- Quit smoking. Quitting smoking is the most important step you can take to help slow the progression of COPD. ...
- Medicines. Medicines to treat COPD symptoms include bronchodilators and a combination of bronchodilators and steroids.
- Pulmonary rehabilitation. Pulmonary rehabilitation is a supervised program that includes exercise training, health education, and breathing techniques for people who have certain lung conditions, have lung problems due to other ...
- Oxygen therapy. Oxygen therapy is a treatment that delivers oxygen for you to breathe. ...
- Surgery. Surgery may benefit some people who have COPD. Surgery usually is a last resort for people who have severe symptoms that have not improved from taking medicines.
- Lung transplant. A lung transplant is surgery to remove a diseased lung and replace it with a healthy lung. ...
What is the latest medication for COPD?
Some of the most common COPD medications include:
- Bronchodilators
- Inhaled steroids
- Combination inhalers (bronchodilators combined with inhaled steroids)
- Antibiotics (during periods of respiratory infection)
What are the common medications for COPD?
The corticosteroids that doctors most often prescribe for COPD are:
- Fluticasone (Flovent). This comes as an inhaler you use twice daily. Side effects can include headache, sore throat, voice changes, nausea, cold-like symptoms, and thrush.
- Budesonide (Pulmicort). This comes as a handheld inhaler or for use in a nebulizer. Side effects can include colds and thrush.
- Prednisolone. This comes as a pill, liquid, or shot. ...
How do you cure COPD?
Treatment for COPD
- Oxygen therapy. If your blood oxygen level is too low, you can receive supplemental oxygen through a mask or nasal cannula to help you breathe better.
- Surgery. Surgery is reserved for severe COPD or when other treatments have failed, which is more likely when you have a form of severe emphysema.
- Lifestyle changes. ...
What is the best treatment for severe COPD?
Your Treatment Choices for Moderate-to-Severe COPD
- Oxygen Therapy. Even with medications, you may have symptoms like wheezing, coughing, trouble catching your breath, and feeling tired.
- Surgery. If drugs and therapy aren't doing enough to help you breathe right, your doctor may suggest surgery.
- Pulmonary Rehabilitation. ...
- Antibiotics and Vaccinations. ...

What is latest treatment for COPD?
There's also a triple inhaled therapy for COPD that combines three long-acting COPD medications. The first approved triple inhaled therapy for COPD was called fluticasone/umeclidinium/vilanterol (Trelegy Ellipta). In 2020, the FDA approved a second: budesonide/glycopyrrolate/formoterol fumarate (Breztri Aerosphere).
What are three drug treatments for COPD?
They include:Albuterol and ipratropium (Combivent Respimat; Duoneb)Budesonide and formoterol (Symbicort)Fluticasone and salmeterol (Advair)Fluticasone and vilanterol (Breo Ellipta)Formoterol and mometasone (Dulera)Tiotropium and olodaterol (Stiolto Respimat)Umeclidinium and vilanterol (Anoro Ellipta)More items...•
Can COPD be cured or reversed?
There is no cure for COPD, but disease management can slow disease progression, relieve symptoms and keep you out of hospital. Treatment aims to prevent further damage, reduce the risk of complications and ease some of the symptoms. Treatment options include pulmonary rehabilitation, medicines and oxygen therapy.
What medication is given for COPD?
The corticosteroids that doctors most often prescribe for COPD are:Fluticasone (Flovent). This comes as an inhaler you use twice daily. ... Budesonide (Pulmicort). This comes as a handheld inhaler or for use in a nebulizer. ... Prednisolone. This comes as a pill, liquid, or shot.
How is COPD treated in the elderly?
Nowadays a therapy that allows modifying the long-term decline in lung function of patients suffering from COPD does not yet exist and, therefore, the treatment of this disease is mainly focused on the administration of bronchodilators and the use of inhaled glucocorticoids.
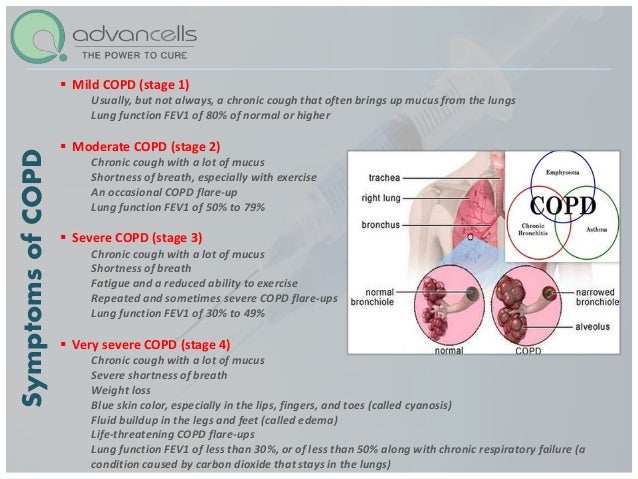
What are the 5 symptoms of COPD?
