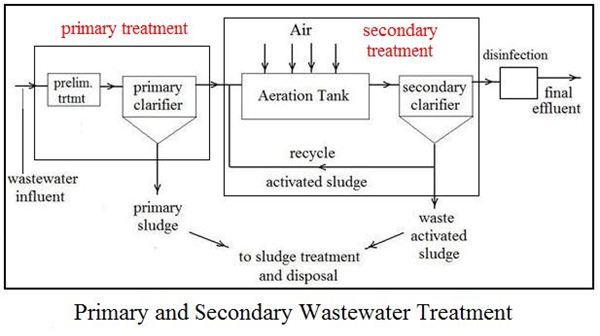
Types of Biological Wastewater Treatment Methods
- Aerobic Treatment Process:. Aerobic treatment may follow some form of pretreatment such as oil removal, involves...
- Anaerobic (Without Oxygen) and Anoxic (Oxygen Deficient) Treatment Process:. Anaerobic (without oxygen) and anoxic...
- Micro-Organisms Involved in Aerobic Digestion Process:. Different types of...
How can we treat waste water with biological methods?
Apr 20, 2021 · What Type of Biology is Wastewater Treatment? Biological wastewater treatments are usually divided into two categories: anaerobic and aerobic processes. Anaerobic describes biological processes where oxygen is absent , and aerobic …
What is the biological treatment for waste water?
8 rows · Biological wastewater treatment method, also known as the conventional method, is a common and ...
What are the biggest problems in wastewater treatment?
Feb 21, 2017 · The Biology of Wastewater Treatment. Rural Research and Science. Feb 21, 2017. By Jamie Welch, Worcester Prep, Berlin, Maryland The upgrades currently taking place at the Berlin Wastewater Treatment Plant are comprehensive, and will allow the plant to fully process all the wastewater that goes through the system down to near drinking water quality. The …
What is wastewater, and how is it treated?
Jun 03, 2020 · The biological wastewater treatment system is a technology used to cleanse water. These technologies uses protozoa, bacteria, and other specific microbes to purify wastewater. Wastewater basically holds organic substances, such as wastes, garbage, and partly digested foods. Moreover, it also contains, in many instances, heavy metals, toxins, and …

What is biological method of wastewater treatment?
Is sewage treatment a biological process?
Is water treatment biotechnology?
What are the types of biological treatment?
What is sewage biology?
What enzymes are used in wastewater treatment?
What is sewage treatment?
What is water treatment system?
How biotechnology helps in waste treatment?
What is microbial wastewater treatment?
What is biological waste treatment?
Biological waste treatment processes the process by which any waste treated biologically includes micro-organism for final discharge within the permissible limit specified by World Health Organisation (WHO).
What is the process of digestion of waste?
Aerobic Digestion/Treatment Process: Aerobic digestion of waste is the natural biological degradation and purification process in which bacteria in presence of oxygen, breaks down and digested the waste.
What is aerobic treatment?
Aerobic treatment may follow some form of pretreatment such as oil removal, involves contacting wastewater with microbes and oxygen in a reactor to optimise the growth and efficiency of the biomass.
Is anoxic treatment similar to aerobic treatment?
Anaerobic (without oxygen) and anoxic (oxygen deficient) treatments are similar to aerobic treatment, but use of micro-organism that do not require the addition of oxygen these micro-organisms use the compounds other than oxygen to catalyse the oxidation of biodegradable organics and other contaminants.
How is a bioreactor accomplished?
Bioreactor is accomplished in one of two general ways: i. Fixed Film Process: In fixed film process micro-organisms are held on a surface of film, the fixed film, which may be mobile or stationary with wastewater flowing past the surface of film media.
What is aerobic digestion?
Aerobic digestion of waste is the natural biological degradation and purification process in which bacteria in presence of oxygen, breaks down and digested the waste. During oxidation process, pollutants are broken down in the CO 2, H 2 O, nitrates, sulphates and biomass (micro-organisms).
Which microorganisms are used to produce protease enzymes?
Micro-organisms like Bacteroides, Butyrivibrio, Clostridium, Fusobacterium, Selenomonas, and Streptococcus may be used for availability of protease enzyme. The amino acids produced during these steps are then degraded to fatty acids such as acetate, propionate, and butyrate.
What is biological wastewater treatment?
In biological wastewater treatment organic material is oxidized by microbial communities maintained in either a suspended growth or an attached growth reactor. Both types of reactors make use of mixed cultures, that is, cultures including a number of microbial species. Such systems are self-optimizing in that the most competitive organisms for a particular set of environmental conditions dominate the culture. If the environmental conditions change (e.g., if temperature rises or falls) the population make-up will shift in species dominance. Bacteria are the dominant group of microorganisms involved in biological wastewater treatment. Higher organisms, such as protozoa, fungi, and invertebrates are present as components of the community but have mostly indirect impacts on the process performance.
What is the most appropriate test for measuring wastewater organic content?
