Treatment depends on what area of the body is affected. You may be given medicine to treat nausea, vomiting, indigestion, or diarrhea. You may also be given medicine to treat problems in the mouth, or pain in the area that receives radiation.
Full Answer
What is an radiotherapy treatment?
All data were related to given radiation dose, and all outcome measures at each time point therefore relate to the same radiation dose (i.e., not to when the patient was included in the study). Results: Opioids were used by 78% of the patients. Most of the patients experienced only mild pain (NRS 0-4), although the majority developed mucositis ...
Can radiation be used to treat bone pain?
If the radiation damages the lining of the bladder, radiation cystitis can be a long-term problem that causes blood in the urine or pain when passing urine. Urinary incontinence. Radiation treatments for certain cancers, such as prostate and bladder cancer, may make you unable to control your urine or have leakage or dribbling.
How painful is internal radiation therapy?
Apr 20, 2022 · You may also be given medicine to treat problems in the mouth, or pain in the area that receives radiation. Lotions, ointments, or creams may be given to treat skin problems caused by radiation therapy. How can I manage my symptoms? Manage your fatigue. Do short periods of physical activity to help decrease fatigue.
Can radiation therapy relieve pain from spinal cancer metastases?
Jan 08, 2019 · External beam radiation may shrink tumors to treat pain and other problems caused by the tumor, such as trouble breathing or loss of bowel and bladder control. Pain from cancer that has spread to the bone can be treated with systemic radiation therapy drugs called radiopharmaceuticals. Types of cancer that are treated with radiation therapy

Does radiation cause pain at site?
Sore skin. In some people, radiotherapy can make the skin sore and red (similar to sunburn), darker than normal or dry and itchy. This tends to start 1 to 2 weeks after treatment begins. Tell your care team if you notice any soreness or changes to your skin.
Is it normal to have pain after radiation treatment?
Types of pain you may feel following cancer treatment include: Skin sensitivity where you received radiation. This type of pain is quite common and can last for many months.
How long does nerve pain last after radiation?
It can get better as nerves heal over time. But for some people, it can last months or even years. It depends on how much chemotherapy you had and the type you had. It can also depend on where the tumor was and the type of radiation or surgery that was done.
How long does it take for pain to go away after radiation?
For some people who get drug treatment, the pain gets worse for a few days right afterward, but that's rare. Usually it takes between 1 and 4 weeks to work, and the relief you get from it can last up to 18 months.
Can radiation cause severe pain?
Pain from external radiation depends on the part of the body that's treated. Radiation can cause skin burns, mucositis (mouth sores), and scarring – all of which can cause pain. The throat, intestine, and bladder are also prone to radiation injury, and you may have pain if these areas are treated.Jan 3, 2019
How do you manage radiation pain?
You should not use a heating pad or warm compress to relieve pain in any area treated with radiation. Mild pain medicine may be enough for some people. If you have severe pain, ask the doctor about prescription drugs or other methods of relief.Oct 5, 2017
Can radiation cause aching legs?
Radiation treatment can make your muscles and soft tissues (for example, ligaments and skin) stiff and tight. This condition is called radiation induced fibrosis. When your muscles are not moving properly they can cause pain or limit movement in other parts of your body.
What is a radiating pain?
The term “Radiating Pain” refers to pain that travels from one body part to another. This pain starts in one place and then spreads into a broader area of the body 1. For example, people with a herniated disc may develop pain in the lower back. This pain will travel with the sciatic nerve that runs down the leg.
What are the symptoms of nerve pain?
10 Signs You May Be Suffering from Nerve PainNumbness or tingling in feet and hands.Loss of balance and falling.Throbbing and sharp pain.Extreme sensitivity to touch.Dropping things with your hands.Muscle weakness.Heavy feeling in arms and legs.Dramatic drop in blood pressure.More items...•Mar 21, 2017
What is the most common acute side effect of radiation treatment?
Fatigue is the most common acute side effect of radiation therapy. It is believed to be caused by the large amount of energy that is used by the body to heal itself in response to radiation therapy. Most people begin to feel fatigued about 2 weeks after radiation treatments begin.4 days ago
Do tumors grow back after radiation?