What Are COPD Symptoms?Chronic cough.Shortness of breath while doing everyday activities (dyspnea)Frequent respiratory infections.Blueness of the lips or fingernail beds (cyanosis)Fatigue.Producing a lot of mucus (also called phlegm or sputum)Wheezing.
What are the early warning signs of COPD?
Signs and symptoms of COPD may include:Shortness of breath, especially during physical activities.Wheezing.Chest tightness.A chronic cough that may produce mucus (sputum) that may be clear, white, yellow or greenish.Frequent respiratory infections.Lack of energy.Unintended weight loss (in later stages)More items...•
What is the life expectancy for someone with COPD?
Many people will live into their 70s, 80s, or 90s with COPD.” But that's more likely, he says, if your case is mild and you don't have other health problems like heart disease or diabetes. Some people die earlier as a result of complications like pneumonia or respiratory failure.
How to treat COPD?
A new method of treating COPD is a minimally invasive procedure called bronchial rheoplasty. It’s currently being tested and may reduce the number of mucus-producing cells in the lungs. During the procedure, electrical bursts destroy the cells that produce too much mucus, paving the way for new, healthy cells to grow.
What are the best ways to treat obstructive pulmonary disease?
These include: medication. therapy. surgery. healthy lifestyle changes. These treatments can: help make you feel better.
What happens if you don't inhale enough oxygen?
Oxygen therapy. COPD interferes with your ability to breathe. If you’re not inhaling enough oxygen, you won’t have enough oxygen in your blood. There are medical devices available that deliver oxygen to your lungs. Many of these devices are small and portable so you can take them with you wherever you go.
What is the best way to reduce nicotine cravings?
Recommended nicotine replacement treatments are available in the form of: gums. patches. inhalers. Some types of antidepressants have been clinically proven to help reduce or eliminate tobacco cravings. If your doctor prescribes a smoking cessation medication, be sure to ask about any possible side effects.
What is the best medicine for a swollen airway?
Corticosteroids. Corticosteroids , such as prednisone, reduce irritation and swelling in the airway. They’re particularly effective if you’ve been exposed to an infection or an irritant such as: secondhand smoke. extreme temperatures. harsh fumes. Corticosteroids can be delivered by: inhaler. nebulizer.
What is pulmonary rehabilitation?
Pulmonary rehabilitation includes breathing techniques, exercise, education, and mental health support. It also provides social support, which can be helpful to older patients. Supplemental oxygen. Some doctors offer a trial of supplemental oxygen as some older COPD patients may benefit.
What are the two classes of bronchodilators?
There are two classes of bronchodilators: β-agonists and anticholinergics. β-agonists bind directly to beta receptors on smooth muscle cells to mediate their bronchodilatory effect. β-agonists may be short-acting (e.g., albuterol) or long-acting (e.g., salmeterol).
What is the best way to treat COPD?
Anticholinergic Inhalers. An anticholinergic inhaler is another type of bronchodilator for the treatment of COPD. It helps prevent muscle tightening around the airways, too. It’s available as a metered-dose inhaler, and in liquid form for nebulizers. These inhalers can be short-acting or long-acting.
What is the best medicine for COPD?
Oral medications. Roflumilast (Daliresp) helps decrease airway inflammation in people with severe COPD. This medication can also counteract tissue damage, gradually improving lung function. Roflumilast is specifically for people who have a history of severe COPD exacerbations.
How does COPD affect the lungs?
COPD can destroy the air sacs in your lungs, resulting in the development of air spaces called bullae. As these air spaces expand or grow, breathing becomes shallow and difficult. A bullectomy is a surgical procedure that removes damaged air sacs. It can reduce breathlessness and improve lung function.
How many people are affected by COPD?
COPD is a condition that affects about 16 million#N#Trusted Source#N#people worldwide. Doctors and researchers are continually working to develop new medications and procedures to improve breathing for those living with the condition.
Does COPD cause breathing problems?
COPD causes lung damage, which also plays a role in breathing problems. According to the American Lung Association, this surgery removes about 30 percent of damaged or diseased lung tissue. With damaged portions removed, your diaphragm can work more efficiently, allowing you to breathe easier.
Can COPD be treated with add on therapy?
