See more

What is the best treatment for interstitial cystitis?
Amitriptyline is the medication most commonly prescribed for interstitial cystitis. Elmiron is the only oral drug approved by the FDA specifically for interstitial cystitis. It improves the bladder lining, making it less leaky and therefore less inflamed and painful. The full effect may take three to six months.
What is the main cause of interstitial cystitis?
The exact cause of interstitial cystitis isn't known, but it's likely that many factors contribute. For instance, people with interstitial cystitis may also have a defect in the protective lining (epithelium) of the bladder. A leak in the epithelium may allow toxic substances in urine to irritate your bladder wall.
Can interstitial cystitis go away?
For about half the cases, interstitial cystitis goes away by itself. Among those who need treatment, most find relief and get their lives back to normal. Treatment is mainly about symptom control.
How long does interstitial cystitis last?
Over time symptoms increase and pain cycles may appear and last for 3-14 days. When these cycles become more frequent and last longer they are likely to be referred to a specialist. The most common misdiagnosis is urinary infection followed by yeast vaginitis, endometriosis and vulvodynia.
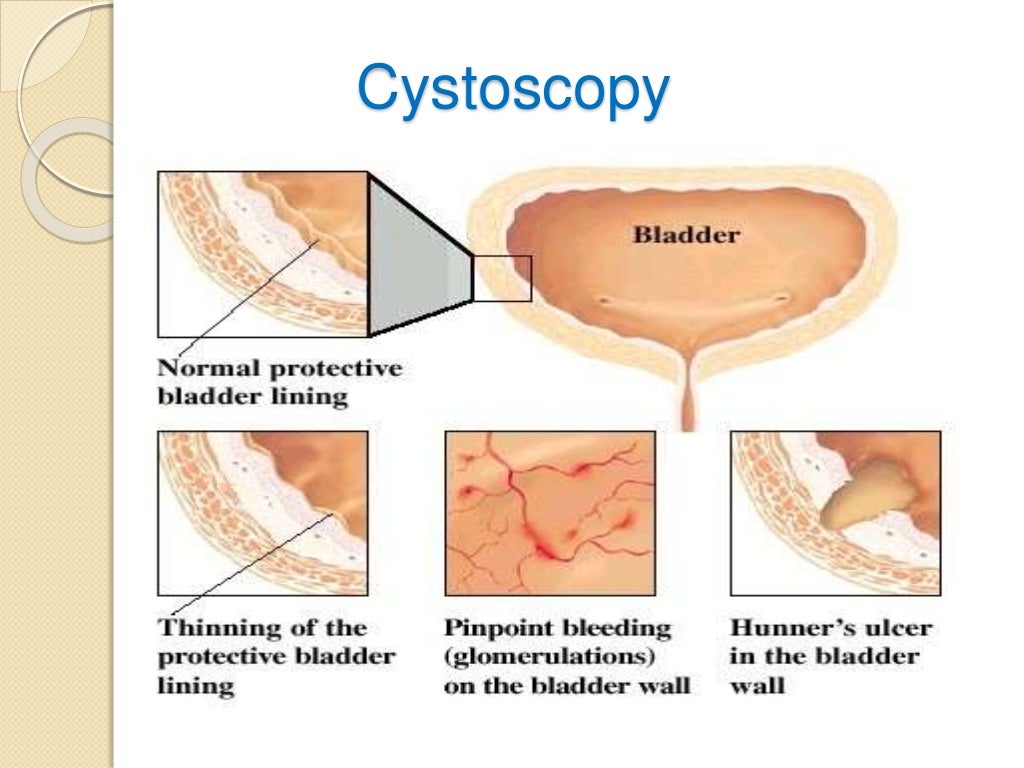
How do you test for interstitial cystitis?
How is interstitial cystitis diagnosed?Urinalysis. Lab testing of urine to look for certain cells and chemicals. ... Urine culture and cytology. Collecting and checking urine for white blood cells and bacteria. ... Cystoscopy. ... Bladder wall biopsy. ... Lab exam of prostate secretions (in men).
Are bananas good for IC?
Allowed: Bananas, coconuts, dates, blueberries, melons and pears Avoid: All other fruits and juices (especially acidic and citrus fruits) Special note: Avoid cranberry juice. The acid is a strong bladder irritant. Avoid: Benzyl alcohol, citric acid, MSG, NutraSweet, saccharin.
What foods aggravate interstitial cystitis?
However, some people with IC find that certain foods or drinks trigger or worsen their symptoms. Coffee, soda, alcohol, tomatoes, hot and spicy foods, chocolate, caffeinated beverages, citrus juices and drinks, MSG, and high-acid foods can trigger IC symptoms or make them worse.
