Medication
Some people with Meniere's disease may benefit from other noninvasive therapies and procedures, such as: Rehabilitation. If you have balance problems between episodes of vertigo, vestibular rehabilitation therapy might improve your balance. Hearing aid.
Procedures
Minimally Invasive Meniere’s Office Surgery. Inner ear perfusion is performed in patients in whom vertigo from Meniere’s disease is uncontrolled with standard medical therapy, and behavioral lifestyle changes. The severity of the vertigo and the frequency of the vertigo attacks are also considered.
Therapy
Balance assessment. Between episodes of vertigo, the sense of balance returns to normal for most people with Meniere's disease. But you might have some ongoing balance problems. Tests that assess function of the inner ear include: Videonystagmography (VNG). This test evaluates balance function by assessing eye movement.
Nutrition
Progress in controlling the symptoms of Ménière’s disease has been frustratingly slow. For the first few decades after Meniere identified the ear as the source of vertigo spells in 1861, his name was applied indiscriminately to a host of chronic dizziness disorders that lacked a common pathology.
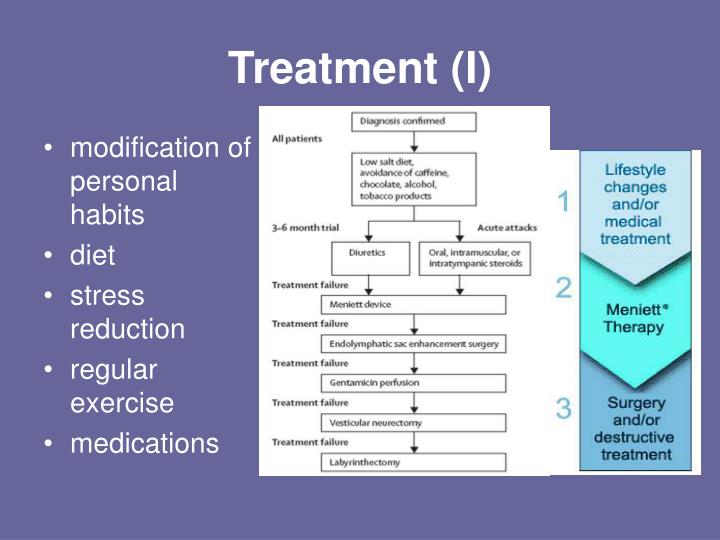
What are the treatment options for Meniere's disease?
What is minimally invasive Meniere’s office surgery?
How do you assess balance in Meniere's disease?
Is progress in Ménière’s disease being made?
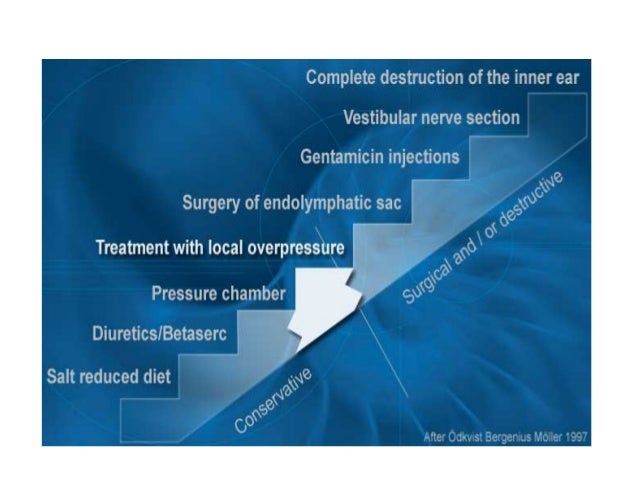
What is the most effective treatment for Meniere's disease?
Diuretics are the most commonly prescribed maintenance medications for Meniere's disease. Diuretics work by restricting the overproduction of fluid in the inner ear. Diuretics are long-term medications. They help reduce the number of vertigo attacks, and in some cases, they help stabilize hearing.
What is ear perfusion?
Summary. Transtympanic chemical perfusion of the inner ear is safe, inexpensive, and easily performed by an otologic surgeon. With inner ear perfusion, high inner ear concentrations of medication can be achieved, and systemic side effects are minimized.
