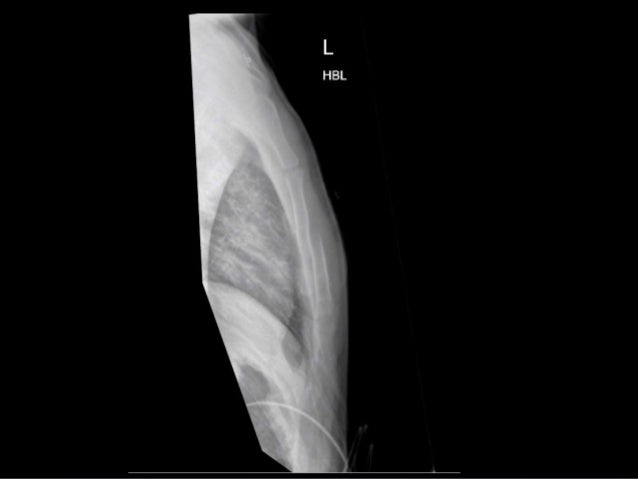
First-line treatment of pneumothoraces depends on a combination of clinical features, and size/type of pneumothorax. It may include observation with supplemental oxygen therapy, percutaneous aspiration of the air in the pleural
Pleural Effusion
An excessive collection of fluid in the pleural cavity.
...
Key Points
- Physical findings can be subtle or normal, particularly if pneumothorax is small.
- Although CT and ultrasonography are more sensitive, chest x-ray is usually considered sufficient for diagnosis.
How long does it take to recover from a pneumothorax?
Pneumothorax Recovery. It usually takes 1 or 2 weeks to recover from pneumothorax. But you have to wait for your doctor to say you’re OK. Until then: Go back to your routine a little bit at a time.
What is the recovery time for pneumothorax?
What you should know about a punctured lung
- Symptoms. The symptoms of a punctured lung can vary. ...
- Treatment for a punctured lung. When there are no symptoms, a doctor may monitor the lungs with repeated X-rays. ...
- Recovery time. The time it takes to recover from a punctured lung will vary. ...
- Outlook. Although a punctured lung can be serious, it is not usually a fatal condition. ...
What are the long term effects of a pneumothorax?
Treatment of pneumothorax
- Observation. If pneumothorax results from a small injury, it may heal without treatment within a few days. ...
- Draining excess air. If the damage is significant or symptoms are severe, a surgeon may need to remove the air or carry out surgery.
- Surgery. ...
What is the standard treatment for a pneumothorax?
Which medications are used in the treatment of pneumothorax?
- Anestacon) Lidocaine hydrochloride is…
- Fentanyl citrate (Sublimaze) The onset of analgesia with fentanyl citrate is immediate…
- Oramorph SR) Morphine is the drug…
- Midazolam. Benzodiazepine used for sedation component… Facebook Tumblr Reddit LinkedIn WhatsApp Messenger Telegram

What is the treatment for traumatic pneumothorax?
Treatment of Traumatic Pneumothorax The goal of treatment is to remove the air from the pleural space and allow the lung to reinflate. Usually, a tube ( thoracostomy. The procedure is done... read more or chest tube) is inserted into the chest between two ribs.
What is the most important intervention used to treat a traumatic open pneumothorax?
Immediate management of open pneumothorax is to cover the wound with a rectangular sterile occlusive dressing that is closed securely with tape on only 3 sides. Thus, the dressing prevents atmospheric air from entering the chest wall during inspiration but allows any intrapleural air out during expiration.
What's the treatment of choice for a client with pneumothorax?
Treatment options may include observation, needle aspiration, chest tube insertion, nonsurgical repair or surgery. You may receive supplemental oxygen therapy to speed air reabsorption and lung expansion.
Which drug should be administered to all patients who have a pneumothorax?
Morphine (Astramorph, Infumorph 200, MS Contin, Oramorph SR) Morphine is the drug of choice for analgesia because of its reliable and predictable effects, safety profile, and ease of reversibility with naloxone. In adults, the initial dose is given intravenously and titrated for effect.
What is the immediate management of tension pneumothorax?
Treatment of tension pneumothorax is immediate needle decompression by inserting a large-bore (eg, 14- or 16-gauge) needle into the 2nd intercostal space in the midclavicular line. Air will usually gush out.
What is the most common medical intervention required for patients with thoracic trauma?
Emergency resuscitation, preferential diagnosis, basic interventions (such as thoracentesis or catheter/tube thoracotomy) and effective treatment are the necessary interventions for patients presenting with a trauma.
