Webmd.com
1. Get in a routine...setting a gentle daily schedule can help you get back on track...
2. Exercise...regular exercise seems to encourage the brain to rewire itself in positive ways, cook says...
3. Get enough sleep...
4. Take on responsibilities...
5. Challenge negative thoughts...
6. Check with your doctor before using supplements...
Learn More...Healthline.com
1. St. johns wort...taking st. johns wort has been linked with increasing the amount of serotonin in the body...
2. Omega-3 fatty acids...its ideal to get a higher ratio of dha to epa, which are both types of omega-3 fatty acids...
3. Saffron...
4. SAM-e...
5. Folate...
6. Zinc...
Learn More...Top10homeremedies.com
1. St. johns wort...it has chemical constituents like hypericin and hyperforin that work like antidepressants...
2. Cardamom...help detoxify the body and rejuvenate the cells...
3. Nutmeg...helps stimulate your brain, eliminate fatigue and stress...
4. Saffron...
5. Cashews...
6. Fish Oil...
7. Apples...
Learn More...What are the options for treatment resistant depression?
Treatment-Resistant Depression: Options to Ask Your Doctor About. The options for the treatment of treatment-resistant depression include: Making changes to your medication: It may be that you need to try a new medication for treatment-resistant depression, or that you need to increase your current dose. Your doctor might suggest a different type of antidepressant or consider tweaking your drug schedule before exploring other treatment-resistant depression options.
What medications are used for treatment resistant depression?
One drug that can be used with an antidepressant is ketamine. Your doctor may suggest it to give you rapid relief from treatment-resistant depression. You'll take it in low doses through an IV. The FDA has approved a nasal spray form called esketamine (Spravato).
How do you treat treatment resistant depression?
Psychedelic-assisted psychotherapy works to create a therapeutic model which improves clinical symptoms and promotes lasting, positive change for patients. Through this partnership with leading psychiatrists and researchers, Beckley Psytech aims to develop a holistic system which will enable delivery of the best care to patients.
How to treat severe depression?
FITCHBURG (WKOW) -- Despite its reputation as a party drug, recent studies have shown ketamine can be used to treat people with severe depression. And now, Fitchburg's first ketamine clinic is set to open in just a couple of weeks. The face behind it all ...
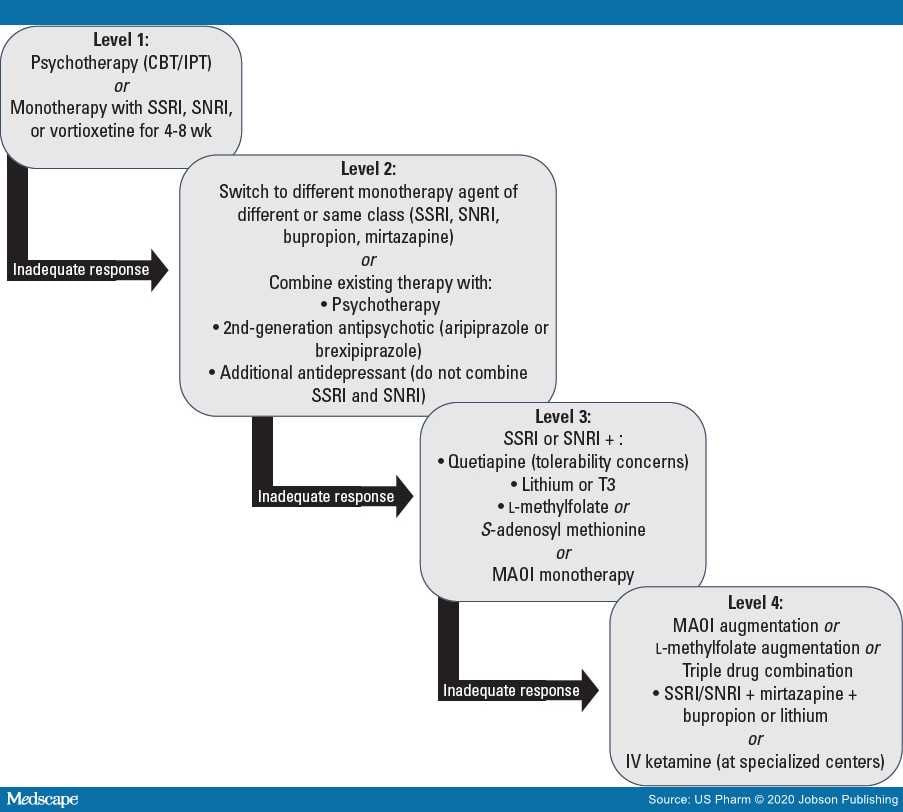
How do doctors treat treatment-resistant depression?