Can cystitis cause kidney damage?
Most people with cystitis will not get a kidney infection, but occasionally the bacteria can travel up from the bladder into one or both kidneys. If treated with antibiotics straight away a kidney infection does not cause serious harm, although you'll feel very unwell.
List of 20 Interstitial Cystitis Medications Compared - Drugs.com
How to Curb Pain from Interstitial Cystitis – Cleveland Clinic
What is the best medicine for interstitial cystitis?
Amitriptyline is the medication most commonly prescribed for interstitial cystitis. Elmiron is the only oral drug approved by the FDA specifically for interstitial cystitis. It improves the bladder lining, making it less leaky and therefore less inflamed and painful. The full effect may take three to six months.
How often do you urinate with interstitial cystitis?
Interstitial cystitis is a chronic inflammation of the bladder that causes people to urinate -- sometimes painfully -- as often as 40, 50, or 60 times a day. Their quality of life, research suggests, resembles that of a person on kidney dialysis or suffering from chronic cancer pain.
What is the best medicine for bladder pain?
Antihistamines. Antihistamines such as hydroxyzine (Atarax, Vistaril) interfere with the mast cells' release of histamine, helping to relieve bladder inflammation and pain, urinary frequency, and nighttime voiding. Because antihistamines can cause drowsiness, they are usually best taken at bedtime. Painkillers.
What is the procedure to remove a bladder?
Surgery is usually a last resort and undertaken only when the pain is crippling. The surgical procedure typically involves removal of the bladder and the creation of a new one (a neobladder) using intestinal tissue. Most people need to catheterize the neobladder themselves in order to empty it.
How to reduce urinary frequency?
Some people report that stress reduction, exercise, biofeedback, or warm tub baths improve their symptoms, but no research has evaluated the effectiveness of these strategies. Bladder training -- that is, learning to urinate only at specific times (despite the urge to go) -- can help reduce urinary frequency.
What is the procedure called when you are able to change the pain pathways?
In a procedure called transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS), pain pathways are modified by a device worn on the body. The device produces electrical impulses, which pass through electrodes that are attached to the body with small adherent pads.
Does DMSO help with bladder lining?
DMSO is sometimes combined with other medications. Hyaluronic acid (Cystistat) Cystistat may help repair the bladder lining. No single treatment alleviates all symptoms, and some may stop working over time, so finding what works is often a matter of trial and error.
What is interstitial cystitis?
Interstitial Cystitis Treatments. Interstitial cystitis (IC) is a chronic inflammation of the bladder wall. It can cause pain in the pelvic area and bladder, as well as an overactive bladder (urgent or frequent urination). It is often misdiagnosed as a urinary tract infection since, like a UTI, it irritates the bladder and has some ...
What is the best medicine for cystitis?
Pain medication can be used to relieve discomfort in the bladder and pelvic area. This includes over-the-counter drugs like aspirin and ibuprofen, as well as narcotic pain relievers. Tricyclic antidepressants, such as amitriptyline, can relieve pain associated with interstitial cystitis. These drugs prevent the reabsorption ...
How long does it take for bladder instillation to work?
Some patients are even able to administer their own treatment at home. Depending on the medication, it can take anywhere from eight to twelve weeks of treatment before patients experience noticeable results. Bladder instillation can cause pain and irritation due to frequent catheterization.
How to remove CI?
This procedure is done under general anesthesia using a hollow tube inserted into the urethra (cystoscope).
What is bladder distention?
Bladder distention is a procedure in which the bladder is filled to capacity with gas or liquid in order to look for damage in the bladder wall. The treatment is done under general anesthesia. Examining the bladder while it is stretched to capacity allows a physician to better see cracks or tears in the bladder lining.
What does a syringe do to the bladder?
The medications may also relax the bladder, minimizing the intensity of bladder contractions and thereby lessening urination frequency.
Can surgery be done for bladder pain?
Surgery is usually only considered after all other options have failed or when the pain is severe. But it is not always a sure thing, and symptoms may still persist. Although researchers are not certain why, it may be a sign of additional inflammation beyond the bladder. There are three different surgical approaches for CI:
What is the treatment for IC?
Some people who have IC find relief after a treatment in which a doctor puts a small amount of liquid medicine into the bladder, called bladder instillation or a bladder wash or bath. The doctor guides a tube called a catheter into your bladder and slowly adds a liquid that eases irritation of the bladder wall.
How to treat IC?
Others find no link between symptoms and what they eat. However, be sure to drink enough water to stay hydrated. Talk with your health care professional about how much liquid you should drink to prevent dehydration based on your health, how active you are, and where you live. Read more about eating, diet, and nutrition and how they relate to IC.