How do nurses treat pneumothorax?
Nursing InterventionsApply a dressing over an open chest wound.Administer oxygen as prescribed.Position the client in high fowler's position.Prepare for chest tube placement until the lung has expanded fully.Monitor chest tube drainage system.Monitor for subcutaneous emphysema.
What is the proper prehospital management for pneumothorax and for tension pneumothorax?
Two main procedures are used in the emergency management of pneumothorax in the prehospital setting: needle thoracostomy for tension pneumothorax and the placement of three-sided occlusive dressing for a communicating pneumothorax.
What is the most appropriate description of traumatic pneumothorax?
Traumatic pneumothorax is air in the pleural space resulting from trauma and causing partial or complete lung collapse. Symptoms include chest pain from the causative injury and sometimes dyspnea. Diagnosis is made by chest x-ray.
Is Traumatic pneumothorax primary or secondary?
A primary spontaneous pneumothorax is one that occurs without an apparent cause and in the absence of significant lung disease. A secondary spontaneous pneumothorax occurs in the presence of existing lung disease....PneumothoraxFrequency20 per 100,000 per year12 more rows
How is hemothorax treated?
The most important treatment for hemothorax is draining the blood out of your chest cavity. Your doctor will likely put a tube through your chest muscles and tissues, through your ribs, and into your chest cavity to drain any pooled blood, fluid, or air. This is called a thoracentesis or thoracostomy.
What is the role of supplemental oxygen in the management of pneumothorax?
It is generally accepted that oxygen therapy increases the resolution rate of pneumothorax (1,2). The theoretical basis is that oxygen therapy reduces the partial pressure of nitrogen in the alveolus compared with the pleural cavity, and a diffusion gradient for nitrogen accelerates resolution (3,10).
What Is A Traumatic Pneumothorax and What Causes It?
A traumatic pneumothorax is when part of your lung collapses. A traumatic pneumothorax is caused by an injury that tears your lung and allows air t...
What Are The Signs and Symptoms of A Traumatic Pneumothorax?
You may have one or more of the following: 1. Shortness of breath 2. Soft bulges under your skin caused by air bubbles. These bubbles may be found...
How Is A Traumatic Pneumothorax Diagnosed?
Your healthcare provider will ask about your signs and symptoms and examine you. He will listen to your lungs. You may need any of the following te...
How Is A Traumatic Pneumothorax Treated?
Treatment will depend on the size of your pneumothorax. If your pneumothorax is small, it may resolve on its own. The goal of treatment is to remov...
What Are The Risks of A Traumatic Pneumothorax?
1. Air may continue to enter the pleural space and you may get a tension pneumothorax. With a tension pneumothorax, the injured lung and trapped ai...
When Should I Seek Immediate Care Or Call 911?
1. You have new or increased shortness of breath. 2. Your throat or the front of your neck is pushed to one side. 3. You are sweating and feel like...
How does a Collapsed Lung Develop?
Among the possible traumatic injuries that an individual might sustain in an auto accident, a traumatic pneumothorax is a severe, potentially fatal, catastrophic personal injury. The lung is filled with small sacs called alveoli that fill with air and transfer oxygen from the lungs into the bloodstream for transport to the body’s vital organs.
What Kind of Treatment Options are Available?
A team of clinical researchers conducted an extensive review of the online databases to find research papers discussing collapsed lungs and tension, traumatic pneumothoraces. They scoured the electronic databases and located close to 300 papers talking about collapsed lungs and how they develop.
A Legal Professional can be Helpful
Someone who has developed a collapsed lung may not be able to return to work for an extended period of time. In this situation, people could be forced to use up a significant amount of their vacation time and might face the prospect of losing their job or have trouble qualifying for worker’s compensation.
Experienced Car Accident Lawyer in Sacramento
I’m Ed Smith, a Sacramento car accident lawyer . People who have suffered lung trauma as a result of a car accident can call my office for free, friendly, and caring advice at (916) 921-6400 or (800) 404-5400.
What is pneumothorax in a patient?
A pneumothorax is defined as the presence of air between parietal and visceral pleural cavity .[4] Tension pneumothorax is the accumulation of air under pressure in the pleural space. This condition develops when injured tissue forms a 1-way valve, allowing air to enter the pleural space and preventing the air from escaping naturally. This condition rapidly progresses to respiratory insufficiency, cardiovascular collapse, and ultimately death if, unrecognized and untreated. Favorable patient outcomes require urgent diagnosis and immediate management.
How to diagnose pneumothorax?