About one-third of people with MDD have treatment-resistant depression. A doctor may recommend adding or changing medications, psychotherapy, electroconvulsive therapy, or new or novel medications. Find encouragement and support through 1-1 messaging and advice from others dealing with major depressive disorder.
Which of the following is used for treatment-resistant depression?
Electroconvulsive therapy (ECT). ECT seems to cause changes in brain chemistry that can relatively quickly reverse symptoms of major depression.
Which Glutaminergic treatment is available for treatment-resistant depression?
The first report of ketamine's potential to alleviate depressive symptoms was a small, randomized, double-blind study demonstrating that a single subanaesthetic (0.5 mg/kg) ketamine infusion improved depressive symptoms within 72 hours in seven patients with treatment-resistant MDD.
Is Effexor good for treatment-resistant depression?
It is well tolerated and has been proven to be effective for the management of patients with treatment-resistant major depression.
What do you do when antidepressants aren't working?
If you've been taking an antidepressant and notice that it's no longer working, there are a few things you can do.Speak to your provider about adjusting your medication. ... Switch to or add another antidepressant. ... Combine medication with therapy. ... Attend a treatment program. ... Attend a self-help group.
What do you do when antidepressants don't work?
If your depression symptoms return for more than a few days, it's time to see your doctor. But even if you feel like your antidepressant isn't working, it's important to keep taking it until your doctor advises otherwise. You may need a dosage increase or a slow tapering off process.
How effective is Spravato?
About seven out of ten people saw a 50% improvement or better from the new pill and Spravato, but a little more than five out of ten people had the same improvement with just the new pill. The Spravato and new pill combination was only about 37% more effective than the new pill alone.
How do I get esketamine nasal spray?
You, your doctor, and your pharmacy must be enrolled in the Spravato REMS program before you can receive this medication. You will use esketamine nasal spray in a medical facility under the observation of a doctor or other healthcare professional. Keep all appointments with your doctor and the laboratory.
Will esketamine be covered by insurance?
Ketamine treatments are not covered by insurance companies because it's experimental and not FDA approved. Therefore, you have to pay out of pocket for it. Esketamine (Spravato) is almost always covered by insurance, including Medicare, because it is FDA approved and well-studied to be effective and safe.
What is the strongest antidepressant?
The most effective antidepressant compared to placebo was the tricyclic antidepressant amitriptyline, which increased the chances of treatment response more than two-fold (odds ratio [OR] 2.13, 95% credible interval [CrI] 1.89 to 2.41).
What two antidepressants work well together?
Escitalopram and sertraline were found to have the best combination of efficacy and acceptability.
Is pristiq stronger than Effexor?
Is Pristiq or Effexor more effective? A meta-analysis looked at the safety and efficacy of Pristiq and Effexor. The researchers concluded that both drugs were similar in terms of efficacy in treating depression, as well as side effects.
