
What is the best treatment for functional dyspepsia?
The diagnosis and treatment of functional dyspepsia is often clinically challenging due to factors such as the heterogeneity of upper gastrointestinal symptoms and the generalized poor response to currently available treatment options.
How dangerous is functional dyspepsia?
Jul 06, 2020 · Acid reflux, the stomach, and the small intestine Because there is no clear cause for symptoms, treating FD is challenging as well. The first step in treatment is usually to check for bacteria called H. pylori that can cause inflammation of the stomach and small intestine. If H. pylori is present, the person is treated with a course of antibiotics.
What is the best treatment to alleviate dyspepsia?
Aug 27, 2017 · Although H. pylori infection may affect gastroduodenal motility and viscerosensory function, the precise mechanism of its benefits in functional dyspepsia is not clear. 15 –18 Therefore, although H. pylori eradication does not have a direct beneficial effect on of the symptoms of functional dyspepsia, recent studies have reported that long-term H. pylori …
What is the prognosis for functional dyspepsia?
Nov 08, 2021 · The treatments of functional dyspepsia improve most of its symptoms. However, no treatment provides a permanent cure for FD. A. Don’t Overthink it. Patients with a functional gut disease like functional dyspepsia are more likely to be stressed and anxious. Functional dyspepsia is a benign medical condition that doesn’t lead to severe complications.
How I cured my functional dyspepsia?
How long does it take to cure functional dyspepsia?
What aggravates functional dyspepsia?
Is functional dyspepsia lifelong?
What is the difference between dyspepsia and functional dyspepsia?
How do you treat functional dyspepsia naturally?
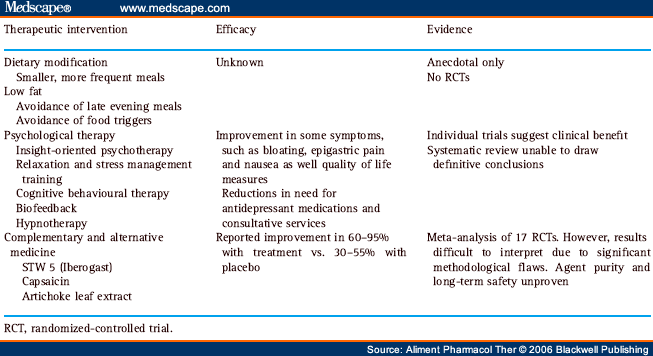
- Eat smaller, more frequent meals. Having an empty stomach can sometimes produce functional dyspepsia. ...
- Avoid trigger foods. Some foods may trigger functional dyspepsia, such as fatty and spicy foods, carbonated beverages, caffeine, and alcohol.
- Chew your food slowly and thoroughly.
How is functional dyspepsia diagnosis?
Can functional dyspepsia cause shortness of breath?
Do probiotics help functional dyspepsia?
Can anxiety cause functional dyspepsia?
What is the best treatment for dyspepsia?
- Over-the-counter gas remedies. ...
- Medications to reduce acid production. ...
- Medications that block acid 'pumps. ...
- Antibiotics. ...
- Low-dose antidepressants. ...
- Prokinetics. ...
- Medications to relieve nausea (anti-emetics).
What is the difference between functional dyspepsia and gastroparesis?
What is the best treatment for FD?
Tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs) are another class of medications that are often used to treat FD. In some people, FD is thought to be due to an abnormal brain-gut interaction. Specifically, these individuals may have overactive sensory nerves supplying the GI tract, or abnormal processing of pain by the brain.
What is the first step in treating FD?
Because there is no clear cause for symptoms, treating FD is challenging as well. The first step in treatment is usually to check for bacteria called H. pylori that can cause inflammation of the stomach and small intestine. If H. pylori is present, the person is treated with a course of antibiotics.
What does FD mean in medical terms?
Functional dyspepsia (FD) is a common condition, loosely defined by some physicians as a stomach ache without a clear cause. More specifically, it is characterized by the feeling of fullness during or after a meal, or a burning sensation in the mid-upper abdomen, just below the rib cage (not necessarily associated with meals). The symptoms can be severe enough to interfere with finishing meals or participating in regular daily activities.
What is the treatment for H. pylori?
