levels in the water.
Is PCB oil hazardous waste?
Ballasts manufactured through 1979 may contain PCBs. PCB containing ballasts become a concern if they are leaking or they will be removed and disposed of as hazardous waste. According to EPA Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA) regulations, the material must be incinerated.
What is PCB contaminated oil?
Polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) are highly carcinogenic chemical compounds, formerly used in industrial and consumer products, whose production was banned by United States federal law in 1978 and by the Stockholm Convention on Persistent Organic Pollutants in 2001.
How do you calculate total PCBs?
Total PCB, calculated by multiplying the sum of the three indicator congeners by 2, showed a strong and highly significant correlation to the sum of all 209 measured congeners for each sample.
What is a PCB congener?
A PCB congener is any single, unique well-defined chemical compound in the PCB category . The name of a congener specifies the total number of chlorine substituents, and the position of each chlorine. For example: 4,4'-Dichlorobiphenyl is a congener comprising the biphenyl structure with two chlorine substituents - one on each of the #4 carbons of the two rings. In 1980, a numbering system was developed which assigned a sequential number to each of the 209 PCB congeners.
Where are PCB regulations found?
Current PCB regulations, published pursuant to the TSCA statute, can be found in Title 40 of the Code of Federal Regulations (CFR) in Part 761 . The Government Printing Office maintains the most current version of the CFR. View PCB regulations in the electronic-CFR. For useful interpretation of the regulations as well as answers to frequently asked questions please visit EPA's Policy and Guidance for PCBs page.
What are PCB homologs?
PCB Homologs. Homologs are subcategories of PCB congeners that have equal numbers of chlorine substituents. For example, the tetrachlorobiphenyls are all PCB congeners with exactly 4 chlorine substituents that can be in any arrangement. Table of PCB Homologs.
What are PCBs made of?
What Are PCBs? PCBs are a group of man-made organic chemicals consisting of carbon, hydrogen and chlorine atoms. The number of chlorine atoms and their location in a PCB molecule determine many of its physical and chemical properties.
How do PCBs affect animals?
PCBs can affect an animal’s immune system, reproductive system, nervous system and endocrine system. The body's regulation of all of these systems is complex and interrelated. As a result, it is not surprising that PCBs can exert a multitude of serious adverse health effects.
What products contain PCBs?
Products that may contain PCBs include: Transformers and capacitors. Electrical equipment including voltage regulators, switches, re-closers, bushings, and electromagnets.
When was the first PCB assessment done?
EPA's first assessment of PCB carcinogenicity was completed in 1987. At that time, data was limited to Aroclor 1260. In 1996, at the direction of Congress, EPA completed a reassessment of PCB carcinogenicity titled "PCBs: Cancer Dose-Response Assessment and Application to Environmental Mixtures".
What is PCB Fast?
The PCB Facility Approval Streamlining Toolbox (PCB FAST) is designed to help Responsible Parties (RPs) and regulators, whenever possible, reduce delays, improve communication, and increase efficiency in the cleanup and disposal of PCBs at a site. PCB FAST focuses on establishing a collaborative working relationship between EPA and the RPs and providing tools to be used by RPs to prepare adequate and appropriate cleanup notifications and applications. The Toolbox includes guidance, process flow maps, and checklists to facilitate streamlined cleanup processes. These resources can be customized to meet each site or Region’s needs.
Is EPA notification required for PCB disposal?
EPA notification and approval is not required under this option, however, you are encouraged to contact your Regional PCB Coordinator with questions. Facilities are required to follow any manifesting, transportation and storage requirements that may apply. Performance based disposal may be used for sites of any size.
Is PCB spill cleanup a regulation?
The PCB Spill Cleanup Policy is an enforcement policy, not a regulation. In addition to other applicability limitations found in 40 CFR section 761.120, this policy only applies to spills less than 72 hours old. The use of the methods in this guidance manuals is an option, not a requirement.
What is PCB used for?
It was primarily used in electrical, heat transfer, and hydraulic equipment and had varying appearances from thin, light colored liquids to black waxy solids. [viii] PCBs are released into the environment by the improper handling and disposal of wastes containing PCBs.
What is PCB in the US?
PCBs describe a broad range of man-made chemicals used for hundreds of industrial and commercial products. Due to its extreme toxicity to humans, it has been banned in the U.S. for production since 1979. It was primarily used in electrical, heat transfer, and hydraulic equipment and had varying appearances from thin, light colored liquids to black waxy solids. [viii]
What are the effects of PCBs on the environment?