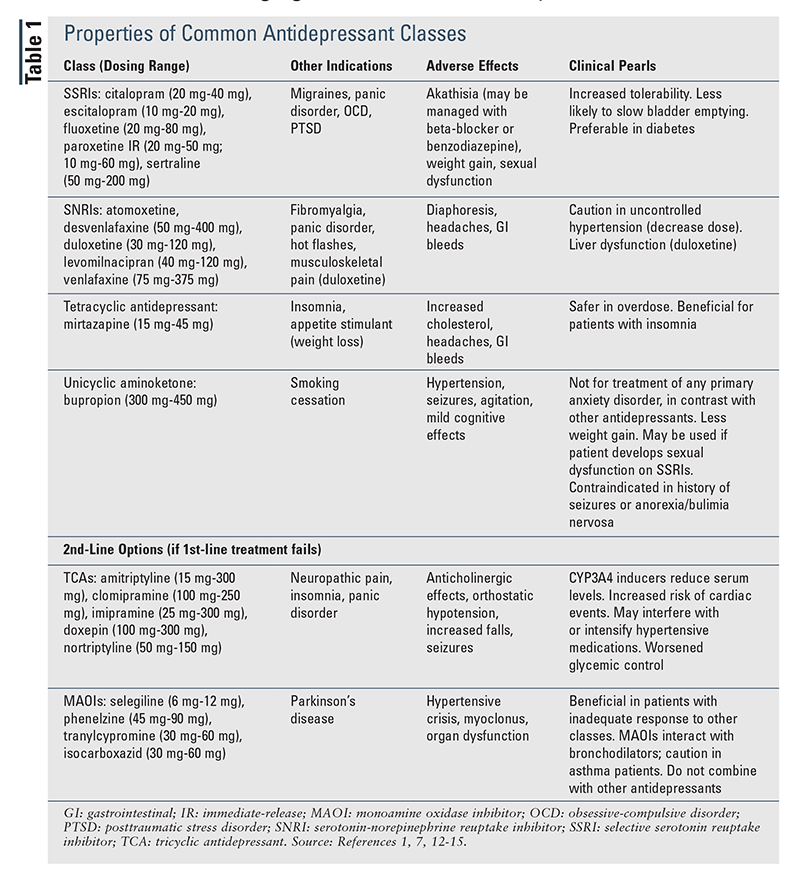
What is the first choice for treating depression?
Antidepressants. Antidepressant medications are the first choice for treating depression. If you’ve tried antidepressants without much success, your doctor will likely start by suggesting an antidepressant in a different drug class. A drug class is a group of medications that work in a similar way.
How long does it take for an antidepressant to work?
However, some research shows that people who show some improvement within a couple weeks of starting an antidepressant are more likely to eventually have a full improvement in their symptoms. Those who don’t have any response early in treatment are less likely to have full improvement, even after several weeks.
What is a drug class?
A drug class is a group of medications that work in a similar way. The different drug classes of antidepressants include: selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors, such as citalopram (Celexa), escitalopram (Lexapro), fluoxetine (Prozac), paroxetine (Paxil), and sertraline (Zoloft)
What is it called when you don't respond to antidepressants?
Depression that doesn’t respond to antidepressants is known as treatment-resistant depression. Some also refer to it as treatment-refractory depression. Read on to learn more about treatment-resistant depression, including treatment approaches that can help.
What is treatment resistant depression?
What is treatment-resistant depression? Feeling sad or hopeless from time to time is a normal and natural part of life. It happens to everyone. For people with depression, these feelings can become intense and long-lasting. This can lead to problems at work, home, or school.
What are the risk factors for depression?
These risk factors include: Length of depression. People who’ve had major depression for a longer period of time are more likely to have treatment-resistant depression. Severity of symptoms. People with very severe depression symptoms or very mild symptoms are less likely to respond well to antidepressants.
What are the factors that affect the effectiveness of antidepressants?
Genetic factors. One or more genetic factors likely have a role in treatment-resistant depression. Certain genetic variations may increase how the body breaks down antidepressants, which could make them less effective. Other genetic variants might change how the body responds to antidepressants.
How to treat depression resistant to anesthesia?
Electroconvulsive therapy (ECT): Perhaps the most effective treatment for resistant depression is ECT. ECT is a procedure that is administered under general anesthesia. Electric currents are passed through the brain triggering a brief seizure. It seems to cause changes in brain chemistry that can reduce depression (and reverse symptoms of other mental illnesses). Although it is generally considered safe, it can have side effects such as some short-term memory loss as well as some physical side effects. ECT is often initially administered two to three times per week. The duration of the treatment can vary but a total of six to 12 sessions is common.
