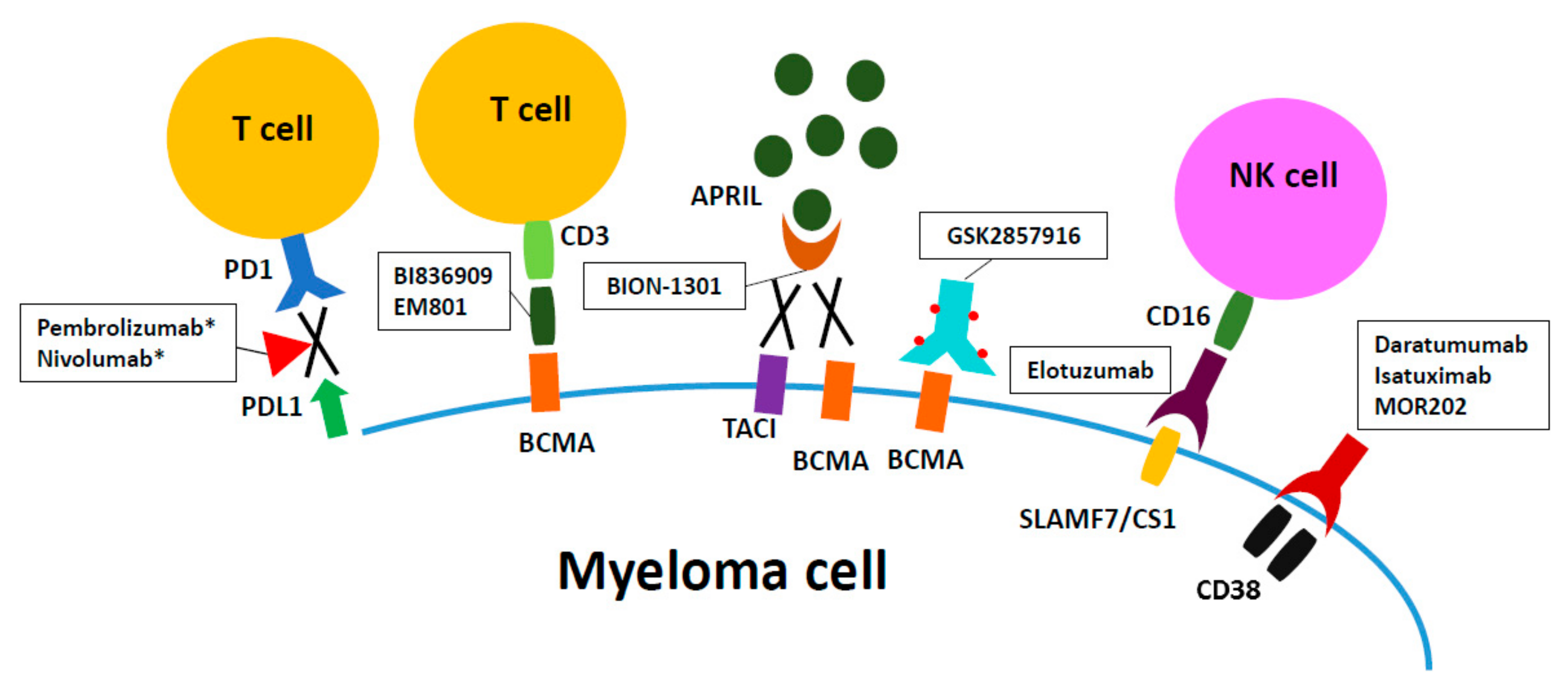
Monoclonal antibody
Monoclonal antibodies are antibodies that are made by identical immune cells that are all clones of a unique parent cell. Monoclonal antibodies can have monovalent affinity, in that they bind to the same epitope. In contrast, polyclonal antibodies bind to multiple epitopes and are usually made b…
Are there side effects of monoclonal antibody treatment?
The most commonly reported side effects were rash (2%) and diarrhea (1%). There was one reported case of anaphylaxis after sotrovimab infusion. Monoclonal antibody therapy is not indicated in severe cases requiring hospitalization.
When to start monoclonal antibodies?
“Monoclonal antibodies should first go to patients at the highest risk of death from COVID-19, but the opposite happened — the healthiest patients were the most likely to get treatment.
How soon should you get monoclonal antibodies?
“It is indicated for people who are high-risk, so not everybody diagnosed with COVID qualifies for monoclonal antibody treatment,” said Dr. Turner Overton at UAB. They have to be given within a couple days of diagnosis. “And it’s really I think been life-saving and helped reduce hospitalization,” said Overton.