Adverse impacts on the environment: PCBs have been shown to cause cancer in animals, in addition to serious effects on the immune system, reproductive system, nervous system, endocrine system and other health effects. [v]
Why are PCBs insoluble in water?
Because PCBs are highly insoluble in water, they are typically associated with solid particulate matter. Contaminated soils and debris can then be transferred into aquatic and terrestrial environments through surface water flows. [ix] Bioaccumulation also plays a transport mechanism within the food-chain. Materials suspect of containing PCBs should ...
What are PCBs associated with?
PCBs are associated with pigments, especially some yellows, greens, and blues. Use all-natural products with the least amount of chemical ingredients. Do not flush or dump into the storm drain oils, pesticides, paints, solvents, or other chemicals.
Where can PCBs be found?
Low levels of PCBs can be found in our wastewater, stormwater, air, groundwater, and even in our own bodies. They enter the environment through a number of different pathways, including inks and dyes (paint, dyed clothing, colored paper and packaging, etc.), motor oil, gasoline, pesticides, personal care products, caulks, and many other products.
How to reduce PCBs in Spokane?
The City is continuing with other work to reduce PCBs entering the Spokane River. Among other things, the City is: 1 Working on a project to disconnect the stormwater outfall from the Union Basin to the Spokane River. Historically, this basin is heavy industrial area, and testing has shown higher concentrations of PCBs than other areas within the City. The City received a grant from the state Department of Ecology for this work. 2 Completing more regular cleaning of sediments in catch basins, particularly in industrial areas, to remove PCBs before they reach the river. Testing of these sediments shows ongoing and diffuse sources of PCBs in some areas. 3 Working to identify sources of PCBs. The City received a grant in late 2013 to test for PCB levels in products that may come in contact with stormwater that are purchased by local governments. See the PCB product testing report on this page for more information. 4 Implementing its new PCB-free product preference purchasing policy. In June, the City Council adopted new policies that require the City to give preference to PCB-free products. 5 Encouraging the use of low-impact development techniques by private developers to more effectively manage stormwater on site.
Where do PCBs accumulate in the food web?
PCB concentrations increase in animals through the food web. Because there are PCBs present in the Spokane River and subsequently high concentrations of PCBs in its fish, the Department of Health has placed limits on the amount of fish you can eat from certain sections of the Spokane River. PCBs Bioaccumulate in the Food Web.
What is the plan for the Clean Water Act?
The plan includes work that is mandated and other voluntary work that just makes sense for the health of the river. The plan takes aim at a variety of pollutants and will deliver magnitudes greater pollution reduction benefits to the river than if the City chose to complete only the work that is required by the Clean Water Act and other mandates.
What is sewage sludge used for?
Application of sewage sludge as soil organic amendment and as a source of macronutrients and micronutrients can contribute not only to restore the soil cover and vegetation on devastated land [ 72] but also can be used in the organization and maintenance of green areas in cities and recreational facilities.
Is sewage sludge a fertilizer?
The use of sewage sludge as plant fertilizer is not only the method of sewage sludge management but also the method for implementation of the Renewable Energy Sources Directive—when using energetic crops (2001/77/EC) and the Kyoto Protocol (OJ L 203 of 2005, p.1684).
Does sewage sludge have a limit?
In case of sewage sludge, the Directive 86/278/EEC on the protection of the environment, and in particular of the soil when sewage sludge is used in agriculture, does not provide any limit values or requirements for organic compounds in sewage sludge.
What is biological water treatment?
A biological water treatment technology commonly used in municipal wastewater treatment systems. Sometimes private industry will harness this technique to reduce certain pollutants, such as BOD and COD (see definitions below), but usually only due to compliance concerns.
What is wastewater permit?
These terms refer to the amount of wastewater flow over a given time period. Most wastewater permits include daily flow limits, so facilities track the flow of treatment systems to stay within overall permit parameters.
What is a control parameter for treating hexavalent chromium wastewater?
A measure that indicates the capacity of wastewater to gain or reduce electrons during a chemical reaction. It is used as a control parameter for treating hexavalent chromium wastewater in the metal finishing industry.
What is PSI in wastewater treatment?
