
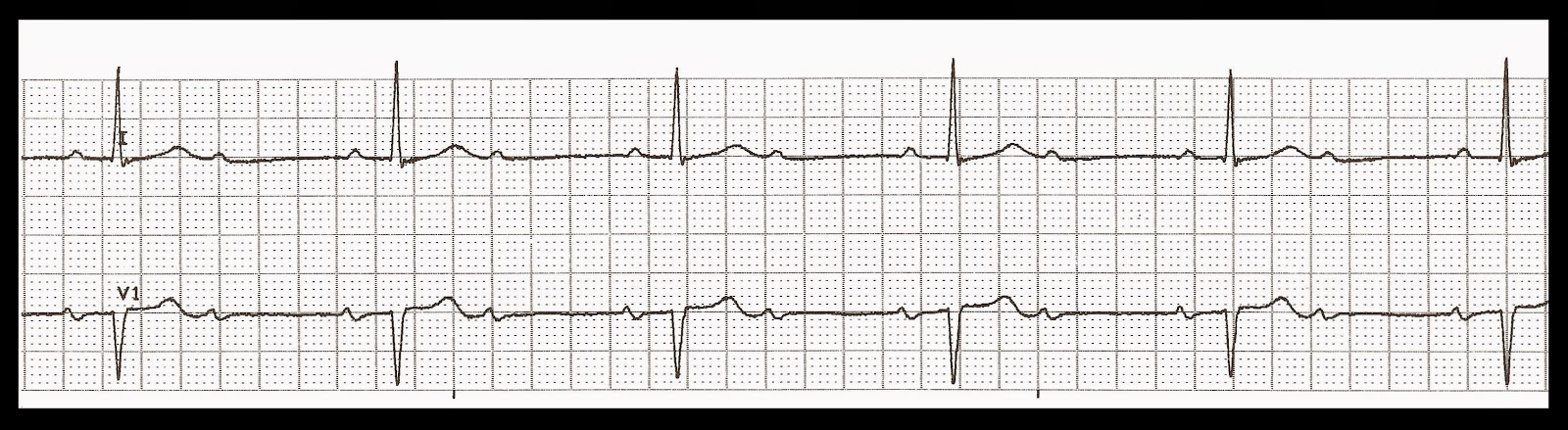
A first degree AV block is indicated on the ECG by a prolonged PR interval
PR interval
In electrocardiography, the PR interval is the period, measured in milliseconds, that extends from the beginning of the P wave (the onset of atrial depolarization) until the beginning of the QRS complex (the onset of ventricular depolarization); it is normally between 120 and 200ms in duration. …
What causes first degree heart block?
Causes. The most common causes of first-degree heart block are AV nodal disease, enhanced vagal tone (for example in athletes), myocarditis, acute myocardial infarction (especially acute inferior MI), electrolyte disturbances and medication. The medications that most commonly cause first-degree heart block are those that increase the refractory time of the AV node, thereby slowing AV conduction.
What is the prognosis for heart block?
With second-degree, you may:
- Get tired
- Feel dizzy or faint
- Have a slow heart rate
- Skip heartbeats
- Have trouble breathing
- Get chest pain
- Feel sick to your stomach
How do you identify first degree heart block?
They should receive counseling on symptoms associated with worsening heart block, such as:
- Dizziness or fainting
- The feeling of a "missed" beat
- Chest pain
- Dyspnea or shortness of breath
- Unexplained nausea
- Easily fatigued
What is the treatment for 3rd degree heart block?
- Basic: Recognize third-degree AV block
- Intermediate: Determine the difference between stable and unstable presentation
- Advanced: Identify the appropriate treatment (s) for this patient
Is 1st degree heart block serious?
Heart block is categorized as first-, second-, or third-degree: First-degree heart block is the least severe. The electrical signals slow down as they move from your atria to your ventricles. First-degree heart block might not require treatment of any kind.
Does a first-degree heart block need a pacemaker?
With first-degree heart block, you might not need treatment. With second-degree heart block, you may need a pacemaker if symptoms are present or if Mobitz II heart block is seen. With third-degree heart block, you will most likely need a pacemaker.
