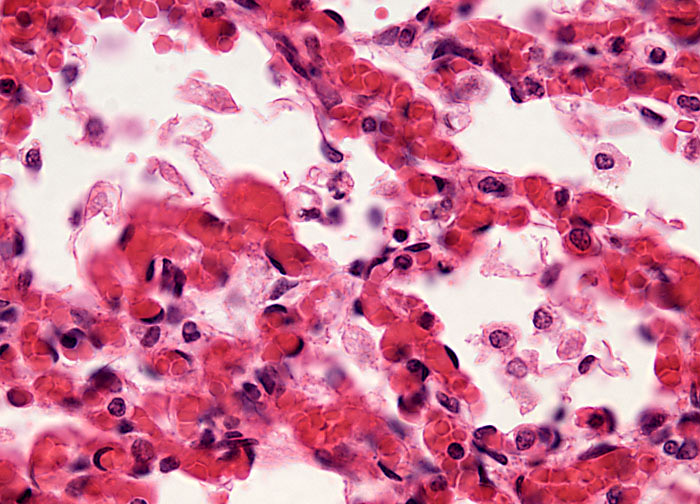
Antibiotics won't help you get better quicker if a virus causes your pneumonia. 2 Bacterial pneumonia is more common and needs to be treated with antibiotics to resolve fully, which may take a month or more. Bacterial pneumonia may be caused by the same pathogen that caused the original illness.
What is the strongest antibiotic for pneumonia?
What is the strongest antibiotic for pneumonia? Levofloxacin is rapidly becoming a popular choice in pneumonia; this agent is a fluoroquinolone used to treat CAP caused by S aureus, S pneumoniae (including penicillin-resistant strains), H influenzae, H parainfluenzae, Klebsiella pneumoniae, M catarrhalis, C pneumoniae, Legionella pneumophila, or M pneumoniae.
Can pneumonia go away without antibiotics?
Walking pneumonia usually does not require bed rest or hospitalization and can be treated with antibiotics. You may feel well enough that you don't even realize you have this lung infection.
Should pneumonia be treated with antibiotics?
You should be given antibiotics as soon as possible if your pneumonia is likely to be caused by a bacterial infection. You will probably not be given antibiotics if the cause is likely to be a virus, such as coronavirus. This is because antibiotics do not work for viral infections.
When pneumonia does not respond to antibiotics?
Re: Help! Pneumonia that will not respond to antibiotics in Draxxin is a 5 day antibiotic and it really should take care of it. I would do 1 more shot of Draxxin and see if it helps. Along with some support stuff too. Certainly the vitamin C is great and I would be giving him a B complex shot. Keep up the Banamine for as long as the vet tells you to.
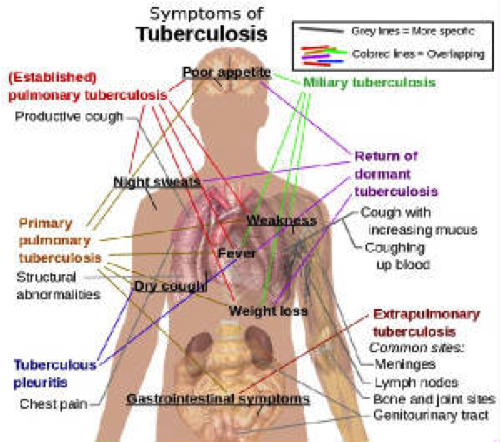
Can antibiotics not work for pneumonia?
Antibiotics Surprisingly Ineffective on Pneumonia. Researchers say as many as 1 in 4 patients will not be cured by an initial prescription. They urge special treatment for younger and older patients. People with pneumonia are failing treatment at an alarming rate, and doctors are in for a wake-up call.
What kind of pneumonia is treated with antibiotics?
Most of the time, walking pneumonia is caused by an atypical bacteria called Mycoplasma pneumoniae, which can live and grow in the nose, throat, windpipe (trachea) and lungs (your respiratory tract). It can be treated with antibiotics.