By considering the bioenergetics of heterotrophic organisms, the most important group in biological wastewater treatment, it is demonstrated that the chemical oxygen demand (COD) test is the most appropriate and convenient for measuring wastewater organic content (strength). The COD measures the electron donating capacity of the organics and this is not only closely linked to the energy content of the wastewater, but also is intimately associated with the reduction - oxidation (redox) reactions whereby organisms degrade organics and grow. This association establishes two important principles in biological wastewater treatment system modelling:
What is the process of nitrification?
Nitrification normally occurs during biological wastewater treatment and is part of the inorganic nutrient removal chain. Ammonia is converted to nitrate during aerobic nitrification and subsequent anoxic denitrification removes the nitrate by producing N2 gas. The first step in nitrification converts ammonia into nitrite (nitritation) by two sequential oxidation steps [5]. First, ammonia (NH 3) is oxidized to hydroxylamine (NH 2 OH) by the membrane-bound enzyme ammonia monooxygenase (AMO), and conversion of NH 2 OH to nitrite is catalyzed by the periplasmic enzyme hydroxylamine oxidoreductase (HOA). The bacteria responsible for the nitritation belong to the genera Nitrosomonas, Nitrosospira (β-Proteobacteria), and Nitrosococcus, (γ-Proteobacteria) [35]. The detection of a unique archaeal amoA gene and the presence of archaeal amoA in various ecosystems showed the involvement of Archaea in nitritation. The next step in the nitrification from nitrite to nitrate is catalyzed by the enzyme nitrite oxidoreductase (NOR) delivered by the genera Nitrobacter (α-Proteobacteria), Nitrospina (δ-Proteobacteria), and Nitrospira (phylum Nitrospirae) [35]. Nitrosomonas and Nitrospira are the dominant nitrifiers in wastewater treatment plants, and Archaea were found as the predominant causal organisms in low-nutrient, low-pH, and sulfide environments [16].
How many pages are there in the first edition of Wastewater Treatment?
The first edition has been expanded from 860 to 1420 pages covering all aspects of the biological processes and organisms associated with secondary treatment unit processes. Each process step is covered in detail giving a unique insight into the biological aspects of wastewater treatment.
What is anaerobic digestion?
Anaerobic digestion (AD) is a biological-based technology that generates methane-enriched biogas. A microbial electrolysis cell (MEC) uses electricity to initiate bacterial oxidization of organic matter to produce hydrogen. This study determined the effect of energy production and waste treatment when using dairy manure in a combined AD and MEC (AD-MEC) system compared to AD without MEC (AD-only). In the AD-MEC system, a single chamber MEC (150 mL) was placed inside a 10 L digester on day 20 of the digestion process and run for 272 h (11 days) to determine residual treatment and energy capacity with an MEC included. Cumulative H2 and CH4 production in the AD-MEC (2.43 L H2 and 23.6 L CH4) was higher than AD-only (0.00 L H2 and 10.9 L CH4). Hydrogen concentration during the first 24 h of MEC introduction constituted 20% of the produced biogas, after which time the H2 decreased as the CH4 concentration increased from 50% to 63%. The efficiency of electrical energy recovery (ηE) in the MEC was 73% (ηE min.) to 324% (ηE max.), with an average increase of 170% in total energy compared to AD-only. Chemical oxygen demand (COD) removal was higher in the AD-MEC (7.09 kJ/g COD removed) system compared to AD-only (6.19 kJ/g COD removed). This study showed that adding an MEC during the digestion process could increase overall energy production and organic removal from dairy manure.
What are the different methods of wastewater treatment?
There are different wastewater treatment methods. These are primarily categorised as biological, chemical and physical methods. In a bid to treat water in natural ways and with minimal use of chemicals, biological methods use microorganisms to break down the organic wastes in water into stable inorganic compounds.
Why is wastewater treatment important?
Wastewater treatment is therefore vital to ensure liquid waste does not harm the water bodies it is released into or the groundwater it leaches into , notes industry expert Waterform. There are different wastewater treatment methods. These are primarily categorised as biological, chemical and physical methods. ...
What is aerobic wastewater treatment?
This is the most commonly used aerobic wastewater treatment option. As the name suggests, it uses a liquid that closely resembles sludge. It involves the degradation of organic waste and the removal of nutrients from the wastewater using highly concentrated microorganisms.
How does oxygen help in wastewater treatment?
The oxygen promotes the oxidation of wastewater and encourages the development and growth of algae and bacteria used for the water treatment. This method takes a long time and involves more than one process.
Can industrial wastewater be treated with aerobic methods?
However, industrial wastewater containing carbon molecules can also be treated using biological aerobic methods. The choice of treatment method depends on factors such as objectives, location and available resources . Share this post on these platforms.
Is water a renewable resource?
Water, being a renewable yet increasingly scarce resource, has been the focus of many innovations in the world of recycling, sustainability and conservation efforts. There are different forms of waste from both residential and industrial applications. Liquid waste make up the biggest percentage of this.
What is aerobic treatment?
The aerobic treatment system is a type of biological treatment that uses oxygen to remove at least 98% of the organic contaminants in your wastewater. It is fast, energy-efficient and produces cleaner water compared to anaerobic treatment. Since there are many other ways to use oxygen to treat wastewater, under this subtype are even more subtypes ...
