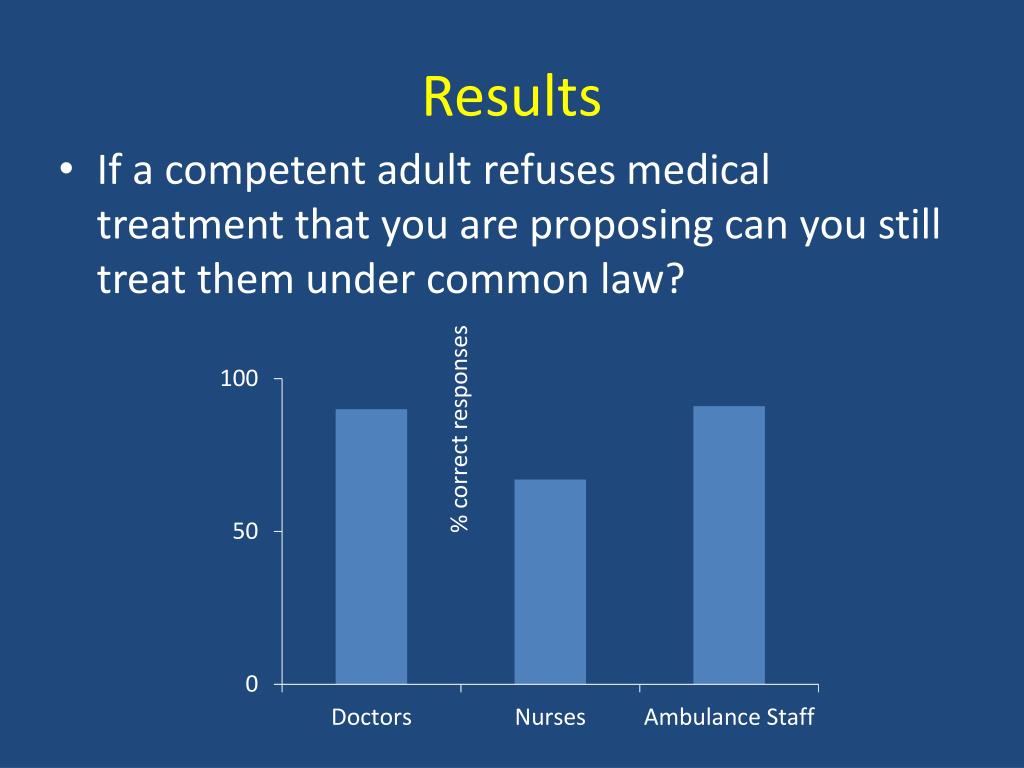
When Patients Refuse Treatment
- Patient Education, Understanding, and Informed Consent. The physician’s first responsibility is to ensure that the...
- Explore Reasons Behind Refusal. Patients may refuse treatments for many reasons, including financial concerns, fear,...
- Involve Family Members and Caregivers. Involving family members and other loved ones in the conversation...
- Be transparent and direct. ...
- Convince them that it's their idea. ...
- Make it a "double-checkup" ...
- Make the rest of the day as enjoyable as possible. ...
- Get someone who is an authority figure to help.
Can I refuse medical treatment?
In addition, there are some patients who do not have the legal ability to say no to treatment. Most of these patients cannot refuse medical treatment, even if it is a non-life-threatening illness or injury.
What to do if your loved one refuses mental health treatment?
If your loved one refuses to move forward, it’s useful to try to understand what is behind his reasons for refusing treatment and then address those issues. A person may refuse to accept mental health treatment for many reasons, including: He may believe it indicates he is a failure. It may make him feel more vulnerable.
What happens when a family member refuses to get treatment?
When someone you love refuses to get professional treatment for their mental health disorder—such as depression, bipolar disorder, or substance abuse—this can put you, as a family member, in a very uncomfortable and difficult position. You care for the person and can see that he or she needs help, but feel powerless and unable to just stand by.
Can a doctor ignore a patient who refuses to have surgery?
But some doctors might conclude that it’s inappropriate to ignore the patient’s refusal because the patient was already blind and the procedure would just reverse a harm that’s already been done—not prevent one from happening. Our questions are designed to help physicians navigate this gray area.

What are the rules for refusing to treat the patient?
As a rule of thumb, if unnecessary delays in care may cause irreparable harm, physicians can face legal liability for their refusal to treat. If you need urgent medical attention, and a doctor refuses to treat you, you can pursue a medical malpractice suit against the physician and/or the establishment they work for.
Is it a constitutional right to refuse medical treatment?