What is the procedure to make the bladder bigger?
make the bladder larger, a procedure called bladder augmentation, remove the bladder, called cystectomy, or. reroute the normal flow of urine, called urinary diversion.
What to do if you have severe pain?
If you have severe pain, you may need your doctor to prescribe narcotic analgesics, or pain-relieving medicines, such as acetaminophen with codeine. or longer-acting narcotics. , sinus medicines, and pain relievers may trigger symptom flares.
What is the procedure called to stretch the bladder?
Bladder stretching. A doctor may use a procedure called bladder stretching, or hydrodistention, to treat your bladder pain, if only for a short time. Bladder stretching occurs when a doctor stretches your bladder by filling it with fluid. You will be given a local or general anesthesia. NIH external link.
What to do if you have IC?
The physical therapist will work to stretch tight pelvic floor muscles and help you keep them relaxed.
Can pain medicine make IC worse?
Talk with your health care professional if these medicines make your IC worse. Long-term use of pain medicines can be dangerous. Talk with your doctor about how to safely manage your chronic, or long-term, pain—possibly with the help of a pain specialist, a doctor who diagnoses, treats, and manages pain.
What is IC in bladder?
IC is a chronic bladder problem. Your bladder holds pee after your kidneys have filtered it but before you pee it out. This condition causes pain and pressure below your belly button. Symptoms can come and go. Or they may be constant. Interstitial cystitis causes urgent, often painful bathroom trips.
What to do if IC doesn't work?
Surgery. In very rare cases when nothing else works, this may be an option. This is a complex operation that diverts your urine away from your bladder. Even if IC treatments don’t work for you, pain management using painkillers, acupuncture, or other methods can keep symptoms at bay.
How long does it take for a swollen bladder to calm down?
And it usually takes weeks or months to calm the symptoms. The first stage of treatment is to try to avoid triggers and try lifestyle changes that may help ease symptoms. Retrain your bladder to hold more urine. For example, if you feel the need to pee every 30 minutes, try to stretch it out to 45 minutes.
How long does IC last?
Because IC has such a wide range of symptoms and severity, most experts think it might be several diseases. If you have urinary pain that lasts for more than 6 weeks and is not caused by other conditions like infection or kidney stones, you may have IC. No matter what it’s called, interstitial cystitis symptoms bring a lot of challenges.
How does IC feel?
The bladder pain people feel with IC can range from a dull ache to piercing pain. Peeing may feel like just a little sting, or it can feel like serious burning. About 5% to 10% of people with the condition get ulcers in their bladder.
How to treat a hunner's lesions?
If it’s helpful, the effect usually lasts less than 6 months. Repeat treatment may help. Steroids. If you have ulcers called Hunner’s lesions on your bladder, a doctor may remove them, burn them, or inject them with steroids.
How many women have IC?
Somewhere between about 3% to 6% of adult women have some form of IC. That’s about 3 million to 8 million American women. About 1.3% of American men also have it. On average, people first start having problems in their 40s.
Interstitial Cystitis Pain Medications
Physicians tend to focus on controlling and/or stopping the pain that comes with interstitial cystitis. And, there are plenty of options for pain medications when it comes to this condition. There are over-the-counter medications, non-narcotic pain medications, topical medications, and narcotic pain medications.
Interstitial Cystitis Diet
You may also be able to relieve the symptoms of interstitial cystitis by adjusting your diet. There are plenty of adjustments that patients have found to work for their condition:
Interstitial Cystitis Surgery
Surgical procedures are reserved for patients with extreme symptoms of interstitial cystitis. Typically, these are the patients who are having painful ulcers.
What is IC/BPS treatment?
IC/BPS treatment is often done in phases with constant monitoring of your pain and quality of life. It is important to talk to your health care provider about how your treatments are working so that together you can find the best treatment option for you. The following are the different phases of IC/BPS treatment:
How to get rid of IC/BPS?
But many do have fewer symptoms using these types of treatments. Manipulative Physical Therapy. Patients with IC/BPS often have tenderness and/or pain in the pelvic floor area, and sometime manipulative physical therapy can reduce symptoms.
How does the bladder work?
If your bladder is working normally, you can put off urination for some time. Once you are ready to pass urine, the brain sends a signal to the bladder. Then the bladder muscles squeeze (or "contract"). This forces the urine out through the urethra, the tube that carries urine from your body.
What are the health issues associated with IC/BPS?
Some people with IC/BPS have other health issues such as irritable bowel syndrome, fibromyalgia, and other pain syndromes. The bladder and kidneys are part of the urinary system, the organs in our bodies that make, store, and pass urine. You have 2 kidneys that make urine. Then urine is stored in the bladder.
How long does it take for IC/BPS to work?