A measurement of pressure. It’s often used when discussing physical wastewater treatment technologies involving filtration, but is also used with pumps. Filtration system PSI can indicate when it’s time to backwash or change a filter.
Why is UV light used in wastewater treatment?
In some industries, ultraviolet light is used to sterilize water treated wastewater prior to reuse or recycling. UV light keeps algae and other bacteria from growing in the recycled wastewater.
What are visible solids in wastewater?
Visible solids present in wastewater that can be filtered out through traditional physical treatment technologies. In the metal finishing industry, for example, FOG (fats, oils and grease) and dirt particles might make up part of the total suspended solids.
What is an indirect reading of the organic content present in wastewater?
Specifically, it refers to the amount of oxygen consumed to biologically degrade the organic material. It’s very expensive to treat, typically requiring a biological treatment technology like activated sludge.

What Are PCBs?
- PCBs are a group of man-made organic chemicals consisting of carbon, hydrogen and chlorine atoms. The number of chlorine atoms and their location in a PCB molecule determine many of its physical and chemical properties. PCBs have no known taste or smell, and range in consistency from an oil to a waxy solid. PCBs belong to a broad family of man-made...
Inadvertent PCBs
- In the United States, PCBs were commercially manufactured from 1929 until production was banned in 1979 by the Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA). However, EPA’s regulations implementing TSCA for PCBs allow some inadvertent generation of PCBs to occur in excluded manufacturing processes, as defined in title 40 of the Code of Federal Regulations (CFR) sectio…
Commercial Uses For PCBs
- Although no longer commercially produced in the United States, PCBs may be present in products and materials produced before the 1979 PCB ban. Products that may contain PCBs include: 1. Transformers and capacitors 2. Electrical equipment including voltage regulators, switches, re-closers, bushings, and electromagnets 3. Oil used in motors and hydraulic systems 4. Old electri…
Release and Exposure of PCBs
- Today, PCBs can still be released into the environment from: 1. Poorly maintained hazardous waste sites that contain PCBs 2. Illegal or improper dumping of PCB wastes 3. Leaks or releases from electrical transformers containing PCBs 4. Disposal of PCB-containing consumer products into municipal or other landfills not designed to handle hazardous waste 5. Burning some waste…
PCB Congeners
- A PCB congener is any single, unique well-defined chemical compound in the PCB category. The name of a congener specifies the total number of chlorine substituentsand the position of each chlorine. For example: 4,4'-Dichlorobiphenyl is a congener comprising the biphenyl structure with two chlorine substituents - one on each of the #4 carbons of the two rings. In 1980, a numberin…
PCB Homologs
- Homologs are subcategories of PCB congeners that have equal numbers of chlorine substituents. For example, the tetrachlorobiphenyls are all PCB congeners with exactly 4 chlorine substituents that can be in any arrangement. 1. Table of PCB Homologs
PCB Mixtures and Trade Names
- With few exceptions, PCBs were manufactured as a mixture of individual PCB congeners. These mixtures were created by adding progressively more chlorine to batches of biphenyl until a certain target percentage of chlorine by weight was achieved. Commercial mixtures with higher percentages of chlorine contained higher proportions of the more heavily chlorinated congeners…
PCB Trade Names
- PCBs were manufactured and sold under many different names. The names in the following table have been used to refer to PCBs or to products containing PCBs. Please note: 1. Some of these names may be used for substances or mixtures not containing PCBs. 2. Many of these names were used with distinguishing suffixes, indicating degree of chlorination, type of formulation, or …
Health Effects of PCBs
- PCBs have been demonstrated to cause a variety of adverse health effects. They have been shown to cause cancer in animals as well as a number of serious non-cancer health effects in animals, including: effects on the immune system, reproductive system, nervous system, endocrine system and other health effects. Studies in humans support evidence for potential car…
Laws and Regulations
- Statute: Toxic Substances Control Act
The Toxic Substances Control Act of 1976 provides EPA with authority to require reporting, record-keeping and testing requirements, and restrictions relating to chemical substances and/or mixtures, including PCBs. Some substances are generally excluded from TSCA, including but no… - PCB Regulations: Part 761 in Title 40 of the Code of Federal Regulations
Current PCB regulations, published pursuant to the TSCA statute, can be found in Title 40 of the Code of Federal Regulations (CFR) in Part 761. The Government Printing Office maintains the most current version of the CFR. View PCB regulations in the electronic-CFR. For useful interpret…