What is the drug of choice for first-degree heart block?
First-degree AV block occurs in <1.5% of patients with AMI admitted to hospital. Generally, it does not require specific treatment. If it is associated with signs of excessive vagal tone (i.e., severe hypotension), administration of atropine may be helpful.
What medication is given for heart block?
Medications that may be used in the management of third-degree AV block (complete heart block) include sympathomimetic or vagolytic agents, catecholamines, and antidotes.
How common is 1st degree AV block?
First degree AV block affects 0.65-1.1% of the population with 0.13 new cases per 1000 persons each year.
Is first-degree heart block reversible?
First-degree AV block (reversible or permanent) has been reported in about 2% of patients who undergo closure of an atrial septal defect using the Amplatzer septal occluder. First-degree AV block can occur following cardiac surgery.
Can you give atropine for 1st degree heart block?
Atropine is useful for treating symptomatic sinus bradycardia and may be beneficial for any type of AV block at the nodal level. The recommended atropine dose for bradycardia is 0.5 mg IV every 3 to 5 minutes to a maximum total dose of 3 mg.
Can you give atropine with a first degree block?
in patients with severe bradycardia or those with the possibility of progression to higher-degree AV block, medications (eg, atropine, isoproterenol) can be used in anticipation of insertion of a cardiac pacemaker.
What are the symptoms of first-degree heart block?
In higher-grade first-degree block (PR interval greater than 0.30 seconds), patients may develop symptoms similar to pacemaker syndrome: dyspnea, malaise, lightheadedness, chest pain, or even syncope due to poor synchronization of atrial and ventricular contractions.
Can heart blockage be treated without surgery?
Through angioplasty, our cardiologists are able to treat patients with blocked or clogged coronary arteries quickly without surgery. During the procedure, a cardiologist threads a balloon-tipped catheter to the site of the narrowed or blocked artery and then inflates the balloon to open the vessel.
Is heart block curable by medicine?
There is no heart-block-specific treatment. Most people with bundle branch block have no symptoms, and they do not require treatment. However, any underlying causes, such as hypertension, will need treatment. Share on Pinterest Patients with second- or third-degree heart block may need a pacemaker.
Does heart block go away?
Heart block may resolve on its own, or it may be permanent and require treatment. There are three degrees of heart block. First-degree heart block is the mildest type and third-degree is the most severe.
What causes a block in the heart?
Other causes of first degree heart block are: 1 Infectious disease – such as Lyme disease, which is associated with carditis (a heart complication of the disease) and usually found in children; viruses can also cause myocarditis or inflammation of the heart muscles 2 Intrinsic disease of the atrioventricular node – part of the heart where electrical impulses are generated 3 Myocardial infarction or an acute heart attack 4 Disturbances in blood electrolytes such as increases in potassium and decreases in magnesium 5 Drugs that can cause slowing of heart rate such as beta-blockers, calcium channel blockers, other antiarrhythmics and magnesium
What is the vagal tone?
Vagal tone is an intrinsic inhibition of heart beats by the vagal nerve that is responsible for slowing down the heart.
What happens when the electrical impulses from the atrium to the ventricle are slowed down?
When the electrical impulses from an atrium to the ventricle are slowed down or disrupted, an atrio-ventricular heart block is said to occur. This results in an arrhythmia, or a disturbance in the rhythm or pattern of heart beats.
What causes myocarditis in children?
Infectious disease – such as Lyme disease, which is associated with carditis (a heart complication of the disease) and usually found in children; viruses can also cause myocarditis or inflammation of the heart muscles. Intrinsic disease of the atrioventricular node – part of the heart where electrical impulses are generated.
What is the electrical system of the heart?
The heart has an electrical system that controls the rate and rhythm of heart beats. An electrical signal spreads across the heart from the two upper chambers (atria) to the two lower chambers (ventricles) with each heart beat causing the contraction of heart muscles. The result is pumping of blood from one chamber to the next, ...
How common is heart block in young adults?