Patients usually try different treatments (or combinations of treatments) until good symptom relief occurs. It is important to know that none of these IC/BPS treatments works right away. It usually takes weeks to months before symptoms improve. Even with successful treatment, the condition may not be cured. It is simply in remission. But, most patients can get significant relief of their symptoms and lead a normal life with treatment.
Does IC/BPS go away?
For some patients the symptoms may come and go, and for others they don't go away. IC/BPS is not an infection, but it may feel like a bladder infection. Women with IC/BPS may feel pain when having sex. The more severe cases of IC/BPS can affect your life and your loved ones.
Does IC/BPS cause bladder pain?
Patients with IC/BPS may have bladder pain that gets worse as the bladder fills. Some patients feel pain in other areas in addition to the bladder, such as the urethra, lower abdomen, lower back, or the pelvic or perineal area (in women, behind the vagina and in men, behind the scrotum).
What are the conditions that cause interstitial cystitis?
Conditions related to IC include: Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) Depression, anxiety. Chronic fatigue syndrome. Fibromyalgia.
How many types of interstitial cystitis are there?
According to the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases and the Interstitial Cystitis Association, interstitial cystitis is also known as: There are 2 types of IC: Non-ulcerative IC: About 9 out of 10 IC sufferers have non-ulcerative IC.
What is IC in 2020?
Nov 5 2020. Interstitial cystitis (IC) is a chronic condition that causes bladder pain, bladder pressure, pelvic pain, and urinary urgency. Although many have not heard of IC, this autoimmune disease affects up to 12 million adults in the United States alone. Below, we talk more about IC symptoms, causes, treatments, and when to see a doctor.
How to practice bladder training?
Bladder training can be done by yourself or with the guidance of a healthcare professional. To practice bladder training, set a schedule for when you urinate, instead of going whenever your bladder tells you to. Also called bladder retraining, this is most effective when IC symptoms are mild.
How to treat IC?
If your IC is caused by autoimmunity, stress relief if a must. 4 tips for reducing stress: Meditation and yoga. Going outside.
Can you get physical therapy for interstitial cystitis?
Interstitial cystitis patients will often turn to physical therapy if lifestyle changes haven’t relieved their symptoms. Physical therapy is particularly helpful if you have pelvic floor dysfunction. The pelvic floor is a group of muscles that attaches your pelvis to surrounding body parts.
Can interstitial cystitis cause pain?
Some IC patients experience more frequent urination or pelvic floor spasms. The symptoms of interstitial cystitis include: Pelvic exams and Pap tests may be painful for IC sufferers. If you require one of these tests, talk with your doctor.
The Gist: What Is Interstitial Cystitis?
Interstitial Cystitis (IC) is a condition whose definition has continually evolved since it was first discovered in the late nineteenth century, as has its criteria for diagnosis and strategies for treatment.
Who Gets Interstitial Cystitis? When Does It Occur For Women?
Today, IC/BPS is considered more than just a "bladder disease" involving damaging lesions; instead, it is viewed as a "complex neuromuscular disorder that can involve the bladder, the pelvic floor muscles and/or the nerves." This recent recognition of the diversity in presentation of IC/BPS symptoms has since expanded the theories of its source of origin.
The Origin Way: Physical Therapy For Interstitial Cystitis
While relatively rare, if Hunner's lesions are present, this will change your course of treatment. All IC/BPS patients will receive conservative lines of treatment initially, but those patients found to have lesions present will often also be treated with medication, fulguration, cystoscopy with hydrodistension, or reconstructive surgery.

Diagnosis
Treatment
- No simple treatment eliminates the signs and symptoms of interstitial cystitis, and no one treatment works for everyone. You may need to try various treatments or combinations of treatments before you find an approach that relieves your symptoms.
Lifestyle and Home Remedies
- Some people with interstitial cystitis find symptom relief from these strategies: 1. Dietary changes. Eliminating or reducing foods in your diet that irritate your bladder may help to relieve the discomfort of interstitial cystitis. Common bladder irritants — known as the "four Cs" — include: carbonated beverages, caffeine in all forms (including chocolate), citrus products and f…
Coping and Support
- Interstitial cystitis can worsen your quality of life. Support from family and friends is important, but because the condition is a urinary problem, you may find the topic difficult to discuss. Find a supportive health care provider who is concerned about your quality of life as well as your condition. Seek someone who will work with you to help relieve your urinary frequency, urgency …
Preparing For Your Appointment
- You may be asked to keep a bladder diary for a few days to record information, such as how often you urinate and how much and what kinds of fluid you consume. For more testing, you may be referred to a specialist in urinary disorders (urologist) or urinary disorders in women (urogynecologist).