
Full Answer
How was homosexuality treated in the 1950s?
Other forms of treatment were electroconvulsive therapy, discussion of the evils of homosexuality, desensitisation of an assumed phobia of the opposite sex, hypnosis, psychodrama, and abreaction. Dating skills were sometimes taught, and occasionally men were encouraged to find a prostitute or female friend with whom to try sexual intercourse.
When did the DSM remove homosexuality from the DSM?
In 1973, the APA removed homosexuality from the DSM, its influential manual of psychiatric disorders, and medical professionals began to distance themselves from techniques they had once embraced. That wasn’t the end of attempts to turn gay people straight.
Was the medicalisation of homosexuality an error?
The medicalisation of homosexuality itself seems to have been the fundamental error, rather than what type of treatment arose as a consequence. Conclusions Homosexuality was removed from ICD-10 (international classification of diseases, 10th revision) only in 1992.
When did doctors start to recognize homosexuality?
In the late 19th century, psychiatrists and doctors began to address homosexuality, too. They labeled same-sex desire in medical terms—and started looking for ways to reverse it. German doctor Eugen Steinach. (Credit: Imagno/Getty Images)
When was homosexuality decriminalised?
Homosexuality had only been de-criminalised in 1967, and mainstream society was still deeply disapproving of it in the 1970s.
What was the idea behind the treatment of homosexuality?
The idea of the treatment was to associate homosexual desire with pain and unpleasant feelings. After Chris had finished all of the sessions, the researchers encouraged him to start romantic relationships with women.
How long did Gareth go to conversion therapy?
Gareth went to gay conversion therapy for four years and says it made him 'feel broken'. "You cannot cure being LGBT, you cannot erase us from society. Major UK health organisations like the NHS, psychotherapy and counselling bodies have rightly condemned these practices.".
Why is conversion therapy banned?
In 2018, the UK government announced that "gay conversion therapies" were to be banned, as part of a plan to improve the lives of gay and transgender people. Campaigners are still waiting for action, even after the Prime Minister promised it again this summer.
Did the University of Birmingham deny Chris' electric shock therapy?
Correspondence seen by the BBC shows that the University of Birmingham did initially deny that Chris ' electric shock therapy ever took place.
Was the University of Birmingham a sanctioned research project?
The University of Birmingham spokesman said: "While we are unable to find any evidence that this was a university sanctioned research project, we are aware that during the late 1960s and 1970s there may have been some isolated activity of this nature.
Did Chris go through conversion therapy?
Gay 'conversion therapy': Man given electric shocks demands apology. A gay man who went through months of electric shock "therapy" in a university psychology department 50 years ago has demanded an apology. Chris - not his real name - went to his GP for advice in the 1970s, when he became aware of his sexuality in his mid-20s.
When was electrocution invented?
ECT was invented in fascist Italy in 1937 by psychiatrist Ugo Cerletti. Darius Rejali, author of Torture and Modernity, wrote of Cerletti "having killed a few dogs by experimentation" and then "discovered that Roman slaughterhouses used electrocution to slaughter pigs." Cerletti "discovered that pigs could be shocked several times and would revive after a few minutes." He then applied ECT to humans, his first victim screaming that it was "deadly." "The torture and 'treatments' of the insane" historically has derived from the "application to animals in abattoirs," Rejali stated. [9]
How much did Alison Steel get for her mother's experiment?
In 2017, 60 years after Cameron's experiments left her mother damaged for life, Alison Steel obtained a $100,000 settlement from the Canadian government over Cameron's experiments. "She was never able to really function as a healthy human being because of what they did to her," Steel stated. "Her emotions were stripped. It took away her soul." [14]
Is electroshock banned in Texas?
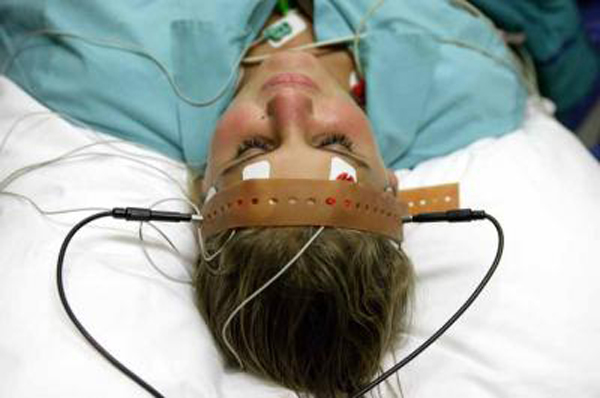
2, 2018 /PRNewswire/ -- The mental health watchdog Citizens Commission on Human Rights (CCHR) International announced that a ban of electroshock treatment — the practice of up to 460 volts of electricity to the brain to "treat mental disorder" — should be imminent in light of increasing reports of patients being damaged and deaths. Texas, the only state to record deaths within 14 days of electroshock being administered, reported a death rate in recent years that represents an estimated 300 deaths nationally each year. The most frequent causes of death have been cardiac events and suicide, according to one study. [1] Electroshock's brutal and sordid history ranges from its use to help slaughter pigs, to punishment, painful "aversion therapy" on homosexuals, inflicting brain damage on children and others, and to torture humans.