What is the best treatment for depression?
Electroconvulsive therapy (ECT): Perhaps the most effective treatment for resistant depression is ECT. ECT is a procedure that is administered under general anesthesia. Electric currents are passed through the brain triggering a brief seizure.
What is the lack of any response to medication or psychotherapy treatment?
A lack of any response to medication or psychotherapy treatment. Not enough of a response to standard depression treatments. Brief improvements followed by a return of depressive symptoms. Because standard treatments do not work well or at all, people may begin to experience profound hopelessness.
How many people are in remission after taking antidepressants?
Studies have found that 30% to 40% of people only experience a partial remission of depressive symptoms after taking antidepressants. 1 Approximately 10% to 15% of people don't respond to antidepressant treatments at all. Consequences for people with treatment-resistant depression can be significant.
What is treatment resistant depression?
Although definitions may vary, when two or more treatment attempts of adequate dose and duration fail to provide expected relief, the disorder may be considered “treatment-resistant depression.”
Why do you start medication at a low dose?
Sometimes medications are started at a low dose to minimize risk or side effects. As it’s tolerated, the dosage may be increased slowly. A physician will want to ensure the dosage is at a therapeutic level before determining whether the treatment is a failure. The Best Online Help Resources for Depression.
What to do if you have been treated for depression but your symptoms have not improved?
If you have been treated for depression but your symptoms have not improved, you should talk to your doctor. Treatment-resistant depression is not an official diagnosis included in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5), nor is it consistently defined.
What is TRD treatment?
Treatment-resistant depression (TRD) is a subset of Major Depressive Disorder which does not respond to traditional and first-line therapeutic options. There are several definitions and staging models of TRD and a consensus for each has not yet been established. However, in common for each model is the inadequate response to at least 2 trials of antidepressant pharmacotherapy. In this review, a comprehensive analysis of existing literature regarding the challenges and management of TRD has been compiled. A PubMed search was performed to assemble meta-analyses, trials and reviews on the topic of TRD. First, we address the confounds in the definitions and staging models of TRD, and subsequently the difficulties inherent in assessing the illness. Pharmacological augmentation strategies including lithium, triiodothyronine and second-generation antipsychotics are reviewed, as is switching of antidepressant class. Somatic therapies, including several modalities of brain stimulation (electroconvulsive therapy, repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation, magnetic seizure therapy and deep brain stimulation) are detailed, psychotherapeutic strategies and subsequently novel therapeutics including ketamine, psilocybin, anti-inflammatories and new directions are reviewed in this manuscript. Our review of the evidence suggests that further large-scale work is necessary to understand the appropriate treatment pathways for TRD and to prescribe effective therapeutic options for patients suffering from TRD.
What are the perils of diagnosing TRD?
One of the perils of diagnosing TRD is that of “pseudo-resistance”.107Pseudo-re sistance may encompass the profile of patients who unfortunately were prescribed suboptimal doses of AD or had early discontinuation of a medication for any number of reasons, including intolerable side effects, patient non-adherence or under-dosing. Further, comorbidities such as anxiety disorders, personality disorders or substance-use disorders may complicate the clinical picture and can have deleterious effects on treatment response.114,127When interviewing patients in assessment of TRD, the potential for recall bias when reporting pharmacological trials and response adds a significant layer of difficulty in diagnosing TRD. Prospectively using objective clinical scales such as the Hamilton Depression Rating Scale48and the Inventory of Depressive Symptomatology124and retrospectively using treatment history forms such as the Antidepressant Treatment History Form (ATHF)127can be very helpful in delineating the nature and course of the treatment resistance. Since the ATHF was initially developed, there have been several developments in the treatment of MDD and specifically TRD, some of which will be elaborated upon in the ensuing sections of this paper. As such, the authors of the original ATHF127developed an updated and revised version, the short form ATHF (ATHF-SF), as well as an instruction manual and scoring checklist, among other documents.128Importantly, the ATHF-SF focuses on the current episode of depression, as opposed to life-time trials of pharmacological treatments, a more streamlined approach to assessing the level of resistance of the current illness episode. Utilizing a standardized approach to understand the level of treatment resistance in the current episode of depression may provide a useful measure of consistency in assessment of TRD.
