The number of different treatment groups that we have in any factorial design can easily be determined by multiplying through the number notation. For instance, in our example we have 2 x 2 = 4 groups. In our notational example, we would need 3 x 4 = 12 groups. We can also depict a factorial design in design notation.
Full Answer
How do you estimate the main effect in a factorial design?
Although balanced factorial designs efficiently estimate the main effects by averaging across other effects, their sample sizes grow geometrically as additional interventional components are added. A key element of these three different design strategies is eligibility to be randomized to a treatment arm.
How to calculate the number of treatment groups in a factorial design?
The number of different treatment groups that we have in any factorial design can easily be determined by multiplying through the number notation. For instance, in our example we have 2 x 2 = 4 groups. In our notational example, we would need 3 x 4 = 12 groups. We can also depict a factorial design in design notation.
What is a factorial design in psychology?
Natalie is a teacher and holds an MA in English Education and is in progress on her PhD in psychology. A factorial design is where a study has two independent variables which are also called factors. Learn the definition of and the main effects of factorial design, and study how the main effect of each factor differs from their interaction.
How do I start learning about factorial design?
Probably the easiest way to begin understanding factorial designs is by looking at an example. Let’s imagine a design where we have an educational program where we would like to look at a variety of program variations to see which works best.

What are treatments in factorial design?
A factorial treatment arrangement is one in which the effects of a number of different factors are investigated simultaneously. The treatments include all of the possible combinations of levels that can be formed from the factors being investigated.
How do you find the factorial effect?
In general for factorials the effect of each factor and interaction is:Effect = ( 1 / 2 ( k − 1 ) n ) [contrast of the totals]Variance(Effect) = σ 2 / 2 ( k − 2 ) n.SS(Effect) = (contrast of totals) 2 / 2 k n.
How do you calculate interactions in a factorial design?
1:0811:31Factorial Designs: Main Effects & Interactions - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipNow this particular design can be further called a 2x2 factorial. Design where each of these twosMoreNow this particular design can be further called a 2x2 factorial. Design where each of these twos corresponds to an independent variable and the number of levels actually in that independent variable.
How many main effects does a 2x2x2 factorial design have?
If you had a 2x2x2 design, you would measure three main effects, one for each IV.
How many main effects are there in a 3x3 factorial design?
7 main effects“Descriptive” effects in a 3-way The 3-way -- significant or not -- is always descriptive ! With 7 main effects and interactions (and myriad simple effects) you have to be careful to get the correct part of the design that is “the replication” of an earlier study.
How do you calculate main effects and interactions?
To determine whether there is a main effect of student age, you would need to test whether the 2.5-point difference is greater than you would expect by chance. each mean by the number of scores that contributed to the mean, added those two weighted means together, and then divided by the total number of scores.
What is interaction effect in factorial design?
There is an interaction effect (or just “interaction”) when the effect of one independent variable depends on the level of another.
What is an interaction in a 2x2 factorial design?
To determine if there is an interaction effect between the two independent variables, we simply need to inspect whether or not the lines are parallel: If the two lines in the plot are parallel, there is no interaction effect. If the two lines in the plot are not parallel, there is an interaction effect.
What is factorial effect?
A factorial design allows the effect of several factors and even interactions between them to be determined with the same number of trials as are necessary to determine any one of the effects by itself with the same degree of accuracy.
How many interactions are there in a 3x4 factorial design?
The number of different treatment groups that we have in any factorial design can easily be determined by multiplying through the number notation. For instance, in our example we have 2 x 2 = 4 groups. In our notational example, we would need 3 x 4 = 12 groups.
What is a 3x2 factorial design?
A 2×3 factorial design is a type of experimental design that allows researchers to understand the effects of two independent variables on a single dependent variable. In this type of design, one independent variable has two levels and the other independent variable has three levels.
Example 5.2
This example was constructed so that the marginal means and the overall means are the same as in Example 1. However, it does not have additive structure.
Factorial Designs with 2 Treatment Factors, cont'd
For a completely randomized design, which is what we discussed for the one-way ANOVA, we need to have n × a × b = N total experimental units available. We randomly assign n of those experimental units to each of the a × b treatment combinations.
Testing Hypotheses
We can test the hypotheses that the marginal means are all equal, or in terms of the definition of our effects that the α i 's are all equal to zero, and the hypothesis that the β j 's are all equal to zero. And, we can test the hypothesis that the interaction effects are all equal to zero.
How to understand factorial design?