Are there any new treatments for Meniere's?
The new drug to relieve the symptoms of tinnitus and sensorineural hearing loss in those with Meniere's disease is on the fast track in the new drug application process. The drug is called SPI-1005 and is a product of the Sound Pharmaceuticals company.
What is dexamethasone perfusion?
Dexamethasone perfusion of the inner ear through the round window plus intravenous dexamethasone often will stop the dizzy spells, reduce the fullness and low-frequency tinnitus, and sometimes improve the hearing in patients with Meniere's disease.
How long does it take for steroid injection in ear to work?
Oral steroids, such as prednisone, are usually prescribed over the course of 2 weeks to restore hearing. There is only a 2- to 4-week window of time for treatment before hearing loss becomes permanent.
Can the Epley maneuver help Meniere's disease?
A single session of Epley's maneuver was sufficient to eliminate positional nystagmus on the Dix-Hallpike test in 80.7% of patients diagnosed as having BPPV associated with Ménière's disease. This finding is significantly higher than the need for using two or three sessions of Epley's maneuver for similar results.
Does prednisone help Meniere's?
Conclusion: Oral prednisone helps to control refractory vertigo in Ménière's disease. These preliminary data suggest that prednisone can be a good noninvasive antivertigo management regimen for these patients.
Do antivirals help Meniere's?
The clinical response to antiviral medication indicated that vertigo due to Meniere's disease was relieved in 85–90% of patients.
Can Meniere's disease go into remission?
Meniere's disease is chronic, but treatments and lifestyle changes can help ease symptoms. Many people diagnosed with Meniere's disease will go into remission within a few years after their diagnosis.
How painful is steroid injection in ear?
The steroid medication is then gently injected into the middle ear, where it sits for a while before being absorbed into the inner ear. This is not a painful procedure, although some patients find it a little uncomfortable.
What happens after Intratympanic steroid injection?
Most patients are able to walk around unassisted after 20-30 minutes after injections. Permanent vertigo and imbalance have not been reported. Hearing loss: most physicians using intratympanic steroids feel that there is little of any risk of hearing loss (Doyle et al, 2005).
How effective are steroid injections for hearing loss?
In the American study, the results show that those who began intratympanic steroid injection treatment more than 36 days after the onset of their sudden hearing loss did not benefit significantly from the treatment. But if those persons are excluded from the results, the improvement rate increases to 39.3%.
What is the most common treatment for meniere's disease?
The severity of the vertigo and the frequency of the vertigo attacks are also considered. Of the two techniques, the Dexamethasone inner ear perfusion has become the most frequent front line treatment for uncontrolled Meniere’s disease. This involves a very strong type of cortisone drug named Dexamethasone.
How to treat Meniere's disease?
The treatments involve the injection of medication through an anesthetized ear drum. The medication then passes into the inner ear through a membrane, named the round window membrane. These techniques are generally called INNER EAR CHEMICAL PERFUSIONS. The two medications which are most frequently used in inner ear perfusions are Dexamethasone and Gentamycin.
How is the endolymphatic sac decompression performed?
The endolymphatic sac decompression operation is performed by making an incision behind the involved ear and exposing the mastoid bone. The mastoid is opened, and the facial nerve is identified in its course through the mastoid. The bone over the endolymphatic sac is then exposed and once identified, the sac is opened.
What is the surgical procedure after perfusion?
Surgical Overview. The most frequently recommended surgical procedure after inner ear perfusion is termed endolymphatic sac decompression (ELS). The risk of further hearing loss from the ELS procedure is quite low. The inner ear contains an endolymphatic sac which drains fluid from the inner ear.
What is inner ear perfusion?
These techniques are generally called INNER EAR CHEMICAL PERFUSIONS. The two medications which are most frequently used in inner ear perfusions are Dexamethasone and Gentamycin. Inner ear perfusion is performed in patients in whom vertigo from Meniere’s disease is uncontrolled with standard medical therapy, and behavioral lifestyle changes.
What is the procedure to drain the inner ear?
