Radiation Necrosis Treatment
- Surgery may be used to remove the necrotic tissue.
- Hyperbaric oxygen treatment involves the breathing of pure oxygen. ...
- Corticosteroid drugs, or steroids, may help to control the unwanted tissue growth.
- Anticoagulants, such as warfarin or heparin, can help to slow the accumulation of necrotic tissue.
What is radiation necrosis in cancer treatment?
Radiation Necrosis Treatment. In some cases, radiation therapy can leave behind damaged body tissue. Or in the months or years following radiation treatment, a mass of dead (necrotic) tissue might form at the site of the tumor. This tissue is called radiation necrosis.
What are the treatment options for radiation necrosis refractory to steroids?
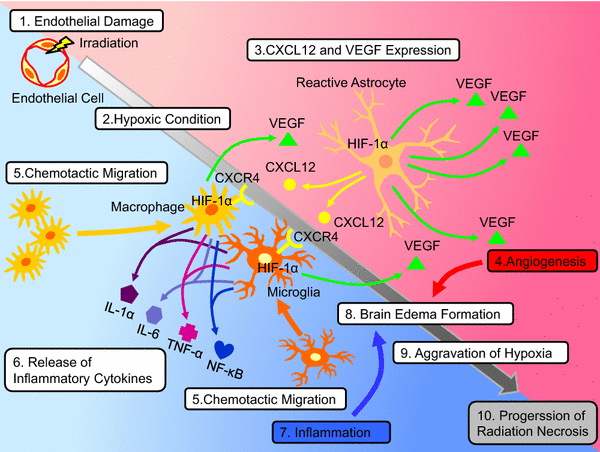
Bevacizumab, a VEGF receptor antibody, is the preferred second-line therapy for management of radiation necrosis refractory to steroids.110,111 Surgical resection to reduce mass effect and edema is an option for surgically accessible regions.
How do you get rid of radiotherapy necrotic tissue?
Radiation Necrosis Treatment 1 Surgery may be used to remove the necrotic tissue. 2 Hyperbaric oxygen treatment involves the breathing of pure oxygen. 3 Corticosteroid drugs, or steroids, may help to control the unwanted tissue growth. 4 Anticoagulants, such as warfarin or heparin, can help to slow the accumulation of necrotic tissue.
What are the treatment options for radionecrosis?
Several options are available to successfully treat radionecrosis, including: Surgery – Necrotic tissue is surgically removed to help restore blood flow and promote healing. Hyperbaric oxygen treatment – Pure oxygen is delivered throughout the body to support the healing process.
Can radiation necrosis be treated?
Several options are available to successfully treat radionecrosis, including: Surgery – Necrotic tissue is surgically removed to help restore blood flow and promote healing. Hyperbaric oxygen treatment – Pure oxygen is delivered throughout the body to support the healing process.
Can you survive radiation necrosis?
The current study was performed to define prognostic factors for survival and the incidence of radiation necrosis in cerebral metastasized patients after treatment with stereotactic radiosurgery. The median overall survival was 282 days.
How long does radiation necrosis last?
Conclusion. Radiation necrosis is a challenging complication after RT and can resemble recurrent tumor. Pseudoprogression is an earlier and reversible form of radiation necrosis that typically occurs within 3 months of chemoradiotherapy for glioma and resolves spontaneously.
Is radiation necrosis a cancer?
The death of healthy tissue caused by radiation therapy. Radiation necrosis is a side effect of radiation therapy given to kill cancer cells, and can occur after cancer treatment has ended.
How does Avastin help radiation necrosis?
In summary, bevacizumab prunes blood vessels, reduces nonvascular permeability in radiation brain necrosis and alleviates brain edema, thereby relieving the patient's symptoms and improving quality of life [31–33].
What are the symptoms of radiation necrosis?
The symptoms of radiation necrosis are varied depending upon the area of the brain involved, but common symptoms include headache, drowsiness, memory loss (especially if the temporal lobe is involved), personality changes, and seizures.
Is necrosis fatal?
Necrosis is the death of cells in living tissue caused by external factors such as infection, trauma, or toxins. As opposed to apoptosis, which is naturally occurring and often beneficial planned cell death, necrosis is almost always detrimental to the health of the patient and can be fatal.
How is radiation necrosis diagnosed?