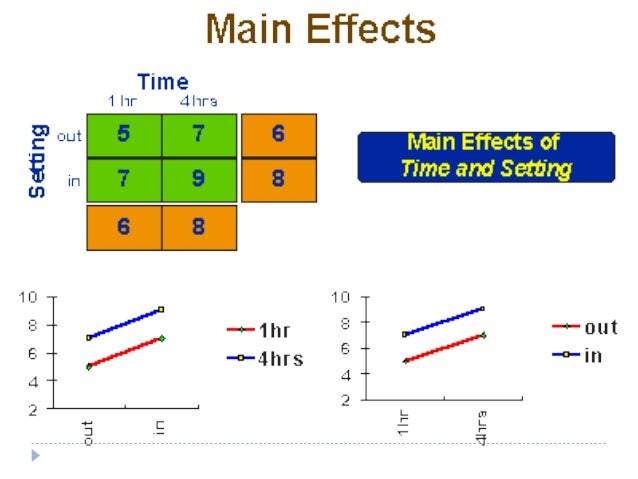
Probably the easiest way to begin understanding factorial designs is by looking at an example. Let’s imagine a design where we have an educational program where we would like to look at a variety of program variations to see which works best. For instance, we would like to vary the amount of time the children receive instruction with one group getting 1 hour of instruction per week and another getting 4 hours per week. And, we’d like to vary the setting with one group getting the instruction in-class (probably pulled off into a corner of the classroom) and the other group being pulled-out of the classroom for instruction in another room. We could think about having four separate groups to do this, but when we are varying the amount of time in instruction, what setting would we use: in-class or pull-out? And, when we were studying setting, what amount of instruction time would we use: 1 hour, 4 hours, or something else?
Why is factorial design important?
Factorial design has several important features. First, it has great flexibility for exploring or enhancing the “signal” (treatment) in our studies. Whenever we are interested in examining treatment variations, factorial designs should be strong candidates as the designs of choice.
What is the main effect?
The Main Effects. A main effect is an outcome that is a consistent difference between levels of a factor. For instance, we would say there’s a main effect for setting if we find a statistical difference between the averages for the in-class and pull-out groups, at all levels of time in instruction.
What is interaction effect?
An interaction effect exists when differences on one factor depend on the level you are on another factor. It’s important to recognize that an interaction is between factors, not levels. We wouldn’t say there’s an interaction between 4 hours/week and in-class treatment.
What is a factorial design study?
Joanne's study has two independent variables, gender and age, and one dependent variable, which type of television program is preferred. When a study has two independent variables, it is a factorial design study. Factorial design gets its name from the fact that independent variables are often called 'factors.'.
What are the main effects of each factor?
The main effects of each factor is how it influences the dependent variable on its own, while interactions are how the factors work together to influence the dependent variable. Learning Outcome. After watching this lesson, you should be able to interpret how main effects are used in factorial design as well as how they contrast to interactions. ...
What does a 5 mean in a box?
Now all that Joanne has to do is fill in the mean, or average, for each of the boxes. For example, let's say that a 5 means that a person prefers live action shows and a 1 means they prefer animated shows. She'd average the numbers for all the 3-year-old boys and put that number in the box for 3-year-old boys.
What is the average score for the row labeled "boys"?
If the average score for the row labeled 'boys' is 1.3 and the average score for the row labeled 'girls' is 4.7, she can see that girls prefer live action shows and boys prefer animated shows. There is a main effect for gender on television preference.
Is interaction more complex than main effects?
Interactions are more complex than main effects, but they can tell us a lot about the world at large. After all, none of us live in a vacuum, and so there are often multiple things that work together to change us. But that doesn't mean that main effects are not as important as interactions.
Why are interventions for geriatric conditions such as injurious falls different from those corresponding to single diseases?
Interventions for geriatric conditions such as injurious falls [1] or disability [2] differ from those corresponding to single diseases because typically more than a single interventional component is used. Accordingly, the interventions often consist of components to modify a number of selected risk factors.
Why is there a small number of subjects eligible for a geriatric health treatment?
As the number of risk factors requiring intervention increases in a geriatric health syndrome, there may be a prohibitively small number of subjects eligible for any particular treatment combination. This affects the generalizability of the results, which depend on the sample in which the trial was conducted.
What is partial factorial design?
As used in the clinical trial literature, the term ‘partial factorial design’ has been used to refer to a trial where the study population is randomized on at least a single factor of interest and a subset of the study population is randomized to one or more factors.
What are the risk factors for fall related injuries?
From pilot or epidemiologic studies, risk factors associated with fall-related injury might include measures of gait speed, balance, lower body strength, and use of a specific medication.