Diagnosis of pneumothorax is done by thorough clinical examination and investigations. However, clinical interpretation of the presenting signs and symptoms is crucial for correctly diagnosing and treating the condition.
What causes iatrogenic pneumothorax?
The leading cause of iatrogenic pneumothorax is transthoracic needle aspiration. Two factors may be responsible for it, depth and size of the lesion. If the lesion is deeper and the size is smaller chances of traumatic pneumothorax increases.
How does a pneumothorax occur?
A traumatic pneumothorax can result from either penetrating or nonpenetrating chest trauma. With penetrating chest trauma, the wound allows air to enter the pleural space directly through the chest wall or through the visceral pleura from the tracheobronchial tree. With non penetrating trauma, a pneumothorax may develop if the visceral pleura is lacerated secondary to a rib fracture, dislocation. Sudden chest compression abruptly increases the alveolar pressure, which may cause alveolar rupture. Once the alveolus is ruptured, air enters the interstitial space and dissects toward either the visceral pleura or the mediastinum. A pneumothorax develops when either the visceral or the mediastinal pleura ruptures, allowing air to enter the pleural space.[11]
How does pneumothorax cause hypoxia?
The volume of this nonabsorbable intrapleural air increases with each inspiration. As a result, pressure rises within the affected hemithorax; ipsilateral lung collapses and causes hypoxia. Further pressure causes the mediastinum shift toward the contralateral side and compresses both, the contralateral lung and the vasculature entering the right atrium of the heart. This leads to worsening hypoxia and compromised venous return. Researchers still are debating the exact mechanism of cardiovascular collapse but, generally the condition may develop from a combination of mechanical and hypoxic effects. The mechanical effects manifest as compression of the superior and inferior vena cava because the mediastinum deviates and the intrathoracic pressure increases. Hypoxia leads to increased pulmonary vascular resistance via vasoconstriction. If untreated, the hypoxemia, metabolic acidosis, and decreased cardiac output lead to cardiac arrest and death.[9,10]
Can you radiologically confirm tension pneumothorax?
In some patients, it may be preferable to radiologically confirm and localize tension pneumothorax before subjecting the patient to potential morbidities arising from decompression. However, this consideration should be limited to patients who are awake, stable, not in advanced stages of tension and when an immediate chest film can be obtained, with facilities to perform urgent decompression if needed.
Is pneumothorax traumatic or nontraumatic?
It is usually classified on the basis of its causes. Pneumothoraces are classified as traumatic and nontraumatic (spontaneous).[7] Nontraumatic pneumothoraces are further subdivided into primary (occurring in persons with no known history of lung disease) and secondary (occurring in persons with a known history of lung disease, such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease).[8]
What are the symptoms of traumatic pneumothorax?
Patients with traumatic pneumothorax commonly have pleuritic chest pain, dyspnea, tachypnea, and tachycardia.
What is pneumothorax in the pleural space?
Traumatic pneumothorax is air in the pleural space resulting from trauma and causing partial or complete lung collapse. Symptoms include chest pain from the causative injury and sometimes dyspnea. Diagnosis is made by chest x-ray. Treatment is usually with tube thoracostomy.
What causes pneumothorax in a patient with a mediastinum wound?
In patients with penetrating wounds that traverse the mediastinum (eg, wounds medial to the nipples or to the scapulae), or with severe blunt trauma, pneumothorax may be caused by disruption of the tracheobronchial tree.
What is pneumothorax in a lung?
Pneumothorax (Traumatic) Traumatic pneumothorax is air in the pleural space resulting from trauma and causing partial or complete lung collapse. Symptoms include chest pain from the causative injury and sometimes dyspnea. Diagnosis is made by chest x-ray. Treatment is usually with tube thoracostomy.
What is tube thoracostomy?
Tube thoracostomy is indicated if pneumothorax causes respiratory symptoms or is moderate or large or if air transport, positive pressure ventilation, or general anesthesia is necessary. Click here for Patient Education. NOTE: This is the Professional Version. CONSUMERS: Click here for the Consumer Version.
What is the most sensitive test for pneumothoraces?
Diagnosis is usually made by chest x-ray. Ultrasonography (done at the bedside during initial resuscitation) and CT are more sensitive for small pneumothoraces than chest x-ray.
What to do if a large air leak persists after tube thoracostomy?
If a large air leak persists after tube thoracostomy, tracheobronchial tree injury should be suspected and bronchoscopy or immediate surgical consultation should be arranged.
Which approach is used to reduce the chance of pneumothorax formation?