Magnetic resonance (MR) imaging is the most commonly used modality to investigate RN. However, the imaging features of radiation necrosis and tumor recurrence overlap considerably, with both entities demonstrating some degree of contrast enhancement and perilesional edema (33, 34).
Is radiation necrosis of brain progressive?
Radiation necrosis can result in progressive neurological symptoms and radiographic changes.
Can radiation necrosis increase in size?
In July 2016 (15 months post-SRS), further imaging found an increase in size and a change in the morphology of the previously treated right frontal lobe lesion, which could signify disease progression or further radiation-induced necrosis.
Can brain necrosis be cured?
Methods: Although asymptomatic necrosis rarely needs treatment, brain necrosis resulting in neurologic change can be treated with steroids, surgery, bevacizumab and/or hyperbaric oxygen therapy.
What is the best treatment for radiation necrosis?
Other possible treatment options include: Glucocorticoids, a general class of steroids. Anticoagulants, or blood thinners. These need to be carefully used as some people with radiation necrosis may be at risk for bleeding. Hyperbaric oxygen, which is where a person inhales 100% oxygen in a specialized chamber.
What are the symptoms of radiation necrosis?
The signs and symptoms of this kind of radiation necrosis include: Hydrocephalus, the abnormal dilation of the cerebral ventricles with excess cerebrospinal fluid. Edema. New seizure or a recurrence of seizures.
What happens if the cerebrospinal fluid is obstructed due to radiation necrosis?
This can lead to mental decline and seizures. Edema, or the accumulation of excess fluid in cells or in the spaces between the cells of a tissue. New seizure or a recurrence of seizures.
Is Bevacizumab an anti-cancer?
The efficacy of this is currently in question. Bevacizumab, a kind of anti-cancer medication. Radiation necrosis refers to the process of irreversible cellular injury and death ( necrosis) as a result of radiation. Radiation is a form of energy and ionizing radiation used in radiotherapy for cancer is the culprit for radiation necrosis.
Does radiation cause cancer?
This high energy form of radiation can damage cancer cells, but it can damage your body's normal cells as well, leading to necrosis. Necrosis is the process of irreversible cellular injury and death. So when radiation leads to necrosis, we simply call this radiation necrosis.
Can radiation necrosis be treated?
Treatment. Treatment for radiation necrosis is highly varied and depends on exactly where the necrosis has occurred and what problems it's causing . Some cases may not necessitate any treatment whatsoever. The patient just needs to be monitored for any issues or worsening of their signs and symptoms.