COPD can range from mild to severe. Your treatment will depend on the severity of your symptoms. If traditional or first-line therapy doesn’t improve your COPD, speak with your doctor. You may be a candidate for an add-on therapy or newer treatments. Last medically reviewed on May 29, 2019.
Does eosinophilic eosinophils help COPD?
It’s been noted that some people with COPD have a large number of eosinophils, a specific type of white blood cell. This biologic drug may limit or reduce the number of blood eosinophils, providing relief from COPD. More research is needed, though.
What is the best way to recover from COPD?
Pulmonary rehabilitation programs typically combine education, exercise training, nutrition advice and counseling.
How to treat a syphilis?
By taking the right medicine at the right time, you can: 1 Breathe better 2 Do more of the things you enjoy 3 Have fewer flare-ups or exacerbations
What is supplemental oxygen?
Supplemental Oxygen. Your body needs oxygen to do everything from digesting food, daily household chores, to going to the grocery store. Sometimes with COPD, you require extra or supplemental oxygen (also called oxygen therapy). Learn how supplemental oxygen works and get safety tips ».
What are some examples of complementary therapies?
Some examples of complementary therapy included massage, yoga and acupuncture.
What is palliative care?
Palliative care is a specialty in medicine focused on treating the symptoms, pain and stress that accompany serious illnesses like COPD. It is available to you from the moment you are diagnosed and through the entire course of your illness.
Do all people with COPD have the same symptoms?
Not all people with COPD have the same symptoms and treatment may differ from person to person. It is important to talk to your doctor about your treatment options and to get answers to all of your questions.
Is there a medicine for COPD?
A variety of medicines are used to treat COPD and there is no "best" medicine for all people. Each person's COPD is different and your doctor and healthcare team will work with you to set up the best plan to address your symptoms and needs. Learn more about your treatment options ».
What are the treatments for COPD?
COPD treatments include both medicines and other important therapies such as pulmonary rehabilitation, smoking/vaping cessation support and immunizations. If you were asked about COPD medicines you would probably think about your inhalers and you’d probably say, "they open up my lungs".
How often should I take a medicine for lung inflammation?
Medicines only work if you take them as you and your doctor or other clinician agree; that usually means at least once a day.
What are the two ways that medicines open up the airways in your lungs?
There are two basic ways that medicines open up the airways in your lungs: They act as Maintenance (controllers or preventers) or Relievers (rescue or quick relief). Here we’ll refer to them as either controllers or rescue relievers.
Can COPD be treated?
COPD can be treated. Some treatments can decrease breathlessness, increase your ability to do activities while others may reduce your risk of exacerbations (x-saa-cer-bay-shun) (flare-ups). These treatments can make it easier for you to breathe, feel better, do more and stay out of the emergency department and hospital.
Does bronchoconstriction cause shortness of breath?
This squeezing down of the airways also called bronchoconstriction (brawn-co-con-stric-shun), causes feelings of chest tightness and shortness of breath. Anticholinergic medicines block these messages from being produced or getting through to the airways and helping keep your airways open. Yes, this is pretty amazing!
Can you use a syringe alone with COPD?
They are currently used only to help prevent exacerbations or flare ups, mainly in people who have multiple (more than 1 each year) or severe (going to the hospital) flare ups. They are not used alone in people with COPD and are not needed for everyone with COPD.
8 new treatments for COPD
Bronchial rheoplasty is a new bronchoscopic method for the management of chronic bronchitis. The clinician inserts a specialized camera called a bronchoscope into the lungs, then delivers short bursts of electrical energy to the inner walls of the small and larger airways called the bronchi.
What are current treatment options for COPD?
Treatment for COPD can ease symptoms, prevent complications, and generally slow disease progression. Therapies include:

Diagnosis
Treatment
- Many people with COPDhave mild forms of the disease for which little therapy is needed other than smoking cessation. Even for more advanced stages of disease, effective therapy is available that can control symptoms, slow progression, reduce your risk of complications and exacerbations, and improve your ability to lead an active life.
Clinical Trials
- Explore Mayo Clinic studiestesting new treatments, interventions and tests as a means to prevent, detect, treat or manage this condition.
Coping and Support
- Living with COPDcan be a challenge — especially as it becomes harder to catch your breath. You may have to give up some activities you previously enjoyed. Your family and friends may have difficulty adjusting to some of the changes. It can help to share your fears and feelings with your family, friends and doctor. You may also want to consider joining a support group for people wit…
Preparing For Your Appointment
- If your primary care provider suspects that you have COPD, you'll likely be referred to a pulmonologist — a doctor who specializes in lung disorders.