How many trials of antidepressants are there for TRD?
Although many definitions for TRD have been proposed, the general consensus appears to be 2 unsuccessful trials of antidepressant pharmacotherapy (AD). Several “staging” models to classify levels of treatment resistance have been proposed. The initial model proposed by Thase and Rush138included treatment resistance levels ranging from one failed AD trial to a lack of response to electroconvulsive therapy (ECT). Further staging models have included the Massachusetts General Hospital Staging method117which carefully documents the optimization of medication doses and number of failed medications. The Souery Operational Criteria for TRD provide a slightly different approach to staging TRD as an illness, by defining TRD as any single failure of an adequate (6–8 week) trial of an AD.133The Maudsley Staging Method (MSM) assesses treatment resistance in depression in a “multi-dimensional” manner.34The majority of investigations into TRD utilize the definition of at least 2 suitable trials of AD without adequate response, although even the term “adequate response” may be fraught with contention, as there is not consensus on what constitutes “adequate.” In fact, even the term TRD may not be the ideal term to define a depressive illness that is not responding to therapeutic interventions. The term “difficult-to-treat depression” has been suggested, with the benefit of not introducing any “therapeutic nihilism” to the psychiatrist–patient relationship.103For consistency in this manuscript, we will use the term TRD. There has been considerable debate regarding what constitutes TRD, and whether medications from more than one class must be trialed prior to meeting criteria for this classification, or that the focus should be regarding homogeneous biological subtypes or endophenotypes.23However, the argument may be made that lack of achieving remission may be classified as an inadequate response as residual depressive symptoms can significantly contribute to difficulty functioning. Chronically depressed patients have a lower chance of recovery,98and often suffer from TRD.25,87
How often is ECT used for TRD?
In the treatment of TRD, ECT is applied 2–3 times per week and acute courses can range between 6–18 total sessions. A report from the Consortium for Research in ECT (CORE)57revealed that over half of the subjects showed an improvement within the first week. Other studies have reported that over 50% of patients who have failed to respond to one or more adequate antidepressant medication trials respond to ECT.120Meta-analyses have shown that ECT is superior to sham ECT, placebo or antidepressant medications.45,111
Why is ECT so stigmatized?
Unfortunately, ECT has suffered from extensive stigma in the public eye, likely due to the invasive nature of the treatment and largely due to subsequent negative and abusive portrayals in the media91including in One flew over the Cuckoo’s Nest, where ECT was portrayed as a punishment, delivered to an individual who did not have a psychotic or affective illness as a form of behavioural control. Along with restriction to access due to availability and risk of memory side effects, this stigma has resulted in ECT being administered to an exceptionally small proportion of individuals with MDD. In fact, a recent investigation of American health insurance databases identified that only 0.25% of almost 1 million patients with a mood disorder received ECT.142This gross underutilization of ECT persists, despite significant progress in reducing the cognitive side effect profile and alterations in the method of ECT, including seizure threshold titration, inclusion of highly tolerable anaesthetic agents and improvements in peri-procedural care. In 2001, however, the American Psychiatric Association published guidelines4advising that ECT should be used more frequently than just in “last resort” scenarios in severe medication-resistant patients or where the psychiatric condition is “life-threatening.”
How long does it take for a patient to go into remission after taking antidepressants?
Several large-scale clinical trials have examined response rates to traditional therapeutic approaches for depression. In the Sequenced Treatment Alternatives to Relieve Depression (STAR*D) study, the cumulative remission rate after 4 trials of antidepressant treatment (within 14 months) was 67%.125Even after sequential treatments, 10% to 20% of the MDD patients remained significantly symptomatic for 2 years or longer.69,70In general, it is accepted that although antidepressant medications can be effective in treating MDD, they fail to achieve remission in approximately 1 out of 3 patients.73
What is the response rate of ECT?
