
Medication
Six tips for preventing snake bites
- Rattlesnakes emerge from winter hibernation to enjoy hot, dry weather. As rattlesnakes move closer to backyards looking for sources of water, UC Davis toxicologists offer tips for preventing snake bites.
- Six tips to prevent rattlesnake bites. ...
- If bitten by a rattlesnake: Protect animals from being bitten by a rattlesnake. ...
Self-care
While waiting for emergency help:
- Wash the bite with soap and water.
- Keep the bitten area still and lower than the heart.
- Cover the area with a clean, cool compress or a moist dressing to ease swelling and discomfort.
- Monitor breathing and heart rate.
- Remove all rings, watches, and constrictive clothing, in case of swelling.
How to properly prevent and treat snake bites?
Which Snake Causes the Most Deaths?
- North America. Fatal snake bites in North America are rare. ...
- South America. South America is home to more species of dangerous snake due to its tropical climate. ...
- Africa. Africa is home to the black mamba. ...
- Asia. Each year in Asia, up to a million people suffer a venomous snake bite. ...
- Australia. ...
- Europe. ...
What is the best treatment for a snake bite?
These are:
- First of all, don’t panic. ...
- Poison Control strictly forbids people from cutting the fang marks and sucking the venom out.
- Don’t apply ice or any other cold thing to the affected area.
- Don’t flush the wound with water.
- Avoid applying a tourniquet or any such tight band that restricts the blood flow as it can damage tissues.
What is the worst snake bite?
What to do if bitten by a copperhead snake?
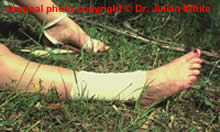
How are venomous bites treated?
Have the person lie down with wound below the heart. Keep the person calm and at rest, remaining as still as possible to keep venom from spreading. Cover the wound with loose, sterile bandage. Remove any jewelry from the area that was bitten.
Which medicine is used for treating snake bite?
Drugs used to treat Venomous Snake BiteDrug nameRatingRx/OTCView information about CroFab CroFab10RxGeneric name: antivenin (crotalidae) polyvalent systemic Drug class: antitoxins and antivenins For consumers: dosage, interactions, side effects For professionals: Prescribing Information13 more rows
Is there a medicine for snake bite How is it made?
If the situation is life threatening, the doctor may administer antivenom. This is a substance created with snake venom to counter the snake bite symptoms. It's injected into the victim. The sooner the antivenom is used, the more effective it will be.
How is antivenom given?
Most antivenoms are given by the intravenous route, although redback spider antivenom and box jellyfish antivenom are more often used intramuscularly. Skin testing for allergy to antivenom is not recommended, as it is unreliable and may delay urgent therapy.
How to treat a snake bite?
If possible, take these steps while waiting for medical help: 1 Move beyond the snake's striking distance. 2 Remain still and calm to help slow the spread of venom. 3 Remove jewelry and tight clothing before you start to swell. 4 Position yourself, if possible, so that the bite is at or below the level of your heart. 5 Clean the wound with soap and water. Cover it with a clean, dry dressing.
What to do if you get bit by a snake?
Their bites can cause severe injuries and sometimes death. If a venomous snake bites you, call 911 or your local emergency number immediately, especially if the bitten area changes color, begins to swell or is painful. Many emergency rooms stock antivenom drugs, which may help you.
What snakes have rounded heads?
Venomous snakes in North America. Most venomous snakes in North America have eyes like slits and are known as pit vipers. Their heads are triangular and they have fangs. One exception is the coral snake, which has a rounded head and round pupils.
How long does it take for a snake to burn?
Typical symptoms of the bite from a nonvenomous snake are pain and scratches at the site. Usually, after a bite from a venomous snake, there is severe burning pain at the site within 15 to 30 minutes.
How to get rid of snake venom?
If possible, take these steps while waiting for medical help: Move beyond the snake's striking distance. Remain still and calm to help slow the spread of venom. Remove jewelry and tight clothing before you start to swell.
Can a snake bite without venom?
Some snakes, such as coral snakes, have toxins that cause neurological symptoms, such as skin tingling, difficulty speaking and weakness. Sometimes, a venomous snake can bite without injecting venom. The result of these "dry bites" is irritation at the site.
What to do if a snake bites you?
First Aid. Workers should take these steps if a snake bites them: Seek medical attention as soon as possible (dial 911 or call local Emergency Medical Services [EMS]). Antivenom is the treatment for serious snake envenomation.
How to get rid of a snake bite?
Identifying the snake can help with treatment of the snakebite. Keep calm. Inform your supervisor. Apply first aid while waiting for EMS staff to get you to the hospital. Lay or sit down with the bite in a neutral position of comfort.
What are the signs of a snake bite?
Symptoms. Signs or symptoms of a snake bite may vary depending on the type of snake, but may include: Redness, swelling, bruising, bleeding, or blistering around the bite.
Can you handle a snake that is venomous?
NEVER handle a venomous snake, not even a dead one or its decapitated head. Do not wait for symptoms to appear if bitten, get medical help right away. Do not apply a tourniquet. Do not slash the wound with a knife or cut it in any way. Do not try to suck out the venom.
What is the treatment for snake bite?
Antivenin therapy is the mainstay of medical treatment of snakebite, along with administration of plasma expanders, pain medication, diazepam, tetanus toxoid, antiseptics, and antibiotics.
What should pharmacists know about snake bites?
Pharmacists--especially those serving rural areas--should be familiar with current snakebite treatments, both local and systemic, and should be prepared to provide important information and dispel any myths about snakebite poisoning.
What is responsible for 99% of snake bites?
Pit vipers (rattlesnakes, copperheads, cottonmouths, and massasaugas) are responsible for 99% of all snakebite poisonings; coral snakes and other foreign exotic species are responsible for the additional 1%.
What is the envenomation of snakes?
Envenomation is characterized by pain, edema, and ecchymoses at or near the site of venom injection, followed by cardiac, hematologic, neurologic, renal, and pulmonary toxicity. The major clinical finding in most snakebite poisonings is local tissue necrosis. Immediate treatment for snakebite includes limiting movement and placing ...
What happens if you bite a snake?
If you suffer a dry snake bite, you’ll likely just have swelling and redness around the area of the bite. But if you’re bitten by a venomous snake, you’ll have more widespread symptoms, which commonly include: Bite marks on your skin. These can be puncture wounds or smaller, less recognizable marks.
What are the different types of snake bites?
The answer might seem obvious, but there are two different types of snake bites. And one is more serious than the other: Dry bites: These occur when a snake doesn’t release any venom with its bite. As you’d expect, these are mostly seen with non-venomous snakes. Venomous bites: These are much more dangerous.
How are antivenoms created?
Fun fact: Antivenoms are created by immunizing horses or sheep with the venom of a particular snake. Their blood serum (the watery part of the blood) is then processed, as it will contain antibodies capable of neutralizing the effects of venom.
How many people die from snake bites a year?
It’s estimated that at least 81,000 to 138,000 people die each year from snake bites.
How to stop venom from spreading?
Keep the area of the bite below the heart in order to slow the spread of venom through the bloodstream. Remain still and calm. If you can, roll over to your side and rest in the recovery position. Moving around a lot will cause the venom to spread faster through the body. Cover the bite with a clean, dry bandage.
What happens if a cobra bites you?
If a cobra bites you, you can die from paralysis of the heart and lungs very quickly after the bite. Vipers: There are more than 200 species of Viperidae, which includes pit vipers (like rattlesnakes, copperheads, water moccasins, or cottonmouths) and Old-World vipers (adders).
Where do snake bites occur?
Those who live in South Asia, Southeast Asia and sub-Saharan Africa are particularly affected by venomous snake bites, as they often don’t have access to adequate healthcare services or antivenoms. Snake bites are also especially common in poor communities, often in rural areas.
What to do if you bite a snake?
Once airway, breathing, and circulation have been established, a rapid, detailed history should be obtained. If a snake bite is suspected, hospital admission should be considered for further follow-up.
What is venomous snake bite?
Venomous snake bites: clinical diagnosis and treatment. Snake bites are life-threatening injuries that can require intensive care. The diagnosis and treatment of venomous snake bites is sometimes difficult for clinicians because sufficient information has not been provided in clinical practice. Here we review the literature to present ...
Is a snake bite life threatening?
Snake bites are life-threatening injuries that can require intensive care. The diagnosis and treatment of venomous snake bites is sometimes difficult for clinicians because sufficient information has not been provided in clinical practice. Here we review the literature to present the proper manageme …. Venomous snake bites: clinical diagnosis and ...
Can you treat a snake bite with antivenom?
If a snake bite is suspected, hospital admission should be considered for further follow-up. All venomous snake bites can be effectively treated with antivenom. Side effects of antivenom should be prevented by sufficient preparation. Approved antivenoms for mamushi and habu are available.
How to stop a snake bite from spreading?
This can slow down the spread of venom. Inform your supervisor (if the bite occurs at work). Apply first aid if you cannot get to the hospital right away.
What is the second phase of snake bite treatment?
Phase two of snakebite treatment. The second phase of treatment consists of stabilization and supportive care, and when medically indicated, administration of antitoxin (antivenin) specific for the snake species and a tetanus booster vaccine.
What is a non-venomous snake?
A nonvenomous (nonpoisonous) snake bite is a bite or puncture wound made by a snake that is incapable of secreting venom. This should be distinguished from a dry bite. A dry bite is a bite by a venomous snake that does not inject any venom.
How many snake bites are there in the US?
Consequently, almost any type of venomous snake bite can be encountered in the US. About 7,000 snake bites are reported in the US per year, but because snake bites are not required to be reported, it is estimated that up to 45,000 bites per year may occur with about 8,000 by poisonous snakes.
Why is it important to identify a snake?
Identification of the snake helps emergency health care professionals to both anticipate the potential symptoms, and it allows for more rapid and appropriate treatment of the venomous snake bite. A detailed description and a picture of the snake will help identify the type of snake and the type of toxin.
How do you know if you have a bite?
Bite symptoms may include. severe burning pain at the bite site, swelling that spreads out from the bite, weakness, trouble breathing, and changes in heart rate. Bite severity depends on many factors, including the amount of venom injected, bite location, and a person's age and health.
What snakes have no pit?
Cottonmouths/water moccasins. Coral snakes. The first three are pit vipers (have a pit used to detect temperature changes and two movable fangs), and the coral snake is an elapid with short fixed fangs and no pit. Brown snakes are also elapid and are very poisonous.