If H. pylori is present, the person is treated with a course of antibiotics. For those without H. pylori infection, or with symptoms that persist despite elimination of this bacteria, the next step is usually a trial of a proton-pump inhibitor (PPI). PPIs, which include omeprazole (Prilosec), esomeprazole (Nexium), and lansoprazole (Prevacid), ...
Can TCAs be used for FD?
When used for FD, TCAs are typically prescribed at a low dose, where they do not exert any significant antidepressant effect. However, a large proportion of people with FD also have ongoing anxiety, depression, or other mental health conditions.
What happens when you eat?
When you eat, the top part of your stomach relaxes, expanding your stomach volume to accommodate your meal. Many FD patients have an impaired accommodation reflex, and this may contribute to the post-meal discomfort experienced by many people with FD.
Is FD a dangerous condition?
FD remains a significant challenge for patients and physicians alike. Some may take comfort that FD is not a dangerous condition in terms of putting patients at increased risk of death.
What is the treatment for functional dyspepsia?
The functional dyspepsia subtypes, epigastric pain syndrome (EPS) and PDS, require different treatment; patients with EPS benefit from acid secretion inhibitors, whereas patients with PDS benefit from prokinetic drugs such as mosapride and acotiamide.2Other treatment options in EPS include H2-blockers and PPIs.
What is the best treatment for dyspepsia?
Several studies have reported that anti-acid therapy and prokinetic agents are effective for certain populations with functional dyspepsia. H2-blocker therapy . H2-blockers (histamine H2receptor antagonists) have been used as a first-line therapeutic drug for functional dyspepsia.
What are the symptoms of dyspepsia?
Based on the Rome III classification criteria, the main symptoms of functional dyspepsia consist of bothersome postprandial fullness, early satiety, epigastralgia, and epigastric bur ning.1In 2014, the guideline for functional dyspepsia ...
Is metoclopramide effective for dyspepsia?
Standard drug treatments: prokinetic drugs. Previous studies have reported that metoclopramide is not effective in functional dyspepsia.36,37By contrast, a placebo-controlled trial reported a beneficial effect of domperidone (10–20 mg three times daily) with placebo.38.
What is vonoprazan used for?
In Japan, a new drug, vonoprazan, a potassium-competitive acid blocker (P-CAB) is used for the treatment of acid-related disease such as reflux esophagitis and gastric ulcers.
What is the best treatment for dyspepsia?
Herbal remedies that may be of some benefit for functional dyspepsia include a combination of peppermint and caraway oils, which relieved pain symptoms in a 4-week trial. Iberogast (STW5), a therapy containing extracts of nine herbs, may improve intestinal motility and relieve gastrointestinal spasms.
How to get rid of dyspepsia?
Nothing but acid in your stomach may make you feel sick. Try eating a small snack, such as a cracker or a piece of fruit. Avoid skipping meals. Avoid large meals and overeating. Eat smaller meals more frequently.
What is the procedure called when you insert a tube down your throat?
An endoscopy procedure involves inserting a long, flexible tube (endoscope) down your throat and into your esophagus. A tiny camera on the end of the endoscope lets your doctor examine your esophagus, stomach and the beginning of your small intestine (duodenum).
What is the camera on the endoscope?
A tiny camera on the end of the endoscope lets your doctor examine your esophagus, stomach and the beginning of your small intestine (duodenum). Your doctor will likely review your signs and symptoms and perform a physical examination. A number of diagnostic tests may help your doctor determine the cause of your discomfort ...
What is the test for H. pylori?
H. pylori testing may use your blood, stool or breath. Endoscopy. A thin, flexible, lighted instrument (endoscope) is passed down your throat so that your doctor can view your esophagus, stomach and the first part of your small intestine (duodenum).
Can you use complementary medicine for dyspepsia?
People with functional dyspepsia often turn to complementary and alternative medicine to help them cope. Further studies are needed before complementary and alternative treatments can be recommended, but when used along with your doctor's care, they may provide relief from your signs and symptoms.
What is STW5?
Iberogast (STW5), a therapy containing extracts of nine herbs, may improve intestinal motility and relieve gastrointestinal spasms. Rikkunshito, a Japanese herbal remedy, also appeared beneficial, with significant improvements in abdominal pain, heartburn and bloating than was reported with placebo.
What is functional dyspepsia?