What are monoclonal antibodies and how do they work?
Under the FDA’s emergency use authorization, those conditions include:
- Being above 65 years of age
- Obesity or being overweight
- Pregnancy
- Chronic kidney disease
- Diabetes
- Immunosuppressive disease or immunosuppressive treatment
- Cardiovascular disease
- Chronic lung diseases
- Sickle cell disease
- Neurodevelopmental disorders such as cerebral palsy

How do monoclonal antibodies work against COVID-19?
Monoclonal antibodies for COVID-19 may block the virus that causes COVID-19 from attaching to human cells, making it more difficult for the virus to reproduce and cause harm. Monoclonal antibodies may also neutralize a virus.
What is a monoclonal antibody?
Monoclonal antibodies are laboratory-produced molecules that act as substitute antibodies that can restore, enhance or mimic the immune system's attack on cells.
How long do COVID-19 antibodies last?
At this time, it is unknown for how long antibodies persist following infection and if the presence of antibodies confers protective immunity.
How many types of monoclonal antibody COVID-19 treatments are there in the US?
In the United States, there are three anti-SARS-CoV-2 monoclonal antibody treatments with FDA Emergency Use Authorization (EUA) for the treatment of COVID-19: bamlanivimab plus etesevimab, casirivimab plus imdevimab,, and sotrovimab.
What is the difference between antibodies and the vaccine in the context of COVID-19?
While antibodies and vaccines are both viable options to counteract the virus that causes COVID-19, there are major differences. While an antibody may immediately help treat an existing infection, a vaccine will train the immune system to protect against future infections. To learn more about differences between antibodies and vaccines visit Vanderbilt University Medical Center for more information.
What does it mean to have antibodies during the COVID-19 pandemic?
When you are infected with a virus or bacteria, your immune system makes antibodies specifically to fight it. Your immune system can also safely learn to make antibodies through vaccination. Once you have antibodies to a particular disease, they provide some protection from that disease.
Can you get COVID-19 if you already had it and have antibodies?
It is important to remember that some people with antibodies to SARS-CoV-2 may become infected after vaccination (vaccine breakthrough infection) or after recovering from a past infection (reinfected).
How long does it take for immunity to wane after receiving the COVID-19 vaccine?
A study published by the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention found that immunity against severe COVID-19 begins to wane four months after receiving a so-called "booster" third dose of the Pfizer or Moderna vaccines.
Can I get reinfected with COVID-19?
Studies suggest that reinfection with SARS-CoV-2 with the same virus variant as the initial infection or reinfection with a different variant are both possible; early reinfection within 90 days of the initial infection can occur.
What is the latest medication for COVID-19?
Paxlovid is the latest COVID-19 treatment that's been all over the news. The drug was granted an emergency use authorization (EUA) by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in December for anyone ages 12 and older who weighs at least 88 pounds, and is at high risk for severe disease.
Are there different variants of COVID-19 in the US?
SARS-CoV-2 is constantly changing, and new variants of the virus are expected to occur. In early 2021, the Alpha variant emerged, followed by the Delta variant later that summer. In late 2021 and throughout early 2022, the Omicron variant swept across the country and continues to be the predominant variant circulating in the United States.
How does Remdesivir injection work to treat COVID-19?
Remdesivir is in a class of medications called antivirals. It works by stopping the virus from spreading in the body.
Who is considered high risk?
People at risk of getting very sick from COVID-19 include: People who are age 65 or older. People who are overweight (with a BMI of 26 or greater)....
Can monoclonal antibodies treat COVID-19?
Increasing data from clinical trials show that when used early in the course of COVID-19, monoclonal antibodies can reduce the need to be admitted...
How long does it take for monoclonal antibody therapy to work?
Healing from COVID-19 is different for each patient. This is true even for patients who have been given monoclonal antibody therapy. Some symptoms...
Will I be protected from getting COVID-19 again after having monoclonal antibody therapy?
The effect of the treatment will last around 90 days. This is based on the normal amount of time that these antibodies stay active in the body. Mon...
Are monoclonal antibodies safe?
Monoclonal antibodies have been shown to be safe in clinical trials, with a rate of adverse reactions that was not different from placebo. Allergic...
Can monoclonal antibodies cause cancer?
COVID-19 monoclonal antibodies target the SARS-CoV-2 virus itself and not human cells, and have not been shown to cause cancer.
What is a monoclonal antibody 'cocktail'?
Monoclonal antibodies are carefully designed to recognize a single target (for example, a specific part of a specific virus). Sometimes two monoclo...
What is the difference between monoclonal antibodies and polyclonal antibodies?