Bitemporal Standard pulse ECT is the most commonly used form,76with a response rate of up to 75%. While the response rate for Right Unilateral Ultrabrief ECT is slightly lower, it remains highly effective. A report by the CORE Group57found that 65% of patients who underwent bilateral ECT 3 times per week achieved remission by the tenth treatment. In the entire sample, 75% of patients achieved remission by the end of the course, reinforcing the impressive efficacy rate of ECT.
What Is Treatment-Resistant Depression?
It describes a person who has major depressive disorder who does not respond adequately to antidepressant therapy within a stated time frame. The definitions vary slightly and specifically refer to non-responsiveness to medication therapy, not psychological therapy. An insufficient response to treatment has historically been referred to as “no clinical response whatsoever.”
How to treat major depressive disorder?
Treatment-resistant depression is complex. There is no one, foolproof way to treat this condition. It takes patience, gra ce, and a lot of support from professionals who are experienced in managing this type of mental health disorder. The first three areas where the work will start are generally medication adjustment, talk therapy, and coping mechanisms.
What is a substitute for antidepressants?
One substitute for antidepressants is the medication ketamine. This medication was originally used as an anesthetic. However, it has since been known to act as a pain reliever and a sedative. Additionally, it affects the part of the brain that deals with depression.
How long does it take for ketamine to work?
The effects of using this medication can be experienced immediately, which is an advantage over most medications that can take up to two months to work.
What is the most effective type of psychotherapy for depression?
The most effective type of psychotherapy for depression is talk therapy that includes cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT).
How long does it take for a low dose of a med to be effective?
Often, doctors will start with a low-dose medication and increase the dose as needed after a minimum of 6-8 weeks. Patients who are non-compliant. This refers to those who do not take the medication as directed. Patients who may be misdiagnosed with depression in the first place.
What does it mean when you are not getting relief from depression?
When someone is not getting the positive results from depression treatment, they are losing out on the ability to enjoy things they once loved.
What are the most effective NMDA agonists?
The most effect treatments were NMDA agonists: Ketamine and two antibiotics: Minocycline and d-cycloserine. These all had effect sizes around 1.5
What is the effect size of psychotherapy?
Although only 10% of the trials were psychotherapy studies, including CBT, mindfulness, and psychodynamic, the average effect size for therapy was 1.4, compared to an average of 1.2 for medications.
What is the best medication for bipolar?
Lithium is one of the most effective medications for bipolar…. What Works Best in Treatment Resistant Depression Part 2 May 3, 2021 A new study looked at what works best after two antidepressants have failed, and it….
What is BPSD in psychology?
BPSD (behavioral and psychological symptoms of dementia)
What is the strongest medication for depression?
Lithium, atypical antipsychotics, ketamine, thyroid… these consistently rank among the most effective medications for treatment resistant depression, but which is the strongest?
How long does it take to do Superman pose?
This studyfound that simply striking a Superman (or Wonder Woman) pose and holding this very upright and chest-out pose for two minutes creates remarkably energizing physiological changes. See herefor more on this technique, including a rebuttal to its detractors. Because this technique is free, takes just two minutes, can be done multiple times a day, and has no downsides, it certainly can be worth a try.
What is the difference between a fight road and a folding road?
Folding leads to depression. Fight Road breeds anger. Freeze (no longer trying to solve the problem but still aware of it) sustains anxiety. Flee leads to addictive and compulsive outcomes. Only the Find Solutions Road leads to a return of well-being.
What test can be used to determine if a person is depressed?
Scientists are developing a blood test that will be able to determine if a depressed person has low levels of this molecule.
Why do people take the fold road?
Taking the Fold Road in response to getting something you want fosters depression.
What is the term for the hairy structure in the hippocampus?
There may be a phenomenon having to do with the length of cilia (tiny hair-like structures) in neurons in the hippocampus that is associated with depressed emotional states.