4.1 Introduction
In the completely randomized designs that we have seen so far, the g g different treatments had no special “structure.” In practice, treatments are often combinations of the levels of two or more factors. Think for example of a plant experiment using combinations of light exposure and fertilizer (with yield as response).
4.2 Two-Way ANOVA Model
We assume a general setup with a factor A A with a a levels, a factor B B with b b levels and n n replicates for every combination of A A and B B (a balanced design). Hence, we have a total of N = a⋅b⋅n N = a ⋅ b ⋅ n observations.
4.3 Outlook
We can easily extend the model to more than two factors. If we have three factors A, B and C (with a a, b b and c c levels, respectively), we have 3 3 main effects, 3⋅2/2 = 3 3 ⋅ 2 / 2 = 3 two-way interactions and one so-called three-way interaction. We omit the mathematical model formulation and work directly with the corresponding R code.
What effect did Schnall and colleagues find on moral judgments?
Schnall and colleagues found a main effect of disgust on moral judgments (those in a messy room made harsher moral judgments). However, they also discovered an interaction between private body consciousness and disgust. In other words, the effect of disgust depended on private body consciousness.
What are the main effects of factorial design?
Main Effects. In factorial designs, there are three kinds of results that are of interest: main effects, interaction effects, and simple effects. A main effect is the effect of one independent variable on the dependent variable—averaging across the levels of the other independent variable. Thus there is one main effect to consider ...
What is interaction effect?
There is an interaction effect (or just “interaction”) when the effect of one independent variable depends on the level of another. Although this might seem complicated, you already have an intuitive understanding of interactions. As an everyday example, assume your friend asks you to go to a movie with another friend. Your response to her is, “well it depends on which movie you are going to see and who else is coming.” You really want to see the big blockbuster summer hit but have little interest in seeing the cheesy romantic comedy. In other words, there is a main effect of type of movie on your decision. If your decision to go to see either of these movies further depends on who she is bringing with her then there is an interaction. For instance, if you will go to see the cheesy romantic comedy if she brings her hot friend you want to get to know better, but you will not go to this movie if she brings anyone else, then there is an interaction. Drug interactions are another good illustration of everyday interactions. Many older men take Viagara to assist them in the bedroom, and many men take nitrates to treat angina or chest pain. So each of these drugs is beneficial on its own (there are main effects of each on older men’s well-being). But the combination of these two drugs can be lethal. In other words, there is a very important interaction between Viagara and heart medication that older men need to be aware of to prevent their untimely demise.
What is the main effect of an independent variable?
In a factorial design, the main effect of an independent variable is its overall effect averaged across all other independent variables. There is one main effect for each independent variable. There is an interaction between two independent variables when the effect of one depends on the level of the other. Some of the most interesting research ...
What is simple effect?
This is where simple effects come into play. Simple effects are a way of breaking down the interaction to figure out precisely what is going on. An interaction simply informs us that the effects of at least one independent variable depend on the level of another independent variable.
What is a simple effects analysis?
To summarize, rather than averaging across the levels of the other independent variable, as is done in a main effects analysis, simple effects analyses are used to examine the effects of each independent variable at each level of the other independent variable (s). So a researcher using a 2×2 design with four conditions would need to look ...
What happens if you are high in private consciousness?
If they were high in private body consciousness, then those in the messy room made harsher judgments. If they were low in private body consciousness, then whether the room was clean or messy did not matter. In many studies, the primary research question is about an interaction.

A Simple Example
The Null Outcome
- Let’s begin by looking at the “null” case. The null case is a situation where the treatments have no effect. This figure assumes that even if we didn’t give the training we could expect that students would score a 5 on average on the outcome test. You can see in this hypothetical case that all four groups score an average of 5 and therefore the row and column averages must be 5. You c…
The Main Effects
- A main effect is an outcome that is a consistent difference between levels of a factor. For instance, we would say there’s a main effect for setting if we find a statistical difference between the averages for the in-class and pull-out groups, at all levelsof time in instruction. The first figure depicts a main effect of time. For all settings, the 4 hour/week condition worked better than the …
Interaction Effects
- If we could only look at main effects, factorial designs would be useful. But, because of the way we combine levels in factorial designs, they also enable us to examine the interaction effects that exist between factors. An interaction effectexists when differences on one factor depend on the level you are on another factor. It’s important to recognize that an interaction is between factors…
Summary
- Factorial design has several important features. First, it has great flexibility for exploring or enhancing the “signal” (treatment) in our studies. Whenever we are interested in examining treatment variations, factorial designs should be strong candidates as the designs of choice. Second, factorial designs are efficient. Instead of conducting a se...