Monoclonal antibodies are designed to target a very specific part of a virus or bacterium, and are carefully selected and tested for effectiveness....
Are monoclonal antibodies considered immunotherapy?
Monoclonal antibodies are not considered immunotherapy, because they do not change the body’s own immune response to the virus. Rather, monoclonal...
How are monoclonal antibodies produced?
Most monoclonal antibodies for COVID-19 are derived from human antibodies that are isolated from a person who has previously recovered from COVID-1...
How Does The Immune System Fight Cancer?
The immune system is composed of a complex team of players that detect and destroy disease-causing agents, such as bacteria and viruses. Similarly,...
What Is A Monoclonal Antibody?
Monoclonal antibodies are laboratory-produced molecules engineered to serve as substitute antibodies that can restore, enhance or mimic the immune...
How Do Monoclonal Antibody Drugs Work?
Monoclonal antibodies are designed to function in different ways. A particular drug may actually function by more than one means. The role of the d...
What Cancers May Be Treated With Monoclonal Antibody Drugs?
Monoclonal antibody treatments have been developed for some but not all cancers, and certain types of cancer cells are more vulnerable than others...
How Are Monoclonal Antibody Drugs Used in Cancer Treatment?
Monoclonal antibodies are administered through a vein (intravenously). How often you undergo monoclonal antibody treatment depends on your cancer a...
What Types of Side Effects Do Monoclonal Antibody Drugs Cause?
In general, monoclonal antibody treatment carries fewer side effects than do traditional chemotherapy treatments.However, monoclonal antibody treat...
What Should You Consider When Deciding on Monoclonal Antibody Drug Treatment?
Discuss your cancer treatment options with your doctor. Together you can weigh the benefits and risks of each treatment and decide whether a monocl...
Overview
Monoclonal antibodies (also called moAbs or mAbs) are proteins made in laboratories that act like proteins called antibodies in our bodies. Antibodies are parts of your immune system. They seek out the antigens (foreign materials) and stick to them in order to destroy them.
Procedure Details
In most cases, monoclonal antibodies are given mostly as intravenous (IV) solution injected right into your vein (sometimes referred to as an infusion). They’re often given in an infusion center where there are several people getting treatment at one time.
Recovery and Outlook
Infusion times can vary. As an example, though, monoclonal antibody treatment for COVID-19 under Emergency Use Authorization took about an hour for infusion and then another hour or so to watch for any reaction to the infusion.
When to Call the Doctor
If you’ve had a monoclonal antibody treatment, and you’re having an expected reaction, call your healthcare provider or go to an emergency room.
What antibody is used to block the virus?
Monoclonal antibodies against COVID-19 attach to the virus to block it from entering human cells. The monoclonal antibody protein also “marks” the virus to be broken down by the immune system and cleared from the body.
What is the function of antibodies?
Antibodies are proteins that exist in our bodies as part of our immune system to recognize and defend against harmful viruses and bacteria. Monoclonal antibodies are made in a laboratory and designed to target a specific virus or bacteria.
Can monoclonal antibodies cause nausea?
Most people tolerate monoclonal antibody infusions very well. Some people may experience infusion-related side effects, such as nausea and dizziness, that are short-lived and go away on their own. As with any medication, there is the potential for mild or more severe allergic reactions, which are uncommon.
How are monoclonal antibodies administered?
Monoclonal antibodies are administered through a vein (intravenously). How often you undergo monoclonal antibody treatment depends on your cancer and the drug you're receiving. Some monoclonal antibody drugs may be used in combination with other treatments, such as chemotherapy or hormone therapy.
What is the role of monoclonal antibodies in the immune system?
Monoclonal antibodies are designed to function in different ways. A particular drug may actually function by more than one means. The role of the drug in helping the immune system may include the following: Flagging cancer cells. Some immune system cells depend on antibodies to locate the target of an attack.
What is the best treatment for cancer?
Preventing blood vessel growth. In order for a cancerous tumor to grow and survive, it needs a blood supply. Some monoclonal antibody drugs block protein-cell interactions necessary for the development of new blood vessels. Blocking immune system inhibitors.
Why do some drugs have monoclonal antibodies?
Similarly, some monoclonal antibodies are attached to a chemotherapeutic drug in order to deliver the treatment directly to the cancer cells while avoiding healthy cells. Binding cancer and immune cells. Some drugs combine two monoclonal antibodies, one that attaches to a cancer cell and one that attaches to a specific immune system cell.
Why do immune cells depend on antibodies?
Some immune system cells depend on antibodies to locate the target of an attack. Cancer cells that are coated in monoclonal antibodies may be more easily detected and targeted for destruction. Triggering cell-membrane destruction.