Why is power important in depression?
Power Poses to combat treatment resistant depression's sense of insufficient power. Interestingly, a study from Harvard confirms the importance of reempowerment in over-coming depression and low self-confidence .
Who wrote the scientific sentence "When the researchers examined euthanised animals' brains under a microscope,?
Enter science writer Peter Dockrill. Writing in a recent issue of Science Alert, Dockrill translates the Japanese neuroscientsts’ technical sentence as follows: “When the researchers examined euthanised animals' brains under a microscope, they found that RGS8-boosted mice demonstrated longer neuronal cilia (in which MCHR1 is localised) than regular mice did, in a region of the hippocampus called CA1.”
How long is a CBT session?
A typical course of CBT is around 12-16 weekly sessions of about 45 minutes each. During this time a person will learn to plan and complete activities that bring enjoyment and reward, and to change thought patterns that contribute to depression. article continues after advertisement.
Why do mental health professionals practice outside of insurance?
Many mental health professionals practice outside of insurance networks because of the low payments in-network providers must agree to and the administrative burden, among other factors . The out-of-pocket cost for either treatment can be considerable, even prohibitive—often $120-200 for a CBT session and $100-180 for brief psychiatry check-ups. Getting medication from one's primary care doctor makes insurance coverage more likely, but s/he probably has less expertise in treating depression compared to a psychiatrist.
Why do people choose not to take medication?
Some people decide against medication because of the side effects, while others choose to tolerate them because of the medication's benefits. While people often promote therapy as having "no side effects," this is not strictly true.
What is the best treatment for depression?
Based on these and other studies, the American Psychiatric Association (APA) recommends psychotherapy or medication as first-line treatments for mild to moderate depression; for individuals with more severe depression they recommend a combination of both. 2.
How long does a syringe last?
Thus the full course of treatment may last from 3 to 6 months, and longer in some cases if needed.
What are the side effects of Zoloft?
Some of the most common side effects associated with SSRIs–Prozac, Zoloft, Paxil, etc.—are nausea, weight gain, agitation, insomnia, loss of sex drive, and difficulty reaching orgasm.
How long does a person with depression need to be treated?
Thus the full course of treatment may last from 3 to 6 months, and longer in some cases if needed . The APA recommends that those with a long history of depression continue to receive therapy on an ongoing basis, often with a reduction in frequency of sessions.
Why do people use ECT?
ECT is usually used for people who don't get better with medications, can't take antidepressants for health reasons or are at high risk of suicide.
What is the term for depression that begins a week before your period?
Premenstrual dysphoric disorder. This involves depression symptoms associated with hormone changes that begin a week before and improve within a few days after the onset of your period, and are minimal or gone after completion of your period. Other depression disorders.
What is the term for a disorder that develops during the teenage years?
This disorder typically develops into depressive disorder or anxiety disorder during the teen years or adulthood. Persistent depressive disorder. Sometimes called dysthymia (dis-THIE-me-uh), this is a less severe but more chronic form of depression.
What are the characteristics of a melancholic personality?
Melancholic features — severe depression with lack of response to something that used to bring pleasure and associated with early morning awakening, worsened mood in the morning, major changes in appetite, and feelings of guilt, agitation or sluggishness. Atypical features — depression that includes the ability to temporarily be cheered by happy ...
How to help depression?
But in addition to professional treatment, these self-care steps can help: Stick to your treatment plan. Don't skip psychotherapy sessions or appointments. Even if you're feeling well, don't skip your medications.
What is a specifier in psychology?
A specifier means that you have depression with specific features, such as: Anxious distress — depression with unusual restlessness or worry about possible events or loss of control. Mixed features — simultaneous depression and mania, which includes elevated self-esteem, talking too much and increased energy.
How to deal with depression and change behaviors?
Identify negative beliefs and behaviors and replace them with healthy, positive ones. Explore relationships and experiences, and develop positive interactions with others. Find better ways to cope and solve problems. Identify issues that contribute to your depression and change behaviors that make it worse.
