Doctors often recommend:
- breath conditioning techniques, such as pursed-lip breathing, slow, deep breathing, or diaphragmatic breathing
- upper and lower limb strengthening and conditioning exercises
- respiratory muscle strengthening exercises
- level walking
- relaxation or visualized meditation
- eating a balanced, nutritious diet
- quitting smoking
Full Answer
What are the treatment options for restrictive lung disease?
Treatment plans depend on the cause or the type of restrictive lung disease. In some cases, delivering oxygen to a person using oxygen therapy may be necessary to help them breathe properly. In severe cases, lung transplant surgery, corrective surgery, or stem cell therapy may be options.
How can I protect my lungs as I age?
A decrease in lung function is a normal part of the aging process but there are steps you can take to stay as healthy as possible. Staying active, avoiding tobacco smoke and stay up to date on vaccinations are just a few ways you can protect and even strengthen your lungs.
What are the treatments for emphysema and COPD?
These typically are used for acute flare-ups of COPD triggered by respiratory infections. Oxygen therapy increases life expectancy in people with emphysema who have below-normal levels of oxygen in the blood.
Can lung damage from emphysema be reversed?
Regardless of the cause, lung damage in emphysema cannot be reversed. Even with treatment, the damage often continues. However, stopping smoking is your best chance of not having the disease get progressively worse. If you smoke, stop. If you don't smoke, don't start. By quitting smoking you can either prevent emphysema or slow its progression.

How can I increase elasticity in my lungs?
Deep breathing exercises may help increase lung capacity. For instance, the British Lung Foundation say that deep breathing can help clear mucus from the lungs after pneumonia, allowing more air to circulate. To perform this exercise: Breathe deeply 5–10 times, then cough strongly a couple of times, and repeat.
Can damaged elastin be repaired?
Genetic Conditions With Elastin Defects To date, there are no specific treatments for cutis laxa; thus, a better understanding of the disruption of, and approaches to repairing, elastic fiber networks could potentially assist patients with this disease.
What disease makes the lungs less elastic?
COPD includes two main types: Emphysema affects the air sacs in your lungs, as well as the walls between them. They become damaged and are less elastic.
What is the treatment for restrictive lung disease?
The main treatment for restrictive lung disease is supportive oxygen therapy. Oxygen therapy helps people with lung diseases get enough oxygen, even when their lungs cannot fully expand. Some people may need oxygen only at night or after exerting themselves. Others need oxygen all or most of the time.
Can you regain elasticity in your lungs?
However, no single COPD intervention except for lung transplantation has proven effective in recovering lung function. Lung elasticity is reduced in COPD lungs, which is for a large part due to chronically enhanced elastin degradation.
How can I increase elastin protein?
But you can help your body produce elastin naturally by eating a well-balanced diet that includes greens, citrus fruits, fish, berries and nuts. You can also help maintain elastin in your body by exercising, establishing a proper skin care routine, quitting smoking and wearing sunscreen every day.
What happens when lungs lose elasticity?
Muscles like the diaphragm can get weaker. Lung tissue that helps keep your airways open can lose elasticity, which means your airways can get a little smaller. Also your rib cage bones can change and get smaller which leaves less room for your lungs to expand.
What is the life expectancy of someone with restrictive lung disease?
This damaged lung tissue becomes stiff and thick, making it difficult for your lungs to work efficiently. The resulting difficulty in breathing leads to lower levels of oxygen in the bloodstream. In general, the life expectancy with IPF is about three years.
Can restrictive lung disease be cured?
For most of these conditions, there is no cure, but a person can manage the symptoms with medication and physical therapy. It is crucial for a doctor to identify the root cause of any lung-related symptoms. In this article, we describe the types of restrictive lung disease and their symptoms.
What causes your lungs to not fully expand?
Lung damage or scarring can cause the lungs to shrink or become unable to expand fully. Conditions, such as tuberculosis, fibrosis, and other chronic destructive lung conditions, often lead to lung damage.
Can a person live with damaged lungs?
The lungs are key organs in the human body, responsible for bringing oxygen into the body and helping get rid of waste gases with every exhale. Though having both lungs is ideal, it is possible to live and function without one lung. Having one lung will still allow a person to live a relatively normal life.
Will an inhaler help with pulmonary fibrosis?
Budesonide, an Inhaled corticosteroid (ICS) is most commonly used in the treatment of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Second most commonly used drug to prevent fibrosis is colchicine [2].
Is it possible to restore skin elasticity?
There's no way to completely reverse the signs of aging. It's much easier to protect your skin while it's healthy than to attempt to repair it later in life. Boosting collagen naturally improves not only our appearance, but the rest of our health.
How do you restore collagen and elastin?
Foods high in vitamin C include: Vitamin C plays a vital role in the production of collagen in your body. It helps to regulate the balance between collagen and elastin in the skin which is what gives you firm but supple skin and beautiful skin, so it's important to include in your diet as well.
Can thin skin be thickened?
