Full Answer
What is an example of tertiary care?
What are the 3 levels of health care in Australia?
- medical services.
- public hospitals.
- medicines.
What is tertiary wastewater treatment, and how does it work?
- Bag filters: Bag filters are ideal for wastewater treatment plants that need to reduce contaminants to a specific micron rating. ...
- Drum filters: A drum filter consists of a drum with a woven cloth filter around it. ...
- Disc filters: A disc filter consists of a central drum attached to multiple discs with cloth filters. ...
What is the definition of tertiary care?
the term tertiary care came into hospital parlance a few decades ago, but only in 2013 was it integrated into the us national library of medicine’s medical subject headings thesaurus, when it was defined as “care of a highly technical and specialized nature, provided in a medical center, usually one affiliated with a university, for patients with …
What does tertiary treatment remove?
What are the 4 stages of sewage treatment?
- Screening and Pumping.
- Grit Removal.
- Primary Settling.
- Aeration / Activated Sludge.
- Secondary Settling.
- Filtration.
- Disinfection.
- Oxygen Uptake.
What is tertiary treatment?
What is the main tertiary treatment process?
What is the most used filtration material in wastewater treatment?
What is used to reduce solids?
When is tertiary treatment necessary?
What are the drawbacks of biological treatment?
Is tertiary treatment more proprietary than secondary treatment?
See more
About this website

What is meant by tertiary treatment?
Tertiary treatment is the advanced treatment process, following secondary treatment of waste water, that produces high—quality water. Tertiary treatment includes removal of nutrients such as phosphorus and nitrogen and practically all suspended and organic matter from waste water.
What are 3 methods of tertiary treatment?
The tertiary treatment methods are: 1.Filtration 2.Air/Steam Stripping 3.Biological Processes 4. Adsorption 5.Membrane Separation Processes 6.Ion Exchange Process 7.Precipitation 8.Oxidation and Reduction and 9.
What is primary secondary and tertiary treatment?
Wastewater is treated in 3 phases: primary (solid removal), secondary (bacterial decomposition), and tertiary (extra filtration). List the steps of wastewater/sewage treatment.
What are some types of tertiary treatment?
Tertiary TreatmentWastewater Treatment.Membrane Bioreactors.Activated Sludge.Advanced Oxidation Process.Microalgae.Nitrogen.Reuse.
Why is tertiary treatment important?
Tertiary treatment eliminates matter from wastewater that could be harmful to the environment. The process involves removing materials such as heavy metals, toxic chemicals, and other pollutants.
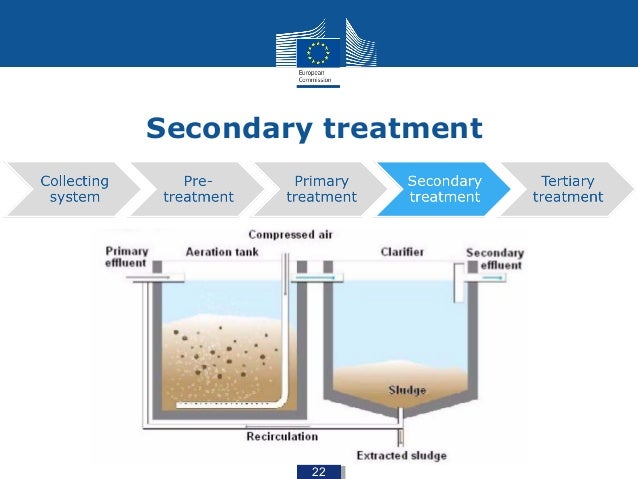
What is meant by secondary treatment?
Secondary treatment is the second step in most waste treatment systems during which bacteria consume the organic parts of the wastes. This is accomplished by bringing the sewage, bacteria and oxygen together in trickling filters or within an activated sludge process.
What is primary and secondary treatment?
The main difference is the way each respective treatment is processed. Primary treatment works on sedimentation, where solids separate from the water through several different tanks. In contrast, secondary treatment uses aeration, biofiltration and the interaction of waste throughout its process.
What is primary treatment?
(PRY-mayr-ee TREET-ment) The first treatment given for a disease. It is often part of a standard set of treatments, such as surgery followed by chemotherapy and radiation. When used by itself, primary treatment is the one accepted as the best treatment.