When was electrical aversion therapy abandoned?
Dr Tommy Dickinson said that use of electrical aversion therapy had been almost totally abandoned by the mid-1970s in the UK. "When I was about 15, I realised I am one of these people who are homosexuals and who are reviled really by the society I grew up in, so it was a big shock to me. "I felt totally alone.".
What was the aim of electrical aversion therapy?
The aim of electrical aversion therapy was for him to associate homosexual desire with pain or unpleasant feelings.
Who decided to call a halt to the treatment he was undergoing at Queen's?
In the end, it was John who decided to call a halt to the treatment he was undergoing at Queen's.
Where did John aversion therapy take place?
John, not his real name, underwent electrical aversion therapy at Queen's University Belfast (QUB) while a student in the 1960s. He was shown pictures of naked men and given electric shocks if he was aroused. A spokesperson for QUB has expressed regret for the use of aversion therapy. John had grown up in the 1950s in a rural Northern Ireland town.
When did gay rights start to turn back?
But in the 1960s and 1970s, as a vocal gay rights movement took to the streets to demand equality, the profession began to turn its back on the concept that people could be “converted” to heterosexuality.
When did psychiatrists start labeling gay men as gay?
In the late 19th century, psychiatrists and doctors began to label same-sex desire in medical terms—and looking for ways to reverse it. In 1899, a German psychiatrist electrified the audience at a conference on hypnosis with a bold claim: He had turned a gay man straight. All it took was 45 hypnosis sessions and a few trips to a brothel, ...
How many hypnosis sessions did Albert von Schrenck-Notzing have?
All it took was 45 hypnosis sessions and a few trips to a brothel, Albert von Schrenck-Notzing bragged. Through hypnosis, he claimed, he had manipulated the man’s sexual impulses, diverting them from his interest in men to a lasting desire for women. He didn’t know it, but he had just kicked off a phenomenon that would later be known as “conversion ...
When did Exodus International close?
And Exodus International, an umbrella group that connected various conversion therapy groups and gay ministry organizations, closed down in 2013 after nearly 40 years of operations after its president, Alan Chambers, decided it’s impossible to change someone’s sexual orientation.
Is homosexuality a sin?
Homosexuality, especially same-sex relationships between men, was considered deviant, sinful and even criminal for centuries. In the late 19th century, psychiatrists and doctors began to address homosexuality, too. They labeled same-sex desire in medical terms—and started looking for ways to reverse it. pinterest-pin-it.
Who was the first person to use brain stimulation?
Robert Galbraith Heath, a psychiatrist in New Orleans who pioneered the technique, used this form of brain stimulation, along with hired prostitutes and heterosexual pornography, to “change” the sexual orientation of gay men.
Was homosexuality a psychological disorder?
Others theorized that homosexuality was a psychological disorder instead. Sigmund Freud hypothesized that humans are born innately bisexual and that homosexual people become gay because of their conditioning. But though Freud emphasized that homosexuality wasn’t a disease, per se, some of his colleagues didn’t agree.
What is electro shock therapy?
Electroshock therapy, also known as electroconvulsive therapy (ECT), is a treatment for severe major depression, bipolar depression, and other mental health conditions. Psychiatrists may recommend ECT when a person does not respond well to other treatments. ECT uses electric currents to stimulate a person’s brain to induce a controlled seizure.
Why is ECT negative?
The negative perceptions of ECT originate from previous misuse and the historical lack of consistent administration of general anesthetics or muscle relaxants. Furthermore, when healthcare professionals first introduced ECT, many people did not consent to the therapy.
How does ECT work?
ECT uses electric currents to stimulate a person’s brain to induce a controlled seizure. Researchers do not exactly know how ECT works, but one theory is that it could regulate neurotransmitter activity. This article looks at how ECT works, whether it is an effective treatment, and its controversial history. It also discusses some alternative ...