If necessary, use the supraclavicular approach rather than the infraclavicular approach while cannulating the subclavian vein to reduce the chance of pneumothorax formation.
How is pneumothorax diagnosed?
Pneumothorax is diagnosed by a detailed clinical review and investigations. However, accurately diagnosing and managing the condition requires a clinical understanding of the presenting signs and symptoms.
How does oxygen affect pleural space?
100 percent oxygen should be administered right away. In both clinical and laboratory settings, supplemental oxygen increases the rate of pleural air absorption. When you breathe 100% oxygen instead of air, the alveolar pressure of nitrogen decreases, nitrogen is washed out of tissue, and oxygen is taken up by the vascular system. This creates a significant gradient between tissue capillaries and the pneumothorax space, resulting in a multifold increase in pleural space absorption. It is recommended that any hospitalized patient with a pneumothorax who is not undergoing aspiration or tube thoracostomy be given high-concentration supplemental oxygen. Normally, 1.25 percent of the volume is consumed every 24 hours, so 10% of the volume is absorbed after 8 days, 20% after 16 days, and so on.
What is the third most common cause of iatrogenic pneumothorax?
The third most common cause of iatrogenic pneumothorax is thoracentesis. If performed under ultrasound control, this can be minimized. Iatrogenic pneumothorax was found to be 13 percent for computed tomography (CT)-directed transthoracic fine-needle aspiration (TFNA), 7.1 percent for pleural biopsy, 16.6 percent for transbronchial biopsy, 7.1 percent for fluoroscopy-guided TFNA, and 1.5 percent for thoracentesis in a sample of 418 invasive procedures.
What percentage of iatrogenic pneumothorax is caused by biopsy?
Biopsy (Transthoracic needle aspiration) – Most common, around 24% of iatrogenic pneumothorax is caused by it.
Why is central cannulation the second most common cause of iatrogenic pneumothorax?
The risk of traumatic pneumothorax raises as the lesion grows deeper and narrower. Because of the rising number of patients needing intensive care , central cannulation is the second most common cause of iatrogenic pneumothorax.
How often should you get a chest X-ray for pneumothorax?
To find out pneumothorax, serial chest radiographs every 6 hours on the first day after trauma (injury) are preferable, but two or three chest X-rays every 4-6 hours will work. A tension pneumothorax is indicated by air in the pleural cavity and contralateral deviation of mediastinal structures.
What are the principles of pneumothorax?
The treatment principles of pneumothorax include five principles: air elimination, reducing air leakage, healing the pleural fistula, promoting re-expand and preventing future recurrences, but treating underlying diseases, preventing and dealing complications are also important. The core of treatment is based on different etiology and pathogenesis. If patients did not get promptly and completely treatment that were combined with pneumothorax or underlying diseases, respiratory failure would be most dangerous. Therefore maintaining necessary respiratory function and stable hemodynamics are the first step of treatment (1-8).
How to treat pneumothorax with needle aspiration?
Air elimination is the first and most important treatment of pneumothorax through needle aspiration and catheter drainage. Their improvements are based on the developments of the material and operation on special positions/circumstances. Needle aspiration is required to exhaust air completely at the first time. In order to approach the target, aspiration should be done in any position of the chest cavity even in some traditional dangerous positions such as the supraclavicular fossa and subclavicular region, guiding by Ultrasound or CT scanning. Additionally, new damage caused by the needle must be avoided during the re-expansion. The current approach is to use cannula or vine remaining needlleiv, even connected to one-way Heimlich valve device to enhance the efficacy and are convenient for patients to activities. In the future there may have sensitive detection method or use the non-metallic needle. Secondary pneumothorax patients especially with pre-existing structuredness lung diseases such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) or tuberculosis, needle aspiration treatment success rate is generally low (9-15).
How long should a pneumothorax tube be clamped?
The ACCP consensus group suggests that the tube should be clamped for approximately 4 hours in primary spontaneous pneumothorax and 5-12 hours in secondary spontaneous pneumothorax. The time is so short but there has some doubts about why BTS 2010 guideline was not refer to clamped observation (15-25).
How to reduce air leakage?
The first step is to find the lung lobe or segment interlinked pleural fistula by using blocking balloon to observe bubbles overflow in the drainage bottle, pressure change or not which can use Chartis system. Without structuredness lung disease or thoracic surgery or trauma, upper lobe is the most likely position of breach and may be treated preliminarily. And CT scanning is needed to infer the possible segment by the image of bulla and adhering band.
Is pneumothorax a recurrent disease?