The Fourteenth Amendment provides that no State shall "deprive any person of life, liberty, or property, without due process of law." The principle that a competent person has a constitutionally protected liberty interest in refusing unwanted medical treatment may be inferred from our prior decisions.
Is it ever ethical to treat someone who refuses treatment?
Competent patients have a right to refuse treatment. This concept is supported not only by the ethical principle of autonomy but also by U.S. statutes, regulations and case law. Competent adults can refuse care even if the care would likely save or prolong the patient's life.
Can a patient's right to refuse treatment be denied?
Although the right to refuse medical treatment is universally recognized as a fundamental principle of liberty, this right is not always honored. A refusal can be thwarted either because a patient is unable to competently communicate or because providers insist on continuing treatment.
Can a person be forced to have medical treatment?
You cannot legally be treated without your consent as a voluntary patient – you have the right to refuse treatment. This includes refusing medication that might be prescribed to you. (An exception to this is if you lack capacity to consent to treatment.)
How do I force someone to go to the hospital?
A person can be involuntarily committed to a hospital if they are a danger to themselves, a danger to others, or gravely disabled. They are considered a danger to themselves if they have stated that they are planning to harm themselves.
What is the term called when a patient refuses treatment?
Informed refusal is where a person has refused a recommended medical treatment based upon an understanding of the facts and implications of not following the treatment. Informed refusal is linked to the informed consent process, as a patient has a right to consent, but also may choose to refuse.
What is the right to refuse treatment called?
Under federal law, the Patient Self-Determination Act (PSDA) guarantees the right to refuse life sustaining treatment at the end of life.
What are some ethical challenges with refusing treatment?
In general, ethical tension exists when a physician's obligation to promote a patient's best interests competes with the physician's obligation to respect the patient's autonomy. “When you don't take your medication, you're more likely to get sick.”
What happens when someone you love refuses to get treatment?
When someone you love refuses to get professional treatment for their mental health disorder—such as depression, bipolar disorder, or substance abuse —this can put you, as a family member, in a very uncomfortable and difficult position. You care for the person and can see that he or she needs help, but feel powerless and unable to just stand by.
Why does my loved one refuse to move forward?
If your loved one refuses to move forward, it’s useful to try to understand what is behind his reasons for refusing treatment and then address those issues. A person may refuse to accept mental health treatment for many reasons, including: He may believe it indicates he is a failure.
What does it mean to distancing yourself from a sick family member?
That, a lot of times, means distancing yourself from the sick family member who refused treatment. Everyone has limits, and when said mentally sick family member has a long history of repeated abusive behavior I say family members have a right to protect themselves from harm.
What are the areas of concern?
Common areas of concern are: alterations in overall appearance. decreased level of energy. fatigue. lack of interest in previously enjoyed people or activities. changes in sleep, appetite, or weight.
How old do you have to be to get a psychotic treatment?
You care for the person and can see that he or she needs help, but feel powerless and unable to just stand by. You cannot force anyone over the age of 18 into treatment, unless they pose a danger to themselves or others or show signs of psychotic thinking (which is not very common).
Can elderly people not participate in treatment?
Other's won't participate, and, if they aren' t a danger to themselves or others, have a right to not participate in treatment. The author mentioned elderly people. Elderly people (probably over the age of 75 or so) didn't grow up with treatment options, and thus, many won' t participate in them.
Is it hard to keep up with meds?
It's really hard to keep up your motivation and keep on trying when so many things don' t go your way, when meds don't work or you have side effects to them. I know, I've been there too. It feels like you have nothing left to do, but actually there's always something else to try. This I know for sure.
What happens if a doctor refuses to give informed consent?
If he does not, the doctor may face disciplinary action by the General Medical Council, plus possible civil and criminal proceedings in battery. Informed refusal, just like informed consent, comprises three elements: The patient must be competent. He or she must have sufficient information to be able to make a choice.
What is an advance refusal of treatment?
Patients may also make advance refusals of treatment – more commonly known as living wills or advance directives. These are statements made by patients when competent about how they wish to be treated should they become incompetent at a later stage.
What happens if you fail to abide by a valid advance directive?
In general, failure to abide by a valid advance directive leaves the doctor vulnerable to civil or criminal proceedings in battery and disciplinary proceedings before the GMC , which has stated in its guidance 2: 'You must respect any refusal of treatment given when the patient was competent.'.
What is the duty of a doctor?
The duty on the doctor is to ensure that patients understand the implications of their proposed course of action. Information must be provided in objective terms, if necessary recruiting colleagues with special expertise to provide further advice, but scaremongering is out of the question.