The surgical procedure involves opening the mastoid and decompressing and removing the bone over this sac. If the sac is identifiable, an opening is generally made in the sac and a shunt, tubing or sheet of Silastic, which is a non-reactive plastic, is placed into the pocket that is created to drain the inner ear.
Can you give dexamethasone to vertigo?
Dexamethas one injections into the inner ear are offered to patients with Meniere’s disease if initial medical therapy over a period of several months has failed to control the attacks of vertigo. Studies have demonstrated up to an 80-90% response rate to Dexamethasone perfusions.
What is the surgical treatment for meniere's disease?
Surgical treatment for Meniere’s disease is performed to prevent the symptom of vertigo. For more information regarding surgical procedures used to treat the vertigo of Meniere’s disease, please see our “Meniere’s Disease Surgery” section.
What is Meniere's disease?
The disease can incapacitate an individual by repetitive episodes of vertigo, hearing loss and tinnitus. A French physician, Prosper Meniere first described Meniere’s disease in 1861. Meniere’s disease is a disorder of the inner ear that causes attacks of vertigo, ringing (tinnitus), a hearing loss (often fluctuating), ...
What is intra gentamicin perfusion?
Intratympanic gentamicin perfusion involves the placement of medication (gentamicin) into the middle ear. Gentamicin is known to destroy the balance portion of the inner ear. This procedure is done in the physician’s office.
What are the two types of fluids in the inner ear?
Two types of fluids are present in the inner ear. These fluids are known as perilymph and endolymph. The inner ear is divided into two chambers; one chamber is filled with endolymph and another with perilymph. The chamber of perilymph surrounds the chamber of endolymph. In Meniere’s disease, it is believed that there is excess endolymph fluid.
What is the term for the physiologic changes of Meniere's disease?
Therefore, another term for physiologic changes of Meniere’s disease is endolymphatic hydrops (i.e. excess endolymph). A Meniere’s attack can produce incapacitating vertigo with violent spinning, nausea and vomiting.
How long does a Meniere's attack last?
The attack may last a few minutes to several hours.
Where is the steroid solution placed in the middle ear?
After the ear drum is anesthetized, the steroid solution is placed into the middle ear through a small opening made in the ear drum.
What is the best treatment for Meniere's disease?
If this is so, then the potent anti-inflammatory steroids are the ideal first treatment for Meniere's disease and other immune-mediated diseases of the inner ear, and streptomycin perfusion is the ideal second treatment for those who do not respond to dexamethasone perfusion.
What is the cause of meniere's disease?
There is ample clinical and animal evidence that, in most patients, Meniere's disease is an immune-mediated disorder in a small, misplaced, malfunctioning endolymphatic sac that causes endolymphatic hydrops, the essential pathology of this disease. If this is so, then the potent anti-inflammatory steroids are the ideal first treatment ...
When was Ménière's disease first described?
Confusion in the nomenclature of Ménière’s disease and lack of a standard definition of the disorder until 1995 has hampered accurate assessment of treatment efficacy since the presently defined disorder was first described in 1938. The lack of a widely accepted mechanism of the disease has also delayed the development of rational treatments.
What is the best treatment for migraines?
Calcium channel blockers such as verapamil, and in Europe, flunarizine, are effective in migraineurs.20The carbonic anhydrase inhibitors have some diuretic effects and so may impact hydrops directly in addition to treating migraine.
What is the best medication for vertigo?
Benzodiazepines, meclizine, other antihistamines such as promethazine or diphenhydramine, and transdermal scopolamine patches have all been used to control the sensation of vertigo during acute attacks. These medications have no effect on the progression of the disorder.
Can steroids help with migraines?
Therapeutic rationale . Steroids are not useful in migraine and there is no plausible mechanism for alteration of hydropic distention by steroids.

Treatment
Mechanism of action
Cause
Prognosis
Specialist to consult
Pathophysiology
- Your doctor will conduct an exam and take a medical history. A diagnosis of Meniere's disease requires: 1. Two episodes of vertigo, each lasting 20 minutes or longer but not longer than 12 hours 2. Hearing loss verified by a hearing test 3. Tinnitus or a feeling of fullness in your ear 4. E…
Risks
Mechanism