What are the best treatment options for prostate cancer?
Surgery for Prostate Cancer. Radiation Therapy for Prostate Cancer. Cryotherapy for Prostate Cancer. Hormone Therapy for Prostate Cancer. Chemotherapy for Prostate Cancer. Immunotherapy for Prostate Cancer. Targeted Therapy for Prostate Cancer. Treatments for Prostate Cancer Spread to Bones.
What is the most successful prostate cancer treatment?
Apr 14, 2022 · These are the main types of prostate cancer treatment, and how they can prevent the spread of cancer cells within the body. Page Contents. 1 Surgery; 2 Radiation; 3 Surveillance; 4 ... Radiation is usually one of the most widely used methods of treating different cancers. This is because it is highly effective at preventing cancer cell growth ...
Which prostate cancer treatment is best?
If that happens, your treatment choices may include: • Activesurveillance • Hormonetherapy • Radiationtherapy,especiallyifyourPSAlevelislessthan 1 ng/ml n If you have high-risk cancer, hormone therapy may be used to shrink the prostate before radiation therapy.
Which is treatment for prostate cancer has the least side effects?
Radical prostatectomy removes the prostate as well as the surrounding tissue. Radiation therapy. Using high-energy rays (similar to X-rays) to kill the cancer. There are two types of radiation therapy— External radiation therapy. A machine outside the body directs radiation at the cancer cells. Internal radiation therapy (brachytherapy).

Which prostate cancer treatment is best?
Radiation therapy is a good choice for many men with early-stage prostate cancer. It is also the best treatment for older men or those who have other health problems. There are different types of radiation therapy: External beam radiation.
What is the most advanced treatment for prostate cancer?
The treatment is called lutetium-177-PSMA-617, or LuPSMA, and it has two components: a compound that targets a cancer cell protein called prostate-specific membrane antigen, or PSMA, and a radioactive particle that destroys the cells. Healthy prostate cells don't contain PSMA, or do at very low levels.Jul 12, 2021
What is the most common type of prostate cancer treatment?
Radiation therapy is the most common treatment for prostate cancer regardless of cancer stage, prostate-specific antigen (PSA) level, and prognosis and risk rating, according to a study published online by JAMA Oncology (2015; doi:10.1001/jamaoncol.Mar 3, 2015
Which prostate cancer treatment has least side effects?
HIFU allows men to avoid or live without such side effects for a period of time if they are ever to require whole gland treatment in the future. How patients recover: Done under general anesthesia, this is a well-tolerated outpatient procedure. It doesn't require hormone therapy or radiation.Oct 19, 2017
Is it better to have prostate removed or radiation?
Radiation may be a better choice for men who want to avoid the side effects of surgery, such as leaking urine and erection problems. It may be a better choice for men who have other health problems that make surgery too risky. You avoid the risks of major surgery.
What are the signs that prostate cancer has spread?
Prostate cancer that's more advanced may cause signs and symptoms such as:Trouble urinating.Decreased force in the stream of urine.Blood in the urine.Blood in the semen.Bone pain.Losing weight without trying.Erectile dysfunction.Jun 4, 2021
What is the injection given for prostate cancer?
LHRH agonists are given by injection or are implanted under the skin. Four LHRH agonists are approved to treat prostate cancer in the United States: leuprolide (Lupron), goserelin (Zoladex), triptorelin (Trelstar), and histrelin (Vantas).Feb 22, 2021
What is the main cause of prostate cancer?
The underlying factor linking diet and prostate cancer is probably hormonal. Fats stimulate increased production of testosterone and other hormones, and testosterone acts to speed the growth of prostate cancer. High testosterone levels may stimulate dormant prostate cancer cells into activity.Jun 9, 2021
How fast does prostate cancer spread?
This is because, unlike many other cancers, prostate cancer usually progresses very slowly. It can take up to 15 years for the cancer to spread from the prostate to other parts of the body (metastasis), typically the bones. In many cases, prostate cancer won't affect a man's natural life span.Feb 12, 2009
Where is the best place for prostate cancer treatment?
“Top hospitals” for cancer and for urologyUCSF Medical Center, San Francisco, CA.New York-Presbyterian University Hospital of Columbia and Cornell, New York, NY.Duke University Medical Center, Durham, NC.Vanderbilt University Medical Center, Nashville, TN.University of Texas M. D. Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, TX.More items...•Jul 22, 2011
What is the life expectancy with a Gleason score of 7?
Maximum estimated lost life expectancy for men with Gleason score 5 to 7 tumors was 4 to 5 years and for men with Gleason score 8 to 10 tumors was 6 to 8 years. Tumor histologic findings and patient comorbidities were powerful independent predictors of survival.