Why can't doctors wash their hands?
Equally, doctors cannot wash their hands of patients simply because they will not toe the line. The duty of care remains despite the refusal. In Good Medical Practice, 3 the GMC states: 'If you feel that your beliefs might affect the treatment you provide, you must explain this to patients, and tell them of their right to see another doctor.'.
Who likened a patient's consent to turning the key in a door to unlock it?
Lord Donaldson, when Master of the Rolls, likened a patient's consent to turning the key in a door to unlock it. It is then up to the doctor to decide if the door should be opened by providing treatment, that decision being dependent upon assessing whether doing so would be in the best interests of the patient.
Did Miss T want a blood transfusion?
The day following admission, Miss T announced that she did not want a blood transfusion, although at that time no transfusion had been contemplated. However, later in the day, she went into labour and the baby was delivered by caesarean section.
Is fast facts medical advice?
This information is not medical advice. Fast Facts are not continually updated, and new safety information may emerge after a Fast Fact is published. Health care providers should always exercise their own independent clinical judgment and consult other relevant and up-to-date experts and resources.
Do you need to consult the prescribing information before using a product?
Some Fast Facts cite the use of a product in a dosage, for an indication, or in a manner other than that recommended in the product labeling. Accordingly, the official prescribing information should be consulted before any such product is used.
What is the best way for a patient to indicate the right to refuse treatment?
Advance Directives. The best way for a patient to indicate the right to refuse treatment is to have an advance directive, also known as a living will. Most patients who have had any treatments at a hospital have an advance directive or living will.
What are the rights of a patient who refuses treatment?
In addition, there are some patients who do not have the legal ability to say no to treatment. Most of these patients cannot refuse medical treatment, even if it is a non-life-threatening illness or injury: 1 Altered mental status: Patients may not have the right to refuse treatment if they have an altered mental status due to alcohol and drugs, brain injury, or psychiatric illness. 6 2 Children: A parent or guardian cannot refuse life-sustaining treatment or deny medical care from a child. This includes those with religious beliefs that discourage certain medical treatments. Parents cannot invoke their right to religious freedom to refuse treatment for a child. 7 3 A threat to the community: A patient's refusal of medical treatment cannot pose a threat to the community. Communicable diseases, for instance, would require treatment or isolation to prevent the spread to the general public. A mentally ill patient who poses a physical threat to himself or others is another example.
What is the end of life refusal?
End-of-Life-Care Refusal. Choosing to refuse treatment at the end of life addresses life-extending or life-saving treatment. The 1991 passage of the federal Patient Self-Determination Act (PSDA) guaranteed that Americans could choose to refuse life-sustaining treatment at the end of life. 9 .
How can a patient's wishes be honored?
Another way for a patient's wishes to be honored is for the patient to have a medical power of attorney. This designates a person to make decisions on behalf of the patient in the event they are mentally incompetent or incapable of making the decision for themselves.
What must a physician do before a course of treatment?
Before a physician can begin any course of treatment, the physician must make the patient aware of what he plans to do . For any course of treatment that is above routine medical procedures, the physician must disclose as much information as possible so you may make an informed decision about your care.
What are the four goals of medical treatment?
There are four goals of medical treatment —preventive, curative, management, and palliative. 2 When you are asked to decide whether to be treated or to choose from among several treatment options, you are choosing what you consider to be the best outcome from among those choices. Unfortunately, sometimes the choices you have won't yield ...
Why do patients make this decision?
Patients make this decision when they believe treatment is beyond their means. They decide to forgo treatment instead of draining their bank accounts. Those who live in a country with a for-profit healthcare system may be forced to choose between their financial health and their physical health.
What Is The Best Course Of Action If A Patient Refuses Treatment?
As a provider, whether the patient consents to a particular course of action or not, your responsibility extends to explaining to the patient why the recommended treatment was given and the potential hazards the treatment could present.
What Does A Cna Do If A Patient Refuses Care?
A resident’s refusal to take care could result in an abrupt departure and return. It is true that sometimes that is the solution. Therefore, let another CNA help you, and if you don’t mind put one of his/her residents to sleep, you should.
Can You Deny A Patient Care?
Yes. There are several factors which contribute to this practice of refusing to treat patients, the most prominent being a patient’s potential financial inability. that refusing patients will harm them cannot harm the patients.
Can Patients Refuse Care?
In most cases, patients who are entitled to refuse treatment may do so when they understand their medical situation and its potential risks and benefits. As far as the process for reviewing decisions is concerned, more of the responsibility lies with the reason for the refusal.
Is It Ever Ethical To Treat Someone Who Refuses Treatment?