Except traumatic or iatrogenic factors, pneumothorax usually is also a recurrent disease, especially caused by structure dness lung diseases which named secondary pneumothorax. Some studies revealed its recurrence rate 70% or more. Therefore, to prevent recurrences is other important aspect of the treatment principles.
Is pneumothorax a primary or secondary condition?
In any case it is a dangerous situation that requires immediate attention and treatment. Pneumothorax can be divided in primary and secondary.
Is a small bore chest drain a good replacement for a large bore chest drain?
But if failed, needle aspiration should not be repeated and small-bore (<14 F) chest drains may be a good replacement. On the other side, small-bore chest drains should be the first choice, especially for the patients with pre-existing structuredness lung diseases.
A traumatic pneumothorax
is a collapsed lung. All or part of your lung may collapse. A traumatic pneumothorax is caused by an injury that tears your lung and allows air to enter the pleural space. The pleural space is the area between your lungs and your chest wall. The air trapped in your pleural space prevents your lung from filling, and it collapses.
Treatment
will depend on the size of your pneumothorax. If your pneumothorax is small, it may get better on its own. The goal of treatment is to remove the air from your pleural space. When your lung is able to fill with air, you will be able to breathe easier. You may need any of the following:
Breathing exercises
You may need to do breathing exercises to strengthen your lungs. Ask your healthcare provider how to do these exercises, and how long you should do them.
Do not smoke
Nicotine and other chemicals in cigarettes and cigars can increase your risk for another pneumothorax. Ask your healthcare provider for information if you currently smoke and need help to quit. E-cigarettes and smokeless tobacco still contain nicotine. Talk to your healthcare provider before you use these products.
For your safety
A change of pressure could cause another pneumothorax. Follow these and other safety precautions from your healthcare provider:
Follow up with your doctor or pulmonologist as directed
You may need to return for more chest x-rays. Write down your questions so you remember to ask them during your visits.
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
What is the goal of pneumothorax treatment?
The goal of treatment is to relieve the pressure on the lung and allow it to re-inflate. The type of treatment selected will depend on the cause and severity of the collapse, and on the patient’s overall health. For a minor pneumothorax, your doctor may simply keep an eye on you, as the lung may re-inflate on its own, ...
What are the Symptoms of Pneumothorax?
Symptoms normally come on almost immediately and commonly begin with chest pain. Other signals that the problem may be a collapsed lung are:
How to remove air from a collapsed lung?
During a needle aspiration, a needle attached to a syringe is inserted between the ribs into the air-filled space that is pressing on the collapsed lung and is used to suction out the excess air. A chest tube involves a similar insertion that involves a one-way valve device that continuously removes air until the lung re-inflates. The tube may need to stay in for a few hours, or even a few days, to ensure that the lung does not collapse again.
How long does a chest tube stay in?
The tube may need to stay in for a few hours, or even a few days, to ensure that the lung does not collapse again.
What is the next step in a lung leak?
In cases that involve an accident, or repeated collapsed lungs, the next step is a non-surgical repair of the leak. This can be done in several ways and is sometimes called pleurodesis.
Can you go to the hospital after a lung collapse?
Avoiding air travel for the first week after a collapse is often suggested. Diving puts patients at high risk, so most doctors suggest permanently avoiding it . Also, people who smoke are at increased risk of a pneumothorax, so quitting is highly recommended.
What is a traumatic pneumothorax?
A traumatic pneumothorax occurs when air escapes from a laceration in the lung itself and enters the pleural space or from a wound in the chest wall.
What are the different types of pneumothorax?
Types of pneumothorax include simple, traumatic, and tension pneumothorax. Simple pneumothorax. A simple or spontaneous pneumothorax occurs when air enters the pleural space through a breach of either the parietal or visceral pleura. Traumatic pneumothorax. A traumatic pneumothorax occurs when air escapes from a laceration in ...
What is Pneumothorax?
Pneumothorax is one of the disorders of the chest and lower respiratory tract.
What is the term for a pleural space that is exposed to positive atmospheric pressure?
Pneumothorax occurs when the parietal or visceral pleura is breached and the pleural space is exposed to positive atmospheric pressure.
What is pleuritic pain?
A: Pleuritic pain is a clinical manifestation of pneumothorax.
Why not clamp chest tube without physician order?
These could indicate an air leak, but do not clamp a chest tube without a physician’s order because clamping may lead to tension pneumothorax.
Which alignment should be assessed in a patient with pneumothorax?
A: Tracheal alignment should be assessed in a patient with pneumothorax.