Can the prostate be removed after radiation therapy?
If your cancer returns after you've received radiation therapy, you may undergo a type of surgery called salvage radical prostatectomy. Radical prostatectomy is complex and requires a high level of technical precision.
Which Treatments Are Used For Prostate Cancer?
Depending on each case, treatment options for men with prostate cancer might include: 1. Watchful waiting or active surveillance 2. Surgery 3. Radi...
Which Doctors Treat Prostate Cancer?
The main types of doctors who treat prostate cancer include: 1. Urologists: surgeons who treat diseases of the urinary system and male reproductive...
Making Treatment Decisions
It’s important to discuss all of your treatment options, including their goals and possible side effects, with your doctors to help make the decisi...
Help Getting Through Treatment
Your cancer care team will be your first source of information and support, but there are other resources for help when you need it. Hospital- or c...
What are the treatment options for prostate cancer?
Depending on each case, treatment options for men with prostate cancer might include: Observation or Active Surveillance for Prostate Cancer. Surgery for Prostate Cancer. Radiation Therapy for Prostate Cancer. Cryotherapy for Prostate Cancer. Hormone Therapy for Prostate Cancer. Chemotherapy for Prostate Cancer.
What are the things to consider when making a decision about cancer treatment?
Some important things to consider include: The stage and grade of your cancer. Your age and expected life span.
What do people with cancer need?
People with cancer need support and information, no matter what stage of illness they may be in. Knowing all of your options and finding the resources you need will help you make informed decisions about your care.
What are the services offered by the American Cancer Society?
These might include nursing or social work services, financial aid, nutritional advice, rehab, or spiritual help. The American Cancer Society also has programs and services – including rides to treatment, lodging, and more – to help you get through treatment.
What is the name of the doctor who treats cancer?
Urologist: A surgeons who treat diseases of the urinary system and male reproductive system (including the prostate) Radiation oncologist: A doctor who treats cancer with radiation therapy. Medical oncologist: A doctor who treats cancer with medicines such as chemotherapy, hormone therapy, and immunotherapy.
Can you continue cancer treatment?
Whether or not you continue treatment, there are still things you can do to help maintain or improve your quality of life.
Is treatment information given here official policy of the American Cancer Society?
The treatment information given here is not official policy of the American Cancer Society and is not intended as medical advice to replace the expertise and judgment of your cancer care team. It is intended to help you and your family make informed decisions, together with your doctor.
What is the best treatment for prostate cancer?
Active surveillance, surgery, and radiation therapy are the standard therapy choices for men with early-stage prostate cancer (see Types of Treatment, starting on page 8). Each has benefits (how treatments can help) and risks (problems treatment may cause). There is seldom just one right treatment choice.
What is the purpose of the prostate cancer booklet?
Its purpose is to help you learn about early-stage prostate cancer, different treatments, and the benefits and risks of each type of treatment. Most men will need more information than this booklet gives them to make a decision about treatment. For a list of groups that provide more information and support, please see the Ways to Learn More section on page 32. Also, see that section if you have prostate cancer that has spread beyond the prostate or that has returned after treatment.
How long does it take for a prostate cancer to grow?
Early-stage prostate cancer means that cancer cells are found only in your prostate. Compared with many other cancers, prostate cancer grows slowly. This means that it can take 10 to 30 years before a prostate tumor gets big enough to cause symptoms or for doctors to find it. Most men who have prostate cancer will die of something other than prostate cancer.
Can you choose prostate cancer treatment?
As a man with early-stage prostate cancer, you will be able to choose which kind of treatment is best for you . And while it is good to have choices, this fact can make the decision hard to make. Yet, each choice has benefits (how treatment can help) and risks (problems treatment may cause).