What is ECT therapy?
ECT can be an effective therapy for treatment-resistant mental health conditions, including depression , schizophrenia, and catatonia.
How to treat ECT?
When a person receives ECT treatment, a doctor will first administer general anesthesia and a muscle relaxant. The doctor will then wait for the anesthesia to take effect before they begin the electrical stimulation. They will also place a bite block in the person’s mouth to stop them from biting their tongue.
Why do doctors recommend ECT?
However, doctors recommend ECT for some people because it is low risk and carries few side effects. Researchers are still not sure how ECT works, but they understand that it has many effects on the brain, including increasing blood flow and triggering the release of neurotransmitters and hormones.
Is ECT a negative treatment?
The media has tended to portray ECT in a negative light — for example, in the film version of “One Flew over the Cuckoo’s Nest.” However, attitudes toward ECT are changing, and people are beginning to view it as an effective treatment for those with mental health conditions that are resistant to medication and therapy.
What was the treatment of homosexuals in the 1940s?
In the 1940s, homosexuals were also involuntarily committed to psychiatric facilities by their families, with the hospitals promising that the patient would eventually leave the facility cured of their "sexual illness." Not only were they not allowed to leave, but they were often subjected to cruel and inhumane treatments, including castrations, torture drugs, shock therapy, and lobotomies.
When did ex-gay ministries start?
In the early 1970s, ex-gay ministries began to emerge. In 1973, the first contemporary ex-gay ministry, Love in Action, was started in Northern California. In 1976, the first national conference of “ex-gay” ministries was held, resulting in the formation of Exodus International.
Do male slides give shock?
In reinforcing heterosexual preference in latent male homosexuals, male slides give a shock while the stimulus relief slides of females do not give shock. The patient is given a “slide change” hand button which enables him to escape or avoid a shock by rejecting a shock cue scene. Advertisement.
Which European country banned conversion therapy?
Albania. In May 2020, Albania became the third European country (after Malta (2016) and Germany (2020)) to ban conversion therapy or any pseudo-therapeutic attempts to change a person's sexual orientation or gender identity.
What is the National Association for Research and Therapy of Homosexuality?
The National Association for Research & Therapy of Homosexuality (NARTH) was the main organization advocating for conversion therapy. Fundamentalist Christian groups, and some other organizations, have used religious justification for the therapy.
Why do mental health organizations not ban conversion therapy?
Haldeman argues that, due to concern for people whose "spiritual or religious concerns" may assume priority over their sexual orientation, mental health organizations do not ban conversion therapy outright.
What is an ex gay ministry?
Main article: Ex-gay. Some sources describe ex-gay ministries as a form of conversion therapy , while others state that ex-gay organizations and conversion therapy are distinct methods of attempting to convert gay people to heterosexuality. Ex-gay ministries have also been called transformational ministries.
How many people failed to change their sexual orientation?
Ariel Shidlo and Michael Schroeder found in "Changing Sexual Orientation: A Consumer's Report", a peer-reviewed study of 202 respondents published in 2002, that 88% of participants failed to achieve a sustained change in their sexual behavior and 3% reported changing their orientation to heterosexual. The remainder reported either losing all sexual drive or attempting to remain celibate, with no change in attraction. Some of the participants who failed felt a sense of shame and had gone through conversion therapy programs for many years. Others who failed believed that therapy was worthwhile and valuable. Many respondents felt harmed by the attempt to change, and reported depression, suicidal ideation and attempts, hypervigilance of gender-deviant mannerisms, social isolation, fear of being a child abuser and poor self-esteem. Of the 8 respondents (out of a sample of 202) who reported a change in sexual orientation, 7 worked as ex-gay counselors or group leaders.
When did the Royal Assent to the Health Complaints Act come into effect?
Royal assent was granted on 5 May 2016. The law, known as the Health Complaints Act 2016, went into effect on 1 February 2017. On 17 May 2018, Health Complaints Commissioner opened an inquiry into conversion therapy, which concluded on 1 February 2019 and which recommended a full ban and support for survivors.
When did Freud's conversion therapy get approved?
During the three decades between Freud's death in 1939 and the Stonewall riots in 1969, conversion therapy received approval from most of the psychiatric establishment in the United States. In 1962, Irving Bieber et al. published Homosexuality: A Psychoanalytic Study of Male Homosexuals, in which they concluded that "although this change may be more easily accomplished by some than by others, in our judgment a heterosexual shift is a possibility for all homosexuals who are strongly motivated to change".