What is the function of an antibody?
An antibody attaches itself to a specific molecule (antigen) on the surface of a problematic cell. When an antibody binds to the antigen, it serves as a flag to attract disease-fighting molecules or as a trigger that promotes cell destruction by other immune system processes.
What is a clinical trial?
Clinical trials, which are studies of new treatments and new ways to use existing treatments, may be available to you. In a clinical trial, the cost of the monoclonal antibody drug may be paid for as a part of the study. Also, you may be able to try new monoclonal antibody drugs. Talk to your doctor about what clinical trials may be open to you.
Why are monoclonal antibodies used in immunotherapy?
Some monoclonal antibodies are also immunotherapy because they help turn the immune system against cancer. For example, some monoclonal antibodies mark cancer cells so that the immune system will better recognize and destroy them.
What is monoclonal antibody?
Monoclonal antibodies are immune system proteins that are created in the lab. Antibodies are produced naturally by your body and help the immune system recognize germs that cause disease, such as bacteria and viruses, and mark them for destruction.
What antibodies kill cancer cells?
Other monoclonal antibodies bring T cells close to cancer cells, helping the immune cells kill the cancer cells. An example is blinatumomab (Blincyto®), which binds to both CD19, a protein found on the surface of leukemia cells, and CD3, a protein on the surface of T cells. This process helps the T cells get close enough to ...
Can cytokine release cause shock?
Capillary leak syndrome may lead to multiple organ failure and shock. Cytokine release syndrome can sometimes occur with monoclonal antibodies, but it is often mild. Cytokines are immune substances that have many different functions in the body, and a sudden increase in their levels can cause: Fever. Nausea.
Can monoclonal antibodies cause side effects?
Monoclonal antibodies can cause side effects, which can differ from person to person. The ones you may have and how they make you feel will depend on many factors, such as how healthy you are before treatment, your type of cancer, how advanced it is, the type of monoclonal antibody you are receiving, and the dose.
What is a monoclonal antibody?
Monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) are antibodies developed in a laboratory to help our bodies fight infection. Nearly 100 mAbs are FDA-approved to treat health conditions including cancers and autoimmune diseases. Monoclonal antibodies are also being studied for the treatment and prevention of COVID-19. They are given through intravenous infusion (i.e., ...
Why are antibodies made?
Antibodies are naturally made in our bodies to fight infection. Without antibodies, a virus can enter and infect a cell. With antibodies, however, when the virus tries to enter the cell, antibodies block the virus. Monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) are antibodies developed in a laboratory to help our bodies fight infection.
What are monoclonal antibodies?
Our bodies naturally make antibodies to fight infections. However, if you haven’t received the COVID-19 vaccine or had a previous COVID-19 infection, your body will not have antibodies designed to recognize a new virus like SARS-CoV-2.
How does monoclonal antibody therapy help?
Monoclonal antibody therapy is a way of treating COVID-19 for people who have tested positive, have had mild symptoms for seven days or less, and are at high risk for developing more serious symptoms.
Who is eligible for monoclonal antibody therapy?
Given that COVID-19 vaccination provides strong protection against severe disease and need for hospitalization, monoclonal antibody therapy is an option for certain high-risk patients with COVID-19.
WHAT IS A MONOCLONAL ANTIBODY?
Your body naturally makes antibodies to fight infection. However, your body may not have antibodies designed to recognize a novel (or new) virus like SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19.
How Can I Get Monoclonal Antibodies?
To receive a mAb you should be referred for treatment by your healthcare professional and directed to available infusion locations. If you do not have a healthcare provider, call the Combat COVID Monoclonal Antibodies Call Center at 1-877-332-6585 to find out who to talk with about your symptoms and treatment.
WHAT IF I DO NOT QUALIFY FOR MONOCLONAL ANTIBODY TREATMENT?
Your healthcare professional may decide you do not qualify for mAb treatment. There could be several reasons for this. You may not meet all eligibility criteria or you may have an underlying health condition that disqualifies you for mAb treatment.
WHAT CAN I EXPECT FROM TREATMENT (INFUSION)?
The mAb treatment is usually offered at an infusion center because the treatment is given through an intravenous (IV) infusion or shots. Depending on the mAb treatment you receive, the whole process takes about 1-3 hours, depending on the treatment..
CAN MONOCLONAL ANTIBODY TREATMENT MAKE ME SICK?
Antibody treatments do not contain any live SARS-CoV-2, so there is no risk you will get COVID-19 from mAb treatment. However, the antibody treatment may have side effects: