
The cell wall in bacteria is essential for survival as it helps to keep the contents of the cell intact. Antibiotics usually work on this principle by targeting the bacterial cell wall and causing lysis. This leads to the expulsion of cellular contents and the eventual death of the cell.
Full Answer
What is the structure and function of a cell wall?
The Structure and Function of a Cell Wall. Cellulose is the major component of cotton fiber and wood, and it is used in paper production. Bacterial cell walls are composed of a sugar and amino acid polymer called peptidoglycan. The main components of fungal cell walls are chitin, glucans, and proteins.
Why are cell walls important to plant cells?
Cell walls are important features of plant cells that perform a number of essential functions, including providing shape to the many different cell types needed to form the tissues and organs of a plant.
Why study bacterial cell wall composition and structure?
The ability to characterize bacterial cell-wall composition and structure is crucial to understanding the function of the bacterial cell wall, determining drug modes of action and developing new-generation therapeutics.
How does the cell wall protect the cell from pathogens?
For example, the cell wall can keep pathogens like plant viruses from entering. In addition to the mechanical support, the wall acts as a framework that can prevent the cell from expanding or growing too quickly. Proteins, cellulose fibers, polysaccharides and other structural components help the wall maintain the shape of the cell.
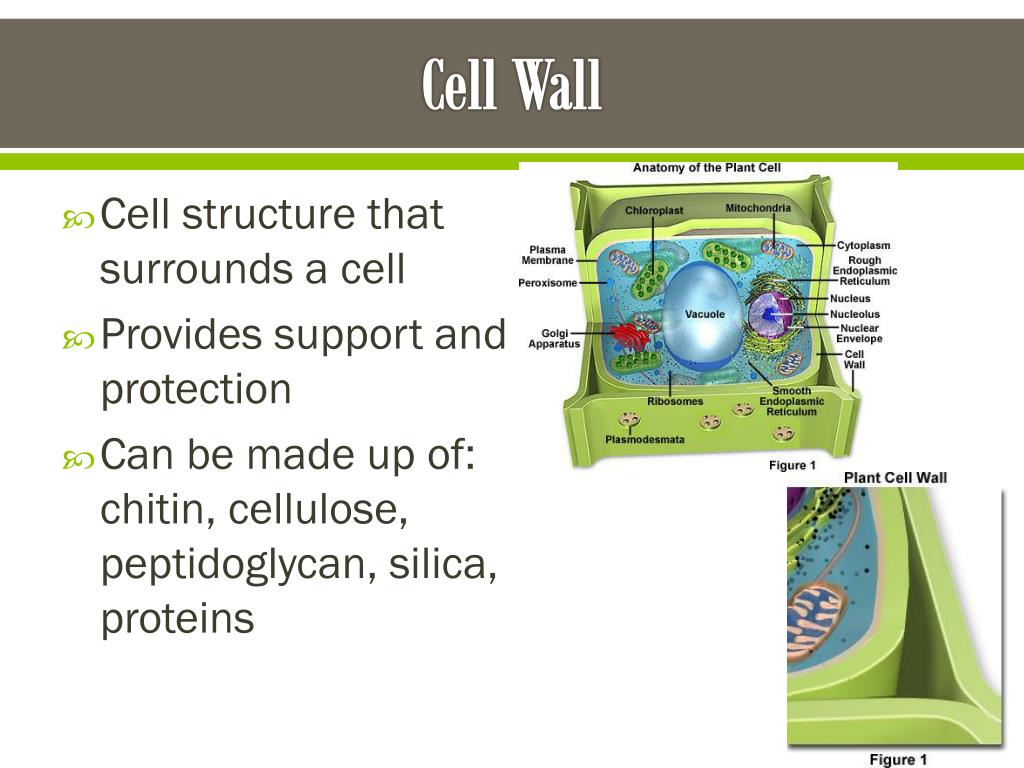
Why is the structure of the cell wall important?
A major role of the cell wall is to form a framework for the cell to prevent over expansion. Cellulose fibers, structural proteins, and other polysaccharides help to maintain the shape and form of the cell. Additional functions of the cell wall include: Support: The cell wall provides mechanical strength and support.
What is the importance of the cell wall structure for the effect of antibiotic?
Many antibiotics, including penicillin, work by attacking the cell wall of bacteria. Specifically, the drugs prevent the bacteria from synthesizing a molecule in the cell wall called peptidoglycan, which provides the wall with the strength it needs to survive in the human body.
Why is a cell wall significant in the understanding of antibiotic therapy?
Bacteria are single-celled organisms and the cell wall that surrounds their plasma membrane, is made from a polymer (rather like a mesh) of amino acids and sugars. This wall is a crucial structure for bacterial shape and division, which makes it a good target for antibiotics.
Why knowledge of an infecting microorganisms cell wall structure is important to healthcare professionals?
The ability to characterize bacterial cell-wall composition and structure is crucial to understanding the function of the bacterial cell wall, determining drug modes of action and developing new-generation therapeutics.
How does the cell wall promote infection in a human host?
Surface proteins called adhesins in the bacterial cell wall bind to receptor molecules on the surface of a susceptible host cell enabling the bacterium to make intimate contact with the host cell, adhere, colonize, and resist flushing.
How does the cell wall affect virulence of bacteria?
Like many other surface components, S-layers contribute to virulence by protecting the bacterium against complement and attack by phagocytes. The cell wall of a bacterium is an essential structure that protects the delicate cell protoplast from osmotic lysis.
What cellular structure do antibiotics typically target?
In principal, there are three main antibiotic targets in bacteria: The cell wall or membranes that surrounds the bacterial cell. The machineries that make the nucleic acids DNA and RNA. The machinery that produce proteins (the ribosome and associated proteins)
Why is peptidoglycan a good target for antibiotics?
When used as an antibiotic treatment, penicillin operates by a very specific mechanism. Penicillin interferes with the production of a molecule called peptidoglycan. Peptidoglycan molecules form strong links that give the bacterial cell strength as well as preventing leakage from the cytoplasm.
What is the main function of the bacterial cell wall?
The cell wall has multiple functions during bacterial growth, including maintaining bacterial cell integrity and shape as well as resisting internal turgor pressure. Furthermore, it must remain flexible to accommodate the remodeling that is required for cell division and growth.
How do cell walls help bacteria living in such environments?
How do cell walls help bacteria living in such environments? Hypotonic environment is where the solute concentration inside the cell exceeds that outside of the cell, so the water will move by osmosis INTO the cell. Cells that have a cell wall can better withstand changes in osmotic pressure and maintain their shape.
Why is the bacterial cell wall of such great importance quizlet?
The peptidoglycan cell wall is meshlike, allowing for easy passage of ions, amino acids, and nutrients and maintaining structural integrity.
How does the structure of an organism enable it to function as a pathogen?
Bacterial surface structures may act as (1) permeability barriers that allow selective passage of nutrients and exclusion of harmful substances (e.g. antimicrobial agents); (3) adhesins used to attach or adhere to specific surfaces or tissues; (3) enzymes to mediate specific reactions on the cell surface important in ...
What cellular structure do antibiotics typically target?
In principal, there are three main antibiotic targets in bacteria: The cell wall or membranes that surrounds the bacterial cell. The machineries that make the nucleic acids DNA and RNA. The machinery that produce proteins (the ribosome and associated proteins)
What type of antibiotics work by affecting cell wall synthesis?
beta-lactamsPenicillins and cephalosporins are the major antibiotics that inhibit bacterial cell wall synthesis. They are called beta-lactams because of the unusual 4-member ring that is common to all their members.
Why is peptidoglycan a good target for antibiotics?
When used as an antibiotic treatment, penicillin operates by a very specific mechanism. Penicillin interferes with the production of a molecule called peptidoglycan. Peptidoglycan molecules form strong links that give the bacterial cell strength as well as preventing leakage from the cytoplasm.
What antibiotics target bacterial cell walls?
β-Lactam antibiotics are a broad class of antibiotics that includes penicillin derivatives (penams), cephalosporins (cephems), monobactams, and carbapenems. β-Lactam antibiotics are bacteriocidal and act by inhibiting the synthesis of the peptidoglycan layer of bacterial cell walls.
Why is the cell wall important?
The cell wall also plays an important role in transport. Since the wall is a semi-permeable membrane, it allows certain substances to pass through , such as proteins. This allows the wall to regulate diffusion in the cell and control what enters or leaves. Additionally, the semi-permeable membrane helps communication among cells by allowing ...
What is the purpose of cell walls?
In addition to the mechanical support, the wall acts as a framework that can prevent the cell from expanding or growing too quickly.
Why do plants have walls?
One of the main reasons for having a wall in a plant cell is that it can withstand turgor pressure, and this is where cellulose plays a crucial role. Turgor pressure is a force created by the inside of the cell pushing out. Cellulose microfibrils form a matrix with the proteins, hemicelluloses and pectins to provide the strong framework ...
What is the function of cellulose?
Cellulose is a complex carbohydrate and consists of thousands of glucose monomers that form long chains. These chains come together and form cellulose microfibrils, which are several nanometers in diameter. The microfibrils help control the growth of the cell by limiting or allowing its expansion.
What are the functions of proteins in the cell wall?
The proteins in the cell wall serve different functions. Some of them provide structural support. Others are enzymes, which are a type of protein that can speed up chemical reactions. The enzymes help the formation of and normal modifications that occur to maintain the plant's cell wall.
How does the cell wall affect antibiotics?
This helps to destroy the protective cell wall and stops the bacteria from growing.
What is the cell wall?
The cell wall is an additional layer of protection on top of the cell membrane. You can find cell walls in both prokaryotes and eukaryotes, and they are most common in plants, algae, fungi and bacteria.
Why is the cell wall important?
The cell wall is an essential part of survival for many bacteria. It provides mechanical structure to bacteria, which are single-celled, and it also protects them from internal turgor pressure.
What is the function of the cell wall?
The cell wall has a few different functions. It is flexible, but provides strength to the cell, which helps protect the cell against physical damage. It also gives the cell its shape and allows the organism to maintain a certain shape overall. The cell wall can also provide protection from pathogens such as bacteria that are trying to invade the cell. The structure of the cell wall allows many small molecules to pass through it, but not larger molecules that could harm the cell.
What are the cell walls of fungi?
The cell walls of fungi contain chitin , which is a glucose derivative that is similar in structure to cellulose. Layers of chitin are very tough; chitin is the same molecule found in the rigid exoskeletons of animals such as insects and crustaceans. Glucans, which are other glucose polymers, are also found in the fungal cell wall along with lipids and proteins. Fungi have proteins called hydrophobins in their cell walls. Found only in fungi, hydrophobins give the cells strength, help them adhere to surfaces, and help control the movement of water into the cells. In fungi, the cell wall is the most external layer, and surrounds the cell membrane.
Why do plants have cell walls?
The cell walls of plant cells help them maintain turgor pressure, which is the pressure of the cell membrane pressing against the cell wall. Ideally, plants cells should have lots of water within them, leading to high turgidity. Whereas a cell without a cell wall, such as an animal cell, can swell and burst of too much water diffuses into it, ...
What are the proteins that are found in the cell walls of fungi?
Glucans, which are other glucose polymers, are also found in the fungal cell wall along with lipids and proteins. Fungi have proteins called hydrophobins in their cell walls. Found only in fungi, hydrophobins give the cells strength, help them adhere to surfaces, and help control the movement of water into the cells.
What is the cell wall of a bacteria?
The cell walls of bacteria usually contain the polysaccharide peptidoglycan, which is porous and lets small molecules through. Together, the cell membrane and cell wall are referred to as the cell envelope. The cell wall is an essential part of survival for many bacteria. It provides mechanical structure to bacteria, which are single-celled, ...
What is the cell wall?
A cell wall is an outer layer surrounding certain cells that is outside of the cell membrane. All cells have cell membranes, but generally only plants, fungi, algae, most bacteria, and archaea have cells with cell walls. The cell wall provides strength and structural support to the cell, and can control to some extent what types and concentrations of molecules enter and leave the cell. The materials that make up the cell wall differ depending on the type of organism. The cell wall has evolved many different times among different groups of organisms.
What is the function of the cell wall?
That is a lot of pressure for the plasma membrane to withstand! The cell wall can keep out certain molecules, such as toxins, particularly for gram negative bacteria. And lastly, the bacterial cell wall can contribute to the pathogenicity or disease –causing ability of the cell for certain bacterial pathogens.
Why is the bacterial cell wall important?
It also helps maintain the cell shape, which is important for how the cell will grow , reproduce, obtain nutrients, and move.
What is the cell wall of Gram positive bacteria?
Gram Positive Cell walls. The cell walls of gram positive bacteria are composed predominantly of peptidoglycan. In fact, peptidoglycan can represent up to 90% of the cell wall, with layer after layer forming around the cell membrane. The NAM tetrapeptides are typically cross-linked with a peptide interbridge and complete cross-linking is common.
How do teichoic acids contribute to cell division?
There is also evidence that teichoic acids participate in cell division, by interacting with the peptidoglycan biosynthesis machinery. Lastly, teichoic acids appear to play a role in resistance to adverse conditions such as high temperatures and high salt concentrations, as well as to β-lactam antibiotics.
What is the cell wall of bacteria?
A cell wall, not just of bacteria but for all organisms, is found outside of the cell membrane. It’s an additional layer that typically provides some strength that the cell membrane lacks, by having a semi-rigid structure. Both gram positive and gram negative cell walls contain an ingredient known as peptidoglycan (also known as murein ).
How are large molecules broken down?
Large molecules are broken down by enzymes, in order to allow them to get past the LPS. Instead of exoenzymes (like the gram positive bacteria), the gram negative bacteria utilize periplasmic enzymes that are stored in the periplasm.
How many types of cell walls do bacteria have?
Having said that though, it is also important to note that most bacteria (about 90%) have a cell wall and they typically have one of two types: a gram positive cell wall or a gram negative cell wall. The two different cell wall types can be identified in the lab by a differential stain known as the Gram stain.
What is the function of the cell wall?
The main function of the cell wall is to provide structural strength and support, and also provide a semi-permeable surface for molecules to pass in and out of the cell.
Why is the cell wall important in bacteria?
The cell wall in bacteria is essential for survival as it helps to keep the contents of the cell intact. Antibiotics usually work on this principle by targeting the bacterial cell wall and causing lysis. This leads to the expulsion of cellular contents and the eventual death of the cell.
What are the cell walls of prokaryotes made of?
The prokaryotic cell walls are composed of large polymers known as peptidoglycans. Cell walls in prokaryotes serve as a form of protection and prevent lysis (bursting of the cell and expulsion of cellular contents). Structurally, prokaryotic cell walls consist of two layers: An inner layer that is made up of peptidoglycans.
What is the primary cell wall?
Primary Cell Wall. The primary cell is situated closest to the inside of the cell and is the first-formed cell wall. It is mainly made up of cellulose, allowing the wall to stretch for the purpose of growth. Several primary cells contain pectic polysaccharides and structural proteins.
What is the cell wall?
The cell wall is the outer covering of a cell, present adjacent to the cell membrane, which is also called the plasma membrane. As mentioned earlier, the cell wall is present in all plant cells, fungi, bacteria, algae, and some archaea.
Why is water important in cell growth?
It helps to control cell expansion due to the intake of water. Also helps in preventing water loss from the cell. It is responsible for transporting substances between and across the cell. It acts as a barrier between the interior cellular components and the external environment.
Why are animal cells irregular?
An animal cell is irregular in their shape and this is mainly due to the lack of cell wall in their cells. The compositions of the cell wall usually vary along with organisms. Also, read Cell Wall and Cell Membrane.
What is a Cell Wall?
The cell wall is a non-living, rigid, and permeable structure surrounding the plasma membrane. It is found in most plants, bacteria, fungi, and algae. Animals and protozoans lack this rigid structure. The composition of cell walls varies greatly among bacteria, fungi, plants, and algae.
Summary
The cell wall is a protective layer present around bacterial, fungal, algal, and plant cells. The cell wall of plant cells is made up of cellulose, hemicellulose, and pectin. The cell wall of a plant cell comprises three layers: middle lamella, which is made up of calcium and magnesium pectate.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on Cell Wall
Q.1. What is lignification? Ans: Lignification is the polymerization of lignin on cell walls to make it harder and make the plant disease resistant.
Footer
Embibe is India’s leading AI Based tech-company with a keen focus on improving learning outcomes, using personalised data analytics, for students across all level of ability and access.

Cell Wall Definition
Cell Wall Functions
- The cell wall has a few different functions. It is flexible, but provides strength to the cell, which helps protect the cell against physical damage. It also gives the cell its shape and allows the organism to maintain a certain shape overall. The cell wall can also provide protection from pathogens such as bacteria that are trying to invade the ce...
Cell Wall Structure
- Plant Cell Walls
The main component of the plant cell wall is cellulose, a carbohydrate that forms long fibers and gives the cell wall its rigidity. Cellulose fibers group together to form bundles called microfibrils. Other important carbohydrates include hemicellulose, pectin, and liginin. These carbohydrates f… - Algae Cell Walls
Algae are a diverse group, and the diversity in their cell walls reflects this. Some algae, such as green algae, have cell walls that are similar in structure to those of plants. Other algae, such as brown algae and red algae, have cellulose along with other polysaccharides or fibrils. Diatoms h…
Related Biology Terms
- Cell membrane– A membrane found on the outside of all cells that separates them from the outside environment.
- Turgor pressure– Water pressure inside cells.
- Chitin– A polysaccharide that is a main component of fungal cell walls and also of the exoskeletons of certain animals like insects.
Quiz
- 1. Which is a function of the cell wall? A. To maintain turgor pressure B. To provide support to the cell C. To control what molecules enter and exit the cell D.All of the above 2. The cells of which group of organisms lack a cell wall? A. Archaea B. Bacteria C. Animals D.Fungi 3. Which organism has a cell wall containing chitin? A. Plants B. Algae C. Fungi D.Bacteria