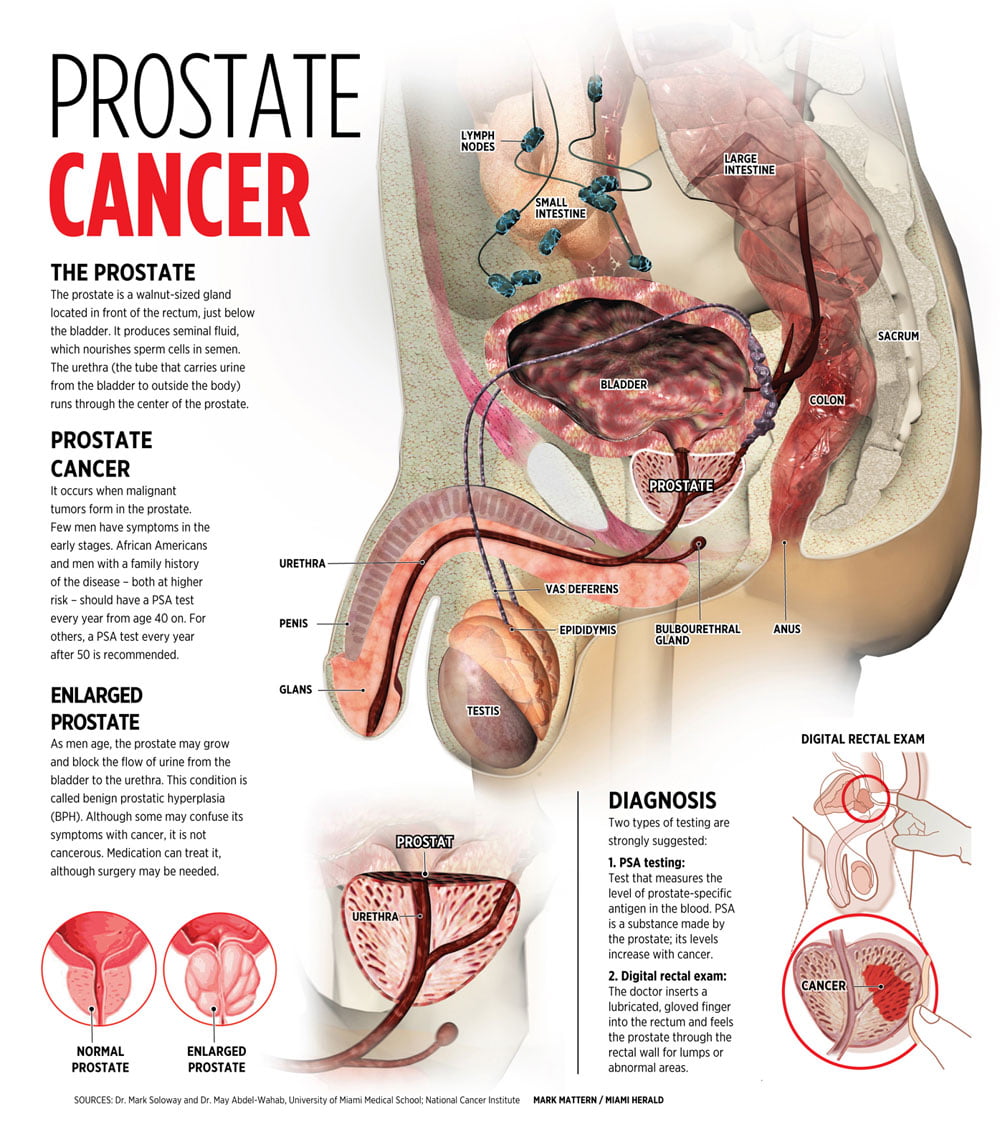
What is the procedure to remove prostate cancer?
Surgery. A prostatectomy is an operation where doctors remove the prostate. Radical prostatectomy removes the prostate as well as the surrounding tissue. Radiation therapy. Using high-energy rays (similar to X-rays) to kill the cancer. There are two types of radiation therapy—. External radiation therapy.
What is the best way to monitor prostate cancer?
Closely monitoring the prostate cancer by performing prostate specific antigen (PSA) and digital rectal exam (DRE) tests and prostate biopsies regularly , and treating the cancer only if it grows or causes symptoms. Surgery.
How does ultrasound help with cancer?
High-intensity focused ultrasound. This therapy directs high-energy sound waves (ultrasound) at the cancer to kill cancer cells.
Treatments include minimally invasive robotic prostate surgery
Other than skin cancer, prostate cancer is the most common cancer among men in the United States. One in nine men will be diagnosed with this cancer during his lifetime.
Get a free guide
Fill out the form to get our free guide, Considering Urologic Surgery? Call 858-346-6707 to get more information about robotic urologic surgery at Scripps.
What is the treatment for prostate cancer?
Brachytherapy is a form of internal radiation therapy. Radioactive substances are inserted into the prostate, giving off radiation over time which kills the cancer cells surrounding the prostate. The radioactive substances that are inserted into the prostate may be left in for different periods of time, depending on their radioactivity. This form of treatment is often used in conjunction with surgery or other prostate cancer treatments.
What is proton therapy?
It is similar to external-beam radiation therapy, but uses protons instead of x-rays. A proton is a positively charged particle that can destroy cancer cells when pushed into the body at very high speeds. A particle accelerator is used to push the protons towards cancer cells, damaging their DNA. Proton therapy is capable of damaging cancer cells that are deep within the body.