Normal cells close to the cancer can also become damaged by radiation, but most recover and go back to working normally. If radiotherapy doesn't kill all of the cancer cells, they will regrow at some point in the future.Jul 6, 2020
If You’Re Getting Radiation Therapy to The Brain
People with brain tumors often get stereotactic radiosurgery (radiation given in one large dose) if the cancer is in only one or a few sites in the...
If You’Re Getting Radiation Therapy to The Head Or Neck
People who get radiation to the head and neck might have side effects such as: 1. Soreness (or even open sores) in the mouth or throat 2. Dry mouth...
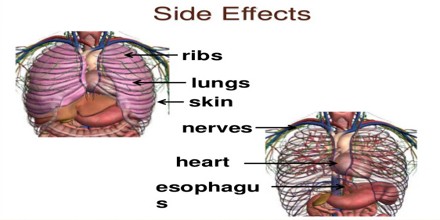
If You’Re Getting Radiation Therapy to The Breast
If you have radiation to the breast, it can affect your heart or lungs as well causing other side effects.
If You’Re Getting Radiation Therapy to The Chest
Radiation treatment to the chest may cause side effects such as: 1. Sore throat 2. Swallowing problems 3. Loss of appetite 4. Cough 5. Shortness of...
If You’Re Getting Radiation Therapy to The Abdomen (Belly)
If you are getting radiation to your stomach or some part of the abdomen (belly), you may have side effects such as: 1. Nausea 2. Vomiting 3. Belly...
If You’Re Having Radiation Therapy to The Pelvis
Radiation therapy to the pelvis (for example, as treatment for bladder, ovarian, or prostate cancer) can cause side effects such as: 1. Bladder pro...
What Are The Side Effects of Radiation Therapy?
The side effects of radiation therapy depend on the area of the body that receives radiation. Early side effects happen shortly after you receive r...
What Causes The Side Effects of Radiation Therapy?
Radiation can destroy or harm healthy tissues during treatment. This may cause side effects to happen anywhere in the body where radiation therapy...
How Are Side Effects of Radiation Therapy Diagnosed and Treated?
1. Your healthcare provider will ask you about your symptoms and decide if they are side effects of radiation therapy. Radiation therapy may preven...
How Can I Manage My Symptoms?
1. Manage your fatigue. Do short periods of physical activity to help decrease fatigue. Walk for 15 to 30 minutes each day. You can also take a sho...
Where Can I Find More Information?
1. 1. American Cancer Society250 Williams StreetAtlanta , GA 30303Phone: 1- 800 - 227-2345Web Address: http://www.cancer.org 2. 1. National Cancer...
When Should I Seek Immediate Care?
1. Your heart feels like it is beating faster than usual or you have shortness of breath. 2. You have a headache, dizziness, or blurred vision. 3....
When Should I Contact My Healthcare Provider?
1. You have a fever. 2. The area of your skin where you received treatment blisters, peels, becomes more painful, or drains fluid. 3. You have trou...
What is the best treatment for radiation?
One way to reduce side effects is by using radioprotective drugs, but these are only used for certain types of radiation given to certain parts of the body. These drugs are given before radiation treatment to protect certain normal tissues in the treatment area. The one most commonly used today is amifostine. This drug may be used in people with head and neck cancer to reduce the mouth problems caused by radiation therapy.
What happens if you get radiation treatment?
After a few weeks, your skin might become dry, flaky, or itchy, or it may peel. This is sometimes called radiation dermatitis.
How long does radiation side effects last?
Remember that the type of radiation side effects you might have depends on the prescribed dose and schedule. Most side effects go away within a few months of ending treatment. Some side effects may continue after treatment ends because it takes time for the healthy cells to recover from radiation. Side effects might limit your ability ...
What are the side effects of brachytherapy?
If your treatment includes brachytherapy (internal radiation implants), you might notice breast tenderness, tightness, redness, and bruising. You may also have some of the same side effects that happen with external radiation treatment.
How long does it take for radiation to cause side effects?
Late side effects can take months or even years to develop. They can occur in any normal tissue in the body that has received radiation. The risk of late side effects depends on the area treated as well as the radiation dose that was used. Careful treatment planning can help avoid serious long-term side effects.
Can radiation therapy cause low blood count?
Rarely, radiation therapy can cause changes in your blood count levels. These blood cells help your body fight infection and prevent bleeding. If your blood tests show low blood counts, your treatment might be stopped for a week or so to allow your blood counts to return to normal. This side effect is more likely if you’re also getting chemotherapy.
How long does it take for brain tumors to show up?
Side effects depend on where the radiation is aimed. Some side effects might show up quickly, but others might not show up until 1 to 2 years after treatment.
What is the treatment for radiation?
You may be given medicine to treat nausea, vomiting, indigestion, or diarrhea. You may also be given medicine to treat problems in the mouth, or pain in the area that receives radiation. Lotions, ointments, or creams may be given to treat skin problems caused by radiation therapy.
How to treat mouth sores from radiation?
Use medicines as directed to decrease pain caused by mouth sores, and relieve dryness. Do not smoke or use products with nicotine. Drink plenty of liquids as directed. Ask how much liquid to drink each day and which liquids are best for you . Liquids may prevent dehydration caused by the side effects of radiation.
What are the side effects of radiation therapy?
Late side effects of radiation therapy may be permanent. Early and late side effects may include any of the following: Fatigue or loss of energy. Pain in the area of the body that is being treated. Skin changes such as a sunburn or red skin. Hair loss in the area receiving radiation. Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, or indigestion.
How to manage radiation side effects?
You can do the following to help get enough nutrition and manage the side effects of radiation: Eat 6 to 8 small meals per day. Eat foods high in protein and calories. Do not eat foods that increase side effects.
How to reduce fatigue?
Do short periods of physical activity to help decrease fatigue. Walk for 15 to 30 minutes each day. You can also take a short bike ride or ride an exercise bike. Take short naps throughout the day. Do not sleep for more than 1 hour at a time during the day.
Does radiation cause low blood count?
Radiation therapy may prevent the bone marrow from making red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. This may cause low blood counts. Low blood counts are diagnosed with a blood test. Treatment depends on what area of the body is affected.
What is oral rehydration solution?
You may need an oral rehydration solution (ORS). An ORS contains water, salts, and sugar that are needed to replace lost body fluids. Ask what kind of ORS to use, how much to drink, and where to get it. Wear a wig, head scarf, or hat to cover your head.
What is radiation therapy?
Radiation therapy is used to treat cancer and ease cancer symptoms. When used to treat cancer, radiation therapy can cure cancer, prevent it from returning, or stop or slow its growth. When treatments are used to ease symptoms, they are known as palliative treatments.
What is external beam radiation therapy?
External Beam Radiation Therapy. External beam radiation therapy comes from a machine that aims radiation at your cancer. The machine is large and may be noisy. It does not touch you, but can move around you, sending radiation to a part of your body from many directions.
How does radiation help cancer?
When radiation is combined with surgery, it can be given: 1 Before surgery, to shrink the size of the cancer so it can be removed by surgery and be less likely to return. 2 During surgery, so that it goes straight to the cancer without passing through the skin. Radiation therapy used this way is called intraoperative radiation. With this technique, doctors can more easily protect nearby normal tissues from radiation. 3 After surgery to kill any cancer cells that remain.
What are the two types of radiation?
There are two main types of radiation therapy, external beam and internal . The type of radiation therapy that you may have depends on many factors, including: The type of cancer. The size of the tumor. The tumor’s location in the body. How close the tumor is to normal tissues that are sensitive to radiation.
How long does it take for cancer cells to die from radiation?
It takes days or weeks of treatment before DNA is damaged enough for cancer cells to die. Then, cancer cells keep dying for weeks or months after radiation therapy ends.
Does radiation therapy cause cancer?
Radiation Therapy Can Cause Side Effects. Radiation not only kills or slows the growth of cancer cells, it can also affect nearby healthy cells. Damage to healthy cells can cause side effects. Learn more about the side effects of radiation therapy.
What is brachytherapy in cancer?
Like external beam radiation therapy, brachytherapy is a local treatment and treats only a specific part of your body.
A Painful Location
When cancer spreads from its original location, metastatic tumors can arise in many distant sites. Bone is a common site of metastasis for a number of cancer types.
Boosting the Radiation Dose
A previous trial didn’t show a difference between SBRT and conventional radiation therapy in their ability to relieve spinal pain#N#Exit Disclaimer#N#in people with three or fewer sites of spinal metastases.
Double the Pain Relief
Three months after treatment, 35% of people in the SBRT group reported that their spinal pain was gone, compared with 14% of the people who received conventional radiation therapy.
What is radiation therapy called?
But it’s also a way to relieve some of the pain the disease can cause. This is called “palliative” radiation therapy. Your doctor might recommend it to ease any pain from skin lesions, tumors, or cancer that has spread to your bones.
How long does radiation therapy last?
Usually it takes between 1 and 4 weeks to work, and the relief you get from it can last up to 18 months. further reading. A Visual Guide to Prostate Cancer. Radiation for Cancer Pain: How Does It Work? Radiation Therapy for Cancer. What You Need to Know About Radiation Therapy for Colorectal Cancer.
How does radiation work?
They can also cause pain when they grow into or destroy tissues around them. Radiation works by killing cancer cells, which makes tumors smaller. That can ease painful pressure on body parts in the area.
How long does it take for a syringe to work?
For some people who get drug treatment, the pain gets worse for a few days right afterward, but that’s rare. Usually it takes between 1 and 4 weeks to work, and the relief you get from it can last up to 18 months. further reading.
How is radiation given?
Radiation therapy can be given in 3 ways: 1 External radiation (or external beam radiation): uses a machine that directs high-energy rays from outside the body into the tumor. It’s done during outpatient visits to a hospital or treatment center. It's usually given over many weeks and sometimes will be given twice a day for several weeks. A person receiving external radiation is not radioactive and does not have to follow special safety precautions at home. 2 Internal radiation: Internal radiation is also called brachytherapy. A radioactive source is put inside the body into or near the tumor. With some types of brachytherapy, radiation might be placed and left in the body to work. Sometimes it is placed in the body for a period of time and then removed. This is decided based on the type of cancer. Special safety precautions are needed for this type of radiation for a period of time. But it's important to know if the internal radiation is left in the body, after a while it eventually is no longer radioactive. 3 Systemic radiation: Radioactive drugs given by mouth or put into a vein are used to treat certain types of cancer. These drugs then travel throughout the body. You might have to follow special precautions at home for a period of time after these drugs are given.
How long does radiation therapy take?
It’s done during outpatient visits to a hospital or treatment center. It's usually given over many weeks and sometimes will be given twice a day for several weeks .
What is the best treatment for cancer?
Radiation may be used by itself in these cases to make the cancer shrink or completely go away. In some cases, chemotherapy or other anti-cancer drugs may be given first. For other cancers, radiation may be used before surgery to shrink the tumor ...
How does cancer spread?
Cancer can spread from where it started to other body parts. Doctors often assume that a few cancer cells might already have spread even when they can’t be seen on imaging scans like CT scans or MRIs. In some cases, the area where the cancer most often spreads to may be treated with radiation to kill any cancer cells before they grow into tumors. For instance, people with certain kinds of lung cancer may get radiation to the head, even when there is no cancer known to be there, because their type of lung cancer often spreads to the brain. This is done to help prevent cancer from spreading to the head even before it can. Sometimes, radiation to prevent future cancer can be given at the same time that radiation is given to treat existing cancer, especially if the area the cancer might spread to is close to the tumor itself.
What is the purpose of radiation treatment?
If a person's cancer has returned (recurred), radiation might be used to treat the cancer or to treat symptoms caused by advanced cancer. Whether radiation will be used after recurrence depends on many factors. For instance, if the cancer has come back in a part of the body that has already been treated with radiation, it might not be possible to give more radiation in the same place. It depends on the amount of radiation that was used before. In other instances, radiation might be used in the same area of the body or a different area. Some tumors do not respond as well to radiation, so radiation might not be used even if they recur.
Can radiation therapy be used for cancer?
Most types of radiation therapy don’t reach all parts of the body, which means they’re not helpful in treating cancer that has spread to many places within the body. Still, radiation therapy can be used to treat many types of cancer either alone or in combination with other treatments. While it's important to remember each cancer ...
What is systemic radiation?
Systemic radiation: Radioactive drugs given by mouth or put into a vein are used to treat certain types of cancer. These drugs then travel throughout the body. You might have to follow special precautions at home for a period of time after these drugs are given.
What to expect when getting radiation therapy?
What to Expect When Having Radiation Therapy. It is normal to feel worried or overwhelmed when you learn that you will need radiation therapy. However, learning more about this type of cancer treatment may help you feel more prepared and comfortable.
How long does radiation therapy last?
It is the most common radiation therapy treatment for cancer. Each session is quick, lasting about 15 minutes. Radiation does not hurt, sting, or burn when it enters the body.
What is informed consent for radiation?
Giving permission for radiation therapy. If you choose to receive radiation therapy, your health care team will ask you to sign an "informed consent" form. Signing the document means: Your team gave you information about your treatment options. You choose to have radiation therapy.
How often should you check for radiation?
During your treatment, your radiation oncologist will check how well it is working. Typically, this will happen at least once a week. If needed, they may adjust your treatment plan.
What is simulation in radiation therapy?
Simulating and planning treatment. Your first radiation therapy session is a simulation. This means it is a practice run without giving radiation therapy. Your team will use imaging scans to identify the tumor location.
What is a thermoplastic mask?
For radiation therapy to the head or neck, you may receive a thermoplastic mask. This is a mesh mask that is molded to your face and secured to the table. It gently holds your head in place. It is important for your body to be in the same position for each treatment. Your radiation oncology team cares about your comfort.
What to do after radiation?
Don’t use skin care products on the treated area. They may bother your skin. And some might affect how much radiation your body absorbs. During radiation therapy and for several weeks after, talk to your doctor before you use: 1 Powders 2 Creams 3 Perfumes 4 Deodorants 5 Body oils 6 Ointments 7 Lotions 8 Hair -removal products 9 Home remedies
How long does it take for skin to itch after radiation?
In general, call the doctor if your treated skin: Gets worse. Itches for 2 or more days. Bleeds. Causes pain or discomfort that keeps you from getting sleep. Forms blisters, turns bright red, or becomes crusty.
How to treat a swollen face?
Wear loose clothes made of soft, smooth material. Avoid wearing tight or stiff clothes with rough textures over treated skin. Don’t starch your clothes, either. Don’t scratch, rub, or scrub. If your doctor tells you to cover or bandage the treated skin, use tape that’s made for sensitive skin, like paper tape.
How to protect skin from sun damage?
Shield your skin from sunlight. It may be more sensitive to the sun’s rays. If you can, cover the treated area with clothes that have a dark color or built-in UV protection. Also ask your doctor or nurse if you should put sunscreen on the treated skin.

A Painful Location
Boosting The Radiation Dose
- A previous trial didn’t show a difference between SBRT and conventional radiation therapy in their ability to relieve spinal painExit Disclaimerin people with three or fewer sites of spinal metastases. But there were several key differences between that trial and the current study, Dr. Sahgal explained. The previous trial used a lower dose of SBRT, given in a single session. The current st…
Double The Pain Relief
- Three months after treatment, 35% of people in the SBRT group reported that their spinal pain was gone, compared with 14% of the people who received conventional radiation therapy. This benefit was sustained over time. At 6 months, 32% of people in the SBRT group were still pain-free, compared with 16% of the conventional radiation group. “That’s a...
Further Pushing The Limits
- “It isn’t surprising that a higher radiation dose is better, but [modern] SBRT technology is what allowed that dose to be delivered safely,” said Dr. Buchsbaum. “In short, careful patient selection and a higher dose yielded the expected results. “Moving forward, it’s important that practitioners apply this treatment approach on patients with limited spinal metastases, and not the general p…