Patients who refuse treatment are allowed to do so without judgement. autonomy concept not only through virtue of their ethical principle, but by way to U.’s role in supporting it. The laws of the state. Statutes, regulations, and cases. Many competent adults refuse medical care even if it can possibly save or prolong the life of a patient.
What Is The Very First Thing You Should Do If A Patient Refuses Treatment?
It’s your responsibility to be sure that your patient knows what consequences his decision could lead to in terms that he can understand. If they don’t know English well or if they speak a very limited amount, you can find a translator for them.
What Can A Nurse Do If A Patient Refuses Treatment?
It is against the law for any nurse to recommend medication to anyone who does not want it. An important aspect is how the nurse handles your refusal of medication as part of your responsibility to prevent your patient from being harmed.
How to help someone who is worried about you?
Keep trying, asking questions, listening, and reflecting. Help them feel heard and ask again. Continue to say things like, “I’m really worried about you. I’m thinking we should just go get checked out by a doctor to see what’s going on.”. Reassure them that you’ll stay with them and help them through the process.
How long do you have to be off drugs before you can be admitted to a hospital?
They’ll need to be off drugs for 72 hours before a hospital can clearly diagnose any type of mental illness, like psychosis. Once they’re admitted, your loved one will be monitored, kept safe, and possibly given medications.
How to tell a family member they are having a psychotic break?
When you admit your family member to a hospital, tell the staff what is going on—for example, that you think they are having a psychotic break. Explain to them whether this is the first time this has happened, or how long it’s been going on and what symptoms you’ve seen. The hospital will want to make sure your loved one has not used drugs. They’ll need to be off drugs for 72 hours before a hospital can clearly diagnose any type of mental illness, like psychosis.
What is an emergency room?
Emergency rooms are designed for physical health emergencies and are not well equipped to handle psychiatric emergencies. If your family member needs some kind of bed and respite but doesn’t meet criteria, some communities also offer peer run respites as alternatives to hospitalization.
How much does a hospital visit cost?
Hospital visits can be very expensive. On average it can cost anywhere from $1,200 to $1,500 a night—sometimes more. If you have health insurance, make sure you know beforehand how much will be covered. If not, the hospital will have someone you can talk to about getting your loved one on Medicaid.
Can you go to the hospital against your will?
Still, there’s a time and a place for taking someone to the hospital against their will. A person can be involuntarily committed to a hospital if they are a danger to themselves, a danger to others, or gravely disabled. They are considered a danger to themselves if they have stated that they are planning to harm themselves.
Can hospital staff treat you differently?
Hospital staff may treat them or you differently, and the process is more difficult for an involuntary commitment. Your loved one may come out of the experience feeling like you don’t respect their decisions, which can set them back in their recovery. Whenever possible, it’s best to make treatment decisions together.
What happens if you don't consent to treatment?
Part of that pressure may be the belief that if they do not consent, they may experience adverse consequences, such as blocked access to needed care in the future.
What is the right to accept or reject medical interventions?
The right to accept or reject what (if any) medical interventions falls along with other core rights, such as where to live, whom to marry, and how to worship. This right to choose or decline medical treatment can only be overridden if there is evidence that an individual lacks decisional capacity.
Why are the patient and spouse surprised when they open the door?
The patient and spouse are surprised because they are under quarantine and are not expecting anyone. They open the door. An individual identifies themself as a nurse from the hospital that provided the IV treatment and states they are there to hospitalize the patient.
Why do patients capitulate to medical advice?
Some patients, despite decisional competence, may capitulate to a medical professional’s advice. This may occur because they are, as in our case example, in a vulnerable position. For example, a patient may be suffering from a condition that is potentially lethal and taking experimental treatment.
What does the nurse say about the patient's fears and distress about being in a hospital?
The nurse insists on the hospitalization and dismisses the patient’s fears and distress about being in a hospital as “silly.”. The nurse intimates that the patient’s IV procedure was approved only if they agreed to the staff’s recommendations. The patient again declines hospitalization.
Can a patient refuse medical treatment?
Patients who are competent have the right to refuse medical treatment. Only those who are deemed by a court to be incompetent (or lacking decisional capacity) may be subject to having their refusal for medical treatment overridden. Lack of competence may stem from cognitive deficits, such as severe dementia, or emotional deficits, ...
Is informed consent an essential underpinning of patients' rights?
However, there is no indication prior to the nurse’s arrival that the patient was informed of imminent initiation of hospitalization. Informed consent is an essential underpinning of patients' rights. Moreover, there is no indication that this patient is decisionally incompetent.