By definition, functional dyspepsia is diagnosed in the absence of an organic etiology for the dyspepsia symptoms. As outlined previously, patients with functional dyspepsia report a range of symptoms that can vary greatly in severity, and symptoms are not a reliable way to differentiate organic from functional dyspepsia. Thus, the goal of evaluation is to rule out organic etiologies for the patient’s symptoms. Evaluation is based on patient age, presence of alarm features, severity of symptoms, risk of malignancy, and physical examination findings. Esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD) is recommended in patients age 60 years or older or in any patient with more than 1 alarm feature (Table), a rapidly progressive alarm feature, clinically significant weight loss (typically >5% of baseline body weight), or overt gastrointestinal bleeding. EGD with gastric biopsies is recommended in any patient age 60 years or older with dyspepsia due to the increased risk of cancer in this age group. In order to ensure detection of H pylori infection, gastric biopsies should be obtained from the lesser curvature of the antrum, greater curvature of the antrum, lesser curvature of the body, greater curvature of the body, and incisura angularis. 24 Duodenal biopsies should be obtained in immunosuppressed patients, particularly bone marrow transplant patients, to exclude graft vs host disease or infection. Additionally, given increasing evidence of duodenal pathology driving functional dyspepsia symptoms, an argument can be made to obtain duodenal biopsies in all patients undergoing EGD for evaluation of dyspepsia.
Is PPI therapy effective for dyspepsia?
However, studies have shown PPI therapy to be effective in treating functional dyspepsia in only 14% of patients. 30,31 A meta-analysis of 10 randomized, controlled trials (RCTs) demonstrated a relative risk of persistent symptoms despite PPI therapy of 0.87 (95% CI, 0.08-0.96) and a NNT of 10. 32 The same meta-analysis also evaluated H 2 -receptor antagonists and demonstrated a relative risk of 0.77 (95% CI, 0.65-0.92) and a NNT of 7. The quality of the studies of the H 2 -receptor antagonists was lower, and many of the trials used in the meta-analysis were performed prior to Rome III classification.
What are the symptoms of dyspepsia?
Dyspepsia symptoms include a constellation of upper gastrointestinal complaints, such as belching, postprandial fullness, early satiety, epigastric pain, and epigastric burning. Functional dyspepsia is diagnosed when an organic etiology for the symptoms is not identified.
Is dyspepsia a heterogeneous disorder?
Despite the Rome IV definition, diagnosis of functional dyspepsia often remains challenging due to the inherent heterogeneity in symptoms as well as the significant overlap in symptoms with other disorders, such as gastroparesis, irritable bowel syndrome, and gastroesophageal reflux disease.
What is the prevalence of dyspepsia?
The community prevalence of dyspepsia is typically quoted in the range of 20% to 40% , and the disorder accounts for 3% to 5% of primary care visits. 7-12 Of patients with investigated dyspepsia, approximately 70% have negative endoscopic studies and approximately 50% to 60% are subsequently classified as functional dyspepsia. 12,13 Admittedly, estimating the prevalence of functional dyspepsia is challenging due to variable diagnostic criteria used in prevalence studies, the overlap in symptoms with other disorders, and inconsistent interpretation of dyspepsia symptoms. Risk factors include female sex, increasing age, Helicobacter pylori infection, high socioeconomic status, smoking, and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug use.
Is dyspepsia a pathophysiologic disorder?
The etiology of dyspepsia has been poorly defined; however, numerous pathophysiologic mechanisms, most of which are directed at gastroduodenal pathways, have been proposed to explain the disorder. Many mechanisms are currently being investigated as potential causes of functional dyspepsia symptoms.
Does dyspepsia cause anxiety?
Psychological distress has been associated with dyspepsia, with research showing both that distress and anxiety can precede symptoms and that symptoms can induce distress and anxiety. Thus, a bidirectional gut-brain pathway mechanism has been proposed. 2
When To Go To The Doctor For Functional Dyspepsia?
When you have persistent symptoms that make you worry, you should seek immediate medical attention. This includes
Common Symptoms Of Functional Dyspepsia
The meaning of functional dyspepsia is recurring signs and symptoms of indigestion that have no obvious cause. The most common symptoms of functional dyspepsia include:

Diagnosis
Treatment
Clinical Trials
Alternative Medicine
Preparing For Your Appointment