What is the most effective treatment for pneumonia?
The main treatment for pneumonia is antibiotics, along with rest and drinking plenty of water. If you have chest pain, you can take pain killers such as paracetamol. Treatment depends on how severe your pneumonia is. Treatment with antibiotics should be started as soon as possible after diagnosis.
Which type of pneumonia is the most serious?
Hospital-acquired pneumonia. It can be serious because the bacteria causing the pneumonia can be resistant to antibiotics.
Case Study 1: After 3 Months of Antibiotics
A 73-year-old male presented to my clinic with pneumonia of 12 weeks’ duration. He reported that his symptoms began several months prior, initially starting as unilateral facial nerve irritation and swelling. This facial nerve issue was treated with antibiotics.
Impressions
Although this patient was supportive of naturopathic medicine in general, he had not sought care with a naturopathic doctor or used natural medicine before this condition.
Follow-up
He did call in 3 days, but to report that he was doing 95% better than he had in 4 months. He felt very grateful. He was told to continue the treatment plan and to follow up in the office in 3-4 days in order to review labs and auscultate his lungs. It took him a month to follow up.
Case Study 2: Dragged in by a Spouse
A 45-year-old male presented with strained breathing. He would lean forward in his chair and off to one side. He had congestion, green-colored sputum, fatigue, wheezing, fever, and chills. His symptoms started with a head cold 2 weeks prior; then his ear became clogged. Muscle aches in his thighs made it difficult to sleep and caused him to moan.
Impressions
This case involves a spouse of a current patient. He didn’t necessarily buy into our office’s philosophy of medicine until he had a need himself. With the nature of his discharge and discomfort, bacteria seemed involved, but I wanted to protect him from a complicated viral infection as well.
Treatment Plan
Antimicrobial product containing vitamin A and 7-8 botanicals: 1 tablet 3 times daily with food. If side effects (eg, headaches, nausea, belly pain, dryness), take only 2 tablets daily. If no problems, increase to 4/day, then 6/day (2 tablets 3 times daily) for 7 days.
Follow-up
I spoke with the patient and his wife by phone the next day to discuss lab results, which included electrolyte imbalances, elevated liver enzymes, WBC elevation (neutrophils primarily involved), and bronchopneumonia per the chest X-ray. Diagnosis was bacterial bronchopneumonia with full lung involvement.
Here's what your doctor might prescribe you
Jennifer Welsh is a Connecticut-based science writer and editor with over ten years of experience under her belt. She’s previously worked and written for WIRED Science, The Scientist, Discover Magazine, LiveScience, and Business Insider.
Types of Antibiotics for Pneumonia
There are multiple types of antibiotics that work in slightly different ways. Some are more commonly used to treat pneumonia than others based on things like: 6
How Your Doctor Chooses
Your doctor will select the right antibiotic for you based on multiple factors, including: 6
Side Effects
Antibiotics are serious drugs and can have some uncomfortable side effects. These can include: 9
Summary
Antibiotics are used to treat bacterial pneumonia. Which antibiotic is prescribed is based on the type of bacteria, your age, health history, and more. You will often take the antibiotics for five to seven days. Completing the full course is important. Side effects may occur, which you should report to your doctor.
How long does it take to get off prednisone?
The patient is transitioned to 60 mg of oral prednisone once daily, with a weekly 10 mg decrease in dose during the following several weeks. Four days after admission to the tertiary hospital, the patient is discharged.
Can elevated procalcitonin be ruled out?
As a rare condition that closely resembles other more common diseases, particularly bacterial pneumonia, AEP may be difficult for physicians to recognize, the case authors wrote, emphasizing that it is vital to realize that elevated procalcitonin levels do not rule out AEP.
Does procalcitonin fall rapidly?
As well, concentrations of procalcitonin fall rapidly during recovery from acute bacterial infections. This points to a potential adjunctive role for procalcitonin in diagnosing and managing patients with suspected systemic infections, and to help guide antibiotic prescribing practices.