#2: Can Thin Skin Be Thickened? The short answer: yes, skin can be thickened. While you can't entirely reverse the process of skin thinning, there are ways to increase collagen, repair elastin, and improve your skin's overall appearance.
Why has my skin suddenly lost elasticity?
This loss of elasticity is also accelerated by decreased production of natural oils and oxidative stress from sun exposure, smoking, pollution, lack of sleep and poor nutrition (including excessive sugar consumption). Gravity has an impact too.
What causes extrinsic restrictive lung disease?
Extrinsic restrictive lung disease is caused by complications with tissues or structures outside of the lungs, including neurological conditions. External factors that cause an extrinsic restrictive lung disease are often associated with weakened muscles, damaged nerves, or the stiffening of the chest wall tissues.
What is restrictive lung disease?
Treatment. Restrictive lung diseases are chronic lung conditions that limit the ability of a person’s lungs to expand during inhalation. Most cases of restrictive lung diseases are not curable, but they are often manageable with medication and exercise regimes.
What is mixed lung disease?
Mixed lung disease most commonly occurs in people with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), who also have congestive heart failure. In cases of obstructive lung diseases, such as asthma, bronchiectasis, COPD, and emphysema, the lungs are unable to expel air properly during exhalation. Restrictive lung diseases, on the other hand, mean ...
What is the third category of lung disease?
These categories are either obstructive or restrictive. A third category, called mixed lung disease , is smaller and has characteristics of both obstructive and restrictive lung diseases.
How to reduce restrictive disease symptoms?
Doing at-home exercises and making some lifestyle changes have been shown to reduce the severity of restrictive disease symptoms. Commonly recommended methods include: breath conditioning, often pursed lip breathing, slow-deep breathing, or diaphragmatic breathing.
What is the term for the buildup of fluid between the tissue layers surrounding the lungs?
pleural effusions, or the buildup of excessive fluid between tissue layers surrounding the lungs. scoliosis, or twisting of the spine. neuromuscular disease or conditions, such as Lou Gehrig’s disease ( ALS ), multiple sclerosis, and muscular dystrophy. obesity.
Is total lung capacity decreased in restrictive lung disease?
The total lung capacity is usually decreased in restrictive lung disease. Other tests may be necessary for a full diagnosis and to ensure the correct treatment plan is arranged. The specific tests used are usually determined by whether the suspected cause of the restrictive lung disease is intrinsic or extrinsic.
What is the role of elastic recoil in the lung?
Elastic recoil refers to the lung's intrinsic tendency to deflate following inflation . A dense labyrinth of elastic fibers and other matrix elements within the lung parenchyma, along with surface tension at the alveolar air-liquid interface, confers this important mechanical property. Elastic recoil maintains the patency ...
What are the principles of lung recoil?
This example illustrates two of the principles that underlie measurement of lung recoil: (1) the pressure required to expand a lung to any volume is equal to the recoil pressure at that volume, and (2) under conditions of no flow, with the glottis open, Palv and Pmouth are identical.
What is elastic recoil?
Elastic recoil maintains the patency of small airways through radial alveolar attachments, similar to the way a tent is held up by its guy ropes, and provides a portion of the driving pressure during expiration.
Why is COPD resistance increased?
The increased resistance in COPD is due primarily to changes in the small airways of less than 2 mm diameter. Compared with normal lungs, peripheral airflow resistance of COPD is larger by an order of magnitude or more. In contrast, airflow resistance in the central airways of lungs from COPD patients differs little from that of normal lungs. ...
Does BMS reduce vessel closure?
By reducing elastic recoil and vascular remodeling, and by compressing the plaque and scaffolding the vessel lumen, BMS has resulted in a significant reduction in acute vessel closure and restenosis. ISR secondary to neointimal hyperplasia remains a significant problem with BMS, however, with 20–30% angiographic and 10–15% clinical restenosis. 14,15
Does oxygen consumption decrease with age?
Oxygen consumption in respiratory muscles, as in all striated muscle, decreases linearly with age , making older muscle more vulnerable to the effects of fatigue in situations of high physical demand, especially in the presence of lung disease or injury. 64. View chapter Purchase book. Read full chapter.
Is elastic recoil a defect?
In general, elastic recoil is increased in a restrictive ventilatory defect associated with decreased lung volumes. Conversely, in almost all forms of airflow obstruction, elastic recoil is decreased. Testing for elastic recoil is time-consuming, difficult to perform, expensive, and invasive.
What is the loss of skin elasticity?
Loss of skin elasticity is a novel observation that may link the common pathological processes that drive tissue elastolysis in the extracellular matrix of the skin and lung in emphysema-susceptible individuals.
What is the elastin breakdown?
Elastin breakdown and the resultant loss of lung elastic recoil is a hallmark of pulmonary emphysema in susceptible individuals as a consequence of tobacco smoke exposure. Systemic alterations to the synthesis and degradation of elastin may be important to our understanding of disease phenotypes in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
Does pulmonary emphysema cause skin aging?
Skin aging is accelerated in individuals with pulmonary emphysema. Loss of skin elasticity occurs as a natural consequence of aging and features of increased skin aging have been shown in patients with COPD [ 13, 28 ].