What is the most common type of prostate cancer?
Of the many types of prostate cancer, one is by far the most common and is diagnosed in up to 99 percent of prostatic cancer cases: prostatic adenocarcinoma. It develops in the gland cells that make prostate fluid. Prostate cancer is second only to skin cancer as the most common cancer in men in the United States.
What is radical prostatectomy?
A radical prostatectomy, which is a surgical procedure to remove the prostate, may be an option when the cancer is limited to the prostate. Some side effects of treatment may include urinary problems or erectile dysfunction. Two main subtypes of adenocarcinoma of the prostate are:
What is the name of the cancer that increases PSA levels?
The disease increases PSA levels. Prostatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDA): This cancer is a rarer but more aggressive form of adenocarcinoma. It develops in the cells lining the tubes and ducts of the prostate gland. When it occurs, it frequently develops along with acinar adenocarcinoma.
Which type of tumor doesn't produce PSA?
Neuroendocrine tumors, or carcinoids, which don’t produce PSA, appearing in the nerve and gland cells that make and release hormones into the bloodstream. Small cell carcinoma, the most aggressive type of neuroendocrine cancer in the prostate that develops in small round cells of the neuroendocrine system. Squamous cell carcinoma, ...
Is BPH cancerous?
The abnormal prostate cell growth in BPH is not cancerous and doesn’t increase your risk of getting prostate cancer. However, symptoms for BPH and prostate cancer can be similar. A condition called prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia (PIN), where prostate gland cells look abnormal when examined under a microscope, ...
Where does prostate cancer develop?
If the cancer metastasizes, making it an advanced prostate cancer, it most likely will develop in nearby tissue, lymph nodes or seminal vesicles first before traveling to the bones or to the liver, lungs, brain, more distant lymph nodes or other organs. doctor_male.
Can prostate cancer be detected by a CT scan?
Prostate cancer is often caught by a doctor performing a digital rectal exam (DRE), through a prostate-specific antigen (PSA) blood test, through a prostate biopsy or with a CT scan. Another condition, prostatitis, is the inflammation of the prostate. While not cancerous, it may cause higher PSA levels in the blood.
What is the treatment for cancer?
Radiation Therapy . Radiation therapy is a type of cancer treatment that uses high doses of radiation to kill cancer cells and shrink tumors. Learn about the types of radiation, why side effects happen, which ones you might have, and more.
How many types of cancer treatments are there?
There are many types of cancer treatment. The types of treatment that you receive will depend on the type of cancer you have and how advanced it is. Some people with cancer will have only one treatment. But most people have a combination of treatments, such as surgery with chemotherapy and/or radiation therapy.
What is targeted therapy?
Targeted therapy is a type of cancer treatment that targets the changes in cancer cells that help them grow, divide, and spread. Learn how targeted therapy works against cancer and about common side effects that may occur.
What is immunotherapy for cancer?
Immunotherapy is a type of cancer treatment that helps your immune system fight cancer. This page covers the types of immunotherapy, how it is used against cancer, and what you can expect during treatment.
What is the procedure that removes cancer from the body?
Surgery. When used to treat cancer, surgery is a procedure in which a surgeon removes cancer from your body. Learn the different ways that surgery is used against cancer and what you can expect before, during, and after surgery.
What is precision medicine?
Precision Medicine. Precision medicine helps doctors select treatments that are most likely to help patients based on a genetic understanding of their disease. Learn about the role precision medicine plays in cancer treatment, including how genetic changes in a person's cancer are identified and used to select treatments.
Treatment Overview
Active Surveillance and Watchful Waiting
Systemic Treatments
Physical, Emotional, and Social Effects of Cancer
Treatment by Stage of Prostate Cancer
- In cancer care, different types of doctors—including medical oncologists, surgeons, and radiation oncologists—often work together to create an overall treatment plan that may combine different types of treatments to treat the cancer. This is called a multidisciplinary team. Cancer care team…
Remission and The Chance of Recurrence
- If prostate cancer is in an early stage, is growing slowly, and treating the cancer would cause more problems than the disease itself, a doctor may recommend active surveillance or watchful waiting. Active surveillance. Prostate cancer treatments may seriously affect a person's quality of life. These treatments can cause side effects, such as erectile dysfunction, which is when some…
If Treatment Does Not Work
- Systemic therapy is the use of medication to destroy cancer cells. Systemic therapies are generally prescribed by a medical oncologist, a doctor who specializes in treating cancer with medication. Common ways to give systemic therapies include an intravenous (IV) tube placed into a vein using a needle or in a pill or capsule that is swallowed (orally). The types of systemic ther…