In the United States 0.65-1.6% of young adults experience a first degree heart block, and it is especially common in trained athletes. Its prevalence increases with age, although it is more common in African Americans than Caucasians.
Is a heart block a symptom?
First degree heart blocks are rarely symptomatic and don’t usually cause disturbances in a patient’s sense of well being. This is because despite the relatively slower conduction of impulses from the atrium to the ventricle compared to a normal heart, each atrial contraction is always followed by a ventricular contraction as in normal hearts.
Is a second degree heart block rare?
The prognosis for patients with first-degree heart block is excellent. Progression to a second-degree heart block is very rare.
Is a heart block asymptomatic?
While first-degree heart block is usually asymptomatic and an incidental EKG finding, patients should have routine follow-up monitoring to ensure the condition does not progress to worse cardiac conduction issues. Patients can generally lead a normal, symptom-free life absent any progression of the condition.
Is AV block a benign condition?
Although generally believed to be a benign condition, cohort studies have shown that patients with first-degree AV block have a higher incidence of atrial fibrillation, pacemaker placement, and all-cause mortality than patients with normal PR intervals.
What medications slow the heart's electrical impulses?
You take medications that slow the conduction of the heart’s electrical impulses including some heart medications (beta blockers, calcium channel blockers, digoxin), high blood pressure drugs, antiarrhythmics; muscle relaxants and sedatives; antidepressants and antipsychotics; diuretics; lithium.
What is the difference between type 2 and type 2?
The electrical signal gets slower and slower until your heart actually skips a beat. Type II, also called Mobitz Type II: While most of the electrical signals reach the ventricles every so often , some do not and your heartbeat becomes irregular and slower than normal.
What is an electrophysiology test?
Electrophysiologists are physicians who specialize in the electrical activity of the heart. Tests you might undergo include: An ECG: An electrocardiogram (ECG) records your heart’s electrical activity – its heart rate and rhythm and the timing of electrical signals as they move through your heart.
What is the name of the block that makes your heart beat?
Heart Block. Heart block, also called AV block, is when the electrical signal that controls your heartbeat is partially or completely blocked. This makes your heart beat slowly or skip beats and your heart can’t pump blood effectively. Symptoms include dizziness, fainting, tiredness and shortness of breath. Pacemaker implantation is ...
What is the purpose of an electrophysiology study?
An electrophysiology study: An electrophysiology study involves inserting a long, thin tube called a catheter through a blood vessel and guiding it to your heart to measure and record electrical activity from inside your heart. If you need this test, you’ll get more detailed information.
How to keep your heart healthy?
Steps you can take to keep your heart and body as healthy as possible include: Lead a heart-healthy lifestyle, which includes eating a heart healthy diet, exercising regularly, getting an adequate amount of sleep each night, reducing stress, limiting alcohol and stopping smoking and use of illicit drugs.
What is the mildest heart block?
First-degree heart block: The electrical impulse still reaches the ventricles, but moves more slowly than normal through the AV node. The impulses are delayed. This is the mildest type of heart block. Second-degree heart block is classified into two categories: Type I and Type II.
What is the difference between a first degree heart block and a second degree heart block?
The electrical signals slow down as they move from your atria to your ventricles. First-degree heart block might not require treatment of any kind. Second-degree heart block means that the electrical signals between your atria and ventricles can intermittently fail to conduct. There are 2 types of second-degree heart block.
What happens when your heart is blocked?
When you have heart block, there is interference with the electrical signals that usually move from the atria to the ventricles. These signals tell your heart when to beat. This is known as a conduction disorder. If the electrical signals can’t move from your atria to your ventricles, they can’t tell your ventricles to contract ...
What is the difference between Mobitz type 1 and type 2?
Mobitz type I: The electrical signals get slower and slower between beats. Eventually your heart skips a beat. Mobitz type II: The electrical signals sometimes get to the ventricles, and sometimes they do not. There is no progressive slowing of the electrical signal.
What causes wire damage in the heart?
Cardiomyopathies which are diseases that weaken the heart muscle can also result in wire damage. Any disease that can infiltrate the heart such as sarcoidosis and certain cancers or any disease that results in heart inflammation such as certain autoimmune disease or infections can result in heart block.
What is the process of electrical signals?
Electrical signals control the beating of your heart. They tell your heart muscle when to contract, a process known as conduction. The normal timing of heartbeats is generated in the upper chamber of the heart (atria) in a structure called the sinus node. When you have heart block, there is interference with the electrical signals ...
How to prevent heart block?
A healthy lifestyle contributes to overall good health — including heart health. Exercise, eat a well-balanced diet, and don’t smoke. Understanding the risks of your medicines and reviewing them with your healthcare provider can reduce the risk of medicine-induced heart block.
How to improve quality of life with pacemaker?
Also, always keep follow-up appointments to make sure your treatment is on track. To improve your quality of life with a pacemaker, you may need to: Avoid situations in which your pacemaker may be disrupted, such as being near an electrical device or devices with strong magnetic fields.
What happens after a heart block?
Life After Heart Block . Your heartisn’t plugged into an outlet. And you don’t use a switch to turn it on. But just like a lamp, your heartruns on an electrical system. Every time your heart beats, an electrical signal travels from the upper to the lower chambers. Along the way, the signal tells your heart to contract and pump blood.
What is the name of the monitor that a doctor will use to check your heart?
They may also ask you to wear a monitor, called a Holter, for anywhere from a day to a month to track the rhythm of your heart. Treatment.
Is a pacemaker considered a minor surgery?
This is considered “minor” surgery and you’ll be sedated for it. Like a backup electrical system, it reminds the heart to beat at a normal rate if it slows or stops. Life After Heart Block. Just like your heart, your pacemaker needs to be treated right to work well.
What are the symptoms of first-degree heart block?
First-degree heart block often does not have any symptoms. It may be found when your healthcare provider is checking you for some other reason.
How is first-degree heart block treated?
First-degree heart block often doesn’t need treatment. Your healthcare provider may ask you to have regular follow-up visits. You may also be asked to take your own pulse and be alert to changes in your heart rate.
What are possible complications of first-degree heart block?
In rare cases, a first-degree heart block may turn into a more serious type of heart block that results in slower heartbeats. This may cause symptoms. You may need a pacemaker.
What to do if patient is unresponsive?
If you find a person unresponsive, you would call for help and a defibrillator and then perform a pulse check. If there is no pulse, then begin CPR.
What medications inhibit AV node conduction?
Medications that inhibit AV node conduction (amiodarone, beta-blockers, calcium channel blockers, digoxin) Acute rheumatic fever (see more in infants and children) Below is a short video which will help you quickly identify first-degree AV block on a monitor.

Clinical significance
- In people with heart block, also called AV block, the electrical signal that controls the heartbeat is partially or completely blocked from reaching the ventricles.
Classification
- Heart block is classified as first-, second- or third-degree, depending on the extent of electrical signal impairment.
Overview
- Type I heart block (also called Mobitz Type I or Wenckebach's AV block) is the less serious form of second-degree heart block. In this condition, the electrical signal goes slower and slower until the heart actually skips a beat.
Symptoms
- In patients with Type II heart block (also called Mobitz Type II), some of the electrical signals do not reach the ventricles, and the pattern is irregular. Individuals with this type of heart block may have a heartbeat that is slower than normal. The area that is blocked is lower in the conduction system and is often associated with more severe conduction disease. Symptoms of second- an…
Mechanism
- In patients with third-degree (complete) heart block, the electrical signal is not sent from the atria to the ventricles. The heart compensates by producing electrical signals from a specialized pacemaker area in the ventricles. These signals make the heart contract and pump blood, but at a rate that is much slower than normal.
Signs and symptoms
- First-degree heart block often does not cause symptoms. It may be detected during a routine electrocardiogram (ECG/EKG), but the patients heart rate and rhythm are usually normal.
Causes
- Acquired heart block has many possible causes, including heart attack (the most common cause), heart disease, an enlarged heart (cardiomyopathy), heart failure and rheumatic fever. Sometimes heart block occurs as a result of injury to the heart during open heart surgery, as a side effect of some drugs, or after exposure to a toxin.