Tertiary Treatment of Waste Water (With Diagram)
ADVERTISEMENTS: Read this article to learn about the tertiary treatment of waste water. The tertiary treatment methods are: 1. Filtration 2. Air/Steam Stripping 3. Biological Processes 4. Adsorption 5. Membrane Separation Processes 6. Ion Exchange Process 7. Precipitation 8. Oxidation and Reduction and 9. Disinfection. After proper primary and secondary treatments a waste water may […]
THE TERTIARY TREATMENT STAGE OF WASTEWATER
Bulletin of the Transilvania University of Braşov CIBv 2013 • Vol. 6 (55) Special Issue No. 1 - 2013 THE TERTIARY TREATMENT STAGE OF WASTEWATER L.M. BOERIU1 I.L. CIRSTOLOVEAN1 M. FRATU1 C. NASTAC1 Abstract: At present many of the substances discharged into the wastewater sewerage are not eliminated by classical methods (mechanical and
Sewage Treatment Processes : Primary, Secondary and Tertiary
The composition of sewage is complex, and it differs depending upon the sources, the type of treatment or lack of it. The process of treating sewage is broadly classified as primary; secondary and tertiary (see Figures 8.3, 8.4 and 8.5).
What is tertiary treatment in water?
Tertiary treatment in waste water is the third and final advanced treatment process used to disinfect water that has already been treated by primary and secondary processes for removing harmful material in a waste water plant. This produces high quality, usable water. This treatment removes phosphorous, nitrogen and other nutrients, as well as any organic and other suspended material from the water.
What is the final stage of water treatment?
This final stage of water treatment is any treatment, going beyond primary and secondary, and is often a disinfection process that can involve the use of ultraviolet (UV) light or chemicals, such as lime, to eliminate pathogens (bacteria or viruses) from the water. Although secondary treatment eliminates most of the bacteria and viruses, there can still be nitrogen and phosphorous and other solids still remaining which will also be destroyed in the final treatment.
What is tertiary treatment?
Tertiary Treatment. Tertiary treatment refers to secondary treatment followed by a filtration step, such as media filtration, so that the turbidity and TOC concentrations are generally lower , and if coagulation with metal salts is used, then the phosphate concentration will also be reduced (Henriksen, 1963).
What is agricultural wastewater treatment?
Agricultural wastewater treatment for continuous confined animal operations (e.g. milk and egg production) may be performed in plants using mechanized treatment units. If sufficient land is available for ponds, settling basins, and facultative lagoons, then the operational cost is lower.
What is treated wastewater in Vadodara?
In Vadodara, tertiary treated industrial wastewater is done is supplies for non-potable industrial purposes throughout the city. Around 75% of the treated wastewater is available for reuse at a treatment cost of INR 36/1000 L. 9
What is used to reduce solids?
If the solids need to be reduced, sand filters or other clarifiers may be used. The collected materials are then usually bulked with the other sludges on site for further treatment and disposal.
How does tertiary treatment work?
Tertiary wastewater treatment often works by using a combination of physical and chemical processes to remove harmful microbiological contaminants from wastewater. The process usually involves filtration followed by additional disinfecting treatment. In some cases, tertiary treatment may also use other specialized treatments like lagoon storage, biological nutrient removal, and nitrogen and phosphorus removal.
Why do plants use tertiary treatment?
Many treatment plants use tertiary treatment specifically to make the water safe for human ingestion. After tertiary treatment, the water has undergone sufficient purification to be as clean and healthy as drinking water.
What Is Tertiary Wastewater Treatment?
What is tertiary treatment in wastewater? To answer this question, let’s look into how treatment plants generally work and how the main stages of wastewater treatment progress.
What are tertiary filtration components?
Tertiary filtration components can contain a few different materials. Sand and activated carbon filters are common, and filters can also contain fine woven cloth. The filters also come in a few different types, including bag filters, drum filters and disc filters: Bag filters: Bag filters are ideal for wastewater treatment plants ...
Why is chlorine used in wastewater treatment?
Wastewater treatment plants can dump chlorine into the wastewater to kill harmful microorganisms like bacteria and viruses.
What happens to wastewater after tertiary treatment?
Once the wastewater has undergone tertiary treatment, it is ready for discharge back into the environment. Many municipalities have specific requirements about the discharge of treated water, and tertiary treatment should be sufficient to meet those standards, keep the environment clean, and preserve human health.
What is secondary treatment?
Secondary treatment applies additional biological processes like aeration and activated sludge treatment to break down dissolved and suspended biosolids using good bacteria. Tertiary treatment adds a third, more advanced and rigorous level of treatment.