What is radiation necrosis?
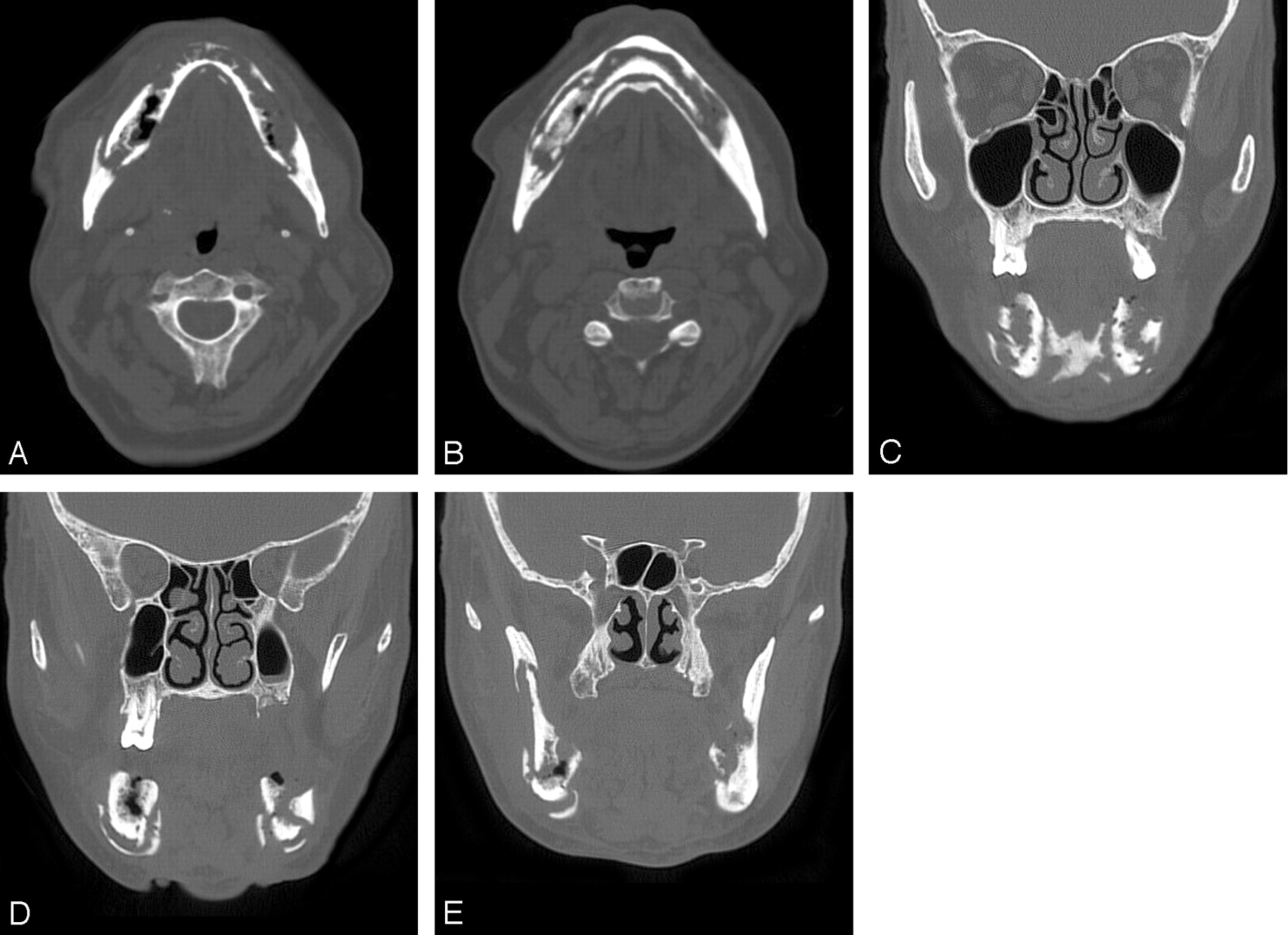
Radiation necrosis is a complication of nasopharyngeal, sinonasal, and skull base neoplasms treated with irradiation.62 ,63,64,77 Because of the radiation portals applied to these various skull base neoplasms and the field covered, the temporal lobes are most commonly affected, followed by the frontal lobes.
What is the second line of treatment for radiation necrosis refractory to steroids?
Bevacizumab, a VEGF receptor antibody, is the preferred second-line therapy for management of radiation necrosis refractory to steroids.110,111 Surgical resection to reduce mass effect and edema is an option for surgically accessible regions.
How long does radiation necrosis last?
Radiation necrosis typically occurs 1–2 years after radiation, but latency as short as 3 months and as long as 30 years have been reported. 31 Recognition of the risk factors for radiation necrosis has resulted in a decrease in incidence.
What is the complication of RT?
Radiation necrosis is a rare complication of RT that results in permanent death of parenchymal brain tissue. The most likely etiology is RT-induced fibrinoid necrosis of vessel walls that leads to infarction. Imaging can show enhancing or non-enhancing lesions accompanied by significant edema.
What are the consequences of radiation necrosis?
Radiation necrosis can result in devastating clinical consequences. Patients present with focal neurological symptoms, often recapitulating the presenting symptoms of the patient’s initial disease in the case of primary brain tumors, severe cognitive deficits, signs and symptoms of ICP, and/or seizures.
How long does it take for a patient to develop radiation necrosis?
Radiation necrosis occurs in patients treated with high focal doses of radiation. Patients present from several months to 10 years after cranial radiation. In 2.8% of patients treated for malignant glioma, focal radiation necrosis develops, but among those surviving a year as many as 9% develop the condition.
How long does it take for a brain tumor to change after radiation?
Delayed radiation changes can be further divided into early (within 3 to 4 months of therapy) and late (months to years after therapy).
What are the symptoms of radiation necrosis?
Reports may be affected by other conditions and/or medication side effects. We ask about general symptoms (anxious mood, depressed mood, fatigue, pain, and stress) regardless of condition.
Does radiation necrosis cause stress?
1 a radiation necrosis patient reports no stress (50%) What people are taking for it. Nothing reported yet. Reports may be affected by other conditions and/or medication side effects. We ask about general symptoms (anxious mood, depressed mood, fatigue, pain, and stress) regardless of condition.