Does skin elasticity decrease with age?
Skin elasticity, a key biomechanical property of skin, decreases significantly with age, is quantifiable, and changes in disease states caused by genetic disruption of elastic fibers, such as cutis laxa [ 20 ].
Is skin elasticity associated with pulmonary emphysema?
This is the first study to associate the biomechanical properties of skin with the severity of airflow obstruction and pulmonary emphysema. Skin elasticity is strongly and independently associated with airflow obstruction, diffusion impairment, gas trapping, and pulmonary emphysema. Moreover, skin aging appears substantially increased in emphysema-susceptible individuals and loss of skin elasticity is associated with elevated blood biomarkers of inflammation and metalloproteinase activity. The findings of our study support the paradigm of complex systemic biological factors in the pathogenesis of COPD and emphysema in those susceptible to the effects of tobacco smoke. Further research into the mechanistic commonality that underlies destruction and remodeling of the ECM, with resultant loss of pulmonary and cutaneous elasticity, may help elucidate common pathological processes and lead to future developments in the field of emphysema and COPD research.
Why do my airways get smaller?
Muscles like the diaphragm can get weaker. Lung tissue that helps keep your airways open can lose elasticity, which means your airways can get a little smaller. Also your rib cage bones can change and get smaller which leaves less room for your lungs to expand.
What is the maximum amount of air you can forcibly exhale from your lungs after fully inhaling
Forced vital capacity: the maximum amount of air you can forcibly exhale from your lungs after fully inhaling. It is about 80 percent of total capacity, or 4.8 liters, because some air remains in your lungs after you exhale.
What is spirometry used for?
Spirometry is a diagnostic test that provides different measures of lung capacity. Often used to diagnose chronic obstructive pulmonary disorder ( COPD) or asthma, spirometry results are also used to see if your breathing has improved after treatment for a lung condition. Some examples of spirometry measurements are:
What are some examples of spirometry?
Some examples of spirometry measurements are: 1 Forced vital capacity: the maximum amount of air you can forcibly exhale from your lungs after fully inhaling. It is about 80 percent of total capacity, or 4.8 liters, because some air remains in your lungs after you exhale. Forced vital capacity can decrease by about 0.2 liters per decade, even for healthy people who have never smoked. 2 Forced expiratory volume (FEV1): the amount of air you can exhale with force in 1 second. FEV1 declines 1 to 2 percent per year after about the age of 25, which may not sound like much but adds up over the course of a lifetime.
When do lungs mature?
Your lungs mature by the time you are about 20-25 years old. After about the age of 35, it is normal for your lung function to decline gradually as you age. This can make breathing slightly more difficult as you get older.
Is it normal to have a decrease in lung function?
A decrease in lung function is a normal part of the aging process but there are steps you can take to stay as healthy as possible. Staying active, avoiding tobacco smoke and stay up to date on vaccinations are just a few ways you can protect and even strengthen your lungs.
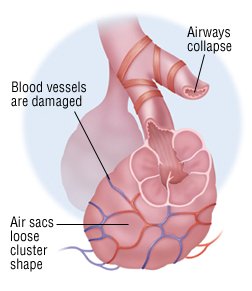
What Is Emphysema?
Symptoms
- During the early stages of emphysema, most people will have few symptoms. The disease usually progresses slowly. Changes in breathing may be hardly noticed. A typical person will not experience symptoms until they have smoked a pack of cigarettes per day for more than 20 years. However, over time, almost all people with emphysema will develop shortness of breath. At first…
Diagnosis
- Your doctor will ask for details about your smoking. He or she will ask how long you've smoked, and how many cigarettes per day. Other questions may include: 1. Do you breathe passive (secondhand) smoke at work or at home? 2. Do you live or work in an area where you are exposed to airborne irritants or noxious materials? 3. Do you live in an area with significant air pollution? …
Expected Duration
- Regardless of the cause, lung damage in emphysema cannot be reversed. If the disease is not treated, damage and symptoms will continue to get worse. If treated, the symptoms can improve.
Prevention
- If you smoke, stop. If you don't smoke, don't start. By quitting smoking you can either prevent emphysema or slow its progression. You also should limit your exposure to air pollution. Restrict your outdoor activity when there are reports of high smog levels. People exposed to harmful chemicals at work should speak to their employers about respirator masks. Or, consult with a sp…
When to Call A Professional
- Call your doctor if you develop: 1. New shortness of breath 2. A persistent cough, with or without phlegm 3. A decrease in your usual ability to exercise 4. Frequent respiratory infections If you smoke, see your doctor about ways to quit. Several different types of treatment can increase your likelihood of success compared to "going cold turkey." These include medications and counselin…
Prognosis
- There is no cure for emphysema. But the condition can be controlled. People with mild emphysema who quit smoking have a normal life expectancy. Those who adopt good health habits can enjoy a fairly normal lifestyle for a long time. Even people whose emphysema is severe have a good chance of surviving for five years or more. In people with emphysema who continu…
Further Information
- Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances. Medical Disclaimer