What is Tertiary Treatment?
Tertiary treatment is the third, and final, stage in a standard wastewater management system. Once effluent has been treated in the primary and secondary stages by removing suspended solids, pH balancing and reducing its biochemical oxygen demand (BOD), it is ready to enter the tertiary stage.
Why is tertiary treatment important?
Incorporating a tertiary treatment system into your operation can dramatically reduce the amount of water your facility uses, which is becoming increasingly important to regions, states, and localities that face shortages.
How long does it take to install a tertiary treatment system?
After collecting data and making a system recommendation, we’ll begin the 2-3 week process of installing your tertiary treatment system. Once the installation is complete, we’ll compile documentation and create a custom service checklist that’s specific to the customer’s site and system.
What is the final stage of water treatment?
The final stage of water treatment involves sterilizing water for reuse, removing potentially harmful contaminants, and may include one or more of the following technologies.
What is tertiary treatment?
Tertiary Treatment of Wastewater – Methods and Process. Tertiary water treatment is the final stage of the multi-stage wastewater cleaning process. This third stage of treatment removes inorganic compounds, bacteria, viruses, and parasites.
What is the final stage of tertiary wastewater treatment?
The final stage of the tertiary wastewater treatment process involves removing the chlorine that was used to disinfect the water. This step is very important because chlorine is harmful to aquatic life. Chlorine also reduces biological water quality when it is present in high concentrations. To remove the chlorine, a compound called sodium ...
What is the purpose of chlorination in wastewater treatment?
Chlorination in wastewater treatment kills bacteria and viruses, and eliminates parasites such as Giardia and Cryptosporidium, which can cause very serious illnesses. In summary, this process disinfects water so that it is safe to reuse or recycle.
What is the primary treatment of wastewater?
Primary treatment of wastewater involves filtering out large solid contaminants. Secondary treatment then purifies the wastewater through biofiltration, aeration, and oxidation. These are all processes that help to remove sediment from the water.
What is the third stage of sewage treatment?
This third stage of treatment removes inorganic compounds, bacteria, viruses, and parasites. Removing these harmful substances makes the treated water safe to reuse, recycle, or release into the environment. To find out how tertiary sewage treatment works, take a look at this overview of the methods and processes involved in ...
What is AOS water treatment?
The municipal water treatment solutions at AOS can help you execute the three stages of wastewater treatment . Through this responsible three-stage water treatment process, we protect both people and the natural environment from the harmful effects of untreated wastewater.
What is tertiary treatment?
Tertiary treatment includes the removal of the remaining inorganic compounds (phosphate, sulfate, ammonium) and other refractory organic compounds by one or more physical separation methods, such as carbon adsorption, deep-bed filtr ation, and in some cases, membrane-based techniques, such as reverse osmosis or electrodialysis.
What is the main tertiary treatment process?
The main tertiary treatment process is then filtration, using either a sand bed or a membrane process, usually microfiltration, possibly followed by ultrafiltration. There may also be too high a content of nitrogen and phosphorus, and this will require additional biological processes, with some more sludge to be separated.
What is the most used filtration material in wastewater treatment?
Sand, activated carbon, and zeolite are the most employed filtering materials in wastewater tertiary treatment. Sand filtration is a conventional wastewater treatment process characterized by its simplicity, low energy inputs, and easy maintenance. In this system, chemical reagents are not required, resulting in lower costs in comparison with other methods. In addition, the use of sand as wastewater filtering material has shown to be effective as tertiary treatment stage achieving high turbidity removal rates. Its use in combination with activated carbon is an effective alternative to the conventional method [20].
What is used to reduce solids?
If the solids need to be reduced, sand filters or other clarifiers may be used. The collected materials are then usually bulked with the other sludges on site for further treatment and disposal.
When is tertiary treatment necessary?
Usually tertiary treatment of wastewater is only regarded as necessary when the nutrient concentrations in the effluent have to be reduced i.e., if the mill discharges to very sensitive recipients. View chapter Purchase book. Read full chapter.
What are the drawbacks of biological treatment?
Although chemical treatment shows good results, the treatment has associated drawbacks such as dewatering and disposal of the generated sludge.
Is tertiary treatment more proprietary than secondary treatment?
Tertiary treatment processes are more commonly proprietary than secondary treatment processes, usually being newer (or at least new variants on old processes). Secondary treatment was developed in large part to deal with the 1912 Reports of the UK Royal Commission.
